IOBC Capital: Current State and Case Analysis of the RWA Sector
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

IOBC Capital: Current State and Case Analysis of the RWA Sector
Tokenized real-world assets could be the next engine for DeFi.
By 0xCousin
Tokenized real-world assets could be the next engine for DeFi.
What is RWA?
RWA stands for Real World Asset—tangible assets from the physical world.
The most popular RWAs today include: cash (e.g., U.S. dollars), metals (gold, silver, etc.), real estate, bonds (mostly U.S. Treasuries), insurance, consumer goods, credit notes, royalties, and more.
The market size of RWA vastly exceeds that of crypto-native assets. For example, the fixed-income bond market is valued at approximately $127 trillion, global real estate totals around $362 trillion, and gold’s market cap is about $11 trillion. In contrast, the current market cap of crypto-native assets stands at $1.1 trillion—only one-tenth of gold's value.
Even a small fraction of these RWAs brought into DeFi could significantly expand its total scale.
How to Bring RWA into DeFi?
Typically, smart contracts are used to create tokens representing RWAs, along with off-chain assurances that issued tokens can always be redeemed for the underlying assets.
RWA has several common applications in DeFi:
1. Stablecoins: Top stablecoins like USDT, USDC, and BUSD fall under RWA. Issuers such as Tether, Circle, and Paxos mint stablecoin tokens backed by audited reserves of U.S. dollars for use across blockchains and DeFi protocols;
2. Synthetic Assets: Synthetics also belong to RWA. Through synthetic derivatives, assets like stocks and commodities can be traded on-chain. Currently, Synthetix leads in this space, having locked over $3 billion in assets at its peak during the 2021 bull market;
3. Lending Protocols: RWA has seen strong development in lending. Borrowers can use RWAs as collateral, enabling DeFi platforms to offer secured loans. Some platforms even provide unsecured credit based solely on brand reputation. The integration of RWA in DeFi lending plays a crucial role in driving sustainable growth and revenue for these protocols.
Current State and Case Studies of the RWA Sector
RWA tokenization helps expand DeFi’s market size and enables traditional financial institutions to explore new business models. Leading DeFi protocols are actively integrating RWA, while many traditional finance players are showing growing interest.
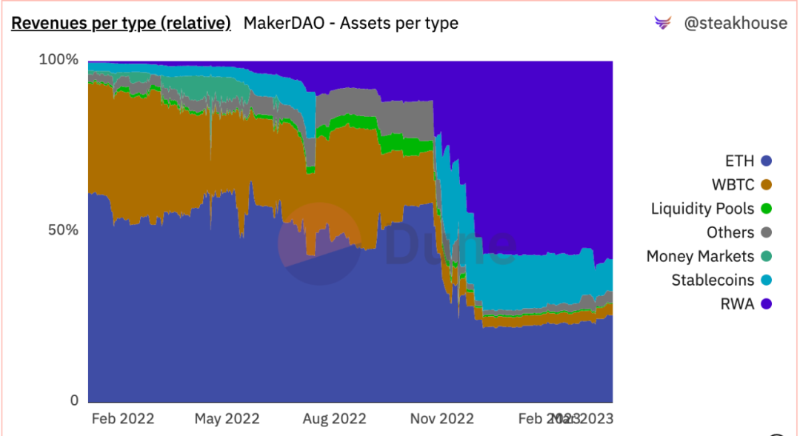
MakerDAO: Over $680 million in RWA exposure, contributing more than 58% of revenue.
Since traditional financial systems now offer higher yields than DeFi protocols—for instance, U.S. Treasury yields (~3.5%) exceed those of top DeFi lending platforms (~2%)—this creates an opportunity for DeFi protocols to generate sustainable income.
