Waterdrip Capital: New Logic for Web3 Entrepreneurship Under the New Global Trade Order
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Waterdrip Capital: New Logic for Web3 Entrepreneurship Under the New Global Trade Order
This article explores the underlying logic of Trump's tariff policies, outlines new directions for blockchain entrepreneurship amid macroeconomic turmoil, and examines how traditional capital inflows could create a revaluation opportunity for the crypto industry.
Author: Waterdrip Capital
This article is adapted from the keynote speech delivered by Da Shan, founder of Waterdrip Capital, at the Wanwu Island sharing session.
Deteriorating Macro Environment – Crises Are Forging a New Order
1.1 Finance Enters a Chaotic Era
Since Donald Trump returned to the White House, a series of unexpected economic and political moves have kept global markets in turmoil. One of the most disruptive measures has been the escalation of tariff policies: starting April 5, 2025, the U.S. imposed a uniform 10% "baseline tariff" on all imported goods, along with higher "reciprocal tariffs" on 60 countries including China and Vietnam (with tariffs on Chinese goods briefly reaching 125%). In the short term, Trump’s tariff hammer triggered massive volatility across global markets: a sell-off in U.S. Treasuries sent the 10-year yield soaring above 4.5%, marking the largest weekly gain in two decades; U.S. equities swung wildly, nearly hitting circuit breakers; the dollar index plunged consecutively, recording its biggest single-day drop in years. Although the U.S. later announced temporary relief for some allied nations to buy breathing room, investor anxiety over future uncertainty remains high. The global financial system appears to have entered a “chaotic era.”
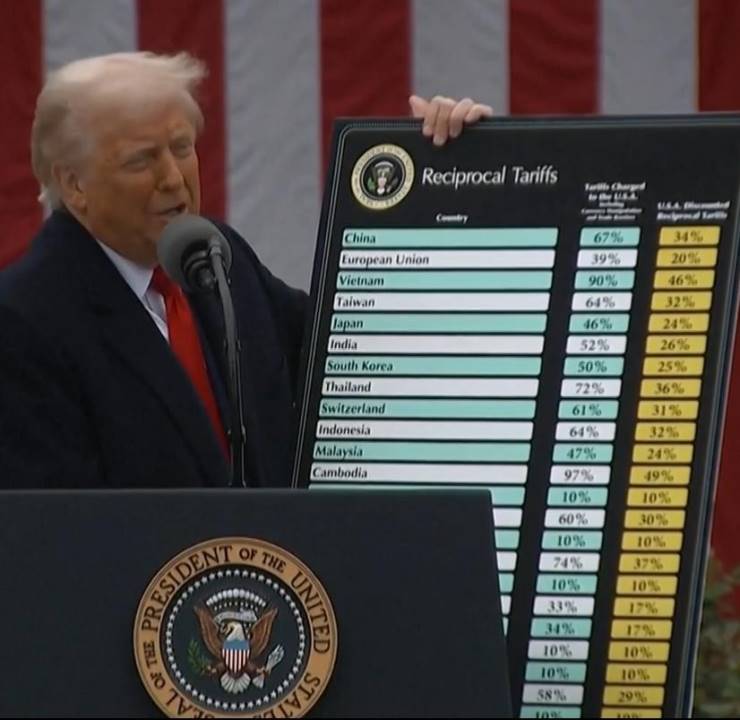
The post-WWII international economic order centered on the United States—such as the Bretton Woods system and WTO framework—is now at risk of unraveling. The rise of emerging economies has eroded America’s relative advantage, while its long-accumulated debt and fiscal deficits continue to undermine the credibility of the U.S. dollar. The share of dollars in global foreign exchange reserves is declining. Particularly since China joined the WTO, its rapid development has brought it close to—or even surpassed—the U.S. in many technological fields, triggering deep anxiety among American elites. Breakthroughs by Chinese firms like Huawei in key technologies such as 5G chip design and communication base stations have signaled that the once-insurmountable technological gap is rapidly closing. America’s traditional manufacturing edge is under threat, while younger Americans increasingly gravitate toward finance and the arts rather than industrial jobs. These shifts indicate that the old order underpinning American dominance is weakening.
Against this backdrop, U.S. policymakers are planning to build a new trade and financial order to maintain global leadership. The Trump administration's strategic goal goes beyond securing better terms in trade negotiations—it aims to “start anew” by establishing a new rules-based system to reassert U.S. centrality. This strategy has two core objectives: first, to weaken major competitors, curtailing the ability of countries like China to leverage existing globalization benefits for rapid growth; second, to seek new value anchors that can stabilize the shaken credibility of the dollar and global trade. Under this vision, the traditional dollar credit system requires stronger backing, prompting the U.S. to turn its attention to assets such as gold and Bitcoin, aiming to rebuild trust in the global financial architecture.
