Hotcoin Research | Tariff "Nuclear Bomb" Detonated: Analysis of U.S. Tariff Policy Direction and Its Impact on the Crypto Market
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Hotcoin Research | Tariff "Nuclear Bomb" Detonated: Analysis of U.S. Tariff Policy Direction and Its Impact on the Crypto Market
This article will analyze the specific measures of Trump's new tariff policy, its macro transmission mechanisms, the future direction of U.S. tariff policy, and its profound impact on the cryptocurrency market, helping investors gain a comprehensive understanding of the associated risks and opportunities.
1. Introduction
After Donald Trump returned to the White House, he swiftly fulfilled his campaign-era promises on tariffs, unleashing an unprecedented tariff storm widely described as sparking a "Tariff War 2.0," triggering severe shocks in both traditional financial markets and the cryptocurrency sector. Under this heavy pressure, Bitcoin and the broader crypto market experienced sharp pullbacks, subjecting numerous blockchain projects to difficult tests. This article analyzes the specific measures of Trump’s new tariff policies, their macroeconomic transmission mechanisms, the likely trajectory of U.S. tariff policy, and their profound impact on the crypto market—helping investors fully understand the associated risks and opportunities.
2. Trump's Tariff Policies Since Returning to Office

February: Wielding the Tariff Stick
(1) Targeting North America: On February 1, the U.S. announced a 25% tariff on all imports from Canada and Mexico (with a 10% tariff on Canadian energy resources), pressuring the two countries to strengthen border security, immigration controls, and combat drug smuggling. Canada immediately retaliated by imposing 25% tariffs on billions of dollars worth of American goods, while Mexico also planned countermeasures.
(2) Targeting China: On the same day, Trump announced a 10% tariff on all Chinese goods entering the U.S., effective February 4. This move was framed as leverage to compel China to take action against fentanyl and other drug smuggling into the U.S. Trump also signed an executive order eliminating the previous de minimis exemption for low-value shipments from China and Hong Kong (under $800), meaning these small parcels would now be subject to the new 10% tariff. These initial actions marked the beginning of the Trump administration’s renewed tariff strategy.
March: The Tariff Negotiation Tug-of-War
(1) NAFTA Tariff Turmoil: On March 4, the Trump administration formally imposed a 25% tariff on all goods produced in Mexico and Canada. Canada responded immediately with reciprocal tariffs on U.S. products, and Mexico signaled it would retaliate as well, reigniting fears of a new trade war. Just one day later, on March 5, Trump temporarily exempted automobiles from Canada and Mexico from the tariffs for one month to relieve pressure on the three major U.S. automakers. On March 6, Trump signed an executive order delaying the implementation of tariffs on Mexico and Canada until April 2 to allow for further negotiations. As a result, Canada and Mexico paused their planned retaliatory measures. Despite this brief de-escalation, on March 7 Trump threatened new tariffs on Canadian lumber and dairy products, criticizing Canada’s long-standing high tariffs on U.S. agricultural goods and vowing “more changes and adjustments” ahead on tariffs. This series of abrupt moves highlighted the aggressive and volatile nature of Trump’s tariff policy, destabilizing the foundation of North American free trade within weeks.
(2) Steel and Aluminum Tariffs Return: The Trump administration also reinstated high tariffs on global steel and aluminum in March. Starting March 12, the U.S. reimposed a 25% tariff on imported steel and a 10% tariff on aluminum under Section 232 national security grounds—a revival of measures enacted during Trump’s first term. In response, the EU imposed retaliatory tariffs ranging from 4.4% to 50% on U.S. steel and aluminum products starting April 1.
April: Escalation of the Tariff War
"Liberation Day" Broad Tariffs: On April 2, Trump announced a new round of aggressive tariff measures at the White House, dubbed “Liberation Day” tariffs. He signed two executive orders regarding “reciprocal tariffs”:
(1) Universal Taxation: Starting April 5, an additional 10% “universal” tariff was imposed on all imports from 185 countries worldwide. This meant that, with few exceptions, the vast majority of imported goods into the U.S. faced a new 10% ad valorem tax. USMCA partners Canada and Mexico were temporarily exempted from this 10% blanket tariff, and low-value e-commerce packages (<$800) were also deferred to minimize disruption to daily consumer spending.
