DeFi's New Changes in 2025: The Year Traditional Finance Meets On-Chain Finance
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

DeFi's New Changes in 2025: The Year Traditional Finance Meets On-Chain Finance
DeFi is no longer an alternative to traditional finance, but is becoming a key pillar of the global financial system.
Author: LSTMaximalist
Translation: TechFlow
In 2025, DeFi stands at a pivotal moment of transformation. Evolving from niche experiments aimed primarily at crypto-native users into a complex and rapidly expanding decentralized financial ecosystem, DeFi has reached new heights in efficiency and accessibility—driven by deep institutional participation, increasingly defined regulatory frameworks, and significant advances in scalability and cross-chain interoperability. The evolution of DeFi extends beyond technology; its application scope continues to broaden—from tokenization of real-world assets and optimization of on-chain derivatives to the introduction of risk management solutions.
This article explores four key trends shaping DeFi in 2025: accelerating institutional adoption, evolving regulatory landscapes, breakthroughs in Layer-2 (L2) scaling and cross-chain technologies, and the emergence of novel use cases. As DeFi matures, it is moving far beyond traditional applications like liquidity mining or decentralized lending, actively redefining the future landscape of finance.
Institutional Adoption
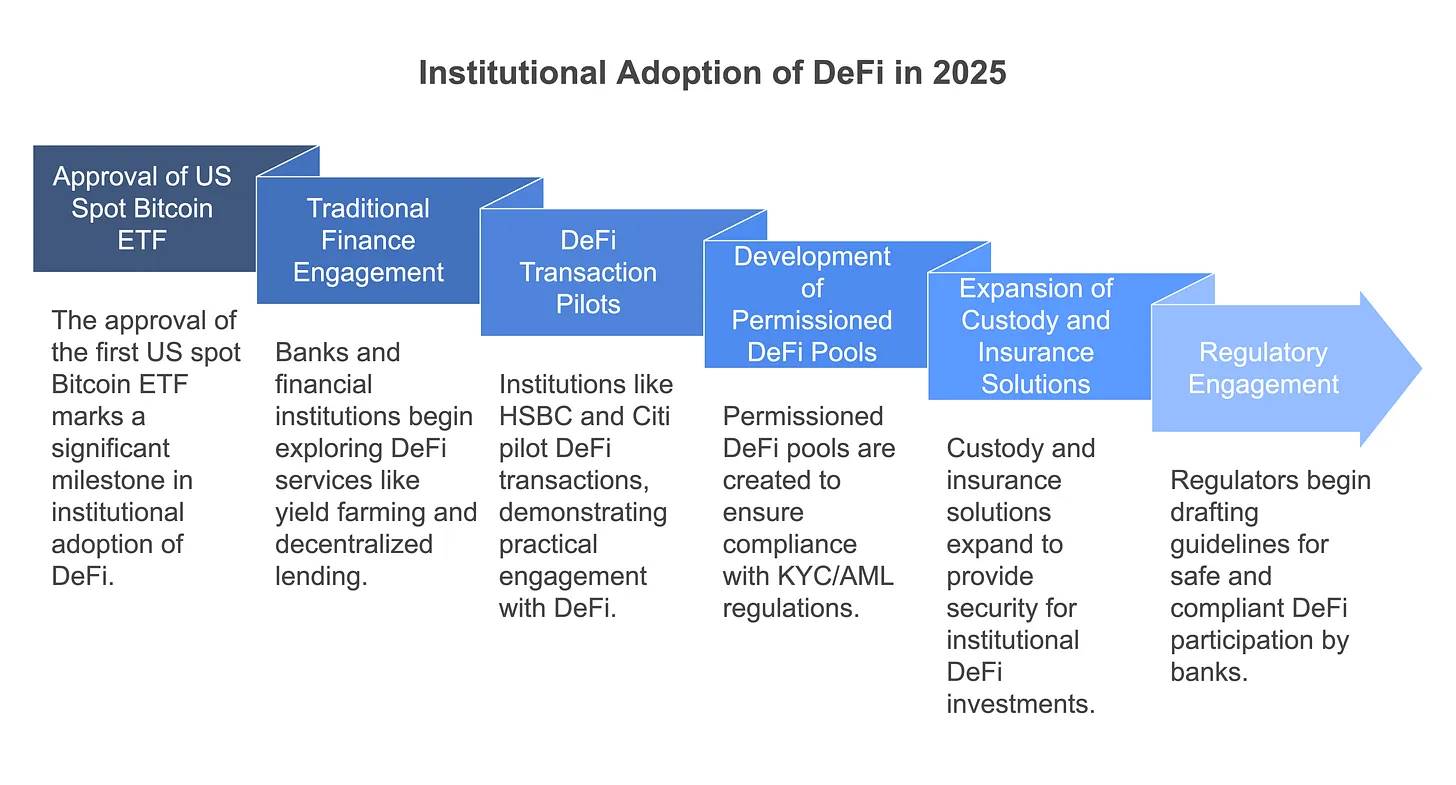
In 2025, DeFi is experiencing a critical phase of integration with traditional finance (TradFi). Once focused mainly on crypto-native individuals and retail investors, decentralized finance is now attracting attention from banks, asset managers, and fintech firms. For example, in January 2025, the U.S. approved its first spot Bitcoin ETF after years of anticipation—an event hailed as “opening the door to mainstream participation” and paving the way for subsequent launches of other ETFs, including Ethereum-based ones, over the following months.
