The Scientific Democratization Movement: The Desci Revolution to Rebuild the Trillion-Dollar Knowledge Economy
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

The Scientific Democratization Movement: The Desci Revolution to Rebuild the Trillion-Dollar Knowledge Economy
Only by establishing sustainable value capture mechanisms, inclusive governance frameworks, and compliant pathways can DeSci evolve from a fringe experiment into the next-generation research infrastructure.
Author: Klein Labs
1. Industry Background and Current Status Analysis
1.1 Overview of DeSci
From handicraft-era workshops relying on human collaboration, to factory systems restructured by steam power in the mechanized era; from standardized economies of scale driven by assembly lines during electrification, to global supply chain revolutions triggered by computer technology in the information age—each technological revolution has reshaped how production factors are organized. The emergence of blockchain technology has, for the first time, enabled "automated trust" through mathematical protocols, making possible on-chain intellectual property rights confirmation, decentralized circulation of data assets, and value distribution led by smart contracts. Through storing knowledge and data on-chain, DeSci (Decentralized Science) is leading a disruptive scientific paradigm shift, seeking to liberate science from closed ivory towers and fundamentally transform the underlying logic of human production relationships.
Previously, the DeSci sector experienced a surge in secondary market enthusiasm, which has now gradually cooled. That wave represented a financial manifestation of expectations, often taking forms such as Memecoins. However, this should not discredit the DeSci space. Instead, we must conduct deeper analysis now to understand the real value behind DeSci and its future impact on technological paradigm shifts.
Hard Tech Paradigm Shift
The core principles of DeSci include several key aspects:
-
Incentive Mechanisms: Restructuring Scientific Value Distribution By introducing blockchain-based incentive systems, DeSci completely transforms traditional models of value allocation in research. Researchers can gain academic recognition and financial returns via token economics, NFT papers, or reputation systems—motivating widespread knowledge sharing and offering new pathways for monetizing scientific outcomes.
-
Disintermediation: Reconfiguring Power Structures in Research In traditional research models, funding allocation and outcome evaluation are often controlled by a few centralized institutions, resulting in unequal resource distribution and constrained innovation. DeSci decentralizes authority to research communities through community-driven models like DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations), enabling democratic resource allocation.
-
Lowering Barriers to Entry: Democratizing Scientific Research Through decentralized infrastructure—such as open data platforms and distributed computing resources—DeSci significantly lowers participation barriers. Researchers from developing countries, independent scientists, and citizen scientists alike can equally access global research resources and contribute meaningfully.
-
Data Transparency: Rebuilding Academic Trust Systems Blockchain’s traceability ensures transparency and verifiability of research data. Every stage—from experimental design and data collection to publication—can be recorded and publicly verified, effectively curbing academic misconduct and enhancing public confidence in scientific research.
The essence of DeSci is a return to the true nature of science—science should be humanity's shared heritage, not an exclusive domain of elite institutions. In traditional research models, the creation and dissemination of knowledge are controlled by layers of intermediaries, causing science to drift away from its original ideals of openness and collaboration. DeSci uses technological tools to break down these barriers, restoring science’s inherent decentralized character. It is not merely a technological innovation but a philosophical revolution in science.
1.2 Fundamental Differences Between DeSci and Traditional Scientific Research Systems
1.2.1 Collaboration Models: From Fragmented Competition to Organic Coordination
Traditional scientific research systems exhibit a typical “triangular fragmentation” structure: funding bodies (governments/corporations), researchers, and publishers form a closed-loop profit system without mechanisms aligning their interests.
-
Funders often assess outputs using short-term KPIs, pressuring scientists to pursue “publishable results” rather than solving substantive problems;
-
Scientists, needing continuous funding, must devote significant effort to grant applications and compliance procedures instead of deep research;
-
Publishers monopolize academic communication channels, charging high subscription fees (the global scholarly publishing market generates over $19 billion annually) while offering inadequate compensation to knowledge producers.
This fragmentation leads to more than 30% of annual global R&D spending (approximately $60 billion) being wasted on redundant or irreproducible studies. DeSci reconstructs this tripartite relationship through smart contract-driven collaboration frameworks:
-
Funders pool capital via DAOs and set long-term goals (e.g., “delay aging”), with community voting determining resource allocation;
-
Scientists earn token rewards based on data contributions, open-sourced code, or experiment replication, directly linking economic returns to actual value creation;
-
The role of publishers is replaced by NFT papers and decentralized storage, reducing knowledge dissemination costs by over 90%.
