Symbiotic Architecture Overview: A Flexible and Permissionless Thin Coordination Layer
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Symbiotic Architecture Overview: A Flexible and Permissionless Thin Coordination Layer
With support from Lido and Paradigm, can Symbiotic break EigenLayer's "dominant" position?
By LINDABELL
Yesterday, the restaking project Symbiotic officially launched and announced a $5.8 million seed round led by Paradigm and Cyber Fund. According to its introduction, Symbiotic is a permissionless shared security protocol. Shared security refers to multiple networks sharing the same set of node operators' services and security guarantees, thereby improving capital efficiency and security. This concept has previously been implemented in EigenLayer’s restaking model.
Although operating in the same restaking space as EigenLayer, Symbiotic differs significantly. It allows users to stake a broader range of tokens, including ERC20 tokens, Ethereum validator withdrawal credentials, or liquidity provision proofs. Additionally, Symbiotic offers more flexible component customization. While the core protocol is defined by immutable core contracts, other components—such as staked assets, reward mechanisms, and slashing rules—can be configured by networks or other agents as needed.

According to CoinDesk, Lido co-founders Konstantin Lomashuk and Vasiliy Shapovalov, along with Paradigm, had secretly funded a new project similar to EigenLayer as early as May this year—the project being Symbiotic. Interestingly, the report also mentioned that Paradigm had previously expressed interest in investing in EigenLayer co-founder Sreeram Kannan but was rejected. Subsequently, EigenLayer chose to raise $100 million from a16z. In response, Paradigm stated it would instead invest in competing projects like Symbiotic.
Symbiotic Architecture Explained: A Lightweight Coordination Layer
Symbiotic is designed as an extremely flexible, permissionless, and reliable thin coordination layer aimed at simplifying system architecture and reducing operational costs, while ensuring efficient transaction processing and protocol execution. According to Symbiotic’s documentation, its network architecture consists of five core components that work together to maintain and enhance the security and efficiency of decentralized networks.

1) Collateral
Role: Ensuring economic security within Symbiotic
Function: In the Symbiotic system, the concept of stakable tokens is broadened to include various on-chain assets such as ERC20 tokens, Ethereum validator withdrawal credentials, or liquidity provision proofs. Users can stake these assets and convert them into specific staking tokens, which are enhanced with extended functionality and can be used for penalties or compensation when necessary.
2) Vaults
Role: Coordinating and managing the staking and restaking processes
Function: Vaults serve as the bridge connecting asset holders with Operators (infrastructure providers) in the Symbiotic protocol. Staking tokens converted from user deposits are stored in Vaults, which then delegate these tokens to Operators across the network to support operations. Moreover, since Vaults are configurable, they can be deployed in various ways to meet different needs and security requirements. For example, Immutable Pre-Configured Vaults offer highly stable and secure environments for applications requiring maximum reliability, while Curated Multi-Operator Vaults allow centralized management of funds and strategies across multiple Operators, enabling customized services.
3) Operators
Role: Infrastructure providers within the Symbiotic ecosystem
Function: By receiving staking tokens from Vaults, Operators gain the necessary economic backing to ensure network security and operations. Symbiotic maintains a registry to track and record Operator performance. Notably, Operators can receive economic support from multiple partners via Vaults without needing to build or maintain separate infrastructure for each partner. In the future, Symbiotic plans to introduce additional validation and evaluation systems, allowing Networks to select Operators based on reputation and historical performance.
4) Resolvers
Role: Acting as arbitrators within the ecosystem, responsible for adjudicating and enforcing economic penalties arising from malicious behavior; can be either entities or smart contracts
Function: Implementation comes in two forms. The first is fully automated, suitable for cases where misconduct can be clearly proven. The second involves more complex setups, such as establishing committees or integrating external dispute resolution frameworks. Vaults and Networks can jointly choose the appropriate type of Resolver. Vaults also have the authority to define specific terms regarding how staking tokens should be handled by Resolvers. Furthermore, Resolvers can be shared across networks, allowing multiple networks to adopt the same mechanism for handling potential disputes.
5) Network
Role: Various protocols or platforms relying on decentralized infrastructure to deliver services
Function: Symbiotic enables these Networks to flexibly obtain required security, including technical services and economic backing from Operators. Through Symbiotic's modular design, Networks can customize their strategies for recruiting and managing node Operators and independently choose which Vaults to collaborate with. Additionally, Symbiotic’s core contracts are open-source and immutable, ensuring operational security and stability without exposure to external governance risks.