Meanwhile, signals of crypto-friendliness from the new U.S. administration have further strengthened institutional confidence in DeFi. Major traditional financial institutions are actively exploring DeFi applications: JPMorgan, Goldman Sachs, and BlackRock are investigating liquidity mining and decentralized lending services, aiming to integrate blockchain-based products into their existing operations. Some large banks have even begun piloting DeFi transactions—for instance, HSBC and Citibank completed a foreign exchange settlement experiment via Aave’s private network in 2024, while Swift is collaborating with Chainlink to test settlement solutions for tokenized assets, bridging traditional finance with decentralized ecosystems.
The motivations behind institutional involvement are clear: DeFi’s highly automated protocols offer higher yields and 24/7 liquidity—features especially attractive to hedge funds, treasury managers, and mutual funds in a low-interest-rate environment. Moreover, institutional engagement accelerates innovation and compliance within DeFi. Permissioned DeFi pools such as Aave Arc are gaining traction, enabling KYC- and AML-compliant institutions to conduct secure borrowing and lending. Enhanced custody and insurance solutions also provide greater peace of mind for professional investors allocating capital to DeFi. The term “Institutional DeFi” has become an industry buzzword, symbolizing the convergence of high-yield DeFi mechanics with TradFi-grade risk management.
As institutional capital flows in, liquidity and market stability in DeFi are expected to improve significantly—though this also brings increased demand for robust regulation. Indeed, by 2025, regulators themselves have begun engaging directly with DeFi research and experimentation. Central banks and regulatory bodies are closely monitoring—and testing—DeFi applications. For example, the European Central Bank and U.S. regulators initiated drafting guidelines for regulated DeFi applications at the end of 2024, ensuring that banks participating in DeFi meet safety and compliance standards. Overall, 2025 marks a turning point for institutional DeFi adoption, a year many predict will be remembered for successfully bridging the gap between DeFi and TradFi.
Regulatory Developments
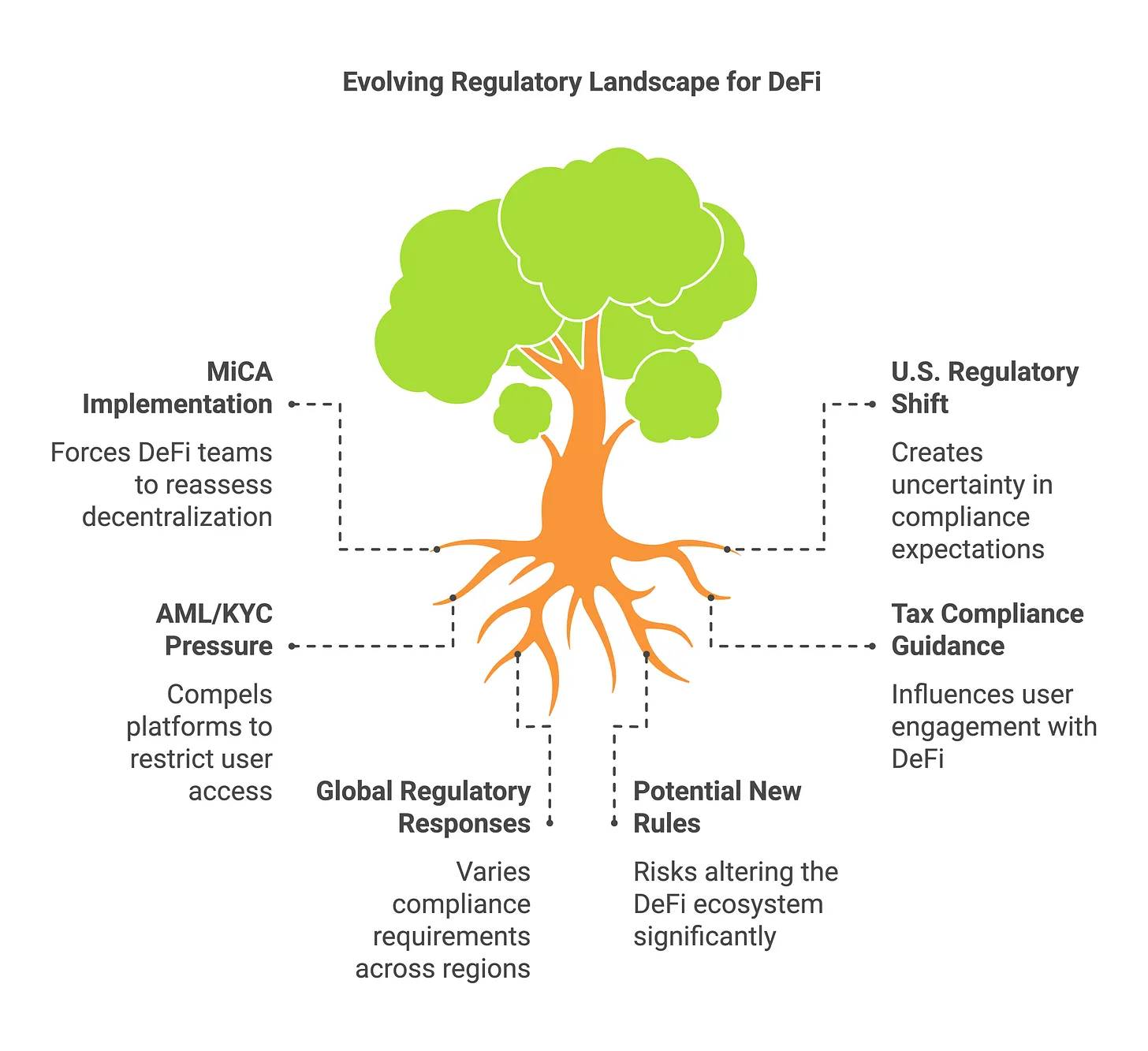