1.2.2 Bridging the 'Valley of Death': From Linear Breakdowns to Closed-Loop Acceleration
The traditional “valley of death” in industry-academia-commercialization reflects systemic failure in knowledge transfer: the pipeline from basic research (papers) → applied development (patents) → commercialization (products) involves different actors at each stage with no connecting incentive mechanisms. For example, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) spends $45 billion annually, yet only 0.4% of basic research advances to clinical trials. Core issues include pharmaceutical companies locking down experimental data for commercial secrecy, leading to costly repeated failures (preclinical stages alone cost $2.6 billion per drug); meanwhile, venture capital favors late-stage mature projects, leaving early breakthrough research underfunded.
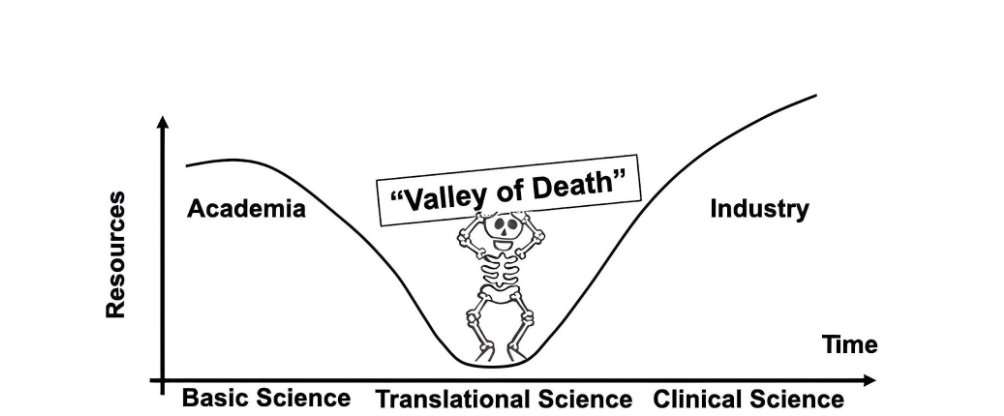
The Valley of Death in Translational Research, Source: Translational Medicine Communications
By integrating blockchain and Web3 technologies, DeSci aims to dismantle interest silos in traditional research and promote more efficient scientific collaboration. Unlike the isolated nature of conventional models, DeSci enables deeper cooperation among funders, scientists, and publishers through decentralized mechanisms, addressing challenges around funding, data sharing, and research transparency. DeSci builds translation accelerators through techno-economic paradigm innovations:
-
Tokenization of Tech IP: Platforms like Molecule convert drug development IP into IP-NFTs, allowing segmented investment. Studies show this reduces financing cycles for early biotech projects by 60%;
-
Data Liquidity: Platforms like Ocean Protocol create data marketplaces where researchers securely share data via privacy-preserving computation and receive compensation. Over 20 petabytes (PB) of biomedical data have already been put on-chain;
-
Community Support Mechanisms: VitaDAO employs a three-phase token distribution model (“research-development-commercialization”), allowing fundamental researchers to continue receiving 5%-15% revenue shares post-drug launch via smart contracts, creating closed-loop incentives;
-
Efficient Funding Allocation: Through DAOs and tokenized economic models, DeSci provides transparent and efficient financial support, minimizing waste. For instance, VitaDAO funds anti-aging research via DAO governance and supports 24 projects;
-
Decentralized Publishing: DeSci changes how scientific findings are produced and disseminated, ensuring transparency and verifiability via blockchain, lowering publishing costs, and reducing publisher monopolies;
-
Research Attribution and Transparent Peer Review: Blockchain immutability secures attribution of research outputs, while smart contracts record review processes, increasing transparency and ensuring fairness and efficiency.
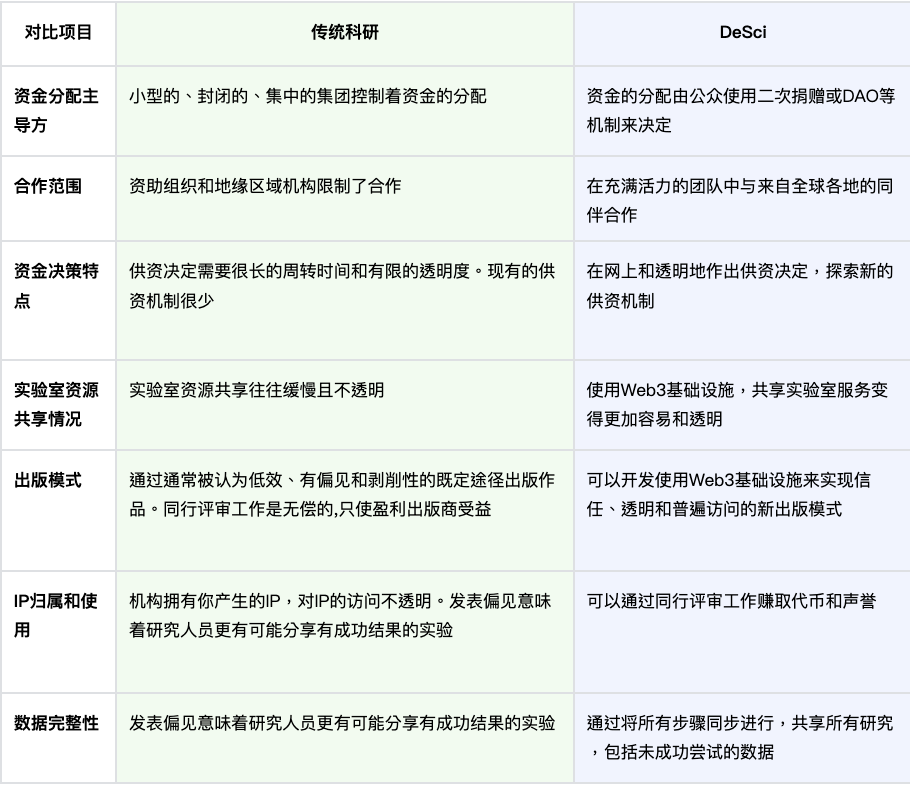
Comparison of Traditional Research vs. DeSci, Source: Bio.xyz
In summary, DeSci promotes transparency, efficiency, and collaboration in research through decentralized technologies, addressing numerous shortcomings of traditional models. It not only transforms funding allocation, data sharing, and publishing but also accelerates research translation through community collaboration, fostering a more open, inclusive, and promising research environment.
