How is Bitcoin's decentralized finance progressing now?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

How is Bitcoin's decentralized finance progressing now?
BTCFi is not merely a technological shift, but could potentially trigger a paradigm shift in Bitcoin's role within DeFi.
Author: CoinMarketCap Research & Footprint Analytics
Translation: Baishuo Blockchain
Bitcoin's role in DeFi (decentralized finance) is undergoing a significant transformation. From its initial function as a simple peer-to-peer payment system, the world’s first cryptocurrency is now emerging as a powerful force within the DeFi space, beginning to challenge Ethereum’s long-standing dominance.
A comprehensive analysis of on-chain data reveals a clear picture of the current state and growth trajectory of Bitcoin’s ecosystem: BTCFi—the integration of Bitcoin with DeFi—is not merely a technical shift, but may represent a paradigm shift in Bitcoin’s role within DeFi. As we will explore in depth, this transformation could redefine the entire landscape of the DeFi sector.
The Rise of BTCFi
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto introduced Bitcoin with the original design goal of serving as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. While revolutionary in the realm of digital assets, this architecture has clear limitations when it comes to more complex financial applications such as DeFi.
Bitcoin’s Original Design and Limitations in DeFi
Core Design Elements and Their Limitations:
1) UTXO Model: Bitcoin uses the Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model, which is effective for handling simple transfers but lacks the flexibility required to support complex smart contracts.
2) Limited Scripting Language: Bitcoin’s scripting language is intentionally restrictive to prevent security vulnerabilities. However, this limitation also hinders its ability to support sophisticated DeFi applications due to a limited set of executable opcodes.
3) Lack of Turing Completeness: Unlike Ethereum, Bitcoin’s scripting language is not Turing complete, making it difficult to implement state-dependent smart contracts—essential components for many DeFi protocols.
4) Block Size and Transaction Speed: Bitcoin’s 1MB block size limit and 10-minute block time result in significantly slower transaction processing compared to other blockchains optimized for DeFi.
These design choices enhance Bitcoin’s security and decentralization, but create barriers to directly implementing DeFi functionality on the Bitcoin blockchain. The lack of native support for loops, complex conditions, and state storage makes building applications like DEXs, lending platforms, or liquidity mining protocols extremely challenging on Bitcoin.
Early Attempts and Development of DeFi on Bitcoin
Despite these limitations, Bitcoin’s robust security and widespread adoption have driven developers to seek innovative solutions:
1) Colored Coins (2012–2013): One of the earliest attempts to extend Bitcoin’s functionality, colored coins assigned unique metadata to specific bitcoins to represent and transfer real-world assets. While not true DeFi, they laid the groundwork for more complex financial applications on Bitcoin.
2) Counterparty (2014): This protocol enabled the creation and trading of custom assets on the Bitcoin blockchain, including the first NFT. Counterparty demonstrated the potential for developing more advanced financial tools on Bitcoin.
3) Lightning Network (2015–present): A Layer-2 scaling solution designed to improve transaction throughput via payment channels, opening possibilities for more complex financial interactions, including early-stage DeFi applications.
4) Discreet Log Contracts (DLCs) (2017–present): Proposed by Tadge Dryja, DLCs enable complex financial contracts without altering Bitcoin’s base layer, offering new possibilities for derivatives and other DeFi instruments.
5) Liquid Network (2018–present): Developed by Blockstream, this sidechain-based settlement network supports issuance of digital assets and more complex Bitcoin transactions, paving the way for DeFi-like applications.
6) Taproot Upgrade (2021): By introducing Merklized Alternative Script Trees (MAST), Taproot compresses complex transactions into a single hash, reducing fees and memory usage. While not a DeFi solution per se, it enhanced Bitcoin’s smart contract capabilities, simplifying and optimizing complex transactions and laying the foundation for future DeFi development.
These early developments expanded Bitcoin’s utility beyond simple transfers, demonstrating the ecosystem’s potential despite challenges. These innovations paved the way for Layer-2 solutions, sidechains, and a wave of innovation in Bitcoin DeFi, which we will now examine in detail.
Key Innovations: Enabling Smart Contracts on Bitcoin
In recent years, several protocols have emerged in the Bitcoin ecosystem aiming to introduce smart contracts and DeFi functionalities to the world’s first cryptocurrency. These innovations are transforming Bitcoin from just a store of value or medium of exchange into a platform for programmable finance. The following are key protocols driving smart contract capabilities on Bitcoin:
1) Rootstock: A pioneer in Bitcoin smart contracts, Rootstock is the longest-running Bitcoin sidechain and has become a foundational pillar of the BTCFi ecosystem.
Leveraging 60% of Bitcoin’s hash power through merged mining, and compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), it allows Ethereum smart contracts to run natively on Bitcoin. Rootstock’s unique Powpeg mechanism ensures seamless conversion between Bitcoin (BTC) and Rootstock Bitcoin (RBTC), while its “defense-in-depth” security model emphasizes simplicity and robustness.
Since its mainnet launch in 2018, Rootstock has seen steady growth in on-chain activity, establishing itself as a stable and scalable solution within the Bitcoin ecosystem, according to Footprint Analytics.
