ConsenSys Leads, Linea Arrives: Breaking ZK Rollup Limits to Achieve Full EVM Compatibility
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

ConsenSys Leads, Linea Arrives: Breaking ZK Rollup Limits to Achieve Full EVM Compatibility
This article will conduct an in-depth analysis of Linea from five aspects: project type, competitor analysis, project highlights, ecosystem development, and project progress and future plans.
Author: Darren, Everest Ventures Group
Abstract
To address Ethereum's scalability challenges, Layer2 solutions emerged, with Rollup becoming the most popular approach among various Layer2 options. Rollups can be categorized into two main types: Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup. Compared to Optimistic Rollup, ZK Rollup offers advantages in security, speed, and gas fees. However, current production ZK Rollups generally suffer from a significant limitation—they do not fully support general-purpose computation on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), instead being optimized for specific applications. This compromises compatibility with existing Ethereum L1 smart contracts and decentralized applications (dapps), making it harder to build new contracts with the same composability and expressive experience.
In contrast, Optimistic Rollup is compatible with Ethereum’s EVM smart contracts, making it relatively easy for developers to migrate their smart contracts to Layer2. This ease of migration is the primary reason why Optimistic Rollup has become the dominant Layer2 solution over ZK Rollup to date.
To overcome the issue of ZK Rollup's incompatibility with EVM, ZK-EVM was introduced—and Linea, the focus of this article, represents Type 2 ZK-EVM that achieves EVM equivalence. It allows developers to build scalable dapps or directly migrate existing dapps without modifying code or rewriting smart contracts.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of Linea from five perspectives: project type, competitive landscape, key highlights, ecosystem development, project progress, and future roadmap.
1. Project Overview
Linea is an innovative blockchain solution combining powerful zero-knowledge proof capabilities with full Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) equivalence. It enables developers to build scalable decentralized applications (dapps) or migrate existing dapps without changing code or rewriting smart contracts, significantly simplifying the development process. Developed by ConsenSys, Linea belongs to Type 2 within the various zkEVM categories, leveraging zkEVM’s scalability properties to deliver faster transaction times and higher throughput. zkEVM is a zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) version of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), ensuring transactions and smart contract executions are verified without revealing sensitive information. This enhances security while enabling a more scalable and efficient platform.
In Q4 2022, ConsenSys launched the internal test version of Linea, granting early access to a limited number of users who processed over 350,000 transactions and deployed various decentralized applications. The testnet allowed Solidity developers to build, test, and launch DApps while conducting large-scale testing of zkEVM.
On March 28, 2023, Linea launched its public testnet, releasing a zkEVM rollup to stress-test Layer2 scaling technology. During the public testnet phase, approximately 5.5 million unique wallets executed over 46 million transactions.
On July 18, Linea launched its mainnet Alpha version. As of July 24, the Linea mainnet hosted over 100 ecosystem projects, bridged in 10,921 ETH, recorded 64,604 transactions, and achieved 58,344 interacting addresses.
According to Linea’s Global Business Lead @hotpot_dao, after the mainnet launch, Linea plans to focus on developing Layer3 and Appchain directions to meet game projects’ demands for high throughput and peer-to-peer transactions, while further advancing Multi Prover collaborations.
2. Background & Team
Linea was designed and is operated by ConsenSys, a leading Ethereum software company founded in 2014 with global operations. The company employs top entrepreneurs, computer scientists, protocol engineers, software developers, and enterprise delivery experts. As one of the largest and most foundational entities in the blockchain space, ConsenSys’ global network of people, projects, and companies builds development tools, decentralized applications, and solutions for enterprises and governments determined to leverage Ethereum’s power. In 2018, the organization was described by The New Yorker as “the most prominent and ubiquitous developer and promoter of decentralized applications in the Ethereum community.” Its current product suite includes Infura, Quorum, Truffle, Codefi, MetaMask, and Diligence.
Joseph Lubin, co-founder of Ethereum and founder of ConsenSys, was born and raised in Toronto, Canada, and graduated from Princeton University with a degree in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. He previously developed autonomous music composition tools at Princeton Robotics Laboratory under Tomandandy Music and worked on autonomous mobile robots at Vision Applications Inc., a private research firm. Lubin focuses on the intersection of cryptography, engineering, and finance.
3. Understanding ZK-EVM Types
Earlier, we mentioned that Linea falls under Type 2 among the four zkEVM types. What exactly are these four types, and what characteristics define each? Vitalik outlined zkEVM types based on Ethereum compatibility in his blog post.
Before proceeding, note this key point: The closer a zkEVM is to Ethereum functionality, the slower and more costly zk-proof generation becomes. Conversely, the more closely a blockchain or rollup aligns with Ethereum specifications and standards, the easier it is for developers to build applications and integrate into the Ethereum ecosystem. Therefore, blockchains highly compatible with Ethereum may hold a competitive edge.
