NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang's latest CES keynote: AI Agents could become the next robotics industry, with a scale reaching several trillion dollars
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang's latest CES keynote: AI Agents could become the next robotics industry, with a scale reaching several trillion dollars
NVIDIA is bringing AI from the cloud to personal devices and on-premises enterprise systems, covering all computing needs from developers to everyday users.
Compilation: Youxin
At the opening of CES 2025 this morning, NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang delivered a landmark keynote address unveiling the future of AI and computing. From the core concept of tokens in generative AI to the launch of the new Blackwell architecture GPUs, and onward to an AI-driven digital future, this speech will profoundly impact the entire industry through its cross-domain perspective.
1) From Generative AI to Agentic AI: The Dawn of a New Era
-
The birth of tokens: As the core engine behind generative AI, tokens transform text into knowledge and breathe life into images, ushering in an entirely new form of digital expression.
-
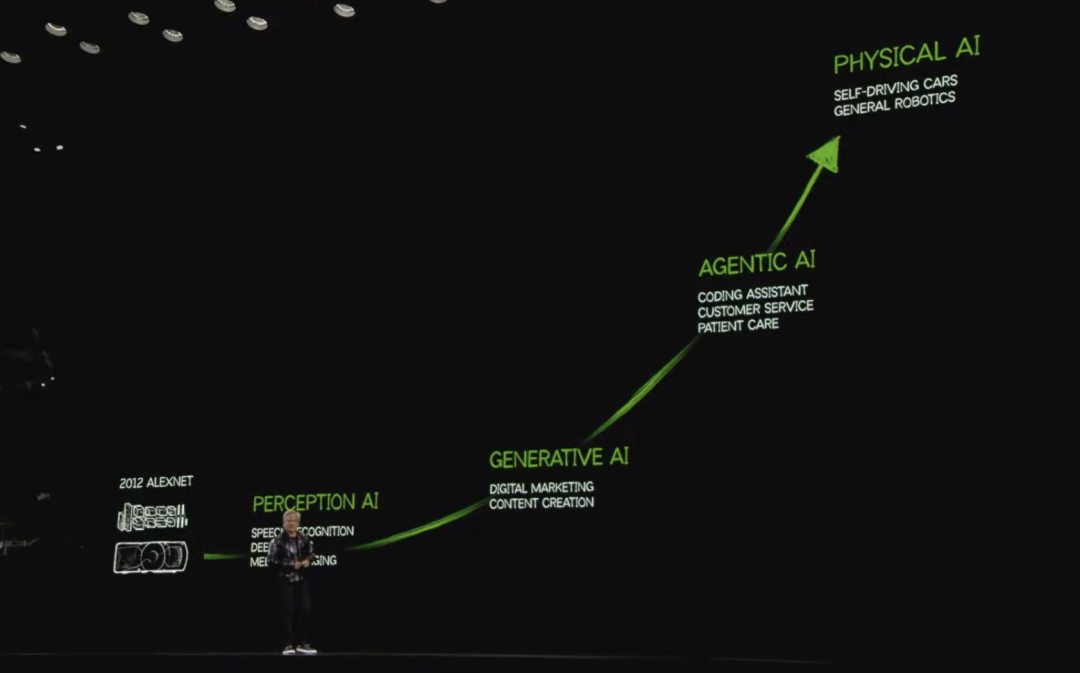
AI evolution path: From perceptual AI and generative AI to agentic AI capable of reasoning, planning, and taking action, AI technology continues to reach new heights.
-
The Transformer revolution: Since its introduction in 2018, this technology has redefined computing methods and completely disrupted traditional tech stacks.
2) Blackwell GPU: Breaking Performance Limits
-
New GeForce RTX 50 Series: Built on the Blackwell architecture with 92 billion transistors, delivering 4,000 TOPS of AI performance and 4 PetaFLOPS of compute power—tripling previous-generation performance.
-
Fusion of AI and graphics: For the first time combining programmable shaders with neural networks, introducing Neural Texture Compression and Neural Shading technologies that deliver stunning rendering effects.
-
Democratizing high performance: The RTX 5070 laptop priced at $1,299 achieves RTX 4090-level performance, driving widespread adoption of high-performance computing.