1.2.3 Value Distribution: From Centralized Extraction to Ecosystem-Wide Win-Win
In traditional systems, research value is monopolized by a few centralized nodes:
-
Publisher Elsevier maintains a gross margin of 37%, far exceeding tech giants like Apple (24%);
-
Nature charges up to $11,390 per paper processing fee, yet 97% of peer reviewers work unpaid;
-
Pharmaceutical giants earn excessive profits via patent barriers (average net profit margin of top 10 pharma firms is 18.7%), while original discoverers are frequently marginalized.
In contrast, DeSci redefines value distribution through programmable value flows:
-
Contribution Quantification: Using on-chain reputation systems (e.g., Karma scoring by DeSci Labs), actions such as paper citations, code submissions, and experiment replications are converted into tradable credit assets;
-
Dynamic Distribution: Smart contracts automatically distribute revenues—for example, a BioDAO project allocates 30% of patent income to a community treasury, 45% to contributors based on contribution level, and 25% to early investors;
-
Long-Tail Activation: African scientists use LabDAO to share lab equipment, cutting research costs by 70%, and gain global funding based on data contributions.
The difference between DeSci and traditional research goes beyond tool upgrades—it represents a restructuring of production relations. When scientific breakthroughs are no longer constrained by institutional boundaries, geography, or rent-seeking, humanity may enter a new era of collective intelligence explosion. Just as the GitHub open-source community gave rise to ChatGPT, collaborative innovation within the DeSci ecosystem involving millions of researchers could solve complex challenges beyond the reach of any single nation or corporation (such as Alzheimer’s treatments or controlled nuclear fusion) in the next decade. The ultimate goal of this transformation is to restore science to its purest essence: evidence-based, openly shared, and serving the well-being of all humanity.
1.3 Market Size and Key Players
1.3.1 Market Size
Currently, the DeSci sector approaches a market size of $1 billion. Though still in early exploration phases, it is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 35% over the next five years, showing exponential expansion potential. This growth stems not only from mature blockchain applications but also from addressing inefficiencies in global R&D funding: traditional research markets invest over $200 billion annually, yet substantial sums are lost due to bureaucratic processes and inefficient management by centralized entities. DeSci is reshaping this landscape—through tokenized incentives, decentralized governance, and open collaboration—and is expected to surpass $50 billion by 2030, becoming a vertical sector in Web3 alongside finance and AI.
DeSci’s potential has drawn dual attention from both the crypto industry and academia. Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has repeatedly emphasized DeSci’s disruptive significance for “open science.” Crypto leaders including Binance founder CZ, BitMEX co-founder Arthur Hayes, and Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong have endorsed DeSci through investments and public advocacy. Top-tier investors such as Paradigm co-founder Fred Ehrsam and former Coinbase CTO Balaji Srinivasan view DeSci as a core direction for next-generation research infrastructure. Leading VCs—including a16z, Polychain Capital, and Digital Currency Group—are actively investing, particularly in biotech-focused DAOs (like VitaDAO) and decentralized data protocols (like Ocean Protocol).