Notably, there has been a significant shift in the U.S. government’s stance toward the cryptocurrency sector since Trump took office. Shortly after his inauguration, Trump publicly expressed interest in virtual currency development, reversing his previous criticism of Bitcoin. Some factions within the Republican Party and certain state governments have also gradually embraced Bitcoin, viewing it as “digital gold” to hedge against dollar risks. It is clear that the U.S. is laying the groundwork for a potential new financial order, bringing Bitcoin into the realm of national strategy.
1.2 Bitcoin and Gold: A Dual Anchor for the Dollar
As global trade and financial rules face reconstruction, the U.S. seeks to establish a “dual-asset anchor” to reinforce the dollar’s credibility—one based on traditional gold reserves and another on emerging Bitcoin holdings. This strategy aims to combine physical and digital assets to bolster the dollar’s standing in the new order.
Gold has long served as a store of value widely held by central banks. The U.S. Treasury’s gold reserves (stored in the famous Fort Knox) remain a critical pillar of dollar hegemony. Now, Bitcoin is being assigned a similar strategic role—as “digital gold” for the new era. As of the end of 2024, Bitcoin’s total market cap was approximately $2 trillion, roughly one-tenth of gold’s $20 trillion valuation. In the long run, if Bitcoin’s market cap ever reaches parity with gold, its price could still appreciate manyfold. Given this growth potential—and Bitcoin’s unique advantages of decentralization, capped supply (21 million coins), and high liquidity—the U.S. is seriously considering incorporating it into its national reserve system.
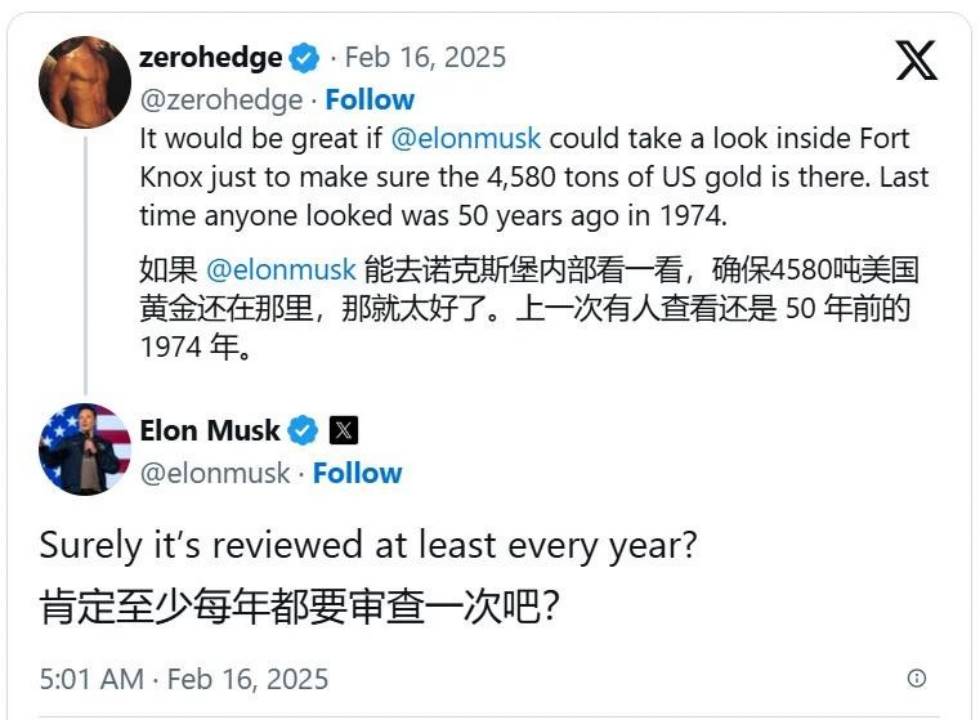
In March 2025, the U.S. government made a series of landmark moves in the crypto space: On March 6, President Trump signed an executive order announcing the creation of a “Strategic Bitcoin Reserve” and a “U.S. Digital Asset Reserve.” The next day, the White House hosted a high-profile crypto summit, inviting industry giants like Coinbase and MicroStrategy, as well as members of Congress and government officials. Trump publicly voiced support for the crypto industry, pledging to push Congress to swiftly pass regulatory legislation on stablecoins and digital assets to provide legal clarity. More strikingly, Trump declared at the summit: “Building a Bitcoin reserve is building a virtual Fort Knox”—signaling that the U.S. views Bitcoin reserves as the digital-age equivalent of national gold reserves. This statement marks Bitcoin’s formal entry into U.S. national strategy, elevating it to a status comparable to gold.