The regulatory landscape for DeFi is rapidly evolving. In the European Union, the landmark Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation officially took effect in early 2025, providing a unified framework across member states. MiCA requires crypto-asset service providers (CASPs) to obtain operating licenses and adhere to disclosure and compliance standards. While MiCA primarily targets centralized actors—such as exchanges and stablecoin issuers—its implementation has prompted DeFi project teams to reassess their level of decentralization and consider how future regulations might apply to them.
European regulators, including the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) and the European Banking Authority (EBA), are beginning to focus on specific risks associated with DeFi. A joint EU report noted approximately 7.2 million DeFi users in the region (about 1.6% of the population), yet fewer than 15% of these users engage regularly. This indicates that regulators are gathering data and may soon develop targeted policies for DeFi.
In the United States, 2024 was marked by aggressive enforcement actions, but a notable shift occurred entering 2025. Under new leadership, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) reevaluated its approach: in February 2025, the SEC announced it would terminate its high-profile investigation into Uniswap Labs without taking further enforcement action. Prior to that, the SEC had paused or withdrawn several actions against other crypto firms—a series of moves widely seen as signs of a potential regulatory "thaw." The Uniswap team called it a “major victory” for DeFi, raising market hopes that regulators may begin offering clearer guidance rather than relying on retroactive penalties.
At the same time, U.S. regulators are examining how existing financial laws—such as securities and commodities regulations—can be applied to DeFi protocols. Industry leaders are advocating for tailored, purpose-built rules to be established in 2025. Globally, other jurisdictions are also exploring regulatory strategies: Singapore and Hong Kong are creating regulatory sandboxes for compliant DeFi projects. Some developing countries view DeFi as a tool for advancing financial inclusion, though they remain cautious about its risks.