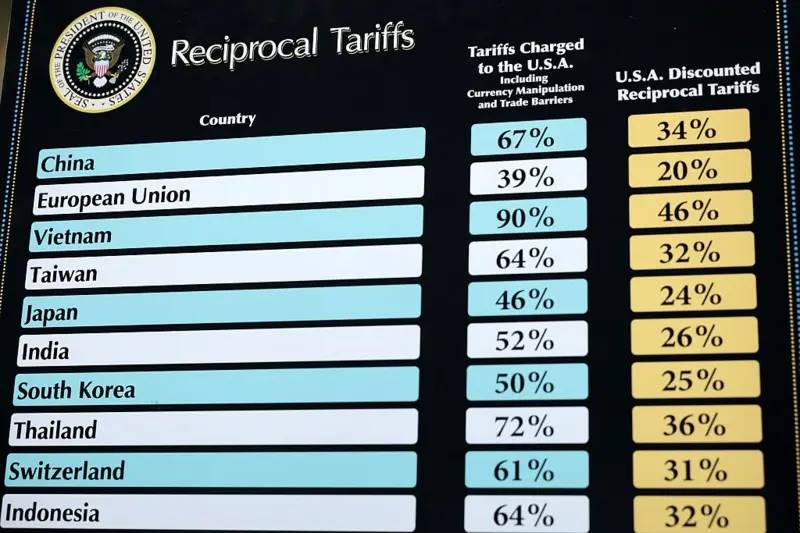
(2) Reciprocal Surcharges: For economies with significant trade surpluses against the U.S., higher reciprocal tariffs were applied on top of the 10% base rate, effective April 9. Specific rates included: China 34%, EU 20%, Japan 24%, South Korea 25%, Taiwan 32%, India 26%, Thailand 36%, among others. Additionally, a 25% tariff was imposed on all imported vehicles and auto parts starting April 3, aimed at pushing automotive manufacturing “back” to the U.S. This wave of tariffs encompassed nearly every major trading nation, with unprecedented breadth and severity—dubbed a “tariff nuclear bomb.”
Source: https://www.bbc.com/
This dramatic escalation inevitably triggered strong global reactions. On April 3, the EU and Canada declared they were “ready to respond,” while Japan urgently sought exemptions. On April 4, China retaliated with equivalent 34% tariffs. Subsequently, Trump threatened an additional 50%, bringing the total on Chinese goods to 104% when combined with prior levies. On the same day, China announced fresh countermeasures: starting April 10, it would impose an additional 50% tariff on all U.S. imports, raising its total tariff rate to 84%. A full-scale trade conflict thus emerged between the U.S. and key economies led by China.
Less than 24 hours after imposing high reciprocal tariffs on dozens of trade partners, Trump abruptly reversed course. On April 9, citing over 75 countries having contacted U.S. representatives for consultations, he announced a 90-day suspension of the new tariffs. During this period, the universal tariff would be reduced to 10%, with the pause taking immediate effect. However, the 90-day suspension did not apply to tariffs on Mexico and Canada. Simultaneously, Trump raised tariffs on Chinese goods from 104% to 125%.
3. Transmission Mechanisms: How Tariff Policy Impacts the Crypto Market
Trump’s new tariff policies have not only reshaped global trade but also affected the Bitcoin and broader crypto market through multiple macroeconomic channels. As a key macroeconomic instrument, tariffs trigger chain reactions across economic growth, inflation, capital flows, exchange rates, and market sentiment—ultimately influencing crypto asset prices. The specific mechanisms are as follows:
- Economic Slowdown and Inflation Concerns: Large-scale tariffs act as taxes on imported goods, directly increasing costs for businesses and consumers. This raises inflationary pressures and drags down economic growth. Rising inflation expectations coupled with slowing growth send dangerous signals to markets, prompting investors to flock to traditional safe-haven assets. Indeed, amid rising tariff uncertainty, investors so far in 2025 have favored gold over emerging assets like Bitcoin: early April saw international gold prices briefly surpass $3,150 per ounce, a historic high. Although Bitcoin is often touted as “digital gold” resistant to inflation, market behavior shows its speculative nature currently outweighs its safe-haven appeal—the flight-to-safety demand has flowed primarily into traditional assets such as gold.
