OTC Trading Off the Spotlight: Decoding the Alternative Game of Crypto VCs
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

OTC Trading Off the Spotlight: Decoding the Alternative Game of Crypto VCs
Funds can focus on acquiring liquid tokens and leverage their expertise and network to scale projects from "1 to 10."
Authors: hedgedhog7, c0xswain, 0xkinnif, 0xlaiyuen, 0xZhouYeMen
Translation: TechFlow

The Current State of Crypto Venture Capital
Recently, meme coins have outperformed many projects backed by venture capital (VC), sparking criticism from market participants toward VCs and their investments. While some of this criticism is justified, other aspects reflect a lack of deep understanding of the complexities inherent in private markets.
Typically, projects scale their products through multiple funding rounds before token generation events (TGEs). In return for early high-risk capital, VCs gain access to tokens at lower valuations. Strategic capital provides resources that small retail investors typically cannot access—such as marketing support, tokenomics consulting, and connections within VC networks. As fundraising progresses and valuations evolve, the types of VCs participating also change, due to differences in each fund's risk appetite and size.
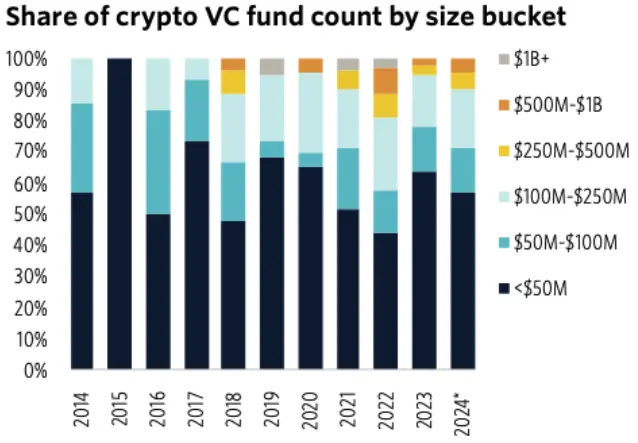
Segmentation of crypto venture capital and their fund sizes
Source: PitchBook
The majority of crypto VCs manage less than $50 million in assets under management (AUM), so they tend to invest in projects that haven't launched products yet and carry lower valuations. To align VCs’ interests with other stakeholders over the long term, tokens acquired via private markets are usually subject to vesting schedules and lock-up periods.
The trade-off between risk and return for VCs
During the vesting period, VCs often see significant unrealized gains and may seek to realize profits through derivatives hedging or over-the-counter (OTC) trades with private buyers. However, they face challenges implementing hedging strategies due to investment mandates, capital requirements, and liquidity constraints. Additionally, some VCs lack the execution expertise and risk management frameworks needed to effectively manage liquid positions, making efficient hedging even more difficult.
As a result, OTC trading has become the primary method for VCs to realize profits prior to TGE. Unlike transparent secondary markets, OTC trades occur privately, making it difficult to consolidate global transaction data. While accurately estimating the size of the OTC market is challenging, activity reports from OTC desks can reveal certain trends.
STIX, an OTC desk backed by Fisher8 Capital, has processed over $200 million in volume since its launch at the end of 2023. STIX primarily trades assets among the top 200 altcoins. Over the past year, OTC activity has been frequent, including liquidations (e.g., FTX selling locked $WLD and $SOL) and direct sales from token foundations (e.g., $SUI, $AVAX). We expect this market to continue growing, driven primarily by VCs seeking earlier profit realization and post-TGE capital needs from projects.
OTC Markets: Price Discovery in Private Rounds
Below is a list of several VC-backed tokens and their performance since TGE. Most tokens struggle to maintain high valuations after three months, making it difficult for VCs to realize full investment value at peak FDV when vesting begins. This price trajectory harms market participants, as both retail investors who bought at high prices and VCs become sellers upon vesting completion.