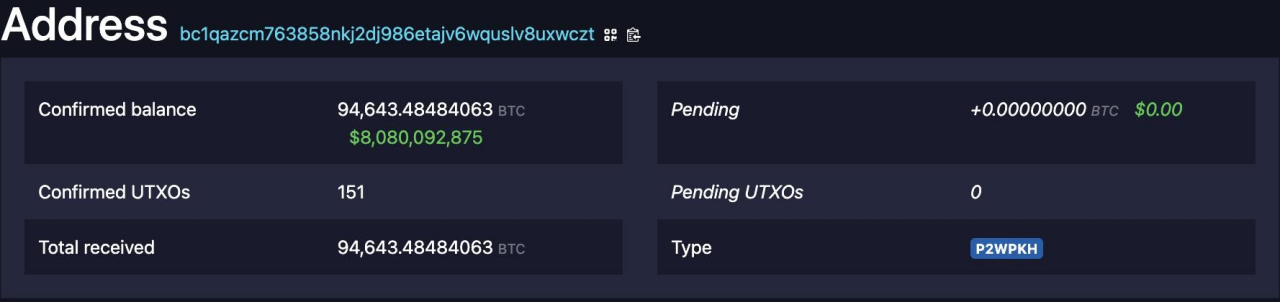
The image above shows wallet addresses of Bitcoin seized by the U.S. government. Compared to centralized gold vaults, the BTC network offers greater transparency and decentralization.
These actions indicate that the U.S. intends to use both Bitcoin and gold as anchor assets for the new financial system. In practice, the U.S. government already holds a significant amount of Bitcoin (primarily obtained through law enforcement seizures) and plans to increase its holdings further. Market speculation suggests a target of accumulating around 1 million Bitcoins (about 5% of total supply), a scale comparable to the proportion of U.S. official gold reserves in global gold holdings. While this goal has not yet been fully achieved, the trend is evident: some U.S. states have taken the lead, approving the use of public funds to purchase Bitcoin for reserves; at the federal level, executive orders and legislative proposals are legitimizing Bitcoin. If the dollar can be partially backed by physical gold and digital gold (Bitcoin), combined with blockchain-based international clearing systems, the U.S. could gain a strategic advantage in future global financial competition and extend the lifespan of the dollar system.
Moreover, incorporating Bitcoin helps address domestic challenges. For instance, the U.S. government’s massive national debt is becoming increasingly unsustainable, raising concerns about creditworthiness. If the U.S. amasses sufficient Bitcoin reserves and drives up their price in the future, it could sell part of these holdings to fill the fiscal deficit, thereby skillfully mitigating debt risks. This idea of “using crypto assets to dilute debt” represents a new dimension in U.S. financial strategy. At the same time, the U.S. is tightening regulation in digital currencies: a recent bill proposes placing stablecoins with circulation exceeding $10 billion under Federal Reserve oversight, indicating Washington’s intent to control the issuance and rule-making power of crypto dollars (USD-backed stablecoins), reinforcing the dollar’s dominance in the crypto world. USD stablecoins + gold + Bitcoin—this trio outlines the early form of a new dollar order: preserving the dollar’s legal status while enhancing resilience through physical and digital asset backing.
Market Correction and What to Do in the Second Half
Over the past year, the global crypto market has undergone a dramatic shift from frenzy to sobriety. The total market capitalization of crypto assets has declined from a historical peak of about $3.71 trillion to around $3.04 trillion (source: CoinMarketCap, data as of April 23, 2025), entering a phase of deep correction and cleansing. Macroeconomic turbulence (such as rising inflation and interest rates), coupled with stricter regulations, has led to the disappearance of numerous projects lacking real value. However, for entrepreneurs who believe in blockchain’s long-term potential, this moment presents an ideal opportunity to strengthen foundations and prepare for new breakthroughs. As the bubbles of the last cycle deflate, it becomes the perfect time to focus on product refinement and lay the groundwork for future success.
In this “second half” environment, entrepreneurs should ask: What makes sense now? Simple traffic-driven strategies no longer work; instead, startups must focus on hard-core value creation. Within the current market context, several directions offer promising opportunities:
-
Bitcoin (BTC) Ecosystem: Financial innovation on the Bitcoin network (“BTC Fi”), infrastructure upgrades, and rebuilding real-world asset and payment networks based on BTC.