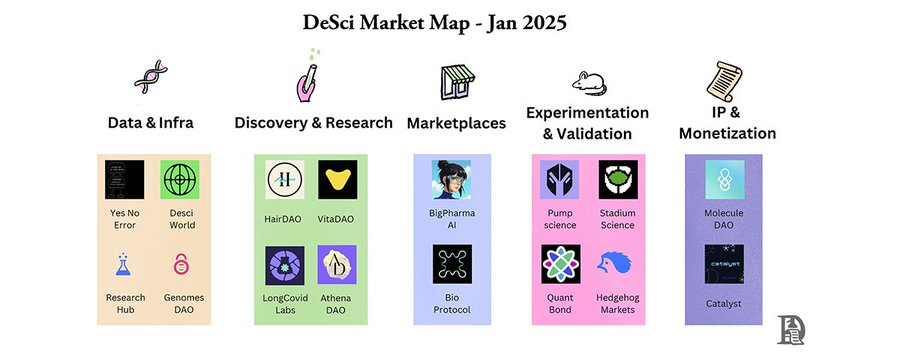
DeSci Ecosystem Project Map, Source: Messari Research
1.3.2 Major Players
1.3.2.1 Molecule
Founded in 2021, Molecule is a decentralized protocol aiming to disrupt traditional biotech R&D models. The project seeks to build a new financing ecosystem for early-stage biological research and pioneered the concept of IP-NFTs by bringing biotech intellectual property (IP) on-chain, earning it the nickname “OpenSea for biotechnology.”
Leveraging IP-NFTs, Molecule has built a marketplace focused on translational research, facilitating efficient connections between researchers and funders. On the Molecule Discovery platform, researchers submit proposals that funders evaluate and negotiate terms with teams. This approach strongly supports the transition of basic research into practical applications, accelerating medical research from theory to practice. As a decentralized drug development platform, it has facilitated over $200 million in research funding through its IP-NFT model and established partnerships with pharmaceutical giants such as Pfizer and Bayer.
1.3.2.2 VitaDAO
VitaDAO is a community-driven Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) dedicated to providing early-stage funding for longevity research. Addressing the lack of early funding and technological monopolies in traditional biopharma—especially in aging research—VitaDAO proposes a novel solution. By integrating blockchain and cryptographic economic incentives, VitaDAO helps critical initial-stage scientific projects in longevity secure essential funding. In return, VitaDAO holds direct rights to the intellectual property (IP) and data generated by supported research, consolidating them into a publicly accessible asset portfolio. These IPs are further developed and commercialized via data markets or traditional biopharma licensing, while being tokenized with native governance tokens—$VITA. Individuals or organizations earn $VITA tokens by contributing work, capital, or other resources (such as data or IP). $VITA holders participate in curation and governance of VitaDAO’s assets and research initiatives.
1.3.2.3 BIO Protocol
As the first DeSci project funded by Binance Labs, BIO Protocol has attracted widespread attention. Beyond Binance Labs, the project has received strong backing from renowned venture capital firms in both crypto and biotech sectors, including 1kx, Boost VC, Sora Ventures, Zee Prime Capital, and Northpond Ventures—a biotech fund managing over $3 billion. In November 2024, BIO Protocol successfully completed its genesis community fundraising round, raising $30.3 million, marking a significant step toward community engagement and decentralized governance.
BIO Protocol’s core mission is to accelerate biotechnological advancement. Through this protocol, patients, scientists, and biotech professionals worldwide can jointly fund, build, and share tokenized biotech projects and intellectual property (IP), injecting greater innovation potential into the field. Its Launchpad platform will provide more efficient funding and liquidity support for innovative projects in the DeSci space and accelerate biotech application deployment by promoting the creation and development of BioDAOs. Founder Paul Kohlhaas revealed that BIO’s Launchpad and token transfer functionality are scheduled to launch in Q1 2025. Focusing on experimental reproducibility, BIO Protocol has built an open-source research protocol library, reducing global collaboration costs through standardization and on-chain verification, currently covering over 1,200 biological experiments.
1.3.2.4 Ocean Protocol
Ocean Protocol received joint investment from Digital Currency Group and Jump Capital, and in 2023 secured $31 million in Series B funding led by Borderless Capital, achieving a valuation exceeding $1 billion. Its core mission is to build infrastructure for a decentralized data economy and overcome the challenge of data silos in research. It has achieved two major technical breakthroughs: 1. Compute-to-Data: Running analytical algorithms without moving data—Mayo Clinic improved breast cancer genomic analysis efficiency by 35x using this method; 2. Data NFTization: Enabling dataset ownership confirmation and tiered trading, hosting 20PB of high-value biomedical data. Additionally, Ocean Protocol collaborates with the UN Food and Agriculture Organization to establish a global agricultural research data pool, encompassing 2.3 million datasets across 67 countries. In Q2 2024, data transaction volume reached $170 million, with privacy computation requests growing 220% quarter-over-quarter.
CEO Bruce Pon announced plans for 2025 to integrate federated learning and ZK-proof technologies to launch a “cross-chain data federation,” enabling secure clinical data sharing among pharmaceutical companies.