AML and KYC compliance remains a central theme in DeFi regulation. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) emphasizes that DeFi must not become a safe haven for illicit funds, urging nations to enforce anti-money laundering measures such as the “Travel Rule” on crypto platforms. In practice, this has led some DEX aggregators and frontends to implement geographic restrictions or user screening, while also spurring development of decentralized identity solutions to support compliance in permissioned DeFi environments.
Tax compliance is another emerging priority. Countries are issuing tax guidance on activities like liquidity mining, staking, and liquidity provision—policies that will directly influence user behavior. Overall, global regulatory clarity is gradually improving: Europe’s comprehensive framework and a potentially more lenient stance in the U.S. send positive signals for DeFi’s growth. Nevertheless, project teams remain cautious, as any new rules regarding DAO (decentralized autonomous organization) liability or protocol registration could profoundly impact the DeFi ecosystem.
Layer-2 Scaling and Cross-Chain Interoperability
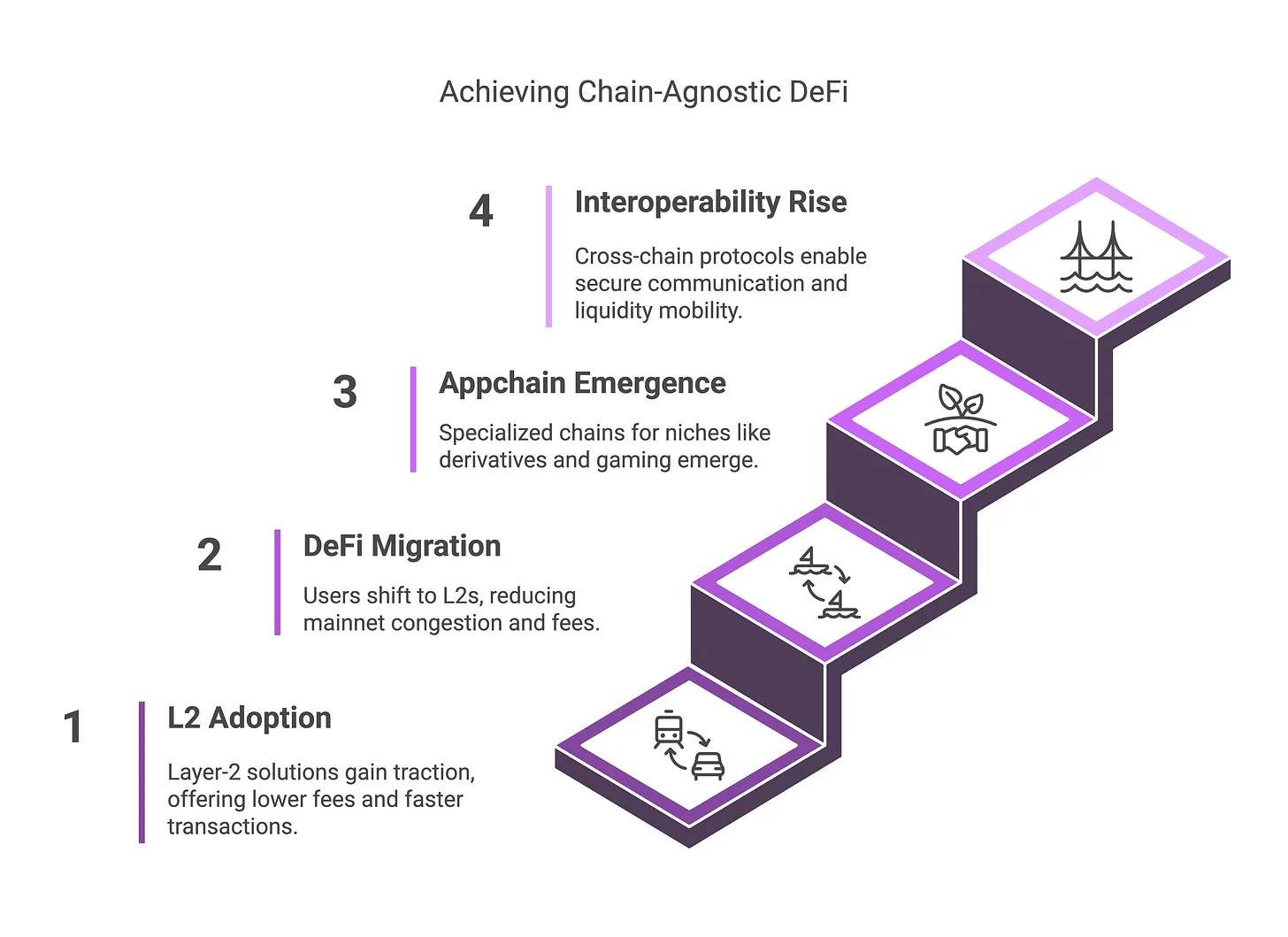
By 2025, DeFi usage is no longer confined to a single blockchain, thanks to major advances in scalability and interoperability. This progress is driven by rapid development in Ethereum’s Layer-2 (L2) solutions—such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and zk-Rollups. These L2 networks dramatically reduce transaction fees and increase throughput while maintaining the security of Ethereum’s mainnet, offering an ideal solution for users previously priced out by high gas costs.
