Layer2's Future: The Path Forward Led by the Cancun Upgrade
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Layer2's Future: The Path Forward Led by the Cancun Upgrade
What new opportunities can the Cancun upgrade bring to L2?
2023 has witnessed two major upgrades in Ethereum's history. The first was the Shanghai upgrade, completed on April 13. With the Shanghai upgrade, withdrawals from beacon chain staking were enabled, marking Ethereum’s full transition from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS). This milestone represented a critical step forward in Ethereum’s long-term roadmap. Now, Ethereum is approaching the upcoming Cancun upgrade, aimed at enhancing data storage capacity to reduce costs and improve efficiency for Layer 2 (L2) solutions. The upgrade is expected to increase L2 transaction speeds by 10 to 100 times while significantly lowering fees. According to the latest Ethereum core developer meeting, the Cancun upgrade is projected to go live by the end of this year.
How will the Cancun upgrade accelerate Ethereum's scalability, and what new opportunities will it bring to Layer 2? R3PO believes that through the Cancun upgrade, Layer 2 will become more deeply integrated into the Ethereum ecosystem, offering users faster and lower-cost transaction experiences. Both Optimistic Rollups and ZK Rollups will benefit from this upgrade, collectively driving the evolution of the Ethereum ecosystem.
I. A Certain Future—Layer 2
In Vitalik Buterin’s latest article, “The Three Transitions,” the co-founder of Ethereum outlines three key technological transitions Ethereum must undergo: transitioning to scaling via Layer 2, where everyone moves to rollups; transitioning to wallet security, where everyone adopts smart contract wallets; and transitioning to privacy, making private financial transfers feasible.
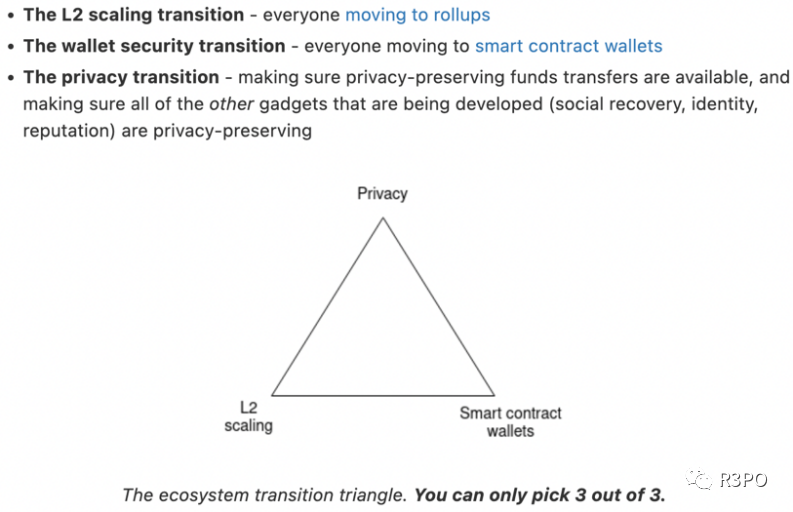
The article highlights the importance of Layer 2 and rollups. Vitalik points out that without the development of Layer 2, Ethereum would fail due to high transaction costs. Compared to VISA, a globally renowned payment system capable of processing tens of thousands of transactions per second, Ethereum’s current throughput of only 15 transactions per second falls far short of normal demand. The average transaction cost of $3.75 also deters many regular users.

Ethereum supports massive transaction activity daily. As the ecosystem grows, block space limitations have led to increasing network congestion. High fees and slow speeds on Ethereum’s Layer 1 mainnet have become increasingly apparent, creating an urgent need for cost reduction and performance improvements.
Scalability has long been a top priority for Ethereum developers. Following the Shanghai upgrade, which resolved consensus mechanism issues, the focus now shifts to scalability. According to Vitalik’s Ethereum roadmap, the goal is to boost Ethereum’s transaction processing capacity to over 100,000 transactions per second.