3) Multi-Domain Expansion of AI Applications
-
Enterprise AI Agents: NVIDIA provides tools like Nemo and Llama Nemotron to help businesses build autonomous reasoning digital employees for intelligent management and services.
-
Physical AI: Through platforms such as Omniverse and Cosmos, AI is being integrated into industrial systems, autonomous vehicles, and robotics, redefining global manufacturing and logistics.
-
Future computing scenarios: NVIDIA is bringing AI from the cloud to personal devices and enterprise environments, covering all computing needs—from developers to everyday users.
Below are the main highlights from Jensen Huang's keynote:
This is where intelligence is born—a new kind of factory: a generator producing tokens. Tokens are the building blocks of AI, opening up a new frontier and marking our first step into an extraordinary world. Tokens turn words into knowledge and bring images to life; they transform creativity into videos, help us navigate safely through any environment, teach robots to move like masters, and inspire us to celebrate victories in entirely new ways. When we need it most, tokens can also bring inner peace. They give meaning to data, helping us better understand the world, predict potential dangers, and find cures for internal threats. They make our visions real and restore what we’ve lost.
All of this began in 1993 when NVIDIA launched our first product—the NV1. We wanted to create computers capable of doing things ordinary machines could not, making it possible to have console-like experiences within PCs. Then, in 1999, NVIDIA invented the programmable GPU, launching over two decades of technological advancement and enabling modern computer graphics. Five years later, we introduced CUDA, using rich algorithms to express the programmability of GPUs. Initially difficult to explain, CUDA’s potential was validated in 2012 by the success of AlexNet, catalyzing breakthroughs in AI.
Since then, AI has advanced at an astonishing pace. Evolving from perceptual AI to generative AI, and now toward agentic AI capable of perception, reasoning, planning, and action, AI’s capabilities continue to grow. In 2018, Google introduced the Transformer, and the AI world truly took off. The Transformer didn’t just transform the landscape of AI—it redefined the entire field of computing. We realized machine learning wasn't merely a new application or business opportunity, but a fundamental reinvention of how computing works. From manually written instructions to optimizing neural networks via machine learning, every layer of the tech stack underwent massive transformation.
Today, AI applications are everywhere. Whether understanding text, images, sound, translating amino acids, or modeling physics—AI can do it all. Almost every AI application boils down to three questions: What modalities did it learn? Into what modalities did it translate? And what modalities did it generate? This foundational concept powers every AI-driven application.
All these achievements have been supported by GeForce. GeForce brought AI to the masses, and now, AI is transforming GeForce in return. With real-time ray tracing, we render graphics with breathtaking realism. Through DLSS, AI goes beyond frame generation—it predicts future frames. Out of 3.3 million pixels, only 200,000 are computed directly; the rest are predicted by AI. This miraculous technology demonstrates AI’s immense power, making computation more efficient and revealing infinite possibilities ahead.
This is why so many incredible things are happening now. We used GeForce to advance AI, and now AI is revolutionizing GeForce. Today, we announce our next-generation product—the RTX Blackwell family. Let’s take a look.
This is the new GeForce RTX 50 series based on the Blackwell architecture. A performance beast, this GPU contains 92 billion transistors, delivers 4,000 TOPS of AI performance and 4 PetaFLOPS of AI compute—three times faster than the previous Ada architecture. All of this serves to generate the stunning pixels I showed earlier. It offers 380 Ray Tracing Teraflops for beautifully rendered calculated pixels, along with 125 Shading Teraflops. Equipped with Micron’s G7 memory, it reaches speeds of 1.8TB per second—double the bandwidth of the prior generation.
We can now combine AI workloads with computer graphics workloads. A remarkable feature of this generation is that programmable shaders can also process neural networks. This allows us to invent Neural Texture Compression and Neural Shading. These technologies use AI to learn textures and compression algorithms, ultimately generating visual effects only AI could achieve.
Even mechanically, this graphics card is a marvel. Featuring a dual-fan design, the entire card functions like one large fan. Inside, the voltage regulation module uses cutting-edge technology. Such exceptional engineering is a testament to the hard work of our engineering team.