- Tightening Dollar Liquidity and Cash-Out Demand: Trade wars disrupt global supply chains and commerce, potentially tightening dollar liquidity. Declines in imports and exports reduce the supply of dollars in trade transactions, while uncertainty leads firms and investors to hoard cash, increasing demand for U.S. dollars. In such conditions, some institutions and investors may be forced to liquidate assets to raise dollar cash. Amid stock market plunges, some investors may sell crypto holdings for liquidity. This selling pressure exacerbates downward price pressure. Risk aversion can also boost the dollar’s exchange rate, weighing on dollar-denominated Bitcoin prices. Currently, market expectations suggest the Fed will cut rates earlier than planned to support growth, driving a sharp drop in Treasury yields (the U.S. 10-year yield fell 20 basis points following tariff announcements). Shifts in interest rate expectations influence capital allocation: safe-haven funds flow into bonds and dollar assets, reducing appetite for high-risk assets.
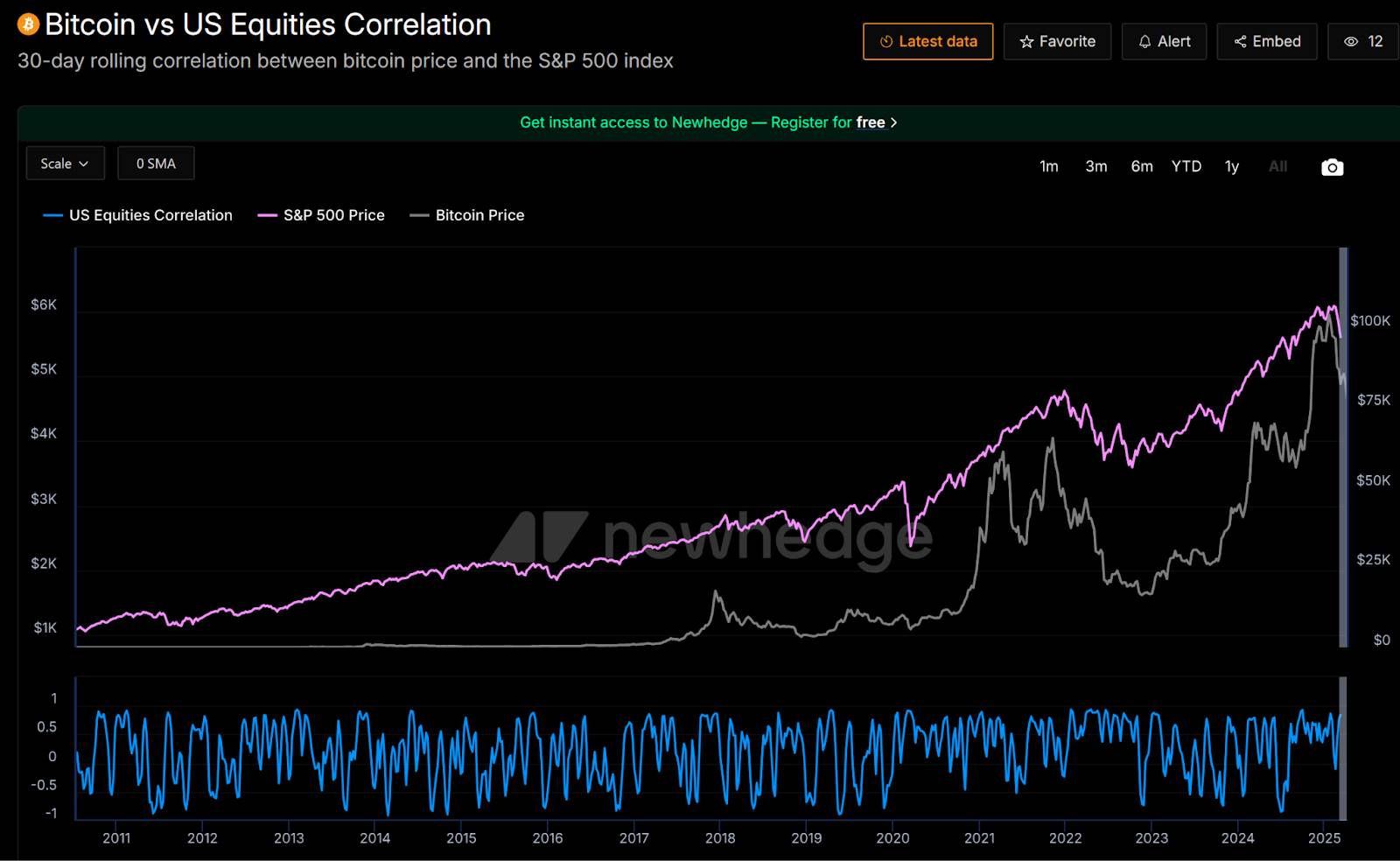
- Market Risk Appetite and Sentiment Shift: Broad-based tariffs are seen as major negative news, directly undermining global investor risk appetite. Trade tensions sparked by Trump’s tariff policy have sent uncertainty soaring, leading investors to adopt a “sell first, ask questions later” stance. Stock market declines and Bitcoin drops have become highly correlated: according to TradingView, Bitcoin’s price correlation with the S&P 500 index stands at 0.66, indicating that under severe risk shocks, Bitcoin is now treated by markets as a risk asset rather than a safe haven. The uncertainty generated by tariff policies has also dampened earlier market optimism. Trump had initially sent friendly signals toward cryptocurrencies during his campaign and early presidency, fueling Bitcoin’s rally to around $109,000 by late 2024. But the shadow of a tariff war quickly loomed; as trade prospects deteriorated and downside economic risks mounted, risk-averse sentiment took hold, sharply weakening the momentum behind crypto’s prior gains.