To manage its RWA operations, MakerDAO established the RWA Foundation. Depending on the type of collateral, different foundations may be formed, and each SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle) can choose the most suitable jurisdiction or legal structure. Its basic architecture is as follows:
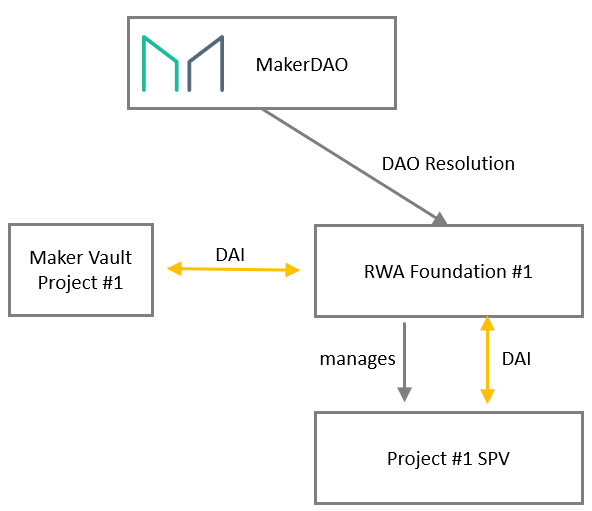
For off-chain RWA collateral, MakerDAO has made adjustments to its lending logic. Notably, liquidations are not executed via on-chain auctions but are instead enforced off-chain by third parties. Key smart contracts enabling this functionality include:
-
RwaLiquidationOracle: Acts as a liquidation beacon for off-chain executors; -
RwaFlipper: Serves as a virtual liquidation module in case of write-offs; -
RwaUrn: Facilitates borrowing DAI and delivering it to designated accounts; -
RwaOutputConduitandRwaInputConduit: Handle DAI payments and repayments; -
RwaSpell: Deploys and activates new collateral types; -
RwaToken: Represents RWA collateral within the system; -
TellSpell: Allows MakerDAO governance to initiate liquidation; -
CureSpell: Enables governance to cancel ongoing liquidations; -
CullSpell: Permits governance to write off loans under liquidation.
When necessary, MakerDAO calls the RwaLiquidationOracle via tell(). This starts a countdown; after the remediation period ends, the oracle begins reporting that the position is under liquidation. If the trigger is resolved, governance can call Cure() to restore normal status. If the remediation period passes without resolution, off-chain executors (e.g., trustees) can call good() to confirm the position is being liquidated. If debt remains after liquidation and MakerDAO determines it won’t be repaid, cull() can be called to trigger write-off. This sets the collateral value to zero, leading to on-chain liquidation via bite(). Unlike standard liquidation modules, the specialized RwaFlipper does not attempt to sell the underlying collateral but marks losses on the system balance sheet by allowing system debt creation.
MakerDAO has made significant progress in adopting RWA. As of now, over $680 million worth of RWAs back the decentralized stablecoin DAI.
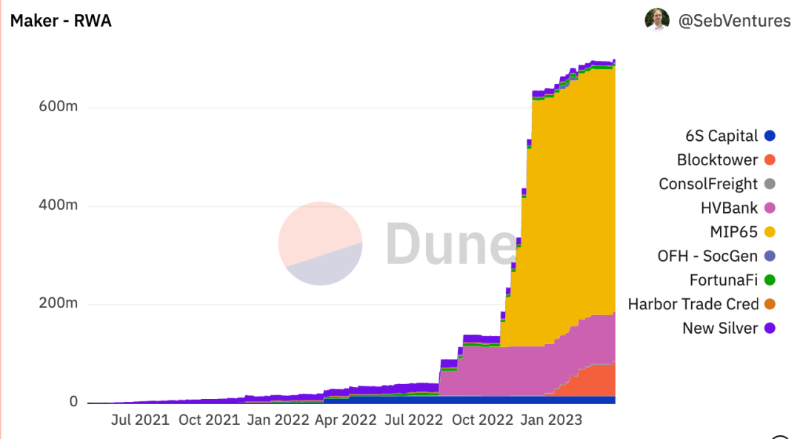
Breaking down MakerDAO’s $680 million RWA exposure, three specific cases stand out:
1. Most of MakerDAO’s RWA collateral (~$500 million) comes in the form of U.S. Treasuries managed by Monetalis (MIP65). These assets provide yield on idle USDC collateral within the MakerDAO protocol;
2. MakerDAO launched a vault backed by a $100 million loan facility from Huntingdon Valley Bank (HVB), a commercial bank based in Philadelphia. HVB uses MakerDAO to support growth in its existing business and investments in real estate and related verticals—marking the first commercial loan bridging regulated U.S. financial institutions and decentralized digital currency;
3. In a separate vault, French bank Société Générale borrowed $7 million from MakerDAO, with its position backed by €40 million in AAA-rated bonds represented as OFH tokens.