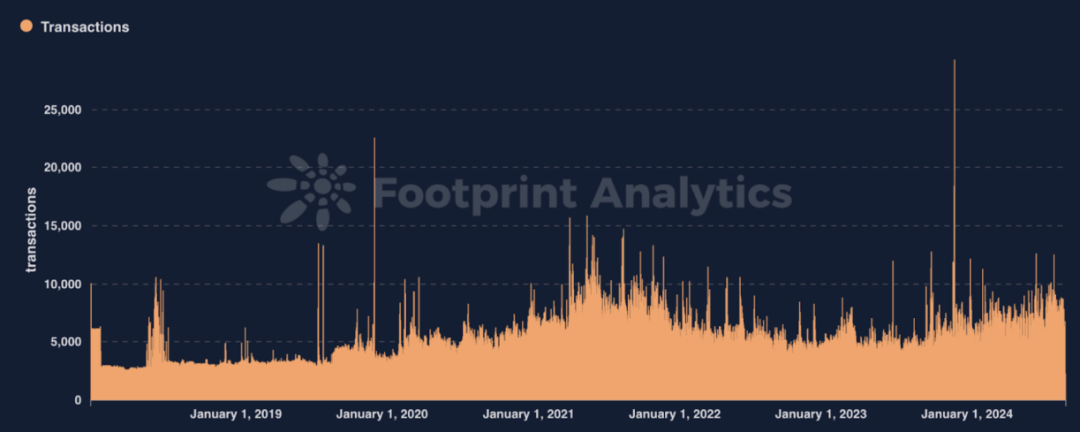
2) Core: Core is a Bitcoin-based blockchain that maintains deep integration with Bitcoin while being EVM-compatible.
Core stands out with its innovative dual-staking model, combining Bitcoin and Core tokens. Through non-custodial Bitcoin staking, Core generates risk-free yield for Bitcoin, effectively transforming it into an income-generating asset. Core reports that 55% of Bitcoin mining hash power has been delegated to its network, enhancing security for DeFi applications.
3) Merlin Chain: A relatively new Bitcoin Layer-2 network focused on unlocking Bitcoin’s DeFi potential, Merlin Chain is gaining increasing attention. By integrating ZK-Rollup technology, decentralized oracles, and on-chain fraud-proof modules, it offers a full suite of DeFi services for Bitcoin holders. Its M-BTC is a yield-bearing wrapped Bitcoin asset, creating new pathways for yield generation and DeFi participation.
4) BEVM: BEVM represents a major step toward bringing Ethereum’s expansive DeFi ecosystem directly onto Bitcoin. As the first fully decentralized, EVM-compatible Bitcoin Layer-2 network, BEVM uses Bitcoin as fuel, enabling seamless deployment of Ethereum’s decentralized applications (DApps) on Bitcoin. Backed by mining giant Bitmain, BEVM pioneers the concept of “hashrate-backed RWA,” potentially unlocking new value dimensions for the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Key Innovations in Bitcoin Layer-2 Networks and Sidechains:
-
Tokenized Bitcoin Assets;
-
Smart Contracts and EVM Compatibility;
-
Yield-Bearing Bitcoin;
-
Scalability and Privacy Enhancements.
These protocols are not simply replicating Ethereum’s DeFi strategies on Bitcoin, but are leveraging Bitcoin’s unique characteristics to forge new paths. From Rootstock’s defense-in-depth mechanism to Core’s dual-staking model, Merlin’s comprehensive DeFi offerings, and BEVM’s hashrate RWA innovation, the BTCFi space is rapidly evolving.
As of September 8, 2024, the total value locked (TVL) across Bitcoin’s Layer-2 solutions and sidechains reached $1.07 billion, marking a 5.7x increase since January 1, 2024, and a staggering 18.4x growth since January 1, 2023.