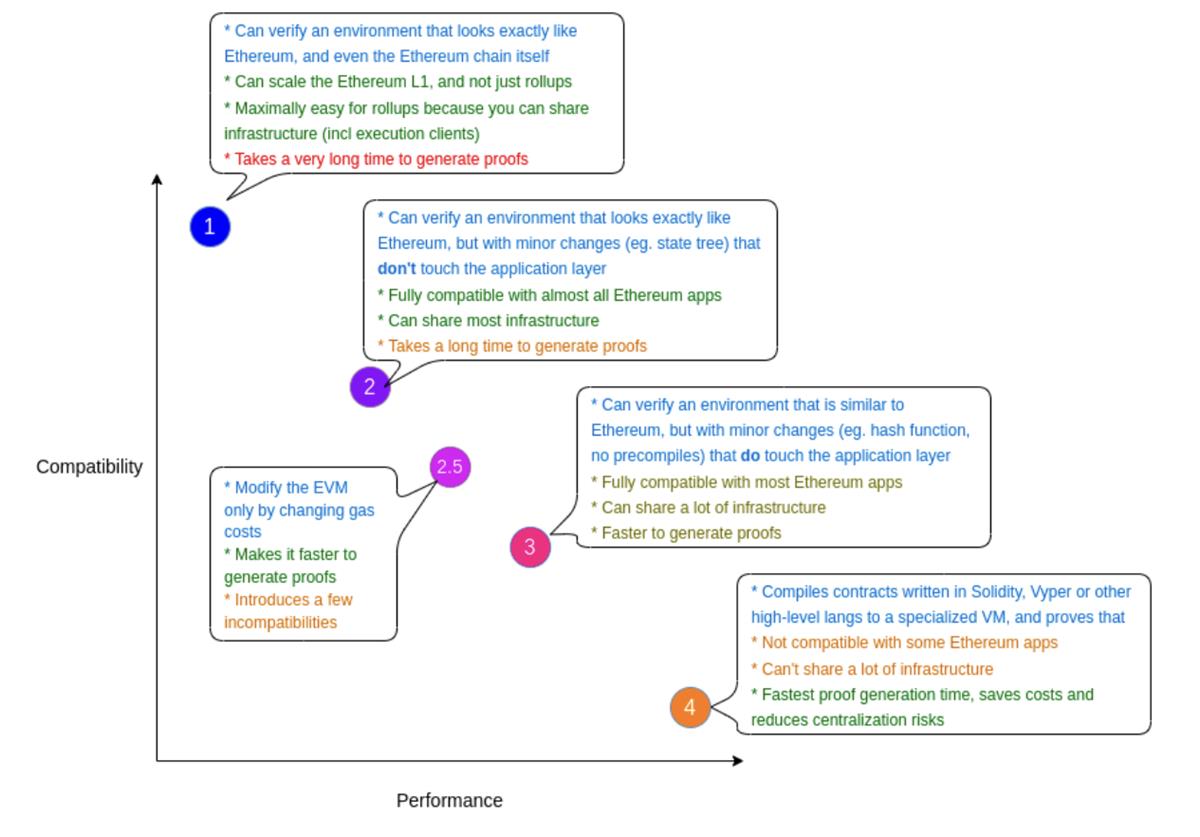
Type 1: Fully equivalent to Ethereum ZK rollups precisely replicate Ethereum across all aspects—including hashes, state trees, transaction trees, precompiles, and any other consensus logic. No zkEVM currently achieves full Ethereum equivalence, but Taiko aims to achieve this eventually, theoretically placing it in this category.
Type 2: Fully EVM-equivalent ZK rollups aim for EVM equivalence but not full Ethereum equivalence. They maintain full compatibility with existing applications but make minor modifications to Ethereum to simplify development and accelerate proof generation. Linea currently belongs to this category.
Type 3: Nearly EVM-equivalent, sacrificing more elements and equivalence to speed up proof generation. Polygon zkEVM and Scroll currently fall into this category, often serving as stepping stones toward Type 2.
Type 4: High-level language equivalence—these accept Solidity-written smart contracts and compile them into another custom, ZK-friendly language. zkSync and StarkNet belong here, though zkSync may gradually add EVM bytecode compatibility and evolve toward higher types like Type 3/Type 2.
It should be noted that these categories are not ranked hierarchically; they represent different technical trade-offs based on implementation choices and proof generation speed, and transitions between them are possible.
As a Type 2 solution, Linea achieves full EVM equivalence. Unlike Type 3 and Type 4 projects, if a team has a dapp on Ethereum mainnet, it can be directly migrated to Linea without any code changes—requiring only a one-click conversion to use Linea’s Layer2 protocol. In contrast, migrating to Type 4 StarkNet requires a compiler and additional steps, potentially introducing security risks and extra development costs.
Given current technology, Type 2 is easier to implement than Type 1. Linea has already launched its mainnet, whereas Taiko (Type 1) has not announced its mainnet launch date. Thus, Type 2 appears more practical, while Type 1 remains more idealistic and earlier-stage.