By incorporating RWA as collateral, MakerDAO has significantly increased its protocol revenue. To date, over 58% of MakerDAO’s income comes from RWA-related activities.
Centrifuge: Bringing RWAs into Crypto via NFTs, with TVL exceeding $170 million.
Centrifuge brings real-world assets into the crypto ecosystem using NFTs. The protocol’s dApp, Tinlake, operates as follows:
1. Asset originators use Tinlake to bridge real-world assets onto the blockchain. These assets are converted into NFTs containing relevant legal documentation;
2. Originators can use these tokenized RWA NFTs as underlying collateral to create asset pools;
3. Upon pool creation, two tokens are issued: DROP and TIN;
4. Investors choose which pool to fund based on risk appetite, purchasing either DROP or TIN tokens;
5. DROP token holders receive fixed returns determined by a fee function, with interest compounded every second;
6. TIN token holders do not have guaranteed returns. They earn variable yields based on the pool’s performance, potentially higher than DROP returns;
7. However, TIN holders absorb first-loss risk—if borrowers default, they bear the initial losses.
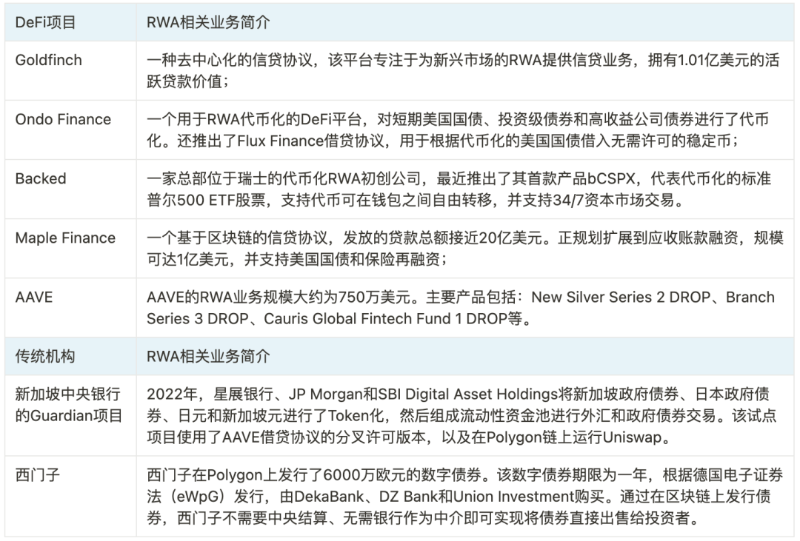
Beyond MakerDAO and Centrifuge, other DeFi protocols and traditional financial institutions are also exploring RWA integration:
Opportunities and Risks of RWA
Trust Assumptions of RWA: Since tokenized RWAs are ultimately backed by off-chain assets, their liquidation cannot be fully enforced through smart contracts and still relies on endorsements from traditional financial institutions. As a result, the trustworthiness of RWAs may never reach the same level as crypto-native assets. Moreover, due to these trust assumptions, fully permissionless DeFi protocols struggle to support RWA. Therefore, most current RWA tokenization projects still involve centralized entities in managing RWA assets.
Potential Opportunities for RWA: Security Token Offerings (STOs) have long been seen as a limited implementation of RWA. While many STOs exist only on private, permissioned platforms and remain niche securities, their adoption hasn't yet reached the scale of public-chain-based RWA. However, STOs are among the few asset tokenization models in the blockchain industry recognized by regulators. The regulatory-compliant path taken by STOs may serve as a reference for future RWA development.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News