-
Other Public Chain Ecosystems: Innovation on chains like Ethereum that returns to fundamentals of efficiency and profitability, moving beyond mere “traffic wars,” and building sustainable decentralized finance (DeFi) applications centered on product excellence.
-
Real World Assets (RWA) and Payment Finance (PayFi): Integrating on-chain technology with real-world assets and payment scenarios to develop new models supported by stable cash flows.
-
Crypto-related Stocks: Watching the rise of “crypto概念股” (crypto-linked stocks) in traditional capital markets and exploring new paths for Web3 startups to become stock-listed entities.
Next, we will analyze these themes in depth to identify specific entrepreneurial opportunities worth pursuing during this macroeconomic downturn.
2.1 Entrepreneurial Opportunities Around BTC: BTC Fi, BTC Infra, BTC RWA & PayFi
Although Bitcoin has long been seen as “digital gold” with relatively simple functionality on its mainnet, recent technological and application advances are injecting new vitality into the Bitcoin ecosystem. Around the BTC network, three major entrepreneurial opportunities are emerging:
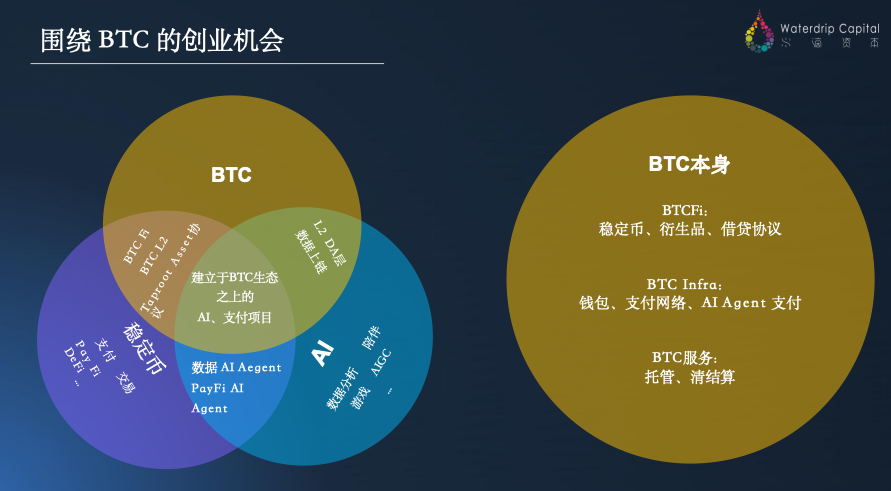
BTC Fi (Bitcoin Finance): Creating new financial assets on the Bitcoin network. Bitcoin is evolving beyond a static store of value into a foundational platform for issuing various financial instruments. Recent protocols like BRC-20 and Runes have sparked a wave of token issuance on the BTC mainchain. Meanwhile, Lightning Labs’ Taproot Assets protocol (TA Protocol) enables the creation of stablecoins, bonds, and other financial assets within the Bitcoin ecosystem. This means the Bitcoin mainnet could carry more value-bearing functions in the next cycle, upgrading from “digital gold” to a rich, asset-supporting value storage network. Projects like Bedrock and Solv are leading the charge, building decentralized financial services such as lending, trading, and derivatives on Bitcoin, driving a leap in BTC’s financing and asset issuance capabilities.
BTC Infra (Bitcoin Infrastructure): Rebuilding intelligent infrastructure on Bitcoin. To overcome limitations in Bitcoin’s native functionality, the industry is developing smart contract layers akin to those on Ethereum. One approach involves creating EVM-compatible Bitcoin sidechains or Layer 2 solutions (e.g., BTC L2s with Ethereum-like smart contract capabilities), expanding the DApp development space on the BTC network. Another path relies on native Bitcoin protocol extensions such as RGB and the Lightning Network—Bitcoin-native Layer 2 technologies focused on improving privacy, scalability, and payment efficiency, providing lightweight and cost-effective execution layers atop the BTC mainnet. Projects like Unisat, Merlin, and B² are building Bitcoin Layer 2s and middleware tools to enhance developer experience and scalability.
BTC-Powered RWA & PayFi: Unlocking Bitcoin’s potential in real-world assets and payments. Tokenization of real-world assets on the Bitcoin network is gaining momentum—for example, tokenizing U.S. Treasuries or physical assets, using Bitcoin as a settlement layer to provide globally verifiable clearing mechanisms, giving these assets strong, credible value anchoring. At the same time, PayFi models built on payment infrastructures like the Lightning Network are bringing Bitcoin back to the payment stage—combining AI agents (AI Agents) with Bitcoin micropayments to enable real-time, machine-to-machine and human-to-machine microtransactions. This offers efficient payment solutions for SaaS services, data exchange, and more. Projects like LNFi aim to improve Bitcoin’s practical utility and user experience in RWA and payment applications, empowering BTC’s circulation and usability.