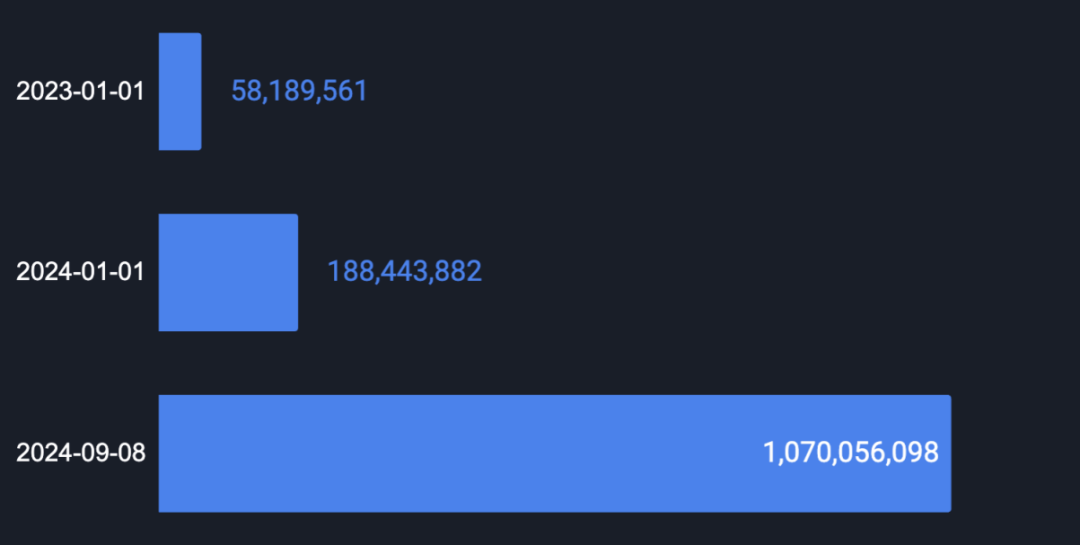
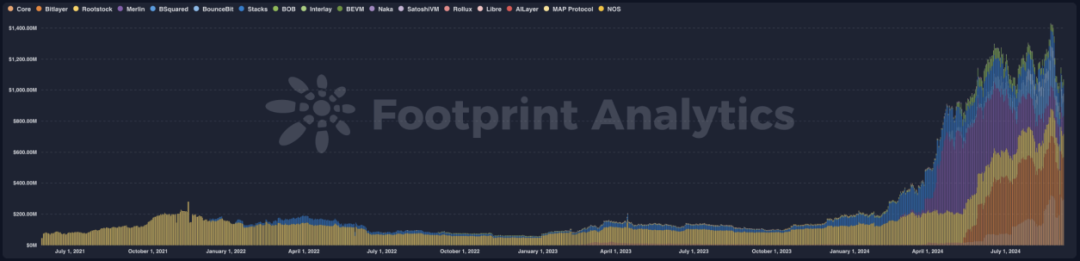
Core leads with 27.6% of total TVL, followed by Bitlayer at 25.6%, Rootstock at 13.8%, and Merlin Chain at 11.0%.
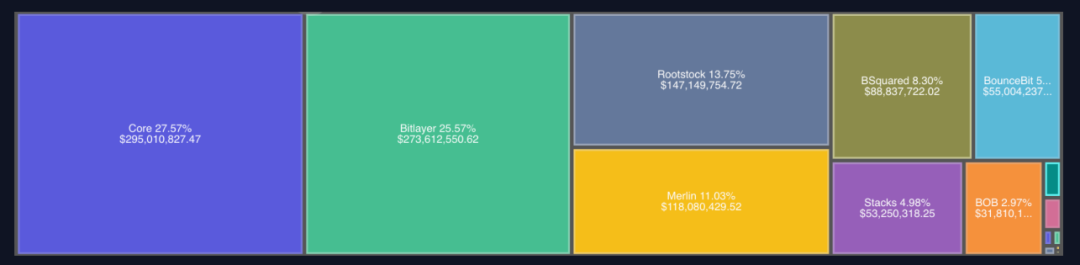
Current State of Bitcoin DeFi
As the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem continues to grow, several key projects have emerged as major players, driving innovation and user adoption. Built on Bitcoin’s Layer-2 solutions and sidechains, these projects offer diverse DeFi services:
1) Major BTCFi Projects
Pell Network (Multi-chain)
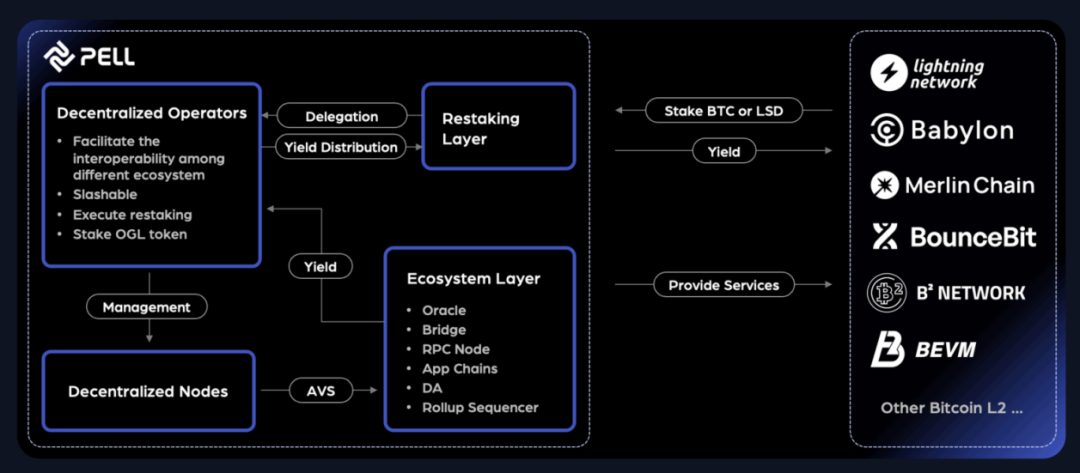
Pell Network is a cross-chain restaking protocol designed to enhance the security and optimize yields within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Users earn returns by staking Bitcoin or liquid staking derivatives (LSDs), while decentralized operators run validator nodes to secure the network. Pell provides active validation services such as oracles, cross-chain bridges, and data availability, supporting the broader Bitcoin Layer-2 ecosystem. With strong infrastructure, Pell aims to be a key player in providing liquidity and cryptographic economic security, fostering sustainable growth in the Bitcoin economy.