1.3.2.5 Gitcoin Grants
Gitcoin Grants received strategic investments from the Ethereum Foundation and Protocol Labs and an additional $15 million from a16z in 2024, bringing total funding to $68 million. Its core mission is to democratize open-source scientific crowdfunding through quadratic funding (QF). Gitcoin Grants has cumulatively funded over 1,700 open-source science projects, achieving a fund utilization rate 3.2 times higher than traditional research grants. It plans to launch “impact derivatives” in 2025, enabling investors to trade prediction markets based on the social value of research outcomes.
1.3.2.6 LabDAO
LabDAO received angel investment from Vitalik Buterin and support from the Arweave ecosystem fund, completing a $12 million seed round in 2024 led by Pantera Capital. Its core mission is to create a distributed laboratory network, lowering global access barriers to research resources. LabDAO has already open-sourced over 1,400 SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) for biological experiments, achieving a 92% on-chain verification pass rate. It connects 420 professional instruments across 67 countries, enabling African teams to reduce R&D costs by 70%. Founder Niklas Rindtorff stated that in 2025, they will launch an “automated experiment protocol engine,” leveraging AI and robotics to fully automate 50% of basic experiments.
1.3.2.7 ResearchHub
ResearchHub was founded by Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong. Believing that scientific records should not be locked behind paywalls or confined within academic ivory towers, ResearchHub envisions science as a universally accessible public resource. Its core mission is to break down the closed nature of traditional academic research. By offering a completely open, paywall-free platform, ResearchHub enables scholars and non-scholars alike to engage in scientific research transparently and collaboratively. Summaries on the platform are written in plain English, further lowering the barrier to accessing scientific knowledge and enabling broader participation in scientific discourse. To incentivize open collaboration, ResearchHub introduced ResearchCoin, rewarding users who actively contribute and share research findings.
On ResearchHub, researchers can freely publish articles (preprints or postprints) and exchange ideas in dedicated open forums discussing related research. This model aims to address the inefficiency of current academic publishing. From applying for funding, conducting research, submitting manuscripts, undergoing peer review, to final publication—the traditional process often takes 3–5 years, severely slowing scientific progress. ResearchHub believes its open-collaboration platform can improve research efficiency by at least an order of magnitude.
ResearchHub Interface Example
2. Value Assessment
DeSci Compared to Other Web3 Sectors
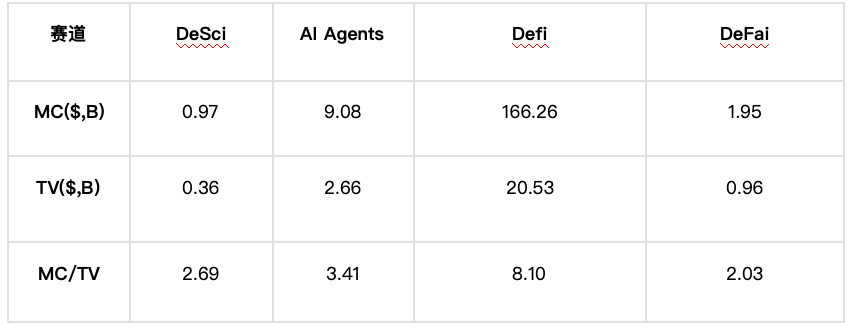
The current total market cap of the DeSci sector is approximately $1 billion, with daily trading volumes ranging between $8 million and $12 million. The market cap to trading volume ratio (MC/TV) stands at 8–15x, significantly higher than traditional tech stocks (S&P 500 average MC/TV ~0.3x) and even mainstream crypto sectors (DeFi average MC/TV ~3x). This abnormal ratio reveals deeper market dynamics:
-
Expectation Premium: Investors view DeSci as a “DeFi revolution for science” and are willing to pay a premium for a technological vision not yet fully realized. Similar phenomena occurred during IPFS in 2017 (peak MC/TV of 28x) and DeFi Summer in 2020 (COMP’s initial MC/TV of 22x). DeSci valuations remain within reasonable ranges for early-stage technologies.
-
Structural Divergence: Leading projects (e.g., Molecule, Ocean Protocol) account for 65% of market cap but only 30% of trading volume, indicating investor preference for long-term holdings of core infrastructure. Smaller projects (e.g., LabDAO, ResearchHub), despite lower market caps, generate 70% of trading volume, reflecting speculative positioning on early-stage innovation.