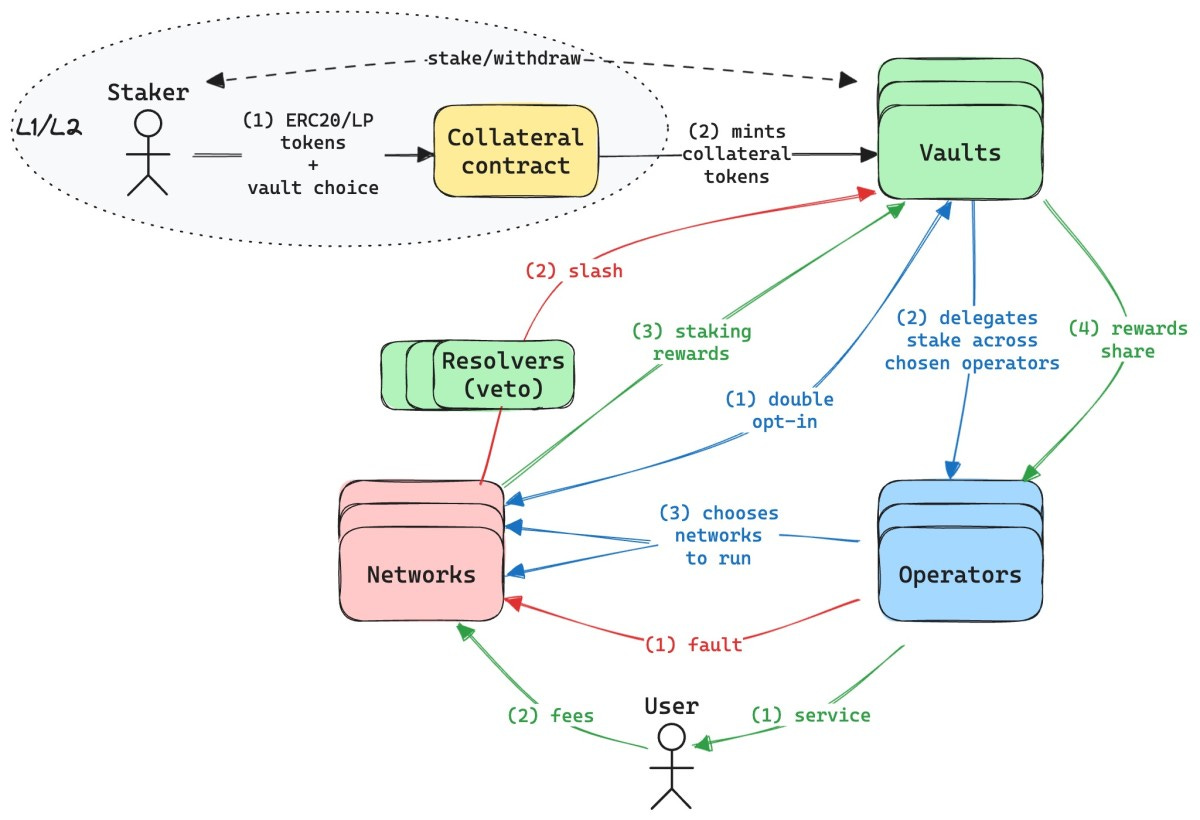
Overall, in the Symbiotic protocol, users first convert their staked assets into Collateral, which is deposited into Vaults. Based on predefined strategies, Vaults delegate these tokens to Operators, providing the necessary economic resources for network operations. Operators then execute tasks such as data processing and transaction validation according to these strategies. Meanwhile, Resolvers play a critical arbitration role, handling any economic penalties triggered by Operator misbehavior. As the ultimate service providers, Networks define and adjust interaction rules with Vaults and Operators, including how stakes are accepted, rewards distributed, and penalties enforced.
Symbiotic Ecosystem
The Symbiotic system offers high flexibility, supporting projects at various stages of decentralization. For instance, projects can initially partner with existing Operators to build trust-minimized, decentralized networks. Alternatively, they can expand their cluster of Operators within their ecosystem to increase attack costs and achieve better alignment.
Currently, Symbiotic has formed partnerships with 16 projects, including USDe developer Ethena, cross-chain application platform Hyperlane, oracle network Ojo, AI verification network Aizel, and omnichain ledger protocol Cycle Network. Among them, Ethena is integrating Symbiotic with LayerZero’s Decentralized Verification Network (DVN) framework to achieve cross-chain security for Ethena assets; Cycle Network plans to use Symbiotic to power its shared sequencer; Rollkit, Celestia’s modular Rollup framework, is exploring integrating Symbiotic restaking into its modular stack to facilitate launching sovereign Rollups on Celestia.

