Efficient and Seamless Cross-Chain Composability: How NEAR's Nightshade Will Spark a DeFi Boom?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Efficient and Seamless Cross-Chain Composability: How NEAR's Nightshade Will Spark a DeFi Boom?
Nightshade is NEAR's solution for scalability and cross-chain composability.
Written by: Res
Compiled by: TechFlow
This article will explore Nightshade from the following aspects:
1. Composability and its importance
2. Interoperability
3. Cross-chain bridges vs Sharding vs NEAR’s Nightshade
4. How NEAR achieves true scalability and cross-chain composability
5. Real-world applications
Now let's dive in one by one.
Composability
Composability refers to the ability to combine different components to create new systems. It allows dApps/DAOs on the same chain to communicate and collaborate seamlessly, as developers can freely use, modify, and integrate open-source code within their applications. For example:
- Token swaps
- Flash loans
- Governance
- Identity management
- Using LP positions from DEXs as collateral in money markets
- NFT lending
- The ability to integrate DeFi functionalities with GameFi, DAOs, and more Web 3.0 infrastructure
Composability Vs Interoperability
Composability enables smart contracts to interact with other contracts on the same chain; interoperability refers to the ability of different chains to communicate, even if they differ in consensus, data availability, or block formation.
Cross-Chain Composability
It can be defined by combining composability and interoperability:
Cross-chain composability is the ability for dApps and DAOs on different chains to communicate and interact with each other in a permissionless and seamless manner.

While composability is one of Web3’s greatest innovations, interoperability remains a complex challenge that many are striving to solve. So far, two main solutions have been proposed:
1) Cross-chain bridges
2) Sharding
This article focuses primarily on sharding.
Cross-chain bridges effectively connect chains with different target use cases and properties that might otherwise be incompatible. However, these bridges face the cross-chain bridge trilemma and do not allow cross-chain composability.
Solutions like Stargate address the trilemma and bring composability by enabling native asset transfers across chains. However, they also introduce additional risks and complexities such as LP depletion, rebalancing issues, etc.
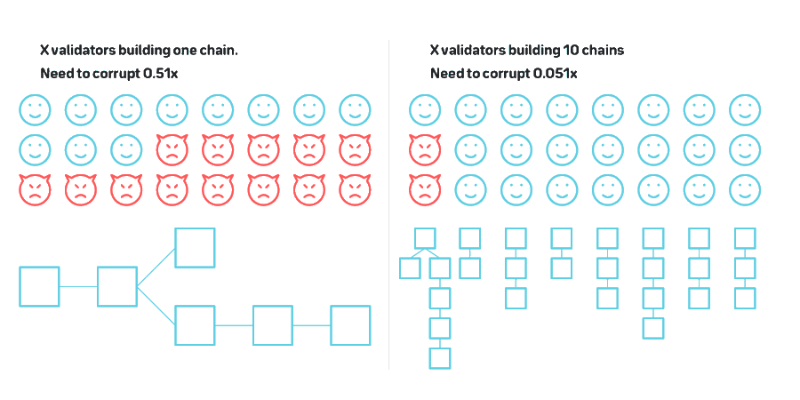
Sharding was introduced to solve scalability and the blockchain trilemma—a concept proposed by Vitalik Buterin. Sharding splits a blockchain into multiple chains (shards), creating a heterogeneous blockchain ecosystem with functional working subsystems.
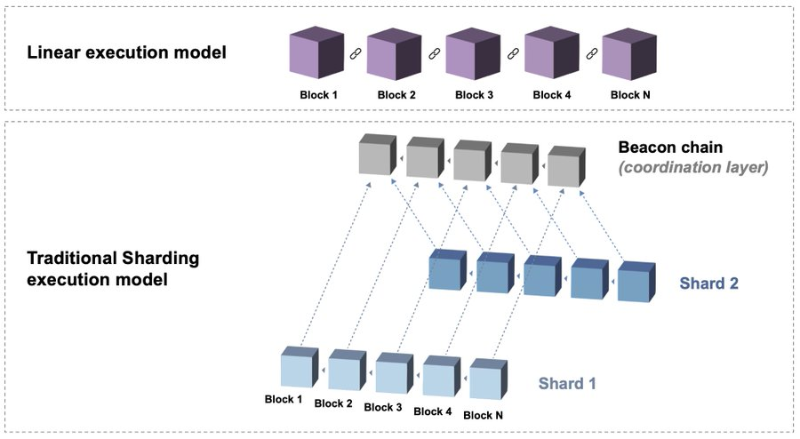
Although sharding may solve scalability and provide an interoperable ecosystem, cross-chain composability remains limited because:
- Users constantly need to move funds across chains
- Fragmentation of liquidity, users, resources, etc.
- Message-passing solutions are unproven
$NEAR: Nightshade
Nightshade is NEAR’s solution to scalability and cross-chain composability. Unlike Cosmos or Polkadot, NEAR is a sharded blockchain designed as a single L1: shards are not separate chains, but smart contracts capable of running optimized execution environments.
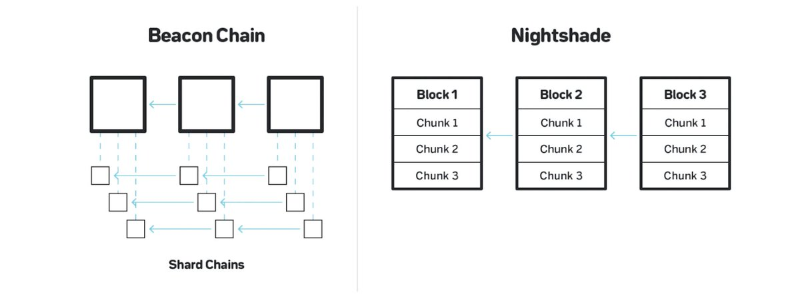
Since Nightshade does not use a Beacon chain but instead uses Chunks, it allows NEAR to scale infinitely as the number of shards increases, and dynamically (thanks to dynamic resharding).