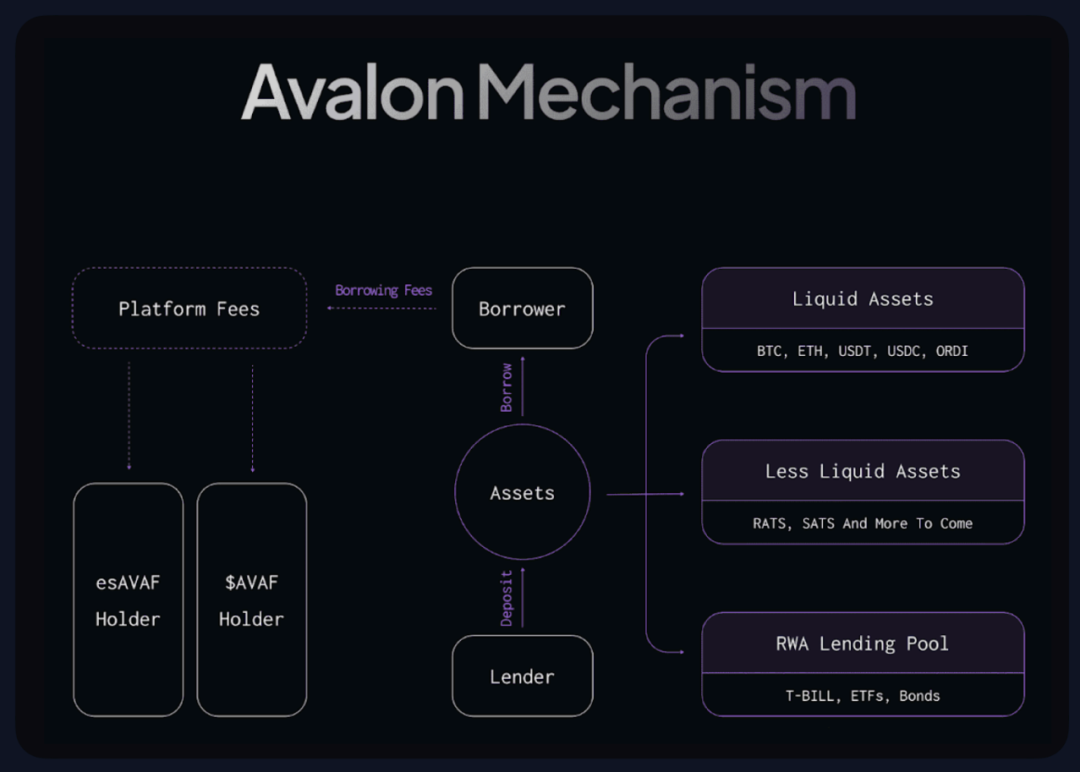
Avalon Finance
Avalon Finance is a multi-chain DeFi platform operating across Bitlayer, Core, and Merlin Chain, known for offering comprehensive lending and trading services within the BTC DeFi ecosystem. Its core offerings include over-collateralized lending for both major and less liquid assets, with dedicated isolated pools. The platform also integrates derivatives trading, enhancing its lending functionality. Additionally, Avalon launched an algorithmic stablecoin to optimize capital efficiency, positioning itself as a versatile and secure DeFi solution in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Its governance token AVAF follows an ES Token model, incentivizing liquidity provision and protocol usage.
Colend Protocol (Core)
Colend Protocol is a decentralized lending platform built on the Core blockchain, enabling users to safely lend and borrow Bitcoin and other assets. Leveraging Core’s dual-staking model, Colend seamlessly integrates with the broader DeFi ecosystem, enhancing Bitcoin’s utility in DeFi. Key features include decentralized and immutable transactions, dynamic interest rate liquidity pools, and a flexible collateral system.
