Bitcoin Spot ETF: Nature, Impact, and Outlook
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Bitcoin Spot ETF: Nature, Impact, and Outlook
The arrival of Bitcoin spot ETFs is now unstoppable.
By: PSE Trading Intern @JohnHol
After rejecting multiple spot Bitcoin ETF applications in recent years, the SEC lost a court case against Grayscale in August this year over its refusal to approve GBTC’s conversion into a spot Bitcoin ETF. Meanwhile, BlackRock—the world's largest asset manager—and several other institutions have simultaneously filed applications with the SEC for spot Bitcoin ETFs. The arrival of spot Bitcoin ETFs is now unstoppable.
What Is a Spot Bitcoin ETF?
A cryptocurrency exchange-traded fund (ETF) tracks the price of one or more digital assets by investing directly in crypto or related instruments. The much-discussed Bitcoin ETF refers specifically to an ETF that tracks the price of Bitcoin, primarily divided into two types: Bitcoin futures ETFs and spot Bitcoin ETFs. The key difference lies in their underlying assets—futures ETF shares are backed by Bitcoin futures contracts, whereas spot ETF shares are directly backed by actual Bitcoin holdings.
Compared to traditional mutual funds, ETFs can be traded on conventional stock exchanges like stocks. This means that once approved, investors could gain exposure to Bitcoin returns without going through complex processes—such as downloading wallet extensions, generating public-private key pairs, or transacting via centralized exchanges—by simply purchasing ETF shares. While these steps may seem trivial to experienced users, they remain significant barriers for those unfamiliar with cryptocurrencies. A spot Bitcoin ETF lowers these entry barriers and offers both retail and institutional investors a familiar financial instrument backed by regulatory oversight and legal protection.
How does a spot Bitcoin ETF work? First, the issuer acquires Bitcoin either directly from holders or through centralized exchanges. These assets are stored securely in Bitcoin wallets protected by multiple safeguards, such as cold storage. Next, the issuer creates tradable fund shares whose value closely tracks the real-time price of Bitcoin. Authorized Participants (APs)—typically large financial institutions—handle the creation and redemption of shares and often act as market makers in secondary markets. Investors can then buy or sell these shares on traditional stock exchanges just like stocks. Additionally, APs arbitrage any premium or discount between the share price and the net asset value to ensure alignment with the underlying Bitcoin value.
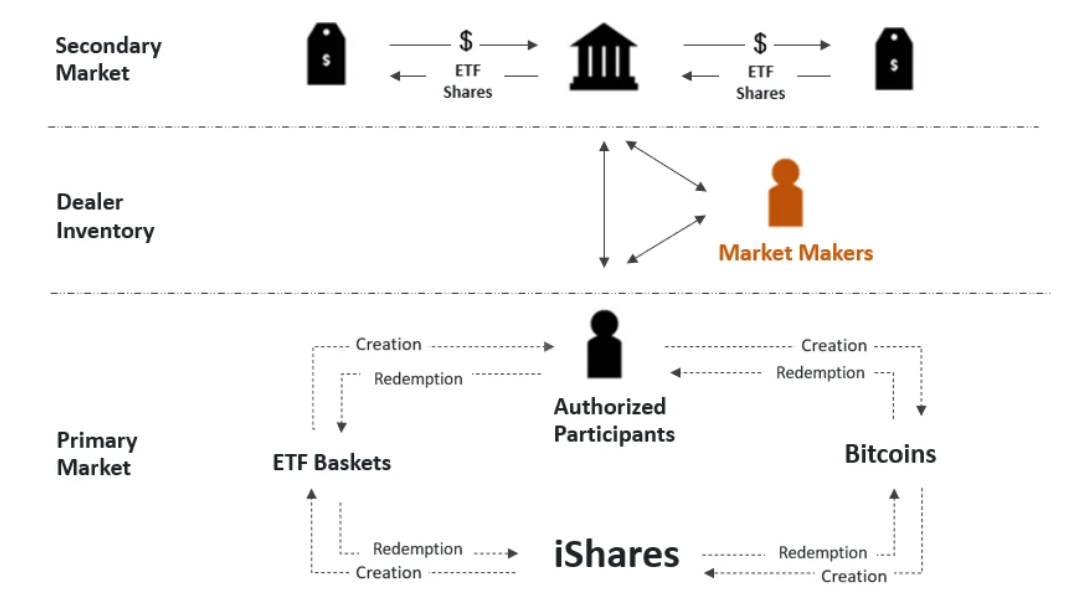
The first Bitcoin ETF was the ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITO), a futures-based ETF launched on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange in October 2021. However, as of now, the SEC has not yet approved any spot Bitcoin ETFs.