Now, let’s compare performance. The well-known RTX 4090, priced at $1,599, has been the centerpiece investment for home PC entertainment. Now, the RTX 50 series offers even higher performance starting at just $549, with models ranging from RTX 5070 to RTX 5090—delivering double the performance of the RTX 4090.
Even more impressively, we’ve put this high-performance GPU into laptops. The RTX 5070 laptop starts at $1,299 yet matches the performance of the RTX 4090. By integrating AI and computer graphics technologies, we achieve both high efficiency and high performance.

The future of computer graphics is neural rendering—the fusion of AI and computer graphics. The Blackwell series can even fit into laptops as thin as 14.9 millimeters, with the full lineup from RTX 5070 to RTX 5090 available in ultra-slim notebooks.
GeForce helped democratize AI, and now AI is completely transforming GeForce. This symbiotic relationship between technology and intelligence is propelling us to new heights.
The Three Scaling Laws of AI
Next, let’s discuss the direction of AI development.
1) Pre-training Scaling Law
The AI industry is accelerating rapidly, driven by a powerful model known as the "Scaling Law." Repeatedly verified by researchers and the industry, this empirical rule states that the larger the training data, the bigger the model, and the greater the computational investment, the stronger the resulting model becomes.
Data growth is accelerating exponentially. Estimates suggest that in the coming years, humanity will produce annually more data than the sum total produced throughout history. This data is increasingly multimodal—encompassing video, images, audio, and more. This vast amount of data trains AI’s foundational knowledge system, laying a solid intellectual foundation.
2) Post-Training Scaling Law
In addition, two other emerging Scaling Laws are gaining momentum.
The second is the "Post-Training Scaling Law," involving techniques such as reinforcement learning and human feedback. With this approach, AI generates responses to human queries and continuously improves based on human feedback. High-quality prompts enable AI to refine skills in specific domains—for example, solving math problems or performing complex reasoning more effectively.
The future of AI isn’t just about perception and generation—it’s about continuous self-improvement and boundary-pushing. Think of it as having a mentor or coach who gives you feedback after completing a task. Through testing, feedback, and self-improvement, AI advances via similar reinforcement learning and feedback mechanisms. Combined with synthetic data generation, this post-training phase resembles self-practice. AI can tackle complex, verifiable challenges—such as proving theorems or solving geometry problems—and optimize its answers through reinforcement learning. Although computationally intensive, this stage ultimately produces extraordinary models.
3) Test-Time Scaling Law
The Test-Time Scaling Law is also emerging. This principle reveals unique potential when AI is actively used. During inference, AI dynamically allocates resources—not limited to parameter optimization, but focused on computational allocation—to produce high-quality outputs.
This process resembles reasoning rather than direct inference or single-step answering. AI breaks down questions into multiple steps, generates several solutions, evaluates them, and selects the optimal one. Extended reasoning significantly enhances model capability.
We’ve already seen this evolution—from ChatGPT to GPT-4, to today’s Gemini Pro—all progressing through stages of pre-training, post-training, and test-time scaling. Achieving these breakthroughs demands immense computing power—the very value proposition of NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture.
Latest Introduction to the Blackwell Architecture
Blackwell systems are now in full production, with astonishing performance. Every major cloud service provider is deploying them. Manufactured across 45 factories globally, they support up to 200 configurations—including liquid-cooled, air-cooled, x86-based, and versions with NVIDIA Grace CPUs.
The core NVLink system alone weighs 1.5 tons, contains 600,000 components—equivalent in complexity to 20 cars—with 2 miles of copper wiring and 5,000 cables. The manufacturing process is extremely complex, designed to meet ever-growing computational demands.
Compared to the previous generation, Blackwell improves performance per watt by 4x and performance per dollar by 3x. This means models can be trained three times larger at the same cost. At the heart of these improvements lies the generation of AI tokens—used widely in ChatGPT, Gemini, and other AI services—and forming the foundation of future computing.