MoneyOnChain (Rootstock)
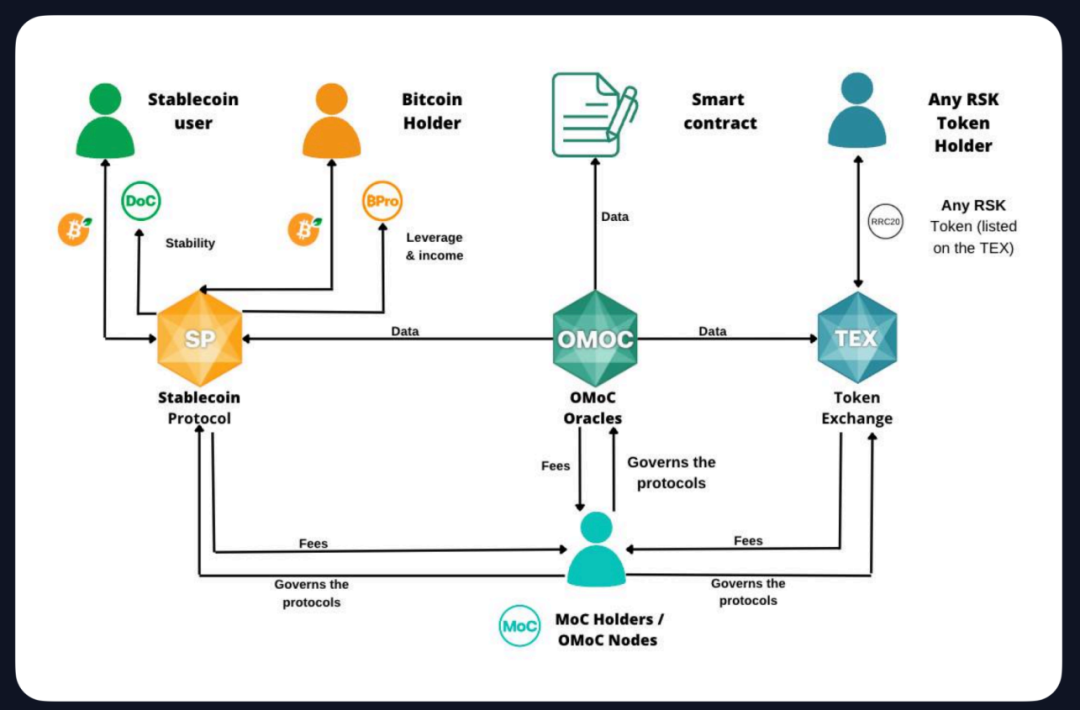
MoneyOnChain is a comprehensive DeFi protocol built on Rootstock, allowing Bitcoin holders to generate yield while retaining full control of their private keys. At its core, the protocol issues Dollar on Chain (DoC), a stablecoin fully backed by Bitcoin, designed for users who want to maintain the dollar-pegged value of their Bitcoin holdings. MoneyOnChain also offers Token BPRO, giving users leveraged exposure to Bitcoin for passive income.
The protocol’s architecture is based on a shared-risk mechanism using a proprietary financial model to withstand extreme market volatility. It also includes a decentralized token exchange (TEX), decentralized oracle (OMoC), and governance token (MoC), enabling user participation in protocol governance, staking, and rewards.
Sovryn (Multi-chain)
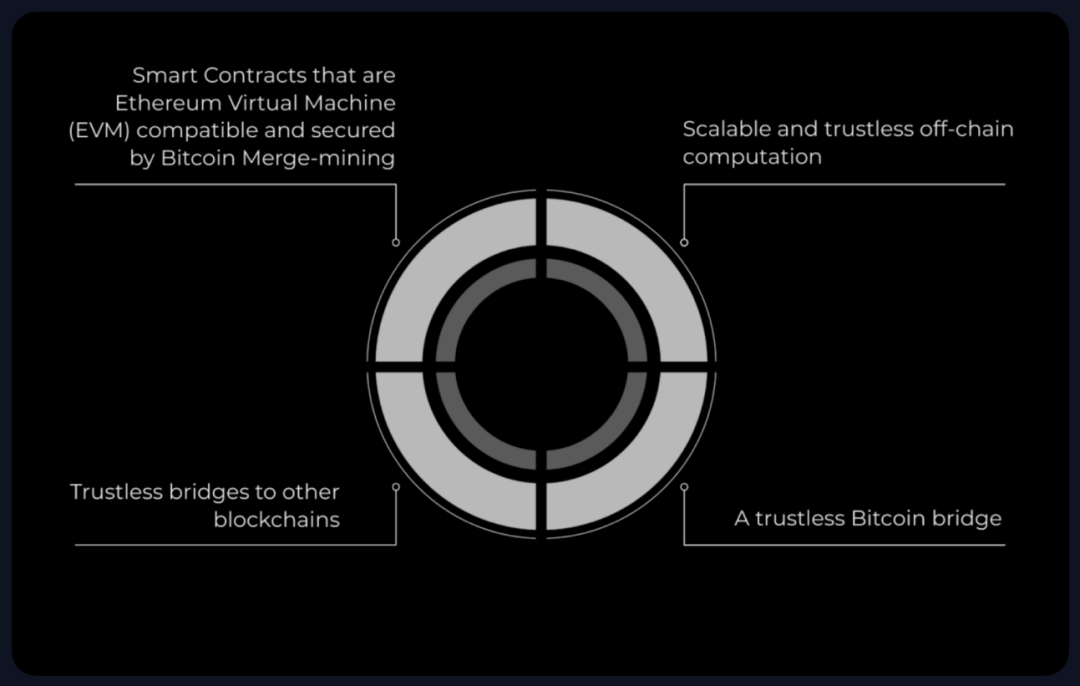
Sovryn is a DEX and one of the most feature-rich DeFi platforms built on Bitcoin, designed to let users trade, lend, and earn yield using Bitcoin. Operating across BOB and Rootstock, Sovryn offers a wide range of DeFi services including trading, swapping, liquidity provision, staking, and lending. Focused on creating a permissionless financial layer for Bitcoin and integrating with other blockchains, Sovryn stands out as a unique multi-chain platform in the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem.
Sovryn’s governance token SOV plays a crucial role in managing the decentralized protocol via the Bitocracy system, representing voting rights and rewarding active participants.