Overall, the Bitcoin ecosystem is awakening across all layers—from base protocols to applications. Whether issuing assets on the BTC mainnet, building smart contract layers, or using BTC to settle real-world assets and enable instant payments, Bitcoin has the potential to become fertile ground for innovation in the next phase. For entrepreneurs, re-examining the possibilities of the Bitcoin network may reveal undervalued golden opportunities.
2.2 Entrepreneurial Opportunities Around Other Public Chains: Efficiency-Driven and Product-Centric Models
Beyond Bitcoin, other public chains (such as Ethereum, BSC, Solana, etc.) are also fostering new entrepreneurial logic and opportunities. After the DeFi boom and chain wars, the industry is returning to rationality, marked by two key trends:
-
Return to the fundamental logic of “making money”: Whether it's lending, trading, market making, or derivatives on-chain, any activity involving capital flow can find ways to validate business models and profit pathways. Over the past few years, many DeFi projects attracted capital through liquidity mining incentives, but after market cooling, models unable to generate sustained fees and profits are being phased out. In contrast, on-chain businesses with clear revenue streams—like transaction fees, lending interest, and derivative spreads—have proven their value, much like traditional finance. This reminds founders to revisit their project’s fundamentals: does it have a genuine profit model? In today’s environment, only businesses capable of “earning money” have the resilience to survive market cycles.
-
Public chain ecosystems shifting from “traffic wars” to “efficiency wars,” fueling product-led startups: Early chains and protocols competed for users and capital by offering high incentives and narrative-heavy marketing—“fighting for traffic.” But growth driven purely by storytelling cannot last. Now, investors favor practical projects that boost efficiency and improve user experience—those succeeding through superior products and technology. Whether it’s a new decentralized exchange, a more profitable market-making mechanism, a low-risk lending protocol, or a secure, efficient platform for issuing on-chain assets or data tools, any project solving real problems and demonstrating a viable business model stands a better chance of success. In short, public chain entrepreneurship is shifting from subsidies and hype to product quality and operational efficiency. For founders, this means that diligently refining products, optimizing performance, and enhancing user experience matter far more than chasing empty narratives.
A new competitive landscape is forming across other public chain ecosystems—efficiency is now the dominant theme, and product-led entrepreneurship is becoming mainstream. This shift serves as a wake-up call for the entire crypto startup community: only applications that create real value and generate income can survive the capital winter and thrive in the next spring.
2.3 Sustainable Startup Models: Cash Flow-Driven Paths
Whether in the Bitcoin ecosystem or on other public chains, building sustainable cash flow has become the dividing line between startups that endure and those that fail. Traditional capital markets are beginning to assess crypto startups using standards for mature enterprises, making “cash flow” and “profitability” key evaluation metrics. Indeed, traditional investors are redefining what a “crypto company” means—opening a window for Web3 startups to access mainstream capital.
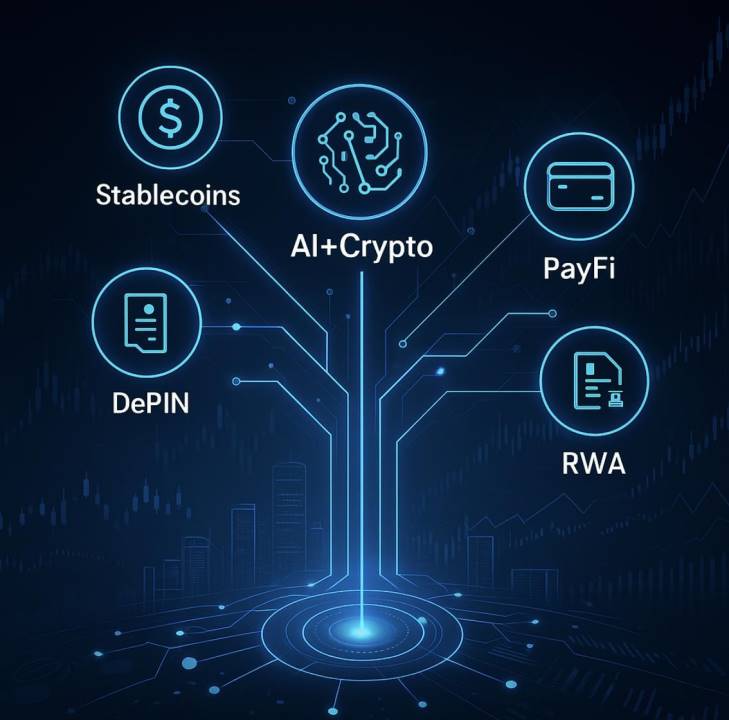
Today, crypto projects with real business models are becoming bridges connecting Web3 and traditional capital. These projects typically have clear revenue sources, predictable cash flows, and strong compliance adaptability, attracting significant attention from traditional institutions. They are seen as prime candidates likely to enter mainstream capital markets via IPO or acquisition.