4. Linea vs Other zkEVMs
1. Funding:
Linea itself has not conducted separate fundraising, but its parent company ConsenSys has raised $726 million, providing ample financial backing. Additionally, MetaMask—one of ConsenSys' flagship products—is the undisputed leader in the wallet sector, generating substantial profits and offering strong indirect support to Linea.
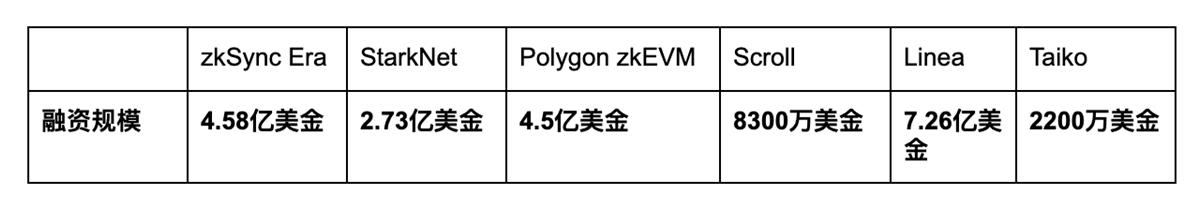
Other zkEVM projects have also secured notable funding: zkSync raised $458 million, StarkNet $273 million, Polygon zkEVM $450 million, Scroll $83 million, and Taiko $22 million. Relative to these, Linea enjoys strong financial resources and institutional backing, positioning it as a frontrunner in the zkEVM race.
2. Technology:
Technologically, Linea benefits from Type 2’s inherent EVM equivalence advantage (currently transitional between Type 2 and Type 3, detailed later). It achieves full equivalence with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to build scalable dapps or migrate existing ones without code modifications or rewrites.
Additionally, Linea employs a unique prover system (detailed in Section 5) to maximize transaction speed and minimize gas fees while maintaining compatibility.
However, due to the inherent difficulty of achieving EVM compatibility in zk-rollups, Linea’s transaction speeds are relatively slower compared to Type 4 and Type 3 zkEVMs such as zkSync, StarkNet, and Polygon zkEVM. Similarly, Linea’s gas fees are slightly higher.
Other technical comparisons are shown below:

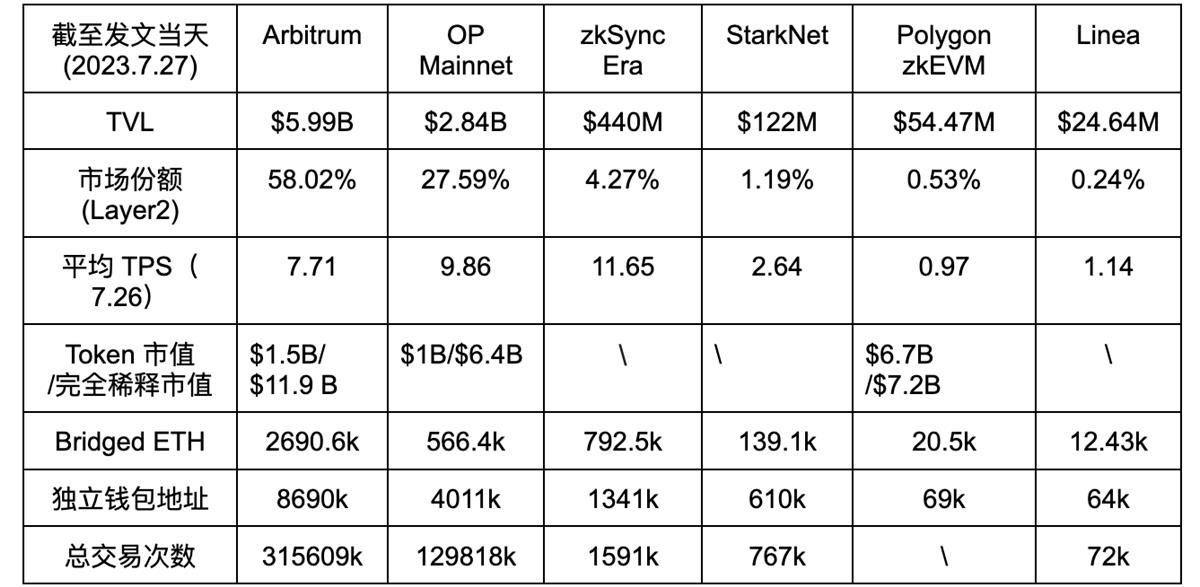
3. Data Comparison:
Note: Since Scroll and Taiko have not launched mainnets, Arbitrum and OP Mainnet are used as substitutes.
Data sources:
[1]https://dune.com/gopimanchurian/arbitrum
[3]https://dune.com/optimismfnd/Optimism-Overview
[4]https://dune.com/KARTOD/zk-evm-mega-dashboard
[5]https://dune.com/tk-research/linea
The above chart displays relevant data for major zkEVM projects. Note that Linea’s mainnet has just launched, so its data is still preliminary and for reference only.