Solv Protocol (Merlin Chain)
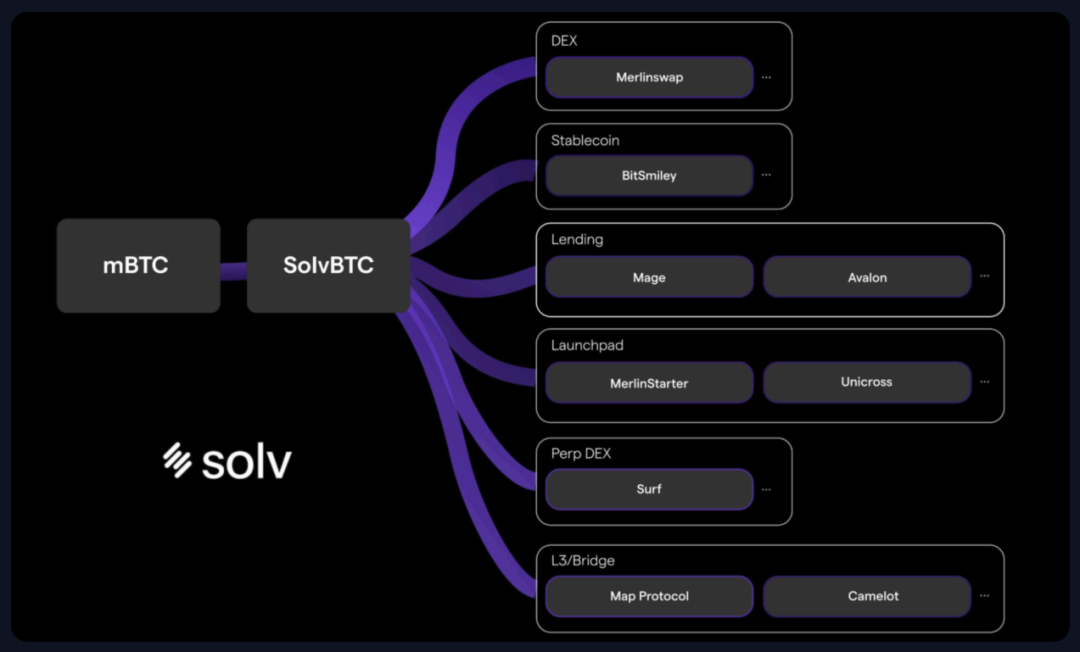
Solv Protocol is at the forefront of NFT financialization, enabling users to create, trade, and manage on-chain credentials. The protocol aims to tokenize and aggregate yields from various DeFi protocols within the Merlin Chain ecosystem. Its flagship product, SolvBTC, is a yield-bearing token that allows Bitcoin holders to earn yield while maintaining liquidity.
Solv Protocol builds a robust liquidity layer through staking and other yield-generating activities. This flexibility makes it a key DeFi project on Merlin Chain, helping unlock new financial opportunities within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
These projects highlight the dynamic and rapid evolution of Bitcoin DeFi, each contributing unique functionalities that expand the ecosystem’s reach. As of September 8, 2024, Core leads in the Bitcoin DeFi space, hosting 25.2% of active projects, reinforcing its central role. Rootstock and Bitlayer are also key contributors, each supporting 13.0% of projects, highlighting their importance in improving liquidity and capital efficiency. Merlin Chain plays a vital role with 9.9% project share in expanding Bitcoin DeFi capabilities. Other platforms like BOB (8.4%), BSquared (6.9%), and Stacks (6.1%) add diversity, while BEVM (5.3%), BounceBit (3.1%), and MAP Protocol (3.1%) drive overall growth through specialized solutions.

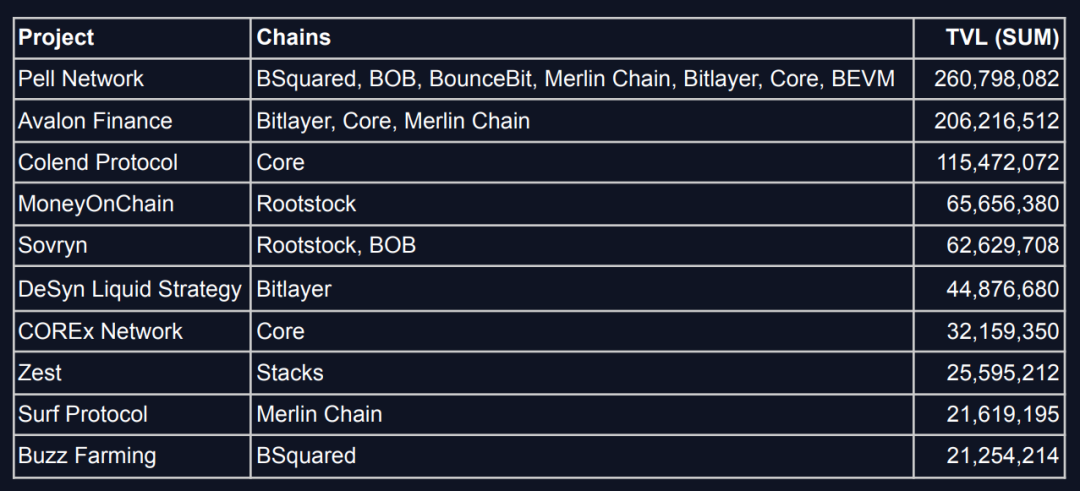
Pell Network leads as the top DeFi project with $260.8 million in total value locked (TVL), solidifying its leadership in NFT finance. Avalon Finance and Colend Protocol follow with $206.2 million and $115.5 million in TVL respectively, also standing as major players. Other notable projects include MoneyOnChain and Sovryn, showcasing the diversity of BTCFi—from liquidity mining to stablecoins.