Built upon this, NVIDIA is pioneering a new computing paradigm: neural rendering, perfectly merging AI with computer graphics. Within the Blackwell architecture, 72 GPUs form the world’s largest single-chip system, delivering up to 1.4 ExaFLOPS of AI floating-point performance and an astounding 1.2 PB/s of memory bandwidth—equal to the total volume of all internet traffic worldwide. This supercomputing power enables AI to handle more complex reasoning tasks while drastically reducing costs, laying the groundwork for more efficient computing.
AI Agent Systems and Ecosystem
Looking ahead, AI inference won’t be simple one-step responses but closer to “internal dialogue.” Future AI won’t just generate answers—it will reflect, reason, and continuously optimize. As token generation rates increase and costs decline, AI service quality will rise dramatically, meeting broader application needs.
To help enterprises build AI systems with autonomous reasoning, NVIDIA offers three key tools: NVIDIA NeMo, AI microservices, and accelerated libraries. By packaging complex CUDA software and deep learning models into containerized services, companies can deploy these AI models on any cloud platform, rapidly developing domain-specific AI Agents—such as enterprise service tools or interactive digital employees.
These models open new possibilities, lowering the barrier to AI adoption and advancing the industry toward Agentic AI (autonomous AI). Future AI will act as digital workers, easily integrated into enterprise tools like SAP and ServiceNow, providing intelligent services across environments. This marks the next milestone in AI expansion—and the core vision of NVIDIA’s technology ecosystem.
Training and evaluation systems. In the future, these AI Agents will essentially function as digital labor, working alongside employees to complete tasks. Introducing specialized agents into your company will resemble onboarding new staff. We provide toolkits to help AI Agents learn your company’s unique language, terminology, workflows, and practices. You’ll provide examples of desired outputs; they’ll attempt to generate them, receive your feedback, undergo evaluation, and improve. You’ll also set boundaries—what actions they cannot perform, what they cannot say—and control their access to information. This entire digital employee lifecycle is called Nemo. In many ways, each company’s IT department will become the HR department for AI Agents.
Today, IT departments manage and maintain vast software infrastructures. In the future, they’ll manage, train, onboard, and refine large numbers of digital agents serving the company. Thus, IT departments will gradually evolve into HR departments for AI Agents.
Additionally, we offer numerous open-source blueprints for the ecosystem. Users can freely modify these templates. We provide blueprints for various types of Agents. Today, we’re announcing something exceptionally cool and smart: the launch of a new model family based on Llama—the NVIDIA Llama Nemotron Foundation Language Model series.
Llama 3.1 is a phenomenon. Meta’s Llama 3.1 has been downloaded approximately 350,650,000 times and has spawned around 60,000 derivative models. It’s one of the core reasons nearly every enterprise and industry has begun exploring AI. We recognized that Llama models could be better fine-tuned for enterprise use cases. Leveraging our expertise, we’ve optimized them into the Llama Nemotron Open Model Suite.
These models come in different sizes: small models offer rapid response; mainstream Super Llama Nemotron serves general purposes; and ultra-large Ultra Models act as teacher models—evaluating other models, generating answers, judging quality, or serving in knowledge distillation. All models are now live.
They perform exceptionally well, ranking at the top of leaderboards in conversation, instruction following, and information retrieval—ideal for global AI Agent applications.
We collaborate closely with the ecosystem, including partnerships with ServiceNow, SAP, and Siemens in industrial AI. Companies like Cadence and Perplexity are also doing outstanding work. Perplexity is disrupting search, while Codium serves 30 million software engineers worldwide. AI assistants will dramatically boost developer productivity—this is the next major application area for AI. With one billion knowledge workers globally, AI Agents may become the next robotics industry, with potential valued in trillions of dollars.
AI Agent Blueprints
Next, let’s explore some AI Agent blueprints developed with partners.
AI Agents represent a new digital workforce capable of assisting or replacing humans in tasks. NVIDIA’s Agentic AI building blocks, NEM pre-trained models, and the Nemo framework empower organizations to easily develop and deploy AI Agents. These agents can be trained as domain-specific experts.