As shown, zkSync leads clearly in data metrics. However, Web3 data often contains inaccuracies, with much activity driven by airdrop farmers—though this also reflects broader community interest.
Another factor behind zkSync’s lead is that shortly before its mainnet launch, Arbitrum—an Optimistic Rollup competitor—launched its token and distributed airdrops to many users, creating windfalls for airdrop hunters. This boosted user enthusiasm, driving nearly 100,000 unique wallets to zkSync within three days of launch. In contrast, Linea launched during a bear market marked by low sentiment and user inactivity. Consequently, Linea attracted fewer than 25,000 unique wallets in its first three days—significantly less than zkSync’s initial surge.
Moreover, only Polygon zkEVM currently has a native token, which may partly explain its lower engagement compared to zkSync Era and StarkNet—without airdrop expectations, it struggles to attract contributors to generate activity.
Finally, the chart shows zkSync Era holds a dominant 4.27% share of the overall Layer2 market, followed by StarkNet, while Linea holds only 0.24%—nearly 20 times smaller. Clearly, for Linea to stand out among zkEVM projects, it must work considerably harder.
5. Key Advantages of Linea
1. Native Integration with ConsenSys Products like Infura, MetaMask, and Truffle:
Developers can easily attract users using MetaMask, a web3 wallet. For example, the Linea testnet is pre-configured in MetaMask’s network selector, eliminating manual setup hurdles and lowering entry barriers.
Furthermore, developers can rapidly deploy and scale dapps using Infura’s user-friendly APIs. Tools like Truffle, Hardhat, Foundry, and Brownie allow developers to build, test, debug, and deploy Solidity smart contracts. Compatible tools Ganache and Diligence support local code testing and auditing, respectively.
Additionally, ConsenSys’ native trustless bridge and MetaMask-integrated bridge enable secure token transfers into and out of the network.
2. Unique Internal Proving System and Compression Method

Linea’s Proof Process
Linea’s technology differs from other zkEVMs in arithmetic schemes and internal proving systems. To prove transaction validity, Linea follows several steps. It begins with arithmetization—converting computer programs into mathematical expressions understandable by zk proofs. This transforms transactions into traces and constraints that verify computational accuracy.
Then, Linea uses internal proving systems Vortex and Arcane, which recursively reduce proof size through optimized computation and specialized algorithms, enhancing efficiency and compactness. Finally, after multiple iterations and internal optimizations, the proof is compressed into the final external proving system Plonk.
This design enables Linea to efficiently generate and verify zk proofs, ensuring transaction privacy and security. By recursively optimizing via internal proving systems and final compression, Linea reduces proof size and improves overall performance, delivering fast and efficient transaction experiences. This innovative technical approach sets Linea apart in the zkEVM space and provides robust support for building scalable dapps.
Internal Proving Systems: Vortex and Arcane
1. Lattice-Based Design:
Vortex is a lattice-based SNARK scheme capable of operating over any field with reasonable binary precision and efficiently handling diverse queries. Lattice-based hashing offers several advantages over traditional cryptographic methods: better performance than popular elliptic curve cryptography and resistance to quantum computing attacks (post-quantum security). Lattices are optimized for recursion, support hardware acceleration, and are compatible with SIMD parallelism. Moreover, lattice-based functions avoid the trade-off between speed and usability in SNARKs (succinct non-interactive arguments of knowledge), making them more versatile.
SNARK schemes also offer advantages over STARKs: SNARKs were discovered years earlier and thus enjoy faster adoption; there are more developer libraries, published codebases, active projects, and contributors working on SNARKs. Secondly, SNARKs are expected to require only 24% of the gas needed by STARKs, making transactions significantly cheaper for end-users. Lastly, SNARK proofs are much smaller than STARKs, requiring less on-chain storage.
2. Transparent Setup:
Vortex’s setup process is transparent and does not require trusted setup participants, making it more secure and reliable.
3. Linear Commitment Scheme:
Vortex uses an innovative linear commitment scheme that efficiently handles commitments to multiple scalar products, resulting in smaller proof sizes than other approaches.
4. Self-Recursive Technique:
Vortex uses self-recursion, reusing different Ring-SIS instances and error-correcting codes, allowing flexible trade-offs between proof size and runtime when selecting parameters.
5. Interactive Oracle Proof (IOP) Model:
Arcane compiles arithmetic into an Interactive Oracle Proof (IOP) model, where verifiers query an oracle—a trusted third party providing probabilistic information. Linea uses the Wizard-IOP framework, enabling more complex queries than standard IOP models. Arcane converts constraint sets into polynomial evaluations, strengthening the mathematical form of proofs. To eliminate reliance on third parties, Linea applies cryptographic assumptions and iterative transformations, replacing oracles with polynomial commitment schemes.