By the end of 2024, Arbitrum and Optimism each achieved billions of dollars in total value locked (TVL), successfully hosting popular DeFi applications like Uniswap, Aave, and GMX, with user activity rivaling that of Ethereum’s mainnet. Additionally, Base—the L2 chain launched by Coinbase in 2023—rose quickly, capturing around 2.8% of DeFi’s total TVL within its first few months. These developments have effectively eased Ethereum’s congestion: as more users shift daily DeFi activities to L2s or sidechains, mainnet gas fees have dropped approximately 98% from their peak levels.
This shift not only makes DeFi more accessible to everyday users—making small transactions and microloans economically viable again—but also fuels the rise of on-chain high-frequency trading strategies. Looking ahead, specialized app-chains and rollups designed for specific use cases (e.g., derivatives trading or gaming assets) are emerging, further driving the multi-chain distribution of DeFi activity.
Simultaneously, cross-chain interoperability has made significant strides, enabling more efficient and flexible movement of liquidity across chains. Early DeFi users had to manually bridge assets between isolated blockchains, but technological breakthroughs in 2024 changed that. Universal message protocols—such as LayerZero and IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol)—are now widely adopted, allowing smart contracts on different blockchains to communicate securely.
Emerging Use Cases in 2025
In 2020, DeFi primarily offered basic functions such as trading, lending, and liquidity mining. By 2025, however, DeFi has expanded into a broader range of financial services.
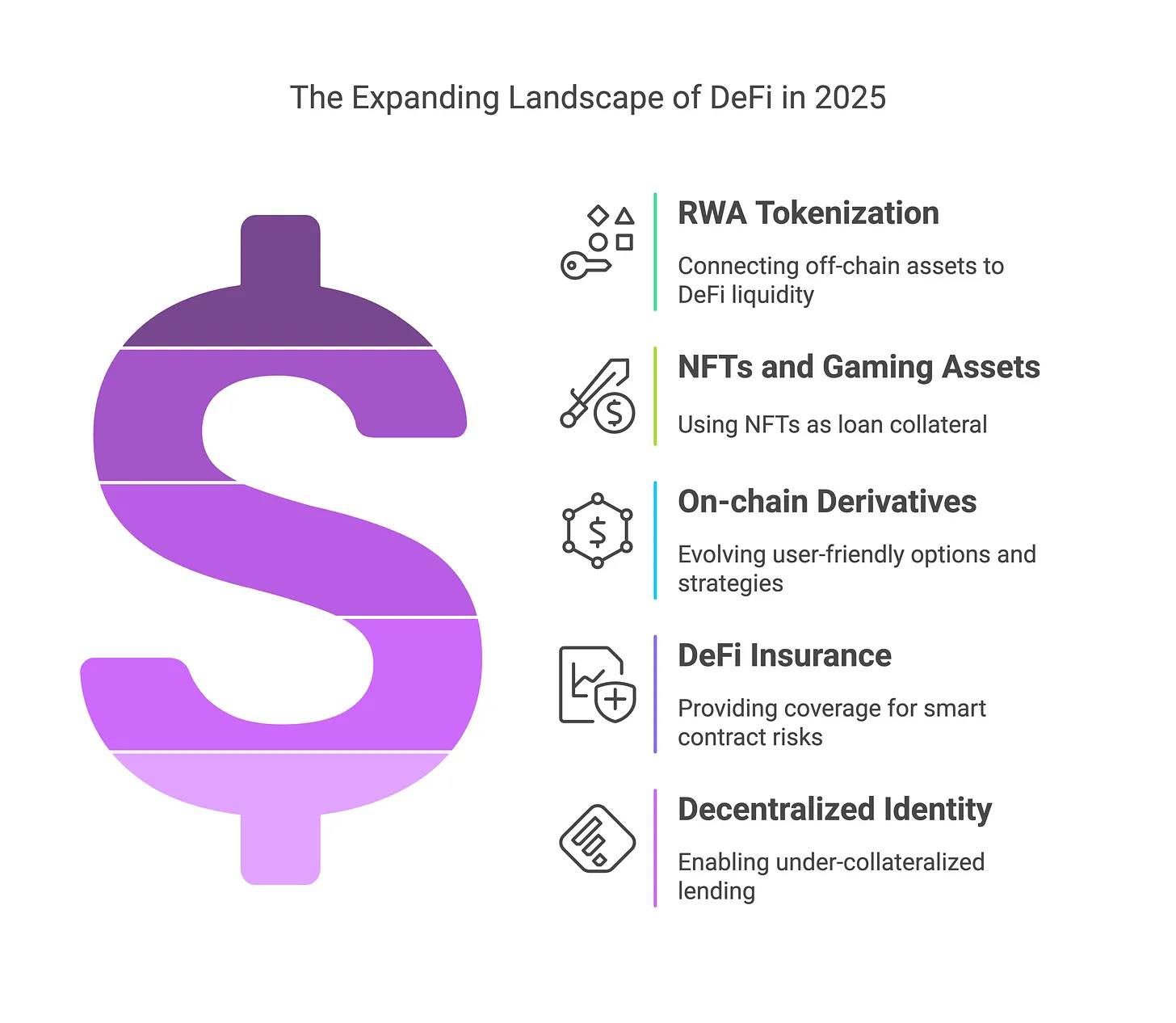
One prominent area is the tokenization of real-world assets (RWA). After experiencing rapid growth in 2024, RWA platforms began connecting off-chain assets—such as government bonds, real estate, and commercial invoices—to DeFi liquidity pools. Through protocols like MakerDAO, Goldfinch, and Centrifuge, real-world loans and bonds are brought on-chain, offering users stable returns backed by traditional assets.
Another fast-growing use case involves DeFi services for NFTs and gaming assets. Previously seen mostly as speculative collectibles, NFTs are now being used as collateral for loans starting in 2024. This trend is expected to accelerate—users can quickly pledge valuable NFTs or in-game assets to borrow stablecoins, transforming otherwise illiquid digital holdings into usable capital.