Four examples include:
-
Research Assistant Agent: Reads complex documents—lectures, journals, financial reports—and generates interactive podcasts for easier learning;
-
Software Security AI Agent: Helps developers continuously scan for software vulnerabilities and recommends corrective actions;
-
Virtual Lab AI Agent: Accelerates compound design and screening to quickly identify potential drug candidates;
-
Video Analytics AI Agent: Based on NVIDIA Metropolis blueprints, analyzes data from billions of cameras to generate interactive searches, summaries, and reports—e.g., monitoring traffic flow, facility operations, and suggesting improvements.
The Arrival of Physical AI
We aim to bring AI to every corner—from the cloud to corporate data centers and personal PCs. NVIDIA is working to transform Windows WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) into the preferred platform for AI. This will allow developers and engineers easier access to NVIDIA’s full AI stack, including language, image, and animation models.
Moreover, NVIDIA introduces Cosmos—the first foundational model development platform for the physical world—focused on understanding dynamic physical properties such as gravity, friction, inertia, spatial relationships, and causality. It can generate physically accurate videos and scenes, widely applicable in robotics, industrial AI, and multimodal language model training and validation.
Cosmos connects with NVIDIA Omniverse to provide physics simulation, generating realistic and credible results. This integration is a core technology for developing robotics and industrial applications.
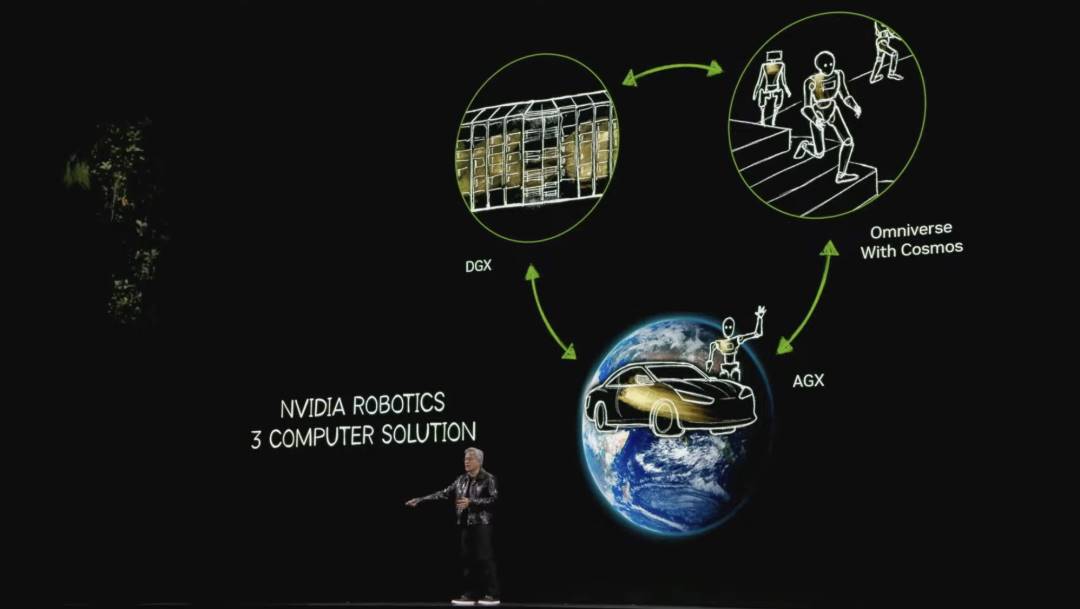
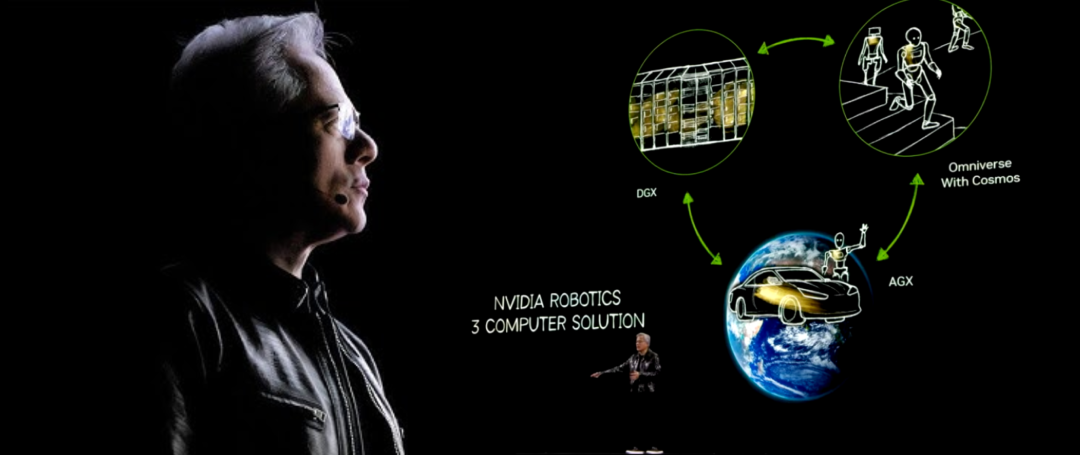
NVIDIA’s industrial strategy rests on three computing systems:
-
DGX systems for training AI;
-
AGX systems for deploying AI;
-
Digital twin systems for reinforcement learning and AI optimization;
Through the synergy of these three systems, NVIDIA is advancing robotics and industrial AI, building the digital world of tomorrow. Rather than a three-body problem, we offer a “three-computer” solution.