Source: https://newhedge.io/bitcoin/us-equities-correlation
- Historical Trends and Shifting Crypto Asset Positioning: The crypto market’s reaction to trade conflicts differs from several years ago. During Trump’s initial trade war in 2018, some investors viewed Bitcoin as a hedge against uncertainty, helping drive its price from lows near $3,700 to $13,000—an “against-the-wind” rally. However, today’s market is more mature and tightly linked to mainstream finance. In the 2025 tariff shock, Bitcoin did not repeat its 2018 strength but instead declined alongside equities. This suggests a shift in Bitcoin’s investor base and market positioning: with greater institutional participation, its trading behavior increasingly resembles that of tech stocks and other risk assets, rather than operating independently. This evolution underscores crypto’s growing integration within the global financial system.
4. Analysis of Crypto Market Performance After Tariff Announcements
In Q1 2025, Bitcoin and the broader crypto market’s performance closely tracked the rhythm of Trump’s tariff policy. Changes in trading volume and capital flows reflected a shift in investor sentiment from optimism to caution. Under such macroeconomic stress, the crypto market entered a short-term phase of stagnation and correction.
February: Cooling Optimism: From late 2024 to early 2025, buoyed by Trump’s election win and pro-digital asset rhetoric, Bitcoin extended the previous year’s bull run, briefly breaching the $100,000 mark. However, as tariff-related news emerged in early February, Bitcoin rapidly reversed course, and the broader crypto market began a steep decline. By end-February, Bitcoin had dropped about 28% from its January peak, falling into a technical bear market. Over the month, global crypto market capitalization shrank by over $1 trillion. The crypto market clearly experienced a “cooling off” during the first round of tariff turmoil.
March: Volatile Consolidation: In March, the Trump administration’s fluctuating tariff policies toward Mexico, Canada, and steel/aluminum caused repeated swings in market sentiment. Early-month news that North American tariffs would be delayed led Bitcoin to oscillate around the $80,000 level. On one hand, the temporary reprieve on allied nations offered some comfort, sparking brief rebounds in risk assets. On the other, Trump’s frequent hardline statements made investors hesitant to commit large positions. Throughout March, Bitcoin traded in a wide range between $75,000 and $90,000.