Final Compression Step: PlonK
To enable direct verification on Ethereum L1, Linea uses PlonK to perform the final compression step. Like Groth16 (which Linea originally used), PlonK is a zkSNARK structure leveraging advanced cryptography. PlonK’s SNARK-friendly properties and lattice-based hashing ensure fast verification and generate compact proofs suitable for efficient L1 validation.
PlonK vs Groth16: The shift from Groth16 to PlonK was driven by the trusted setup process. Groth16 requires repeated setups whenever circuits change, while PlonK performs a single, circuit-independent setup. Linea’s iterative circuit design would necessitate frequent Groth16 trusted setup reruns, raising trust concerns. By adopting PlonK, Linea maintains protocol integrity while giving the community confidence in fair participation.
After this transition, a proof will be generated for Linea’s verifier contract to validate on Ethereum L1. Upon successful verification of the proof, state commitment, and call data, the new rollup state will be finalized on the L1 smart contract.
What Benefits Does This Technology Bring to Linea?
In short, the technologies described above enable Linea to improve transaction speed and reduce user gas fees while maintaining high EVM equivalence and compatibility. Since zk-rollups inherently struggle with EVM compatibility, compatibility and speed are negatively correlated. As a highly compatible Type 2 zkEVM with full EVM equivalence, improving speed is especially difficult. Thus, Vortex’s lattice-based SNARK scheme represents a remarkable and rare technical breakthrough.
3. Driving Multi-Prover Adoption
Multi-Prover treats Linea as an Ethereum client, similar to how multiple clients exist today, including Layer2 projects like zkSync and Polygon zkEVM. Having multiple clients ensures Ethereum’s security—if one fails, others serve as backups.
Declan Fox, Senior Product Manager at Linea, stated that to mitigate potential risks, Linea will promote a Multi-Prover approach—where multiple provers (understood as different Layer2 products) jointly verify transactions using diverse zkEVM implementations. If one prover fails or becomes unavailable, the system continues reliably as long as a quorum of other provers remain functional.
ConsenSys’ Global Business Lead @hotpot_dao explained: “Multi-Prover is a product where three different Layer2s perform proofs. Only when all three agree is the product validated and settled back on the mainnet, greatly enhancing Ethereum’s security. This is one of Linea’s intended roles in building Layer2 protocols. As ConsenSys, we’re primarily focused on advancing Multi-Prover. This aligns closely with Ethereum’s overall direction and our vision for the future internet, while posing a major technical challenge.”
Multi-Prover is crucial for the entire Layer2 landscape. As its initiator, advocate, and potential leader, if Linea successfully implements Multi-Prover, it will gain greater market recognition and trust, unlocking more opportunities and advantages in the future.
6. Ecosystem Development
To date, Linea has attracted over 100 ecosystem partners. The mainnet launched alongside this extensive ecosystem, offering users, builders, and developers opportunities to create the next generation of scalable Ethereum dapps.
Based on our long-term observation of Linea, during the early ecosystem phase, Linea focused on building infrastructure such as cross-chain bridges and wallets, establishing positions in DeFi sectors like DEXs and lending, while also investing in Social and GameFi to continuously attract users and developers toward mass Web3 adoption. As ConsenSys’ Global Business Lead put it: “Social networks need network effects, facing cold-start problems that are hard to solve on Layer2. So we’ll start with DeFi, then small GameFi projects, letting users first experience our platform and network, lay the foundation, and then hope good social apps come to develop on it.”
With the mainnet launch, we analyze some of the more active and trending projects within the Linea ecosystem. For more comprehensive details, refer to the official website.