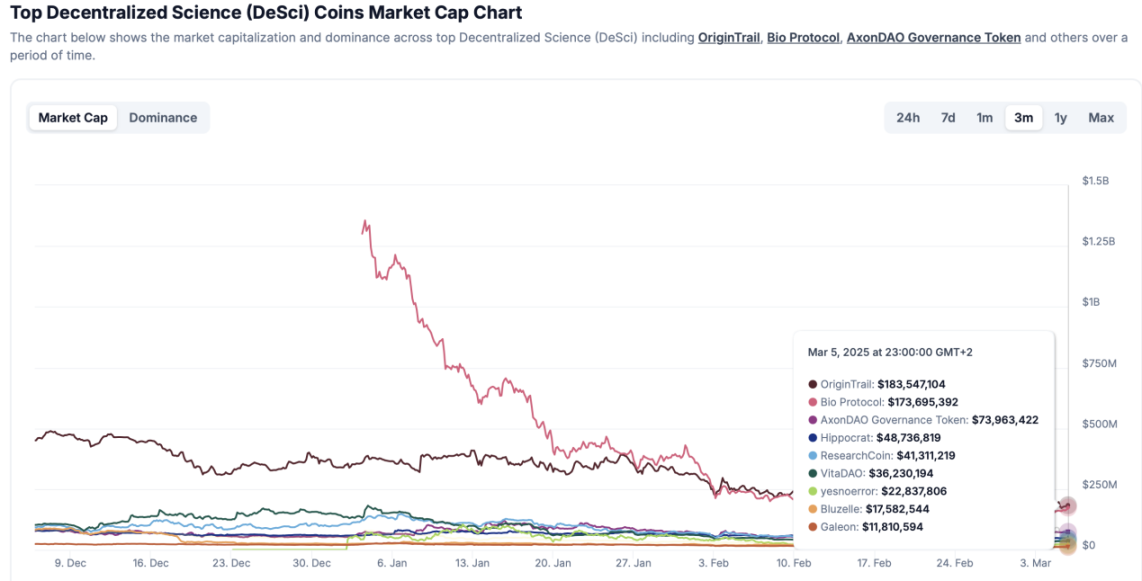
Market Cap Rankings of DeSci-Related Tokens, Source: Coingecko
Despite its relatively small overall size, institutional participation in DeSci exhibits unique characteristics:
-
Top Fund Investment Logic: a16z allocates 80% of its DeSci investments to foundational protocols (data storage, IP tokenization tools) and only 20% to application-layer projects, demonstrating adherence to a “build infrastructure first” strategy—mirroring their early bets on Ethereum (2014) and Coinbase (2013).
-
Whale Behavior Patterns: On-chain data shows that 55% of addresses holding over $100,000 worth of DeSci tokens have held their positions for more than one year—far above the crypto market average of 28%. These investors focus on technical roadmaps rather than short-term price movements—for instance, VitaDAO’s $VITA token maintains a staking rate above 72%.
-
Cross-Sector Synergy: Traditional pharmaceutical companies are beginning to leverage DeSci ecosystems for innovation. For example, Pfizer outsources early drug discovery via NFT licenses on Molecule, saving 40% in R&D costs. This hybrid model of “traditional capital + DeSci technology” is reshaping valuation frameworks.
Moreover, traditional financial metrics are losing explanatory power in the DeSci space, necessitating new evaluation frameworks. For example, NFT papers on the DeSci Labs platform receive an average of 7.2 citations—three times the rate of traditional open-access journals.
3. Future Outlook
3.1 Innovative Project Analysis: Pythia—Where Brain-Computer Interfaces Meet Cryptoeconomics
Three months after Neuralink successfully implanted its first human brain-machine interface, a breakthrough study by Neiry Laboratory at Moscow State University [10] transformed brainwaves into crypto assets, sparking sensation in the crypto community. The lab implanted an AI chip into an experimental mouse named Pythia, connecting it to custom GPT and DeepSeek models, enabling it to answer simple yes/no questions via brainwave-controlled buttons. This seemingly futuristic experiment not only highlights the potential of merging biology with artificial intelligence but also gave birth to the PYTHIA token, whose market cap surged to $50 million within just ten days of launch, becoming one of the most controversial crypto stories in Web3. The Pythia project not only demonstrates the vast potential of brain-computer interfaces but also pioneers a new “bio-mining” model—converting brainwaves into tradable digital assets—marking the birth of a bio-data economy.
Today, the PYTHIA token’s market cap has steadily rebounded from a low of $4 million to $11 million. Unlike fleeting meme projects, Pythia has solidified its position in the DeSci space through sustained development and innovation. Even amid overall market downturns, the $PYTHIA token continues to show strong upward momentum. So what exactly is Pythia? And why has it stirred such waves in the crypto world?
The core of the Pythia project lies in its pioneering “Brain-Machine Interface Cryptographic Singularity” technology. Neiry Lab connected the brain of the experimental mouse Pythia to a customized GPT-4 model, successfully translating neural signals into programmable instructions, enabling bidirectional interaction between biological entities and AI. This breakthrough includes not only linguistic interpretation of neural pulses (transforming EEG signals into executable commands) but also assetization of brainwave data—using ERC-1155 standard NFTs to turn brainwave data into tradable digital assets. Based on this experiment, the Pythia project rapidly evolved from a scientific endeavor into a symbol of cryptoeconomics, giving rise to the $PYTHIA token.