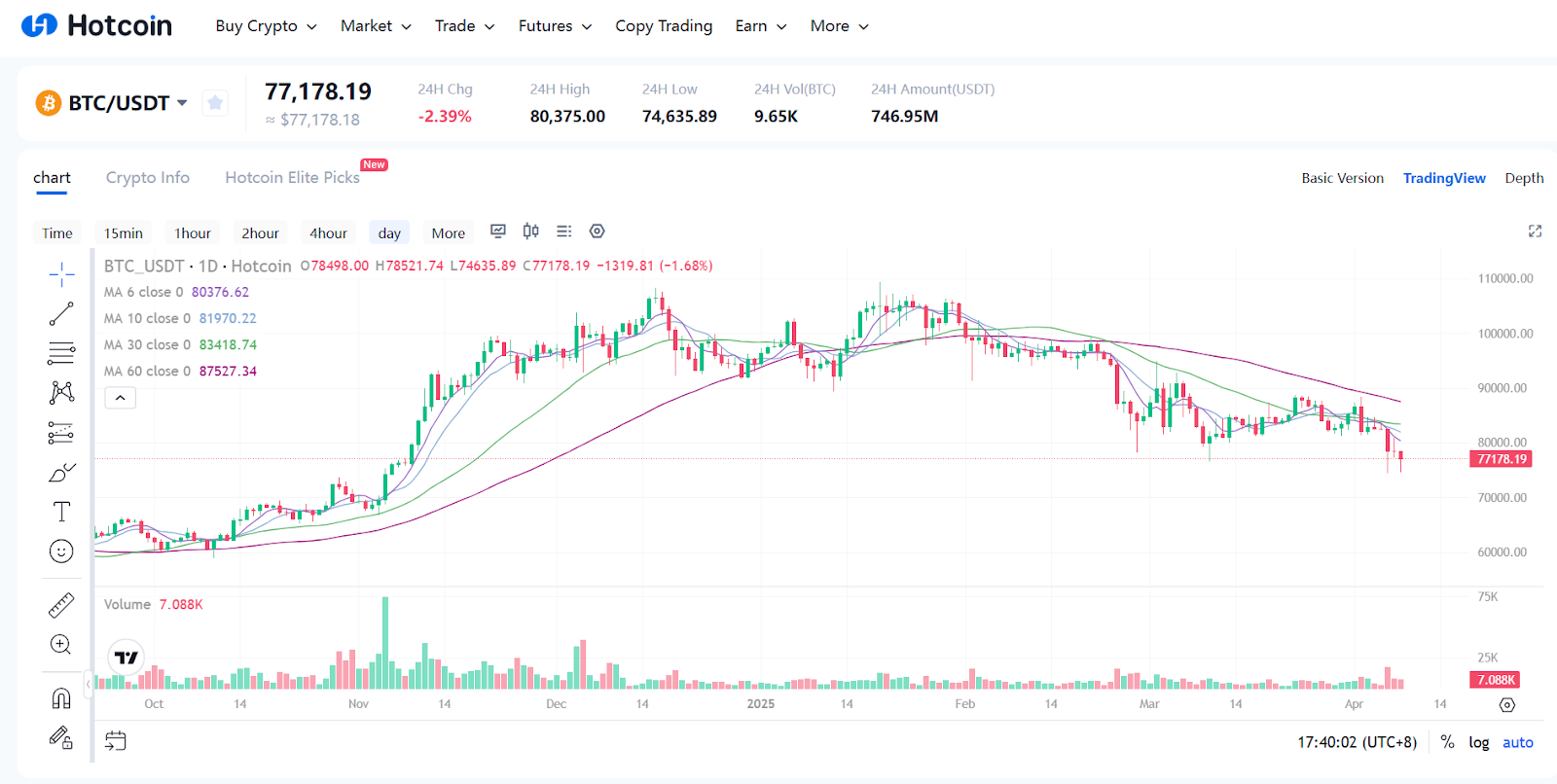
"Liberation Day" Tariffs Trigger April Turbulence: In early April, Trump’s formal signing of sweeping tariff executive orders became the catalyst for another market shock. On April 2, the day the broad tariff plan was unveiled, Bitcoin initially spiked—briefly jumping to ~$87,400—as some capital misinterpreted the announcement as inflation-driven buying pressure. It then sharply reversed, plunging to around $82,000, resulting in over 6% intraday volatility. By April 9, the downtrend continued, with Bitcoin hitting a year-low of $74,508.
Source: https://www.hotcoin.com/en_US/trade/exchange
According to CoinMarketCap, on April 2—the day tariffs were announced—global crypto investment products (such as ETFs) saw approximately $8.6 billion in net outflows, with Bitcoin ETFs alone experiencing $8.7 billion in single-day net outflows. This indicates institutional capital swiftly exited to seek safety upon the news. Furthermore, the total crypto market cap erased about $500 billion in value during the week following the tariff shock. Meanwhile, CME Bitcoin futures open interest declined, suggesting institutional investors reduced their risk exposure. These signs collectively indicate that under the risk-off environment created by tariff policies, capital is temporarily exiting the crypto market, tightening on-chain liquidity.
5. Outlook: Tariff Policy Trajectory and Crypto Market Prospects
At the start of 2025, the global economy was already navigating a mix of slowing growth and easing inflation. Following the 2024 rate-hiking cycle, U.S. inflation had cooled somewhat, though growth momentum weakened. Europe teetered on the edge of stagflation, while emerging markets like China struggled with recovery. The eruption of a full-blown trade war cast an even darker shadow over an already fragile recovery outlook.