Let me illustrate NVIDIA’s robotics vision with three examples.
1) Industrial Visualization Applications
Currently, millions of factories and hundreds of thousands of warehouses form the backbone of the $50 trillion manufacturing sector. The future demands that all of this become software-defined, automated, and infused with robotics. We’re partnering with Keon, a leading warehouse automation solutions provider, and Accenture, the world’s largest professional services firm, focusing on digital manufacturing to create groundbreaking solutions. Our go-to-market approach mirrors other software and tech platforms—leveraging developers and ecosystem partners, with growing numbers joining the Omniverse platform because everyone wants to visualize the future of industry. Within this $50 trillion segment of global GDP, there is massive waste—and even greater opportunities for automation.
Consider this joint project with Keon and Accenture:
Keon (supply chain solutions), Accenture (global professional services leader), and NVIDIA are bringing Physical AI to the trillion-dollar warehouse and distribution center market. Managing efficient warehouse logistics involves navigating complex decision networks influenced by constantly changing variables—daily and seasonal demand fluctuations, space constraints, labor availability, and integration of diverse robotic and automation systems. Today, predicting key operational KPIs for physical warehouses is nearly impossible.
To solve this, Keon is adopting Mega—an NVIDIA Omniverse blueprint—to build industrial digital twins for testing and optimizing robot fleets. First, Keon’s warehouse management solution assigns tasks to the industrial AI brain within the digital twin—e.g., moving goods from buffer zones to shuttle storage. Robot fleets operate in a simulated physical warehouse environment within Omniverse, using perception and reasoning to execute tasks, plan next actions, and act accordingly. Sensor simulations in the digital twin allow the robot brains to observe post-action states and determine subsequent moves. Under Mega’s precise tracking, this cycle repeats continuously, measuring operational KPIs such as throughput, efficiency, and utilization—all before modifying the actual warehouse.
With NVIDIA’s collaboration, Keon and Accenture are redefining the future of industrial autonomy.
In the future, every factory will have a synchronized digital twin. Using Omniverse and Cosmos, you can generate countless future scenarios. AI will determine the optimal KPI scenario and apply it as constraints and programming logic for real-world deployment.
2) Autonomous Vehicles
The autonomous driving revolution has arrived. After years of development, successes from Waymo and Tesla prove the maturity of this technology. Our solution provides three computing systems for the industry: AI training systems (like DGX), simulation and synthetic data generation systems (like Omniverse and Cosmos), and in-vehicle computing systems (like AGX). Nearly every major automaker globally collaborates with us—Waymo, Zoox, Tesla, and the world’s largest EV maker BYD. Innovators like Mercedes, Lucid, Rivian, Xiaomi, and Volvo are launching new models. Aurora is developing autonomous trucks using NVIDIA technology.
Each year, 100 million vehicles are manufactured, with 1 billion on roads worldwide, accumulating trillions of miles annually. These will gradually become highly or fully automated. This sector is expected to become the first trillion-dollar robotics industry.