Currently, there are two primary scalability solutions for Ethereum: Layer 2 and sharding. Layer 2 is an off-chain solution designed to scale the base blockchain (Layer 1). It works by executing blockchain transactions off-chain, performing computation and execution off-chain, and then submitting minimal on-chain transactions to verify final validity. The dominant Layer 2 solution today is rollups. Rollups bundle dozens or even hundreds of transactions executed on-chain into a single transaction summary, sending only the summary data to Ethereum. By storing just the summary instead of performing full computation and storage on the Ethereum chain, rollups achieve scalability while maintaining Ethereum’s security.
II. Optimistic Rollup vs. ZK Rollup
Rollups are primarily divided into two types: Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup (Zero-Knowledge Rollup).
Optimistic Rollup uses a fraud proof mechanism. The system assumes transaction data is valid and proceeds with execution without immediate verification, entering a challenge period. During this period, if any node raises an objection and provides evidence of malicious activity, the transaction is reverted. If no challenges occur, the transaction is confirmed and written into the block after the waiting period. By omitting large-scale validation, this approach saves computational resources while ensuring transaction accuracy. Notable implementations include Arbitrum and Optimism.
ZK Rollup uses zero-knowledge validity proofs. It generates a zero-knowledge proof to verify all transactions as valid and uploads only the final state changes to Ethereum. Unlike Optimistic Rollups, ZK Rollups do not need to submit compressed details of every transaction—only the zero-knowledge proof and final state data are required. Major players in the ZK Rollup space include ZKsync, Starkware, and Scroll.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Optimistic Rollup:
Advantages:
- Compatibility: Optimistic Rollup is relatively easy to support general-purpose contracts and Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility, enabling developers to build and migrate applications more easily.
Disadvantages:
- Time delay from fraud proofs: In cases of malicious transactions or disputes, withdrawal periods in Optimistic Rollup can be long—typically up to one week—potentially locking funds and limiting liquidity.
- Network stagnation: When disputes arise, the entire Optimistic Rollup network may stall, halting transactions until the dispute is resolved and verified.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ZK Rollup:
Advantages:
- Privacy protection: Using zero-knowledge proof technology, ZK Rollup verifies transaction validity while preserving user privacy. Transaction details remain confidential—only the correctness of the proof needs to be validated—offering stronger privacy guarantees.
- Security: The verification process in ZK Rollup relies on mathematical proofs, providing robust security. Zero-knowledge proofs ensure transaction validity and consistency without revealing transaction details.
Disadvantages:
- Computational cost: Generating and verifying zero-knowledge proofs requires significant computational resources. This results in higher computational overhead and longer processing times.
- Limited smart contract functionality: Since ZK Rollup is optimized for transaction processing, support for complex smart contracts is limited. Some sophisticated contracts may not be directly deployable on ZK Rollup.
Due to its lower development difficulty and earlier launch, the OP stack currently dominates over 90% of total value locked (TVL) in the market, while the ZK stack holds a smaller share. The ZK ecosystem needs faster progress and stronger ecosystem development to compete in user growth. As the Layer 2 ecosystem matures and rollup fees drop significantly post-Cancun upgrade, user adoption and ecosystem expansion will likely become the decisive factors in the competition between ZK and OP stacks.
III. The Future of Layer 2: Advancing Under the Cancun Upgrade
Earlier, we compared the strengths and weaknesses of Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup as Layer 2 solutions. With the upcoming Cancun upgrade, Layer 2 is poised for new growth opportunities. The Cancun upgrade marks a major milestone for Ethereum, aiming to enhance scalability and performance. Through this upgrade, Layer 2 will integrate more seamlessly into the Ethereum ecosystem, delivering faster and lower-cost transaction experiences. Both Optimistic Rollups and ZK Rollups will benefit from these improvements. After the Cancun upgrade, Ethereum Layer 2 speeds are expected to increase 10–100 times while transaction costs decrease, opening new possibilities for high-throughput, low-cost decentralized applications.