5.1 Future Direction of U.S. Tariff Policy
Trump may use maximum pressure as a negotiating tactic, then selectively reduce certain tariffs once trade partners concede, securing political wins. For example, tariffs on Canada and Mexico could be lifted or lowered if agreements are reached on immigration and drug issues; EU auto tariffs might be suspended via new trade talks; U.S.-China tariffs could see partial “phased cancellations” in exchange for expanded Chinese purchases or market access.
The Trump administration emphasizes that tariff revenues can support domestic industries and infrastructure. While some tariff adjustments may occur through negotiation, high tariffs in strategic sectors such as clean energy and semiconductors are expected to remain entrenched. Should the economy significantly deteriorate in the second half of 2025, the administration may be forced to recalibrate its tariff strategy.
5.2 Impact of Tariff Policy on Monetary Policy
The tariff shock is expected to worsen growth prospects, forcing the Federal Reserve to ease policy earlier than originally planned. Investors anticipate the Fed could begin rate cuts in the second half of 2025. According to J.P. Morgan Private Bank analysis, markets expect the Fed to lower rates to around 3.5% by year-end, with growth risks outweighing inflation risks as the main driver for lower yields. Yet, while trade tensions fuel recession fears, tariff-driven inflation simultaneously constrains central bank easing capacity. This policy dilemma heightens uncertainty about the economic outlook.
If tariffs persist long-term, elevated import duties would effectively impose a stagflationary shock on the U.S. economy. If fully implemented, the resulting price increases could trap the Fed in a bind: cutting rates might fuel inflation and asset bubbles, while holding rates steady could deepen economic downturns. Conversely, progress in trade negotiations and partial tariff rollbacks could improve growth expectations, ease inflationary pressures, and open space for Fed rate cuts—potentially improving liquidity and benefiting all asset classes, including Bitcoin.
5.3 Potential Impact of Future Tariff Trends on the Crypto Market
If trade tensions ease in the short term, global risk appetite could rebound, potentially lifting cryptocurrencies into a new rally. Particularly if the Fed proceeds with rate cuts—or even restarts quantitative easing—Bitcoin and Ethereum, having undergone deep corrections, may regain strength. Given Trump’s personal and team-level relatively favorable stance toward cryptocurrencies, a stronger economy could encourage him to embrace digital asset innovation to attract investment—such as advancing regulatory reforms or approving more compliant products.
Conversely, if the trade war remains protracted or worsens, the global economy could slide into recession, dragging down traditional financial markets. In such an environment, cryptocurrencies would likely continue to fall alongside other risk assets in the short term. However, after enduring this turbulence, Bitcoin may have an opportunity to reassert its role as a store of value. As nations engage in competitive monetary easing and fiat currencies lose credibility, Bitcoin—as a scarce asset immune to central bank money printing—could attract renewed investor interest.
6. Conclusion
In the short term, tariff policies have a predominantly negative impact on the crypto market, with the market struggling to find a bottom amid risk-off sentiment. In the medium term, the outcome will depend on how the trade war evolves and the effectiveness of macroeconomic offsetting policies; the crypto market may remain highly volatile, undergoing a prolonged consolidation phase. In the long run, these developments could push the global financial system in new directions—within which Bitcoin and the broader crypto ecosystem may seize unexpected strategic opportunities.
Regardless of the outcome, this round of tariff shocks offers the crypto industry a critical test of its resilience: whether Bitcoin can truly serve as “digital gold” will be judged over a longer horizon. If protectionism drives the global economy toward fragmentation, Bitcoin may emerge as a unifying value anchor and hedging instrument across disparate economic systems.
About Us
Hotcoin Research, as the core research hub of the Hotcoin ecosystem, is dedicated to providing professional, in-depth analysis and forward-looking insights for global crypto investors. We have built a three-pillar service framework of “trend assessment + value discovery + real-time tracking,” offering precise market interpretation and actionable strategies to investors at all levels. Through deep dives into industry trends, multi-dimensional evaluations of promising projects, and 24/7 market volatility monitoring—combined with our bi-weekly《Top Coin Selection》strategy livestreams and daily《Blockchain Headlines》news briefings—we empower investors with timely intelligence. Leveraging cutting-edge data analytics models and extensive industry networks, we help novice investors build cognitive frameworks and enable institutional clients to capture alpha, jointly seizing value-growth opportunities in the Web3 era.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile and inherently risky. We strongly advise investors to fully understand these risks and invest strictly within a robust risk management framework to ensure capital safety.
Website:https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
Mail:labs@hotcoin.com
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News