DeFi
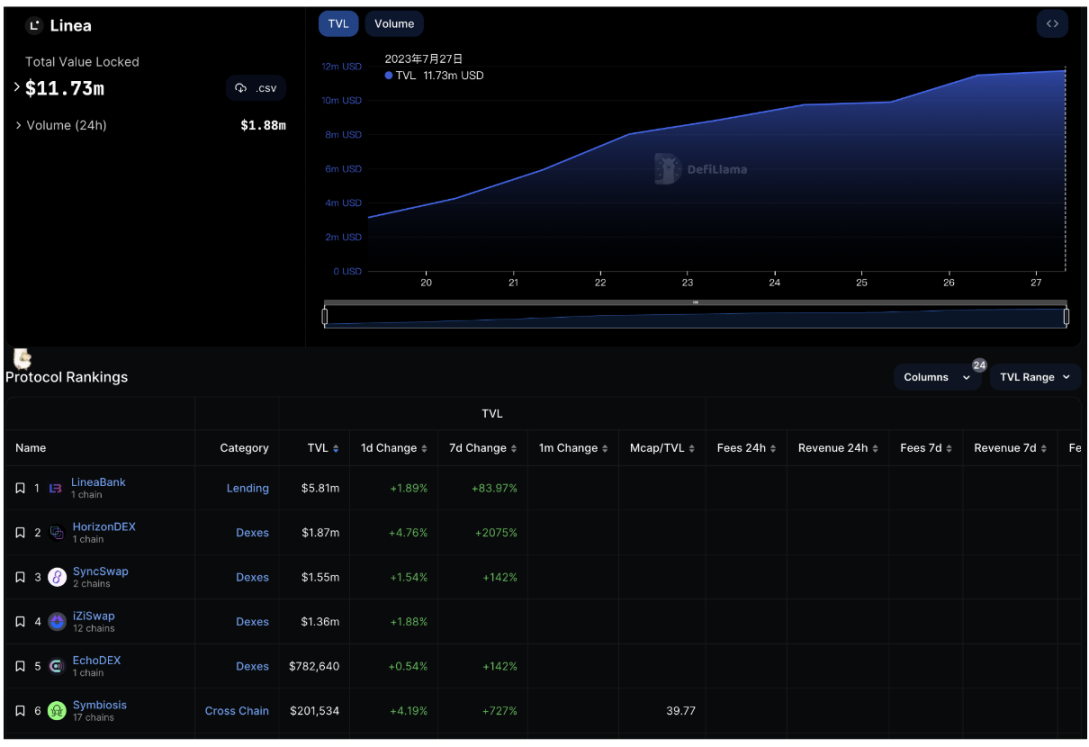
Linea Ecosystem TVL Rankings
LineaBank
LineaBank is a lending protocol built on Linea, emphasizing privacy protection and scalability. The protocol gives users full control over their assets and eliminates intermediaries through decentralized markets, offering competitive interest rates. As its name suggests, LineaBank is a native project on the Linea blockchain. According to the chart above, LineaBank currently ranks first in TVL on Linea, reaching $5.81 million as of today (July 27).
Notably, following Linea’s mainnet launch, LineaBank ran a “pre-mining” campaign, during which users could earn 100% of the protocol’s revenue.
iZUMi Finance
iZUMi Finance is a liquidity optimization protocol built on Ethereum and part of the Uniswap V3 ecosystem, offering “programmable liquidity-as-a-service” based on Uniswap V3 for blockchain projects.
iZUMi’s LiquidBox helps projects attract liquidity by designing effective incentive programs. It also provides a shared liquidity box that maps a token’s liquidity across multiple chains, allowing LPs to stake liquidity from one chain and farm across multiple chains.
iZUMi has also launched iZiSwap on BNB Chain and zkSync—a discrete liquidity AMM upgraded from the Uniswap V3 concentrated liquidity model. iZUMi is also developing iUSD, a USD-pegged stablecoin backed by USDC, used in iZUMi bond mining programs.
Other user-centric DeFi products include impermanent loss insurance, refunding LPs for losses on their LP tokens, and fixed-income opportunities offering up to 10% APY over 30-day terms.
To date, iZUMi Finance has raised $57.6 million, with investments from Mirana Ventures, Everest Ventures Group, IOSG, and others—backed by strong capital and resources.

As shown above, on July 11, iZUMi announced its collaboration with Linea. As of today, iZUMi Finance ranks fourth in Linea’s TVL leaderboard with $1.36 million in TVL (as of July 27). This indicates growing recognition and active participation within the Linea ecosystem. Through this partnership, iZUMi will expand its influence and contribute to Linea’s ecosystem growth.
Mendi Finance
Mendi Finance is an EVM-compatible lending protocol launching on the Linea network.
Mendi Finance offers peer-to-peer lending in a fully decentralized, transparent, and non-custodial manner. As a native Linea project, it aims to become the primary lending platform on Linea by offering competitive incentives and deepest liquidity in money markets.
After launch, users can lend any supported asset on Mendi Finance and borrow supported assets using their funds as collateral, including ETH, BTC, USDC, USDT, and DAI. Collateral factors range from 0–90%, representing the maximum borrowable amount against a specific asset. If an account’s borrowed balance exceeds the collateral factor limit, it will be liquidated.
HorizonDEX
HorizonDEX is a concentrated liquidity decentralized exchange allowing users to allocate liquidity within custom price ranges, maximizing trading efficiency and minimizing slippage. As a native Linea blockchain project, HorizonDEX ranks second in TVL on Linea, reaching $1.87 million as of today (July 27).