1. Key Components
The Cancun upgrade includes five Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), focused on increasing data storage and reducing fees. Centered around EIP-4844, the upgrade also incorporates EIP-1153, EIP-4788, EIP-5656, and EIP-6780. While no exact date has been set, the upgrade is expected to launch by the end of 2023.
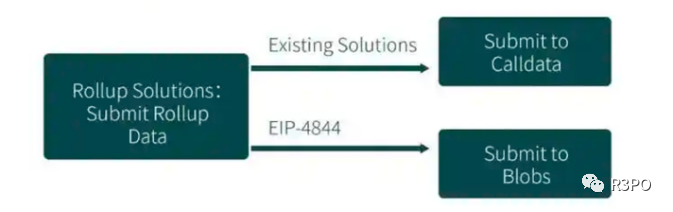
EIP-4844: As the centerpiece of the Cancun upgrade, EIP-4844—also known as Proto-Danksharding—is a rollup-focused scalability solution and the first step in Ethereum’s broader scaling journey. Before this upgrade, rollup data was permanently stored on Ethereum, leading to high storage costs—accounting for roughly 90% of users’ rollup transaction fees. To address this, EIP-4844 introduces a new transaction type: Blob Transactions. Data is temporarily stored in “blobs” for about one month before being deleted. Long-term data storage will be handled separately by third-party service providers as needed. Once blobs become part of the Ethereum protocol via Proto-Danksharding, additional blobs can be added to Ethereum blocks, potentially increasing throughput by over 100x while drastically reducing transaction costs.
Other included EIPs:
-
EIP-1153: Reduces on-chain data storage costs, improving block space efficiency.
-
EIP-4788: Enhances cross-chain bridge and staking pool designs.
-
EIP-5656: Introduces minor code changes related to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
-
EIP-6780: Removes code that could potentially terminate smart contracts.
2. What Opportunities Should You Watch?
① The Grand Narrative of Layer 2

The era of Ethereum congestion has given rise to the grandest narrative in crypto. Total TVL across the L2 ecosystem has more than doubled since the beginning of the year, reaching approximately $8 billion.
As the first step in Ethereum’s scaling journey, the Cancun upgrade will make Layer 2 solutions 10x to 100x faster and cheaper. The scalability and reduced fees from EIP-4844 will benefit all L2 ecosystems: the OP stack will grow more diverse, the ZK stack will become more usable thanks to improved data availability, and high-cost standalone Layer 2 projects will see rapid growth. Lower on-chain fees will lead to richer L2 ecosystems and growing user bases.
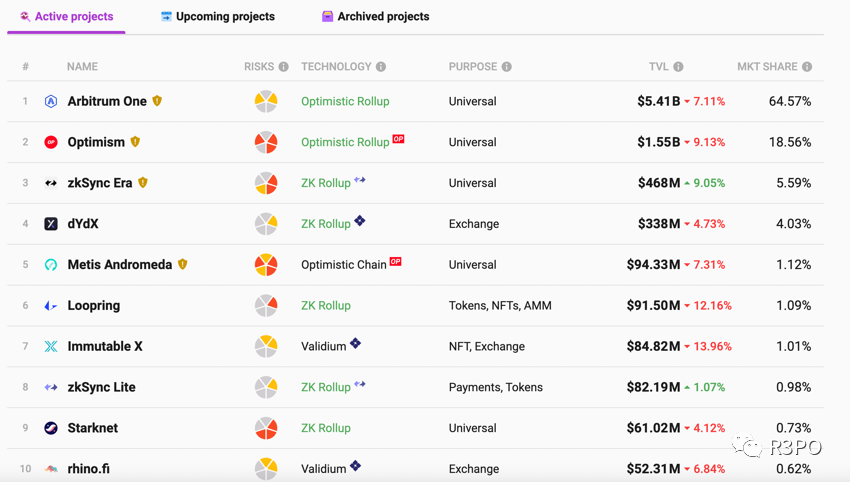
Among existing projects, leaders such as Arbitrum, Optimism, rising star ZKsync, and established player dYdX already dominate half of the current L2 landscape. The strong continue to strengthen, and leading protocols in popular sectors hold even greater potential post-Cancun upgrade.