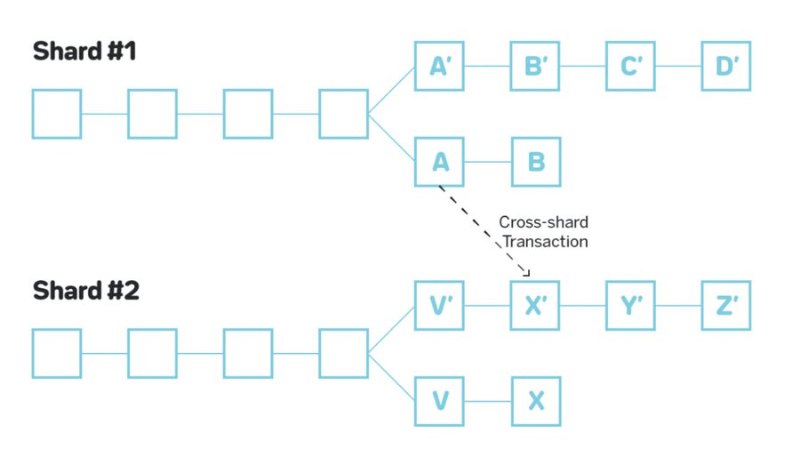
Achieving Cross-Shard Composability
Aurora and other shards are not rollups, but execution environments supported as smart contracts. Transaction data for Aurora is actually wrapped inside NEAR transactions and then sent to the Aurora contract. All settlement, data availability, and execution occur on NEAR.
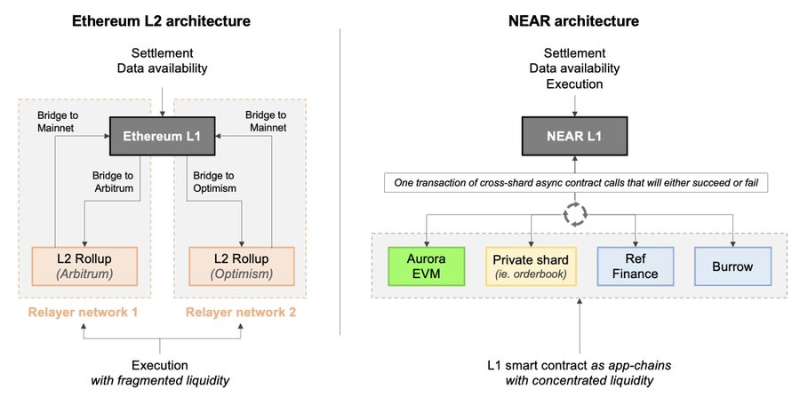
Because $NEAR is built as a single L1, contracts can be composed even when they execute on different shards and run code in different environments. For example, NEAR-native contracts and EVM contracts can now be combined on NEAR’s mainnet.
Swapping across different L2s on Ethereum requires multiple transactions. But due to NEAR’s architecture, when making cross-shard contract calls from one environment to another, users only see a single transaction.
This means developers and users can use any execution environment suited to their needs—without cross-chain bridges or complex UX:
You can run smart contracts for EVM, rollups, new privacy environments, or even private shards for individual applications to enhance performance.
dApps gain the benefits of running their own chain:
- Customization and flexibility
- L1 performance: instant finality, higher TPS
- Improved UX/UI: no cross-chain bridges, direct access to centralized liquidity
- Higher security
All without needing to build extra components such as consensus, storage, or validators.
Real-World Applications
1) Forget Cross-Chain Bridges
Even if users interact with other shards, they won’t notice—it will feel like using their NEAR wallet on NEAR’s mainnet. Funds don’t need to be bridged via cross-chain bridges when switching between different shards or execution environments.
For example, you might trade on Ref, but if Trisolarislabs offers a better quote, the trade executes under the Aurora environment—and the user won’t even notice. You could even trade tokens on NEAR’s mainnet that only exist on Aurora!
Cross-shard contract calls don't require Rainbow Bridge: the UI simply asks the user to sign the required transaction.
This differs from cross-chain bridges built atop omnichain protocols, and from other sharded blockchains requiring interconnection through interoperable bridges.
2) Say Goodbye to Fragmented Liquidity
Unlike other scalability solutions, liquidity on NEAR is not fragmented. Thanks to the L1 data-sharing design, users and developers can directly access the entire NEAR ecosystem’s liquidity through a single interface.
On ETH, you must connect to Arbitrum to access deeper liquidity.
On NEAR, you can access all liquidity without leaving the mainnet, as DEX aggregators can trade across the entire ecosystem (i.e., AMMs on mainnet + AMMs on Aurora + order books on private shards + AMMs on rollups).
3) Abundant Scalable dApps
When an application becomes popular and congested, it may choose to develop its own chain. Or perhaps it simply wants greater customization and to bypass the limitations of standard EVM smart contracts.
Examples include dYdX or DeFi Kingdoms.
With NEAR, we not only have a more decentralized blockchain ecosystem, but dApps also gain L1-level performance and customizability.
Previously, users had to bridge funds to use a new chain. Now, even to use a specific DApp, users still need to bridge funds. This is especially true in Ethereum’s ETH2.0+L2 scaling model, where both liquidity and applications are scattered across multiple L2s.
But this won’t happen on NEAR.
An order book can be moved to a shard, and traders won’t even notice the change. This removes barriers to mass adoption and creates massive opportunities for projects aiming for high performance and customization without sacrificing user experience.
Reminder: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Please DYOR before investing.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News