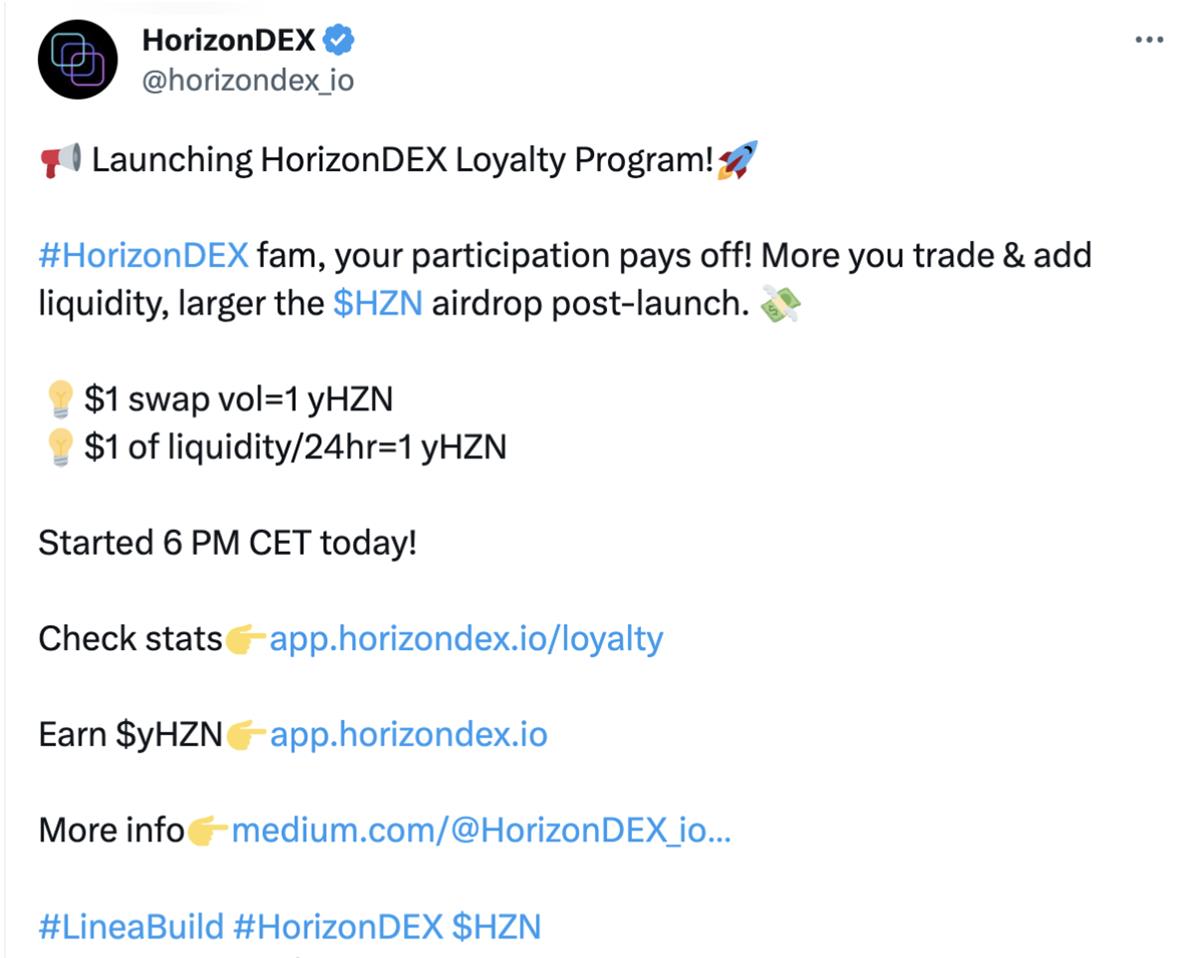
Additionally, as shown above, after Linea’s mainnet launch, HorizonDEX launched an airdrop campaign where users earn $HZN tokens by trading or providing liquidity. During the event (July 19–August 2), every $1 traded or $1 of liquidity provided for 24 hours earns 1 yHZN token. After the event, $HZN airdrops will be distributed proportionally based on yHZN holdings—the more yHZN held, the larger the airdrop.
EchoDEX
EchoDEX is a decentralized exchange built on the Linea Consensys network and a native Linea blockchain project. It was the first DEX launched on Linea and currently ranks fifth in TVL on Linea, exceeding $780,000 as of today (July 27).

Notably, its token ECP currently has a market cap of $37.4M and garnered significant community attention upon launch.

Like the two projects mentioned earlier, EchoDEX also has airdrop expectations. On July 19, they announced users can earn points—and a chance at airdrops—by swapping, adding liquidity, farming, or even daily check-ins.
Owlto Finance
Owlto Finance is a decentralized Cross-Rollup bridge offering low-cost, secure, and fast asset transfer solutions, with smart contracts audited by security firm Beosin. Notably, after Linea’s mainnet launch, Owlto Finance initiated a 7-day zero-fee cross-chain campaign for Linea.
Importantly, Owlto Finance states in its documentation that unlike other Cross-Rollup bridges based on secure rollup technology, asset transfers occur directly between EOAs (externally owned accounts) of senders and liquidity providers on the source and destination networks—senders do not interact with smart contract addresses. This design reduces risk, as smart contract addresses may be vulnerable to attacks, while EOAs are typically more secure.
NFT
NFTs2ME
To simplify NFT creation, deployment, and management on the Linea network, NFTs2ME claims to offer utilities enabling users to create and manage NFTs without writing a single line of code. Additionally, NFTs2Me states the platform is open and free to use.
Platform tools include a design panel allowing creators to define NFT attributes. It features AI-powered art and image generation tools, enabling users to create artwork, define metadata, and set mint prices—all within the platform. It supports multiple NFT smart contract standards and allows collectors to pay mint fees in any (crypto) denomination.
