One Article to Understand the First Modular Blockchain, Celestia
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

One Article to Understand the First Modular Blockchain, Celestia
What Exactly Is Modular Blockchain Celestia?

Author: Chole
Blockchain has always been a distributed network that replicates state machines, divided into three layers: data, consensus, and execution. This structure is key to creating digital currency over the internet—introducing a consensus system immune to external interference. Satoshi Nakamoto’s original solution was the "Nakamoto Consensus," enabling people worldwide to maintain and operate Bitcoin.
In these monolithic blockchains, all three layers—data, consensus, and execution—are handled by a single network. Nodes are responsible for everything from data validation to transaction execution.
Because blockchains are globally replicated distributed state machines, higher complexity leads to greater cost and difficulty in maintaining system synchronization. Rollups address part of this issue by separating the execution layer to handle complex transactions. For example, Arbitrum embeds specific opcodes into L1, allowing nodes to deliberately bypass EVM calls for data—they store and verify transactions without executing them.
However, rollups must monitor L1 and execute transaction calls for computation, then return results to L1 in various ways. These transactions must actually be routed through the ETH network before they can be executed on the rollup.
Currently, Ethereum already hosts several rollup-based scaling solutions such as Optimism, ZKsync, and Starknet, along with execution-layer bridges like Connext, Composable, and Axelar. However, these scaling solutions still rely on Ethereum's consensus and execution layers for data availability. Moreover, the cost of using Ethereum’s execution layer remains high, significantly limiting developers’ deployment flexibility.
The first modular blockchain network, Celestia, is set to launch this year and will support rollups as its data availability (DA) layer.
1. Project Overview
Previously named LazyLedger, Celestia is considered the first modular blockchain network—a pluggable consensus and data availability layer that enables anyone to quickly deploy decentralized blockchains without bearing the additional costs of building a consensus layer. In other words, Celestia is a public chain dedicated to storing transaction records and providing data availability.
Celestia adopts a modular architecture that decomposes blockchain into data, consensus, and execution layers. Most current blockchains still bundle consensus and execution functions within a single layer, where smart contracts are built. Users are locked into this execution environment, severely limiting opportunities for optimization and specialization for specific use cases.
Celestia’s modular architecture allows the execution layer to exist independently on its own blockchain, enabling optimization and specialization for particular use cases. Developers building decentralized applications on this architecture gain enhanced security and scalability compared to traditional monolithic chains. Furthermore, in Celestia’s modular blockchain, data availability sampling is possible—nodes can verify blocks using only small samples, enabling even low-end hardware devices like home computers or smartphones to serve as nodes.
Developers can directly choose their preferred execution environment to build dApps on Celestia and run any number of execution environments in parallel. In contrast, monolithic architectures tightly couple consensus with execution rules, restricting users to only the execution environments supported by the main chain. Celestia has partnered with Tendermint and Cosmos zones to serve as a data availability layer. These public chains will leverage fraud proofs to minimize trust, thereby delivering unified security levels across the Cosmos ecosystem.
2. Use Cases
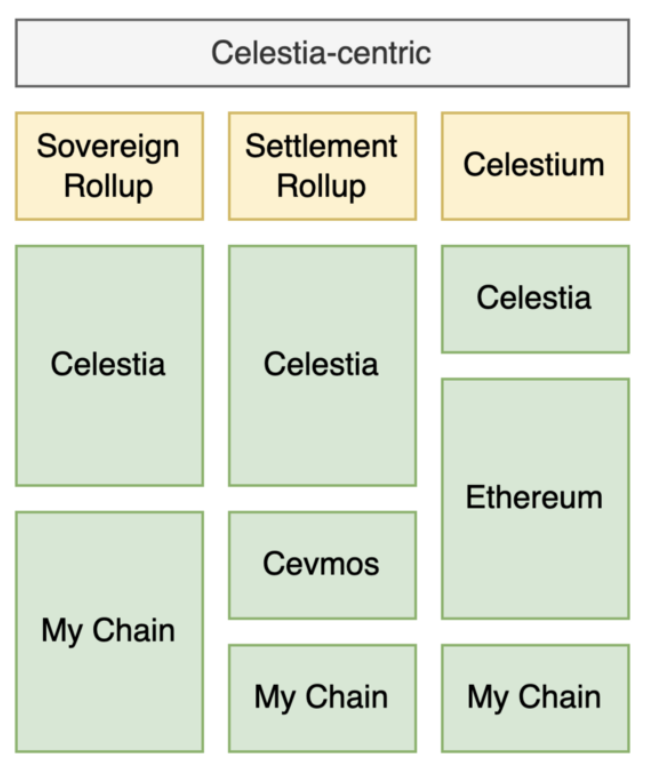
Celestia-Centric Architectures:
Sovereign rollups can be built directly on Celestia, using Celestia’s consensus to treat DA as a standalone module, forming chains entirely based on Celestia. Settlement rollups occur on Cevmos, an EVM-embedded SDK built with the Cosmos SDK framework, specifically designed for rollup settlement. Aggregators on Cevmos publish their data to Cevmos first, then to Celestia.