Across multiple verticals, DePIN stands out. By putting real-world resources—computing power, electricity, bandwidth—on-chain and combining them with incentive mechanisms, DePIN builds distributed infrastructure networks for the physical world, naturally adopting a SaaS-like revenue model. Representative projects such as PEAQ, Jambo, OORT, Swan are building critical layers of the DePIN ecosystem—from device connectivity and Web3 mobile hardware to AI data storage and compute-sharing.
The AI+Crypto space shows strong integration potential. By combining AI Agents, on-chain identity, and micropayment systems, it enables intelligent agents to exchange data and coordinate resources. Projects like Footprint, focusing on analytics engines, and DeAgent.ai, building decentralized AI Agent protocols, are delivering services for Web3’s intelligent infrastructure.
The RWA (Real World Assets) sector is advancing rapidly, with ongoing tokenization of U.S. Treasuries, corporate bonds, real estate, and more—projected to reach a market size of $10 trillion. Notable projects like The PAC offer compliant asset mapping frameworks, enabling RWA circulation on-chain within regulated environments.
PayFi (Payment Finance) has become the most active segment on-chain. In 2024, stablecoin transaction volume exceeded $15.6 trillion, surpassing Visa for the first time. Projects like Aisa are integrating stablecoins with AI-powered wallets to build automated, real-time settlement infrastructure serving e-commerce, cross-border, and machine-to-machine payment scenarios.
In summary, crypto startups that “generate cash flow, are easy to value, and have compliant pathways” are gaining favor with Wall Street and mainstream investors, positioning themselves as frontrunners to enter the traditional financial system.
For entrepreneurs, the lesson is clear: design business models with cash flow as the guiding principle. From the earliest stages, consider how to generate stable revenue—not rely solely on token appreciation or subsidy-fueled expansion. Only when your project has real-world revenue and profit models can it attract both crypto-native capital and more conservative traditional investors. In a turbulent macro environment where capital preferences lean conservative—the so-called “second half”—pragmatic, cash-flow-healthy crypto startups are actually more likely to break through.
Crypto-Linked Stocks: Structural Integration with Mainstream Finance
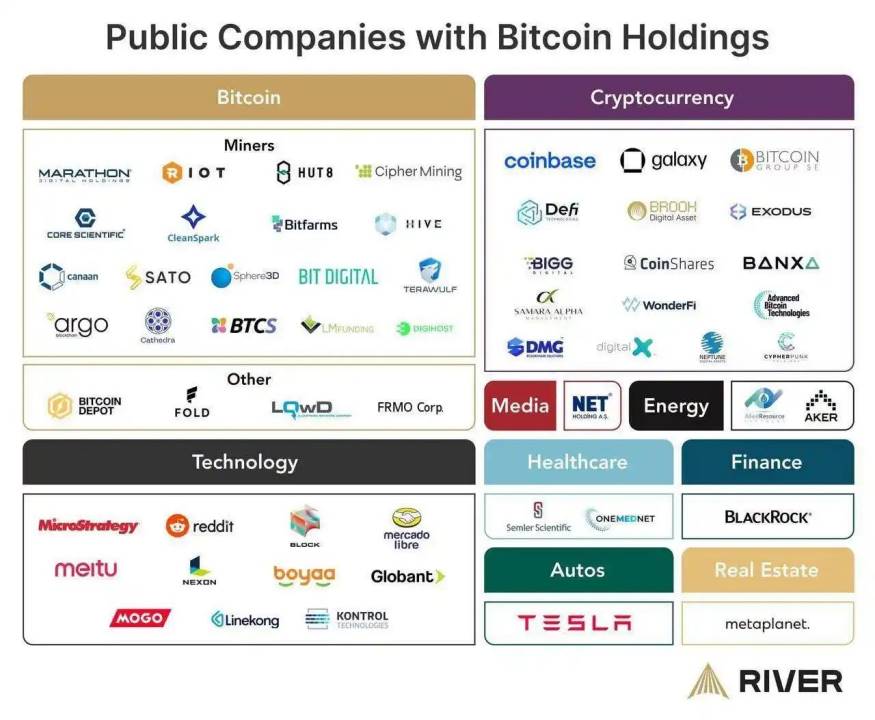
3.1 Categorizing Crypto-Linked Stocks
The emergence of “crypto-linked stocks” in traditional capital markets marks a significant step toward convergence between the crypto industry and mainstream finance. These listed companies participate in the blockchain sector in various ways, offering diversified investment options. Based on differences in business models and strategic focus, crypto-linked stocks can be broadly categorized as follows:
-
Asset-Driven (BTC Reserves as Core): These companies treat cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin as core assets on their balance sheets, amplifying corporate value through large-scale holdings. Prominent examples include MicroStrategy in the U.S., Semler Scientific, and Hong Kong-listed Boya Interactive. They view BTC as a “strategic reserve asset,” with an investment logic akin to “crypto version of cash flow + market cap amplifier”—benefiting from both core business cash flow and BTC price appreciation. Their strategies often involve buying BTC, issuing debt, and raising equity to acquire more tokens—a leveraged approach appealing to investors bullish on Bitcoin’s long-term rise. From an entrepreneurial perspective, this highlights potential opportunities in BTC asset management and corporate BTC purchasing services.