Summary
DefiLlama data shows that EigenLayer’s total value locked (TVL) has surpassed $18 billion, making it the second-largest protocol by TVL after Lido and the clear leader in the restaking sector, with all other projects falling below $1 billion in TVL. These figures underscore EigenLayer’s dominant market position. However, the launch of Symbiotic could introduce new competition, especially given its support for restaking assets like Lido’s stETH and others incompatible with EigenLayer—potentially giving it an edge in TVL growth. According to Symbiotic’s Twitter, the protocol reached its cap of 41,290 wstETH in just five hours.
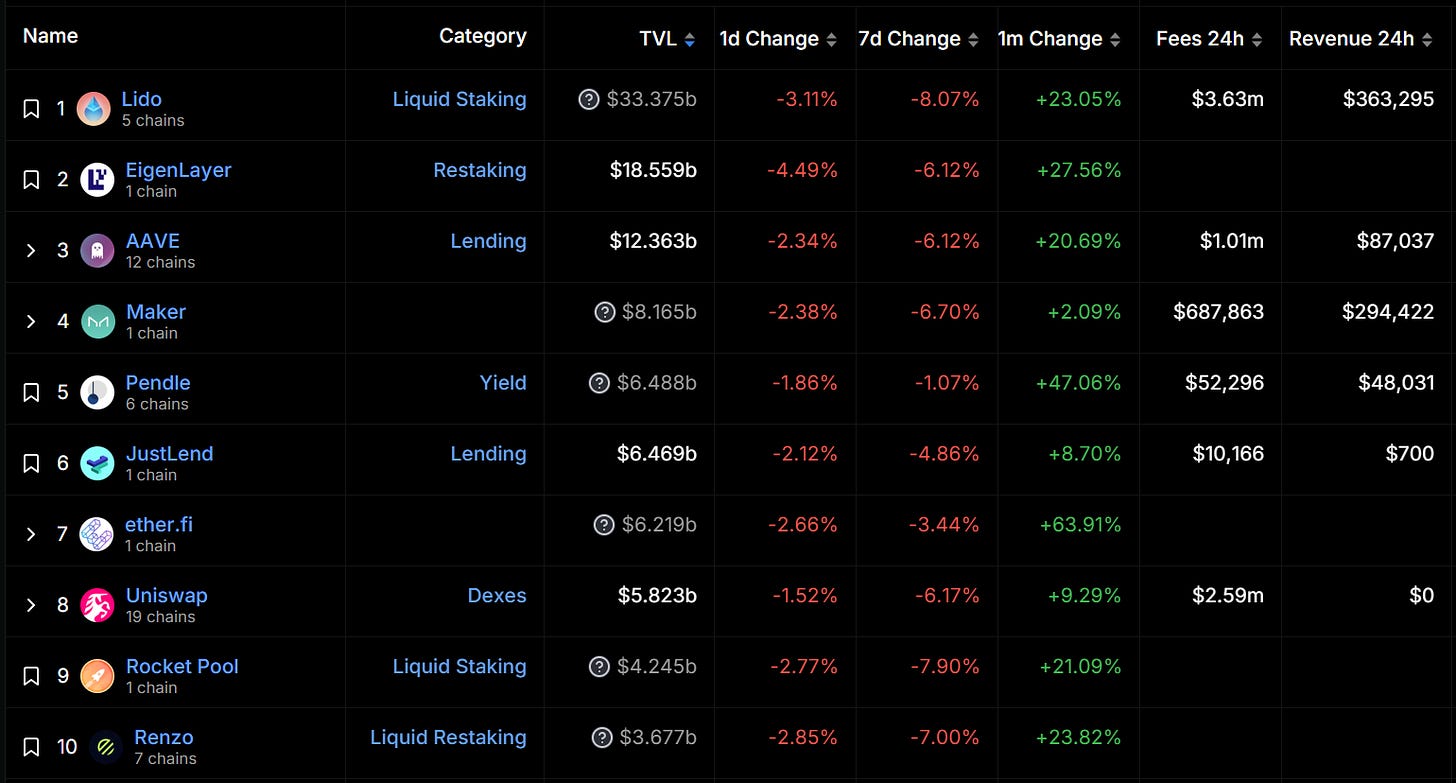
Moreover, backed by Paradigm, Symbiotic demonstrates broader applicability in terms of technical support and use cases. Paradigm stated in a blog post: “In the short term, Symbiotic will primarily be used to launch new consensus instances, such as electing new L1 operators and enabling decentralized sequencing. Long-term, it will also support use cases like block production and multi-party computation.” Additionally, Paradigm has developed Reth Execution Extensions (ExEx) to further enhance shared security services built on Symbiotic.
However, EigenLayer has already established a solid market position and strong ecosystem in the restaking domain. Whether Symbiotic can leverage its advantages to challenge EigenLayer’s dominance remains to be seen.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