Cevmos aims to allow Ethereum rollups to launch natively on Celestia without modifying their codebase. Rollups would no longer run as contracts on Ethereum, achieving stronger scalability.
Celestium uses the Quantum Gravity Bridge, making Celestia a Layer-2 data availability solution for Ethereum, offering a secure and low-cost Validium design for Ethereum.
Sovereignty Advantages:
The Celestia network itself only verifies data integrity and does not involve a full consensus mechanism. Therefore, rollups built atop Celestia are essentially sovereign blockchains, and nodes can freely fork their software.
In traditional L1s, forking means both execution and consensus layers are forked. If a rollup on Ethereum suffers a bug or attack, it requires redeployment or a full network fork to update state. Celestia’s technological iteration, however, allows chains to fork without sacrificing security—since the DA layer remains unchanged post-fork, updates become easier and the execution layer can focus on optimizing performance and speed.
Technology for Easy Chain Deployment:
Deploying a blockchain used to require significant resources and high costs, including establishing consensus and incentivizing node participation. Although PoS development and tools like Cosmos SDK have made creating new blockchains easier, developers still need to recruit validator nodes.
Thus, Celestia introduces Optimint to more efficiently assist developers in deploying chains, as Celestia provides complete consensus and security. Multiple chains sharing the same DA layer achieve minimal-trust bridging between blockchains, enhancing the security of inter-chain communication. Finally, Celestia combines Cosmos' open ecosystem with Ethereum's shared security model, enabling an open, multi-chain environment with shared security.
3. Team Introduction
CEO Mustafa Al-Bassam holds a PhD from University College London. He previously co-founded Chainspace, a smart contract platform acquired by Facebook. Mustafa also authored several pioneering papers on the security of sharded blockchain systems.
CRO John Adler previously worked at ConsenSys as an L2 scalability researcher, focusing on Phase 2 of Ethereum 2.0. Adler discovered novel applications of data availability from Mustafa’s work and created one of the earliest pioneers of the Optimistic Rollup scheme.
CTO Ismail Khoffi is a well-known research engineer in the industry. Beyond building academic research models, Khoffi has made substantial contributions to various non-blockchain and blockchain projects, including Google UK and Tendermint.
COO Nick White holds a master’s degree from Stanford University. Before joining Celestia, White co-founded Harmony, a blockchain protocol focused on scalable blockchain infrastructure, contributing momentum to the decentralization revolution. White also served as a senior AI expert at Zeroth.ai, an accelerator program for AI startups in Asia.
4. Investment Institutions
Celestia has launched its "Mamaki" testnet, supporting user-operated nodes, testnet token distribution, validator delegation, and transactions between wallets. The mainnet is expected to go live in early 2023.
Prior to the testnet, a developer network was launched, consisting of three core components: Optimint, Celestia-app, and Celestia-nodes. Celestia-nodes are responsible for achieving consensus and forming the network, determining how light and full nodes create new blocks, sample data from blocks, and synchronize multi-dimensional aspects of new blocks. With Optimint, Cosmos Zones will be deployed directly on Celestia.
5. Community Status
Twitter:
https://twitter.com/CelestiaOrg
5.9k followers
Discord:
https://discord.com/invite/YsnTPcSfWQ
35,491 members
Telegram:
https://t.me/CelestiaCommunity
9,580 members
6. Chain Tea Review
Scalability has long been one of the biggest obstacles to widespread blockchain adoption. While numerous L1 scaling solutions exist, most focus on the consensus layer rather than data availability.
Celestia, as a modular blockchain, builds a public chain that decouples the data layer, allowing developers to focus on designing above the data layer without worrying about underlying data recording. Many believe that this modular data availability layer will not only enable faster scaling solutions but also greatly reduce the barrier for developers entering web3.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News