Today, we announce the next-generation in-vehicle computer, Thor. A universal robotic computer, Thor handles massive data from sensors like cameras, high-resolution radar, and LiDAR. An upgrade to the industry-standard Orin, Thor offers 20x the computing power and is now in full production. Additionally, NVIDIA Drive OS is the first AI computing operating system certified to the highest functional safety standard (ISO 26262 ASIL D).
Autonomous Driving Data Factory
NVIDIA leverages Omniverse AI models and the Cosmos platform to create autonomous driving data factories, vastly expanding training data through synthetic driving scenarios, including:
-
OmniMap: Integrates maps and geospatial data to build drivable 3D environments;
-
Neural Reconstruction Engine: Uses sensor logs to generate high-fidelity 4D simulation environments and create variant training scenarios;
-
Edify 3DS: Searches asset libraries or generates new assets to build simulation scenes.
With these technologies, we expand thousands of real-world drives into billions of miles of data, accelerating the development of safer, more advanced autonomous systems.
3) General-Purpose Robotics
The era of general-purpose robots is approaching. Breakthroughs in this field hinge on training. For humanoid robots, collecting imitation data is challenging—but NVIDIA’s Isaac Groot provides a solution. It generates massive datasets through simulation, combined with Omniverse and Cosmos’s multi-universe simulation engines, enabling policy training, validation, and deployment.
For example, developers can remotely operate robots via Apple Vision Pro, capturing data without physical robots and teaching tasks in risk-free environments. Through Omniverse’s domain randomization and 3D-to-real scene expansion, exponentially growing datasets provide abundant resources for robot learning.
In summary, whether industrial visualization, autonomous vehicles, or general-purpose robotics, NVIDIA’s technology is leading transformative changes in physical AI and robotics.
Finally, there’s one last important element I’d like to share—all of this stems from a project we started internally a decade ago called Project Digits, officially named Deep Learning GPU Intelligence Training System, abbreviated as Digits.
Prior to official release, we aligned DGX with our internal RTX, AGX, OVX, and other product lines for consistency. The arrival of DGX1 truly changed the course of AI—and stands as a milestone in NVIDIA’s contribution to AI development.
The Revolution of DGX1
DGX1 was conceived as an out-of-the-box AI supercomputer for researchers and startups. Imagine past supercomputers requiring custom facilities and complex infrastructure just to exist. DGX1, by contrast, is a supercomputer purpose-built for AI development—no setup required, ready to use right out of the box.
I remember delivering the first DGX1 in 2016 to a startup—OpenAI. Elon Musk, Ilya Sutskever, and many NVIDIA engineers were present—we celebrated together. That machine significantly accelerated AI computing.
Today, AI is everywhere—not just in research labs and startups. As I mentioned at the start, AI has become a new way of computing and software development. Every software engineer, creative artist, and even casual computer user now needs an AI supercomputer. But I always hoped DGX1 could be smaller.
Latest AI Supercomputer
Here is NVIDIA’s latest AI supercomputer. It still belongs to Project Digits—we’re still looking for a better name, so suggestions are welcome. This device is truly astonishing.
This supercomputer runs NVIDIA’s complete AI software stack, including DGX Cloud. It functions as a cloud-based supercomputer, a high-performance workstation, or even a desktop analytics station. Most importantly, it’s powered by a secretly developed new chip codenamed GB110—our smallest Grace Blackwell chip yet.
I’m holding the chip here—let me show you its internal design. Developed jointly with MediaTek, a world-leading SoC company, this CPU SoC is custom-designed for NVIDIA and connected via NVLink chip-to-chip interconnect to the Blackwell GPU. This compact chip is now in full production. We expect this supercomputer to launch around May.
We even offer a “double compute” configuration, linking multiple units via ConnectX with GPUDirect support. It’s a complete supercomputing solution meeting diverse needs in AI development, analytics, and industrial applications.
In addition, we announced mass production of three new Blackwell system chips, the world’s first foundational model for Physical AI, and breakthroughs across three robotics frontiers—autonomous AI Agent robots, humanoid robots, and autonomous vehicles.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News