NFT creators can use platform tools in various ways to manage generated artworks. NFTs2Me’s user dashboard includes analytics to help track NFT performance. Users can also plan and execute airdrops, take snapshots, design NFT-gated programs, and prepare whitelists for NFT mints via their NFTs2Me profile.
NFTs2Me is multi-chain compatible, available on Ethereum, Polygon, Taraxa, and Layer2 networks Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync Era, and Linea.
ghostNFT
ghostNFT is one of Linea network’s official testnet projects and is expected to soon launch on mainnet with Linea’s Alpha release.
ghostNFT claims to leverage the ERC-721Envious standard (an improved version of ERC-721) to provide additional monetization features for NFTs through NFT staking. It claims to merge NFTs and DeFi through its NFT 2.0 initiative, empowering creators and collectors in multiple ways. Creators can define staking plans, collect stakes, and fundraise for NFT launches. Users can also perform this via the “fragment” feature on individual NFTs or entire collections.
ghostNFT is multi-chain compatible and already available to users on Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, Avalanche, and several other networks.
Infra
Thirdweb
Thirdweb is a UK-based Web3 software developer offering free Web3 development tools that allow developers to build, launch, and manage web3 projects without writing code—adding features like NFTs, social tokens, currencies, token markets, and NFT trading with just a few clicks.
On August 25, 2022, Thirdweb raised $24 million in a strategic round at a $160 million valuation, led by Haun Ventures, with participation from Coinbase Ventures, Shopify, Protocol Labs, Polygon, Shrug VC, and others. Individual investors include Joseph Lacob, partner at Kleiner Perkins and major shareholder of the NBA’s Golden State Warriors. Earlier, in a $5 million seed round, Thirdweb received investment from Mark Cuban, owner of the Dallas Mavericks, and renowned entrepreneur Gary Vaynerchuk, bringing total funding to $29 million—with strong financial backing.
Additionally, Linea published a tutorial titled “How to Quickly Build with Thirdweb,” detailing how to deploy smart contracts using Thirdweb’s Solidity SDK, manage them via dashboard, and build an app to interact via SDK.
SocialFi
QuestN
QuestN is a Web3 quest and activity platform incubated by Hogwarts Labs. Users can earn tokens and NFT badges by participating in quests and activities.
QuestN aims to provide various permissionless on-chain and off-chain quests for GameFi, DAOs, and other projects, bringing continuous benefits to users and the Web3 ecosystem and its native value.
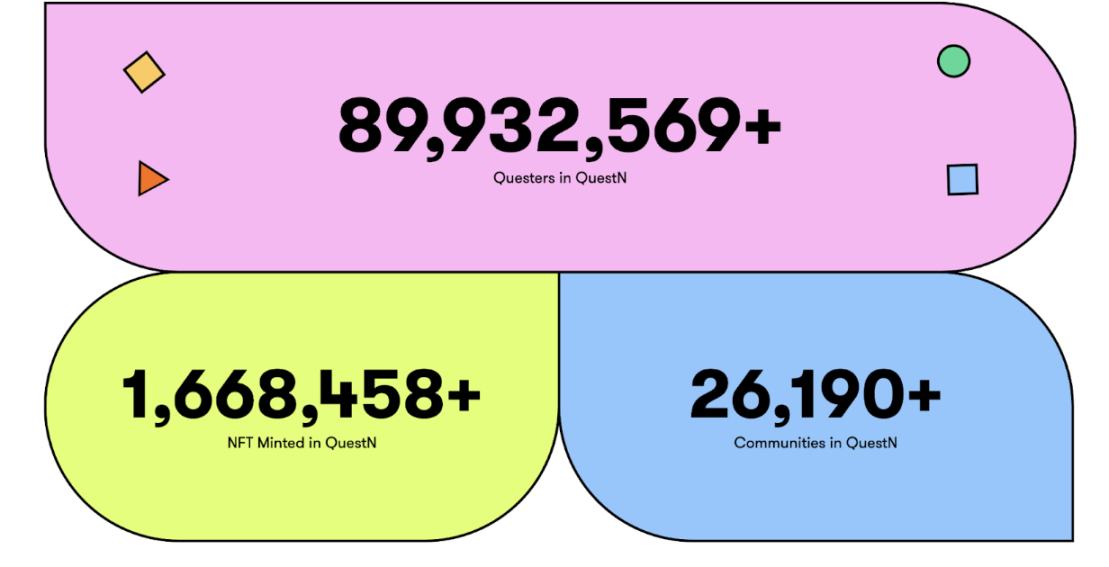
As shown above, QuestN has seen nearly 90 million tasks completed to date, issued over 1.6 million NFTs, and gained support from over 26,000 communities.
Additionally, on June 1 this year, QuestN’s parent company Hogwarts Labs completed a Pre-A round, raising $8 million.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