The first financial product tracking Bitcoin was the Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC), introduced in 2013 and publicly traded starting in 2015. In January 2020, GBTC received SEC registration approval, becoming the first crypto investment vehicle compliant with SEC standards. However, GBTC is not an ETF but a closed-end fund traded over-the-counter. Although it allows investors to gain Bitcoin exposure without direct ownership, its share price is determined by supply and demand in the secondary market rather than the net asset value of its Bitcoin holdings. As a result, GBTC shares frequently trade at significant premiums or discounts relative to the value of the underlying Bitcoin.
Grayscale has long sought to convert GBTC into a spot Bitcoin ETF, but all attempts were rejected until August 2023, when the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia ruled that the SEC’s rejection was unjustified. The SEC chose not to appeal the decision, forcing it to reevaluate the application. While this ruling doesn’t guarantee approval, it sent a strongly positive signal to the market.
The SEC Approval Process
In simple terms, when an institution submits an ETF application to the SEC, the SEC confirms receipt and publishes a Form 19b-4 in the Federal Register. This triggers a 240-day review period during which the SEC must respond by Day 45, Day 90, Day 180, or Day 240—or announce a delay to one of these dates.
Historically, the SEC has expressed concerns about insufficient regulation in the cryptocurrency market, which has been the primary reason for rejecting crypto ETF applications. In past rejections, the SEC emphasized risks of fraud and manipulation due to lack of transparency, inadequate supervision, and challenges in ensuring asset security—arguing that robust information sharing and market surveillance mechanisms are essential.
Following the court loss to Grayscale, the SEC can no longer use "potential fraud and manipulation" as grounds to reject spot Bitcoin ETFs. However, it may still find alternative reasons to deny approval.
Status of Spot Bitcoin ETF Applications
Besides Grayscale, several major institutions submitted spot Bitcoin ETF applications in 2023, including BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust, Fidelity’s Wise Origin Bitcoin Trust, and Ark Invest’s ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF. Notably, most of these applicants had previously engaged in prolonged negotiations with the SEC and resubmitted their applications almost simultaneously this year—including BlackRock, applying for the first time. Known for its index-tracking funds, BlackRock’s iShares holds nearly 50% market share in the U.S. ETF space, with an approval success rate approaching 100%. This significantly boosts market confidence that a spot Bitcoin ETF will be approved in 2024.

Moreover, institutions like BlackRock have refined their strategies to address SEC concerns. To mitigate risks of market manipulation and fraud, they’ve proposed Surveillance-Sharing Agreements—arrangements between cryptocurrency exchanges and regulators enabling shared monitoring of trading data. If suspicious activity is detected, alerts are sent simultaneously to regulators, ETF issuers, and exchanges. Both BlackRock and Ark Invest have selected Coinbase Custody Trust Company as their Bitcoin custodian and BNY Mellon as their cash custodian.
Historically, the SEC rarely approves ETFs before the final decision date. The closest upcoming deadline is for Ark Invest’s ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF, set for January 10, 2024. BlackRock and several others face final deadlines around March 15, 2024. According to Reuters sources, discussions between the SEC and applying asset managers have reached advanced stages, covering critical technical details including regulatory arrangements, subscription, and redemption mechanisms. This suggests the SEC may soon approve these products. We could see the first spot Bitcoin ETF greenlit as early as January 10, 2024.
Market Impact of a Spot Bitcoin ETF
Looking at the precedent of gold ETFs: the first physical gold ETF, ETFS Physical Gold, was approved in Australia on March 28, 2003. Then, on November 18, 2004, the world’s largest gold ETF, SPDR Gold Trust, was approved in the U.S. These approvals profoundly impacted the global gold market. Over the next decade, gold prices surged from $332 per ounce to $1,600 per ounce.
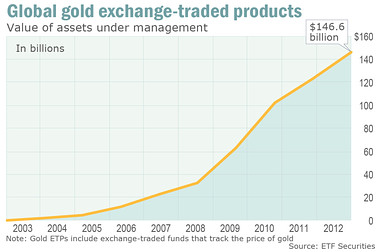
Before gold ETFs, investors faced difficulties accessing gold directly, typically limited to buying bullion—an illiquid and inefficient method that deterred many. Gold ETFs enabled exposure to gold without physical ownership and allowed easy trading like stocks. This integration of gold into mainstream portfolios injected massive liquidity into the gold market, fueling its decade-long price surge.
In many ways, Bitcoin—often called “digital gold”—shares similarities with gold. It is increasingly viewed by mainstream finance as a hedge, safe-haven, and diversification asset. Despite its volatility, numerous asset managers are eager to include Bitcoin in their portfolios. However, compliance and regulatory hurdles prevent direct Bitcoin ownership by traditional institutions. There is strong demand for a compliant financial vehicle to overcome these obstacles—this is precisely why spot Bitcoin ETFs have been so persistently pursued.