NeiryLab-Pythia Official Website
Another major innovation of the Pythia project is its “thinking-as-mining” system. Users wear an EEG headset developed by Neiry Lab to convert mental activities like meditation and concentration into token rewards. This “biological StepN” model converts cortical activity into economic value, creating a novel way to acquire digital assets. Simultaneously, Neiry Lab launched two revolutionary devices—Mind Tracker and Brainy headphones—offering brainwave monitoring and stress management features. These devices help users reduce emotional interference during cryptocurrency trading and enhance attention and decision-making through real-time brain activity tracking. Users paying for device fees with $PYTHIA tokens receive discounts, further boosting the token’s utility and circulation.
The vision of the Pythia project extends beyond token economics. Neiry Lab is developing Neural Data Oracle technology, aiming to transform brainwave signals into verifiable sources of randomness, promoting deeper integration between blockchain and biological data. Additionally, the lab plans to launch a cognitive enhancement DApp store powered by real-time brainwave data, offering apps for meditation, learning, and mental health optimization. These technological advances not only lay the foundation for the future of brain-computer interfaces but also open possibilities for the emerging “consciousness economy.” Pythia may become a blueprint for integrating Web3 with brain-computer interfaces. Furthermore, under the backdrop of U.S.-Russia cooperation, potential collaboration between Pythia and Elon Musk’s Neuralink is worth watching.
3.2 Future Development Directions for DeSci
DeSci is following a disruptive path to reshape the foundational logic of human knowledge production. At the heart of this transformation is the construction of a global research network transcending geographical borders and breaking free from power monopolies—achieved through dual innovations in technological tools and collaboration paradigms.
3.2.1 DeSci + AI Agent—Redefining Scientific Research Paradigms
With the deep integration of DeSci and AI Agents, scientific research is undergoing an unprecedented paradigm shift. DeSci breaks down centralized barriers in traditional academic systems through blockchain, enabling transparency, verifiability, and openness of scientific data; AI Agents, with their powerful data processing and automation capabilities, inject new levels of efficiency and insight into research. Their convergence will not only accelerate scientific discovery but also redefine how research collaboration functions.
In the future, the combination of DeSci and AI Agents will spawn a range of innovative applications. For example, smart contract-based research funding systems could use AI Agents to evaluate project feasibility and potential impact, ensuring efficient resource allocation; decentralized research collaboration platforms could employ AI Agents for peer review and enable real-time, cross-disciplinary, cross-border collaboration, breaking down the silo effects of traditional research; even AI Agents could analyze global research data to predict emerging fields and offer forward-looking guidance to scientists.
3.2.2 From Funding Research to Real-World Applications: Building a Sustainable Scientific Ecosystem
Currently, DeSci primarily focuses on raising and allocating research funding, using blockchain to ensure transparent and decentralized financial flows. However, as the DeSci ecosystem matures, participants and supporters increasingly seek tangible outcomes and perceivable value beyond abstract visions. Therefore, DeSci’s future development must evolve from “Funding Research” to “real-world application,” building a sustainable scientific ecosystem capable of driving both innovation and measurable output.
Taking Asia as an example, DeSci activities are currently concentrated in research fundraising and donations. Due to cultural differences between East and West, this model is often perceived by Asian users as “too conceptual,” limiting regional acceptance. Yet, the Asian market possesses strong purchasing power and immense innovation potential, representing a crucial force in the global scientific ecosystem. To overcome this bias, DeSci must emphasize demonstrable results and adopt localized outreach strategies so Asian users can tangibly experience its value. For instance, DeSci could deeply collaborate with Asian research institutions, enterprises, and communities to advance locally relevant projects such as modernization of traditional Chinese medicine or environmental remediation technologies, thereby gaining broader recognition and support.
In doing so, DeSci can transcend cultural barriers and establish a solid user base in Asia, injecting fresh vitality into the sustainable development of the global scientific ecosystem.
4. Deep Summary: DeSci’s Paradigm Revolution and Future Vision
DeSci (Decentralized Science) is disrupting the core elements of scientific research—funding models, knowledge-sharing mechanisms, and intellectual property management—through blockchain technology. Although still in its early stages, the sector’s explosive growth already far outpaces the evolutionary speed of traditional research systems. This transformation is not merely about applying technology, but a return to the democratic and global essence of science—its impact will transcend both academia and the blockchain industry, reshaping the future of human knowledge production.