2) Key Narratives in Major BTCFi Projects
Security and Decentralization First: The Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem prioritizes security and decentralization as core principles. Bitcoin’s unparalleled security framework forms the foundation of the BTCFi ecosystem, ensuring all innovations adhere to these fundamental tenets.
Bitcoin as a Programmable Token: BTCFi is redefining Bitcoin’s role—not just as a store of value, but as a programmable token. This shift, enabled by smart contracts, opens the door to a new generation of sophisticated financial applications. For example, SolvBTC from Solv Protocol is dubbed the “first yield-bearing Bitcoin,” generating returns through neutral trading strategies in yield vaults and across DeFi protocols on Ethereum, Arbitrum, and Merlin Chain.
Interoperability with Ethereum: BTCFi bridges the gap with Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem through EVM-compatible solutions, leveraging the strengths of both networks. This interoperability creates powerful synergies, combining Bitcoin’s security with Ethereum’s flexible smart contract capabilities. For instance, Core executes smart contracts via EVM, meaning dApps developed for Ethereum can be easily ported to Core with minimal modifications.
Unlocking Bitcoin’s Capital: The BTCFi ecosystem is unlocking vast amounts of capital for DeFi use, offering yield opportunities while preserving Bitcoin exposure, thereby expanding Bitcoin’s utility and appeal in DeFi.
3) Comparative Analysis with Ethereum DeFi
As Bitcoin DeFi evolves, comparing it with Ethereum DeFi becomes increasingly important—particularly in understanding how Bitcoin operates within Ethereum via wrapped assets like wBTC and renBTC, and what lessons can be drawn from Ethereum’s development path.
4) Ethereum DeFi vs. Native Bitcoin DeFi
The integration between Bitcoin and Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystems primarily occurs through wrapped assets such as wBTC and renBTC. These tokens allow Bitcoin holders to convert BTC into ERC-20 tokens, granting access to Ethereum’s extensive DeFi ecosystem and enabling usage on platforms like MakerDAO, Aave, and Uniswap.
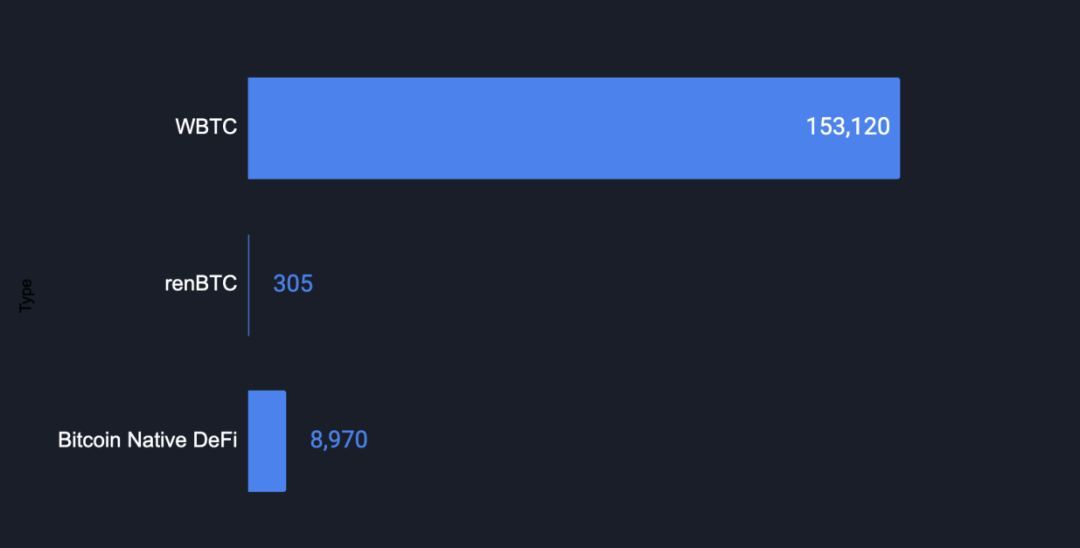
There are significant differences in BTC usage between the two ecosystems. As of September 8, the amount of BTC locked in Ethereum DeFi protocols was 153,400, far exceeding the 8,970 BTC in native Bitcoin DeFi. This trend benefits from Ethereum’s mature and diversified DeFi infrastructure, offering a wider range of financial products including lending, trading, and liquidity mining.
While wrapped Bitcoin tokens like wBTC offer liquidity and advanced DeFi functionality, they rely on custodians and cross-chain bridges, introducing additional risks. In contrast, native Bitcoin DeFi projects, though smaller in scale, operate within Bitcoin’s own secure framework, avoiding many risks associated with cross-chain transfers. However, Bitcoin DeFi remains in its early stages, offering a narrower range of financial services compared to Ethereum.