Spot Bitcoin ETFs will serve as the largest bridge connecting the ~$50 trillion mainstream asset management industry with the sub-$1 trillion Bitcoin market, injecting trillions in new liquidity. Potential market impacts include:
-
Increased Direct Investment in Bitcoin: A spot Bitcoin ETF will attract mainstream financial investors. High learning curves and lack of accessible financial tools have historically limited effective Bitcoin investment channels for traditional asset managers. Due to compliance and procedural constraints, many institutional investors cannot offer clients direct access to Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. A spot Bitcoin ETF provides them with a familiar, regulated instrument to gain Bitcoin exposure.
-
Enhanced Legal Recognition of Bitcoin: A spot Bitcoin ETF will elevate Bitcoin’s standing in the traditional financial system. Many asset managers are legally restricted from holding Bitcoin directly or purchasing it via centralized exchanges. A regulated ETF solves this issue by offering legally protected exposure, thereby boosting institutional confidence and reinforcing Bitcoin’s legitimacy in mainstream finance.
-
Expanded Portfolio Diversification for Asset Managers: A spot Bitcoin ETF offers asset managers better diversification tools. Compared to existing futures ETFs or trust-based products, a spot ETF provides direct exposure to Bitcoin and minimizes the valuation gap between fund shares and underlying Bitcoin reserves. This makes it a superior financial instrument for institutions seeking meaningful participation in the Bitcoin market.
Outlook for Bitcoin’s Future
Over the past decade, Bitcoin’s recognition within mainstream finance has steadily grown. Driven by investor and institutional demand, regulators—even reluctantly—are being forced to acknowledge the value of crypto assets like Bitcoin at the legal level, opening the door for mainstream asset managers to enter the Bitcoin market.
The approval of a spot Bitcoin ETF marks only the beginning of mainstream finance entering the crypto ecosystem. This year, global regulators have actively worked to build comprehensive regulatory frameworks for crypto markets. Importantly, regulatory actions do not undermine the censorship-resistant nature of crypto assets—this is ensured by cryptography and decentralization. Instead, regulation helps eliminate scams disguised under technological pretenses and clears the path for institutional adoption by establishing clear rules.
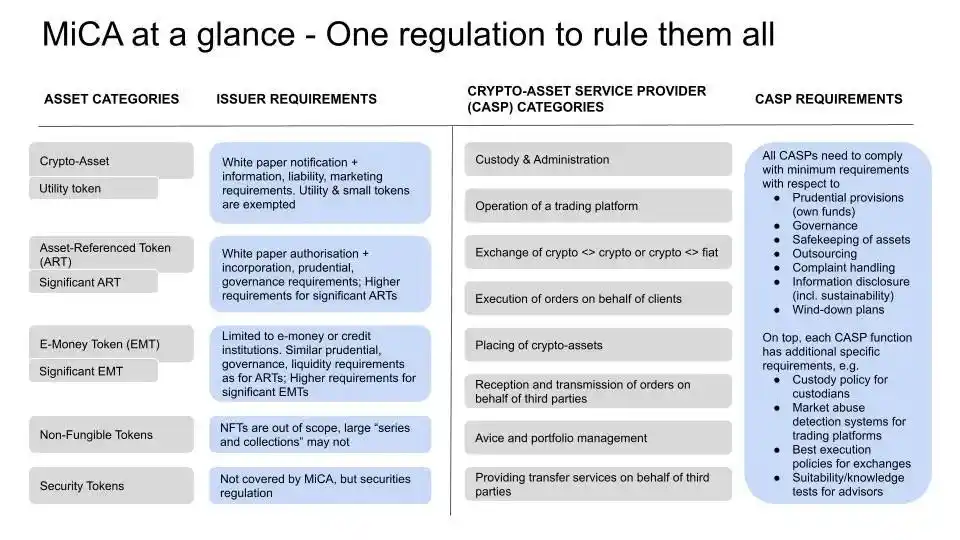
The European Union has made significant progress in building a regulatory framework for the crypto industry. The European Commission began developing such a framework in 2018 and passed MICA (Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation) on April 20, 2023—the most comprehensive crypto regulatory framework globally. By establishing clarity during the current regulatory vacuum in the U.S., the EU aims to provide legal certainty for big tech firms and asset managers entering the crypto space, positioning itself as a global leader in crypto regulation.
While the spot Bitcoin ETF focuses on creating an investment vehicle for Bitcoin, MICA has broader ambitions—to enable all institutions to directly invest in or participate in the crypto market.
Markets widely expect unprecedented growth in Bitcoin’s market cap driven by the potential launch of spot ETFs, the upcoming Bitcoin halving, and the end of the Fed’s rate-hiking cycle. But in the long term, this may only be the beginning. The approval of a spot Bitcoin ETF will undoubtedly mark a pivotal moment—not just for Bitcoin, but for the history of global finance. In the future, we will see comprehensive regulatory frameworks implemented worldwide, leading to deeper integration between Bitcoin and mainstream financial systems, solidifying its role as the universally recognized digital gold.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