Nevertheless, every emerging phenomenon born of historical evolution must be viewed dialectically. Take Bio Protocol: a 2023 audit sampling 1,200 experimental protocols on its platform found only 68% passed basic peer review, significantly below the 85% benchmark in traditional journals. This double-edged sword effect of “data democratization” exposes weaknesses in quality control within open collaboration models—when entry barriers to research processes are lowered, unverified “junk data” may pollute the knowledge commons under the banner of decentralization. A deeper challenge lies in lagging legal frameworks: 23% of IP-NFT transactions on the Molecule platform were halted due to jurisdictional conflicts over recognizing on-chain IP carriers, revealing regulatory blind spots regarding the novel concept of “tokenized research assets.” These contradictions reveal a profound paradox: DeSci attempts to deconstruct traditional research authority through technology, yet inevitably needs to build new trust infrastructures and consensus rules of its own.
1. Three Core Reconfigurations and Breakthrough Practices
-
Decentralized Funding Models: 70% of traditional research funding is tied to government or corporate agendas, whereas DeSci channels funds toward genuinely value-driven projects via DAO crowdfunding, IP tokenization (e.g., Molecule’s IP-NFTs), and community governance. For example, VitaDAO has cumulatively funded over 50 longevity research projects through tokenized crowdfunding, with three already entering clinical trials—far surpassing the early-stage conversion rates of traditional biotech funds.
-
Upgraded Knowledge-Sharing Paradigms: Through NFT papers (e.g., DeSci Labs) and open-source protocol libraries (e.g., Bio Protocol), reuse costs of research data drop by 80%, and global collaboration efficiency increases fourfold. In 2023, on-chain papers averaged 7.2 citations—three times that of traditional journals—proving open sharing substantially accelerates scientific progress.
-
On-Chain Revolution in IP Management: DeSci migrates intellectual property from closed patent systems to programmable smart contracts. For instance, Pfizer converted early drug discovery research into IP-NFTs via Molecule, optimizing R&D costs by 40%, while original contributors receive ongoing 15% revenue shares during commercialization—finally breaking the industry-wide “inventor poverty” problem.
2. Growth Flywheel: Triangular Drivers of Technology, Capital, and Policy
-
Matured Tech Stack: From data layer (Arweave permanent storage) to application layer (LabDAO’s distributed labs), the DeSci tech stack now supports 90% of research workflows on-chain. In 2023, developer activity in DeSci (GitHub commits) grew 220% YoY, outpacing DeFi.
-
Structural Capital Shift: Traditional VCs (e.g., a16z, Digital Currency Group) and pharma giants (e.g., Bayer, Novartis) have invested over $420 million into DeSci, with 35% of funds flowing to research nodes in developing countries, rebalancing the global innovation network.
-
Regulatory Sandbox Formation: The EU’s draft Digital Science Act explicitly recognizes DAO governance legality, while Singapore and others have opened tax-exemption channels for research tokens, unlocking multibillion-dollar compliant markets.
3. Challenges and Resolution Pathways
-
Tech-Academia Gap: Currently only 12% of researchers are familiar with blockchain tools, but products like DeSci Labs’ “no-code DAO builder” are reducing participation barriers by 70%.
-
Short-Term Speculation Risks: While mid- and small-cap projects face spreads as high as 8%, leading protocols (e.g., Ocean Protocol) maintain stable staking rates above 65%, indicating growing long-term value consensus.
-
Regulatory Battles: The SEC has investigated 17% of DeSci projects, but the industry has successfully brought 83% of projects into compliance via “scientific utility token” designs.
4. The Next Decade: From Fringe Experiment to Mainstream Infrastructure
According to ARK Invest forecasts, by 2030, the DeSci market will exceed $50 billion, covering 30% of global early-stage research projects. Its evolution may unfold in three phases:
-
2023–2025 (Infrastructure Boom): Standardization of IP tokenization protocols and decentralized peer-review systems (e.g., DeReview) drives market size beyond $5 billion;
-
2026–2028 (Vertical Integration): First DeSci unicorns valued over $10 billion emerge in specialized sectors like biomedicine and climate science, with 20% of traditional journal content migrating on-chain;
-
2029–2030 (Paradigm Dominance): DeSci models solve at least three global scientific challenges (e.g., Alzheimer’s treatment) and become the primary source of research funding for 70% of developing countries.
The ultimate goal of DeSci is not to replace traditional research, but to build a “Global Scientific Collaboration Network” through technological democratization—where a botanist in Brazil can instantly access Norway’s gene database, African medical discoveries can rapidly commercialize via DAOs, and every data contributor earns perpetual rewards through smart contracts. When scientific breakthroughs are no longer constrained by geography, institutions, or capital monopolies, humanity may witness the greatest collaborative revolution since the internet: for the first time, the production and distribution of knowledge truly belong to all of humanity. But this transformation must cross the “valley of death” between technological idealism and real-world constraints—only by establishing sustainable value capture mechanisms, inclusive governance frameworks, and compliant pathways can DeSci evolve from fringe experiments into next-generation research infrastructure.
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News