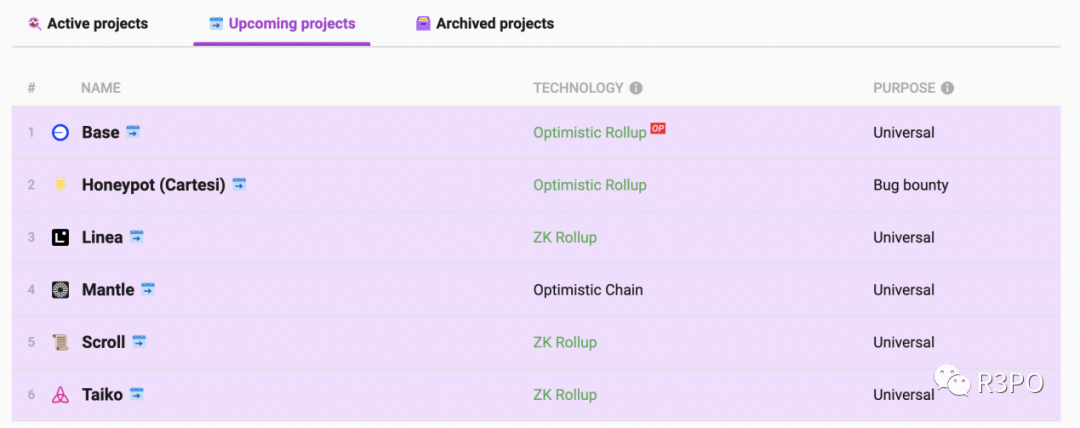
Beyond launched projects, upcoming mainnet launches like Scroll, Linea, and Taiko are also worth watching.
Moreover, faster transaction speeds and lower fees on L2 will inevitably spark a new wave of growth for L2-based applications. On-chain futures and options, whose performance is highly sensitive to Ethereum’s low TPS, will see substantial improvements—projects like GMX and GNX will benefit directly, unlocking further growth potential.
② The Data Availability (DA) Layer Sector
Since blob data is only stored temporarily, accessing historical data becomes challenging. This creates demand for decentralized storage solutions. Additionally, Layer 2 scaling strategies require dedicated data availability layers. The Cancun upgrade will also benefit L1 storage expansion networks such as Ethereum Storage, Arweave, and Filecoin—projects building Ethereum’s DA infrastructure.
3. Where Is Layer 2 Heading?
Looking ahead, as the Cancun upgrade ushers in a new phase of Ethereum scalability, higher throughput and lower transaction fees will allow Layer 2 applications to process more transactions and deliver faster, near-instant confirmations. Whether in finance for payments and settlements, or in gaming and NFTs, the high performance of Layer 2 will provide users with smoother and more efficient experiences.
However, technological advancement alone cannot attract users. To achieve true prosperity on Layer 2, innovative applications are essential. According to L2beat data, there are currently 29 Layer 2 projects either live or in development. Among them, Arbitrum One, Optimism, zkSync Era, and dYdX already control 92.75% of the market share, leaving other L2s to compete for the remaining 6.25%.
It’s like having spent enormous time and effort building highways, but with almost no vehicles using them—this is the common problem faced by most L2s. Without quality applications, the value of Layer 2 cannot be realized. Arbitrum, for instance, built its thriving ecosystem largely due to the rise of DeFi applications like GMX. Only by developing more convenient, innovative, and practical applications that meet real user needs can Layer 2 truly capture attention and participation. Developers and entrepreneurs must boldly experiment and innovate on Layer 2, leveraging its advantages to create unique and compelling use cases. Only then can Layer 2 become truly embedded in everyday life. Therefore, beyond technical progress, user migration and application adoption will be key to Layer 2’s future success.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News