-
Mining-Focused Stocks (Computing Infrastructure): These companies are directly involved in cryptocurrency mining and related operations, with some expanding into broader computing infrastructure. Key players include Marathon Digital, CleanSpark, Riot Blockchain, Core Scientific, TeraWulf, and Hut 8. Some miners are now applying their computing power to artificial intelligence and high-performance computing (HPC), while adopting clean energy to reduce costs and meet environmental goals—AI demand and green energy are becoming new valuation drivers. These developments suggest entrepreneurial opportunities in areas such as upgrading Bitcoin mining infrastructure, integrating green energy into blockchain computing, and building next-gen data centers combining Web3 and AI.
-
Infrastructure and Solution Providers: This category includes firms offering underlying hardware, cloud services, and technical solutions for blockchain networks. Notable examples are Canaan (mining hardware manufacturer), Bitdeer (mining services), and BitFuFu (cloud mining platform). They serve as the “water sellers” of the crypto industry—core suppliers of hardware and cloud computing power. Their existence signals viable entrepreneurial avenues, such as Bitcoin ecosystem middleware (e.g., solutions improving mining efficiency or connecting miners with financial services) and “mining-as-a-service” (packaging mining capacity as cloud offerings for enterprises or individuals).
-
Exchange-Focused Stocks: These companies operate regulated crypto exchanges or custody services, such as Coinbase (COIN) in the U.S. and Bakkt (BKKT), a digital asset trading platform. With strict regulatory licenses and compliance systems, their business models are highly sensitive to macro policies and user trading activity. Their success indicates that compliant financial services will be a mainstream direction amid tightening regulations. For entrepreneurs, areas like compliant custody, on-chain transaction data analytics, wallet abstraction, and bridges connecting centralized exchanges with decentralized finance (e.g., CeFi-DeFi interoperability services) represent promising frontiers—extensions of exchange-focused business models.
-
Payment-Focused Stocks: These companies originate from traditional payment giants that have expanded into blockchain payments, such as Block (formerly Square) and PayPal. Leveraging stable cash flows from core payment operations, they add Bitcoin or stablecoin strategies to unlock new growth. For example, Block supports Bitcoin trading in its app, while PayPal offers crypto buying and transfer services. Their success proves the viability and value of crypto payments. For startup teams, opportunities lie in stablecoin-based payment solutions (e.g., cross-border settlements using USDT), innovative PayFi products, and AI-integrated smart wallets (e.g., AI wallets for automated investing/payment)—all fertile ground for innovation in this domain.
The rise of crypto-linked stocks is prompting more entrepreneurs to rethink funding strategies. Beyond token fundraising, equity-based paths are becoming a vital complement for the next generation of Web3 projects—especially for those with stable revenues and clear compliance structures, offering longer-term, more sustainable capitalization routes.