Lessons Between Ethereum and Bitcoin
1) What Bitcoin Can Learn from Ethereum:
Product Diversity: Ethereum’s success in DeFi largely stems from its wide array of financial products and services, such as DEXs and synthetic assets. To advance Bitcoin DeFi, expanding product variety beyond lending and stablecoins is essential. Developing more sophisticated financial tools and interoperability solutions could attract broader user adoption.
Developer Ecosystem: Ethereum has cultivated a vibrant developer community continuously innovating and launching new projects. Bitcoin DeFi can similarly benefit from fostering a more active developer ecosystem to encourage creation of new protocols and applications that leverage Bitcoin’s strengths.
Interoperability: Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem excels in internal and cross-chain interoperability. Enhancing interoperability between Bitcoin DeFi and other chains—including Ethereum—could open new opportunities, allowing users to harness the strengths of both ecosystems.
2) What Ethereum Can Learn from Bitcoin:
Security and Decentralization: Bitcoin’s unwavering focus on security and decentralization is unmatched. Ethereum projects can learn from Bitcoin’s conservative approach, ensuring these core principles aren’t compromised amid rapid innovation. This is especially relevant as Ethereum transitions to more scalable solutions like Layer-2s, where security must be carefully managed.
Simplicity and Robustness: While Bitcoin’s scripting capabilities are simpler and more robust, they are less flexible—resulting in fewer vulnerabilities than Ethereum’s complex smart contracts. Ethereum developers can prioritize simplicity and robustness in smart contract design to reduce security risks.
Focus on Store of Value: While Ethereum is renowned for its smart contract functionality, Bitcoin’s dominance as a store of value remains strong. The Ethereum ecosystem could explore ways to enhance its value storage capabilities, perhaps by integrating more Bitcoin-based assets, attracting users who prioritize security and asset preservation.
Although Bitcoin DeFi is still in its infancy, it holds substantial growth potential by learning from Ethereum’s mature ecosystem. At the same time, Ethereum can draw insights from Bitcoin’s strengths in security and decentralization to further strengthen its DeFi offerings. As both ecosystems evolve, collaboration and mutual learning may drive the next phase of DeFi growth.
Challenges and Opportunities
As this field advances, overcoming technical and regulatory hurdles is essential, while technological progress and emerging growth areas present significant expansion opportunities.
1) Technical Barriers
Developing DeFi on Bitcoin faces numerous technical challenges. Scalability is a primary concern, as Bitcoin’s base layer has limited transaction capacity due to block size and block time constraints. Unlike Ethereum, which already has multiple mature Layer-2 solutions, Bitcoin’s Layer-2 and sidechain ecosystems are still nascent, limiting the scope of DeFi applications they can effectively support.
Secondly, interoperability remains a major challenge. Connecting Bitcoin securely and without compromising decentralization to other blockchain ecosystems is highly complex and requires innovative solutions.
2) Regulatory Concerns
As Bitcoin DeFi grows, increased regulatory scrutiny is expected. Governments and financial regulators may impose stricter rules on DeFi services, particularly around AML and KYC compliance. Bitcoin’s decentralized and pseudonymous nature complicates compliance, potentially affecting the adoption and development of Bitcoin DeFi. Therefore, finding balance within these regulatory environments is critical for the sustainable growth of Bitcoin DeFi.
Future Opportunities
1) Technological Advancements
Bitcoin DeFi has substantial room for technological advancement. Improving Layer-2 solutions—such as more efficient and secure sidechains—and developing more scalable and interoperable frameworks could significantly enhance the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem. Additionally, advancements in technologies like Discreet Log Contracts (DLCs) and privacy-preserving tools (e.g., zero-knowledge proofs) could enable more complex and secure financial applications.
2) Predicted Growth Areas
As the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem matures, several areas show strong growth potential. Yield-generating products, DEXs, and cross-chain liquidity pools are expected to attract increasing attention. Moreover, as institutional interest in Bitcoin continues to rise, demand is likely to grow for institutional-grade DeFi products such as custody solutions, compliant financial instruments, and Bitcoin-backed stablecoins. These developments offer high-return opportunities for early adopters and innovators in the Bitcoin DeFi space.
Conclusion
Looking ahead, the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem will continue to expand, driven by technological innovation and growing institutional interest. Developing more scalable Layer-2 solutions, enhancing interoperability, and launching more sophisticated financial products are critical to this expansion. As the ecosystem matures, yield-generating products, DEXs, and institution-focused DeFi services are expected to attract significant attention and capital.
However, this growth will face challenges, particularly in navigating evolving regulatory landscapes and overcoming technical hurdles related to scalability and security. Addressing these issues is essential to sustaining Bitcoin DeFi’s momentum and ensuring its long-term success.
In summary, the future of Bitcoin DeFi appears promising, filled with innovation and growth opportunities. As the ecosystem evolves, it has the potential to profoundly impact the entire DeFi landscape and position Bitcoin as a central player in decentralized finance.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News