On-chain derivatives and structured financial products are also advancing. Beyond the continued expansion of perpetual futures exchanges, 2025 sees the emergence of more user-friendly options products, yield vaults, and automated strategy tools, giving users a wider array of choices.
DeFi insurance and risk management are becoming increasingly recognized sectors. Platforms such as Nexus Mutual, InsurAce, and Risk Harbor now offer coverage against risks like smart contract vulnerabilities or stablecoin de-pegging events. By 2025, it is expected that mainstream DeFi platforms will integrate insurance features directly, helping users mitigate exposure.
Decentralized identity and credit scoring represent another emerging use case, albeit still in early stages. Projects leveraging on-chain reputation systems are exploring undercollateralized lending, a development that could bring broader consumer financial services into the DeFi ecosystem.
Overall, DeFi in 2025 goes well beyond trading and liquidity mining—it is progressively encompassing core functions of traditional finance, including asset management, insurance, payments, and credit services—all delivered through decentralized infrastructure.
Conclusion
The DeFi ecosystem in 2025 is unrecognizable compared to its early days. With accelerating institutional adoption, gradually clarifying (though slow-moving) regulatory frameworks, and continuous improvements in underlying technology, DeFi is transitioning from experimental phase to a more mature stage—one increasingly integrated with traditional finance.
Yet challenges remain. Regulatory uncertainty continues to hinder industry growth, security risks persist, and the sector must balance innovation with compliance and user asset protection. But one thing is certain: DeFi is no longer merely an alternative to traditional finance—it is becoming a foundational pillar of the global financial system. Whether through permissioned DeFi, real-world asset tokenization, or advanced cross-chain liquidity solutions, the space demonstrates remarkable adaptability and resilience.
Looking ahead, the question is no longer whether DeFi will succeed, but how it will continue to evolve. The focus now shifts toward optimizing user experience, fostering sustainable growth, and ultimately bridging the divide between decentralized and traditional finance—delivering inclusive financial services to a much broader audience.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