Several companies are validating this path in practice. For instance, Boya Interactive (00434.hk), mentioned earlier, has successfully achieved market revaluation through dual drivers: holding BTC and transforming its core business. Meanwhile, Hutao Capital (00905.hk) represents another model—engaging in crypto assets and Web3 projects via investment and holding structures, planning to integrate traditional securities, private funds, derivatives, and blockchain assets. The company has already partnered with Waterdrip Capital to explore collaborative, capital-driven ecosystem development. This “capital collaboration” model in Web3 doesn’t rely on in-house development but uses financial expertise and industry resources to empower the ecosystem—an important piece in today’s equity-based strategies. Additionally, Hydro Asia Holdings (01723.hk) has transitioned from traditional construction and prepaid retail into digital asset management. In early 2025, it officially purchased Bitcoin as a strategic reserve, reshaped its management team by bringing in crypto experts, and clearly defined its Web3 transformation path. Also notable is Nano Labs (NA.Nasdaq), a leading Chinese blockchain hardware maker, which in early 2025 announced allocating part of its USD reserves to purchase Bitcoin, formally integrating BTC into its corporate asset allocation—a new paradigm for Chinese blockchain tech firms entering global capital markets.
The diversity of crypto-linked stocks demonstrates how blockchain technology is integrating into traditional capital markets through various business models. This not only provides investors with new channels to access the blockchain sector but also guides entrepreneurs: showing which models resonate with mainstream capital and which have already been validated in public markets. From holding crypto for market cap management, to expanding mining into computing services, to providing foundational exchange and payment services—each model reflects a point of convergence between blockchain entrepreneurship and traditional business.
3.2 Equity-Based Web3 Startup Paths: Tokens, Stocks, or Both
Facing these trends—especially the success of crypto-linked stocks—Web3 entrepreneurs are rethinking funding and development strategies. In the past, crypto projects relied primarily on issuing tokens (Token) for fundraising. Today, however, the path toward equity financing and public listing is becoming increasingly viable. Overall, Web3 startups can choose from three main paths, each with distinct pros and cons:
“Token” Path (Crypto Token Fundraising): Raising funds and incentivizing communities through token issuance. This route is highly flexible and fast to launch, ideal for early-stage product validation and community building. During bull markets, rising token prices can bring substantial capital. However, it is highly sensitive to market conditions—the amount raised and token valuations fluctuate dramatically with crypto market swings. Regulatory uncertainty across jurisdictions also casts a shadow over pure token models. Teams choosing this path must navigate challenges in tokenomics design, ongoing market cap management, and compliance risks.
“Stock” Path (Equity Financing and IPO): Following the traditional startup model—raising equity investments, focusing on business execution and revenue growth, then seeking IPO or acquisition exit. This approach treats the company as a legal entity accepting equity investment, aligning better with regulatory frameworks and appealing to conservative institutional investors. Its strength lies in valuing the company based on fundamentals (revenue, profit), insulated from token price volatility, enabling more stable long-term growth. The downside is that initial fundraising may be harder than with tokens, and user and community growth might be slower, requiring a longer runway to prove value. This path suits projects with clear business models, sustainable cash flows, and long-term commitment.
“Dual-Track” Path (Tokens + Equity in Parallel): Combining both crypto and traditional financing methods, leveraging their respective strengths at different stages. Typically, a project issues tokens early to raise seed funds and build a community, then establishes a legal entity for equity financing once it achieves stable revenue—potentially paving the way for an IPO. This “dual-track” model allows flexibility across development phases: using tokens to incentivize users and grow the ecosystem early on, then tapping larger capital markets via equity later. However, it demands strong balancing skills—managing both token communities and shareholder expectations regarding governance and financial compliance. Some projects have already experimented with this model—for example, DeFi protocols issuing governance tokens while their parent companies accept VC equity funding and consider future IPOs. Though complex, when executed well, the dual-track model can deliver synergistic 1+1>2 outcomes.
Regardless of the chosen path, alignment with the project’s identity and external environment is key. Founders should weigh factors like project type, revenue model, regulatory landscape, and team strengths to select the optimal funding and growth strategy. In today’s context, relying solely on one path may be limiting. Flexibly adjusting—or even switching or combining—strategies based on real-world conditions increases survival odds and the likelihood of success.
4. Conclusion
Periods of macro instability are both challenges and opportunities. The “second half” of the market tests entrepreneurs’ resilience and wisdom: only teams rooted in real value and committed to long-termism can endure the winter. Driven by waves of innovation in the BTC ecosystem, efficiency revolutions on new public chains, real-world asset tokenization, cash flow-driven models, and integration with capital markets, a new generation of blockchain entrepreneurs is encountering unprecedented opportunities. By choosing the right赛道, validating business models, and wisely selecting financing paths, crises can be transformed into breakthroughs—enabling true 0-to-1 leaps in blockchain entrepreneurship in the next cycle.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News