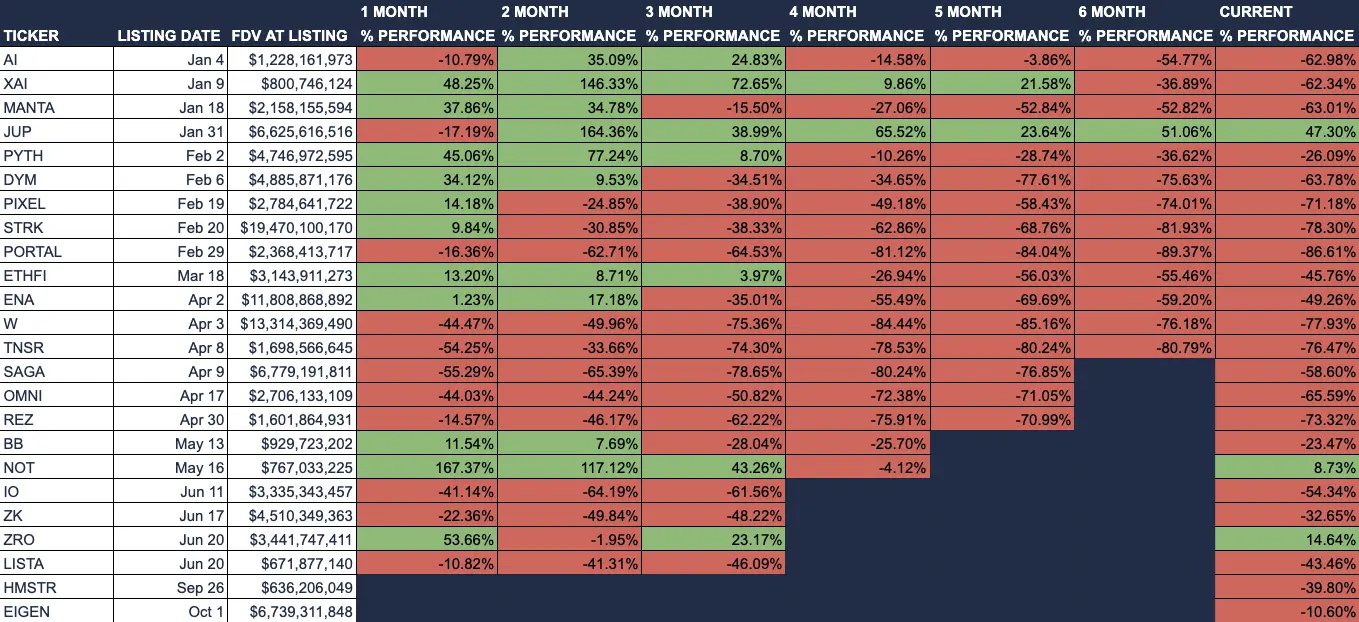
Post-listing performance of tokens on Binance in 2024
Source: Artemis
Frequent valuation increases during fundraising mean that returns and optimism are largely concentrated in the private market. This dynamic leaves public market participants exposed primarily to downside risks after TGE. Without sufficient incentives to support projects, public market participants may end up in a lose-lose situation. As the market reverts toward fair value, both VCs and retail investors will face challenges in the long run.
Examples of token performance
Source: 0xLouis
We believe that leaving room for upside in the secondary market helps build stronger community support, thereby extending a project’s lifespan. One existing approach involves facilitating price discovery for retail investors before TGE using spot and/or pre-markets. In pre-market trading, spot-traded tokens function as IOUs (I Owe You), redeemable for actual assets at TGE. Alternatively, perpetual pre-markets are synthetic markets designed to track asset prices, often hedged via call options issued by project foundations.
Pre-market trading occurs on accessible derivative platforms such as Aevo, Whales Market, and major centralized exchanges (CEXs). However, these products carry liquidity and delta risks. When liquid market buyers purchase tokens before TGE, the exchange acts as counterparty and could suffer substantial losses if the token performs well post-TGE. Moreover, participants must consider counterparty risk—such as lacking legal claims to underlying assets or exchanges being unable to cover losses incurred by profitable pre-market traders.
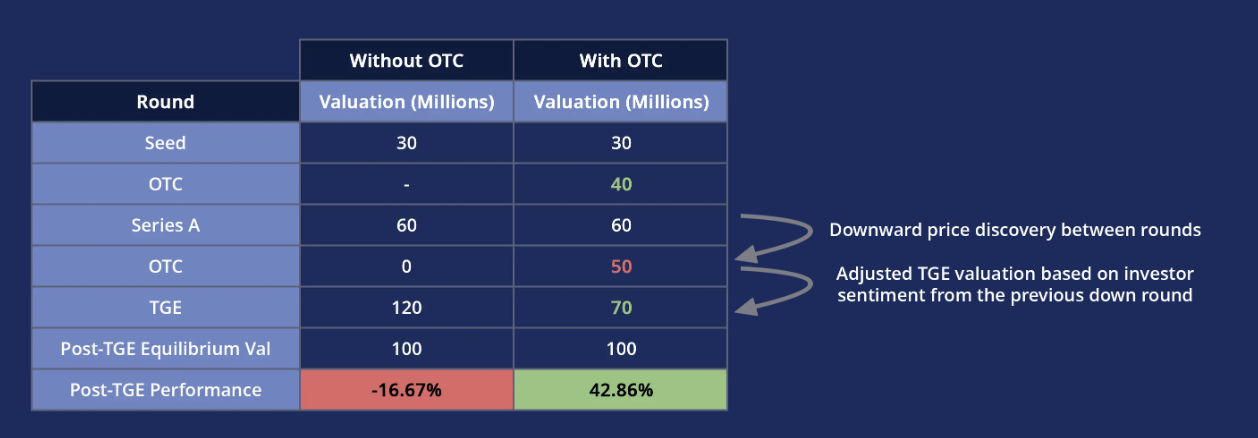
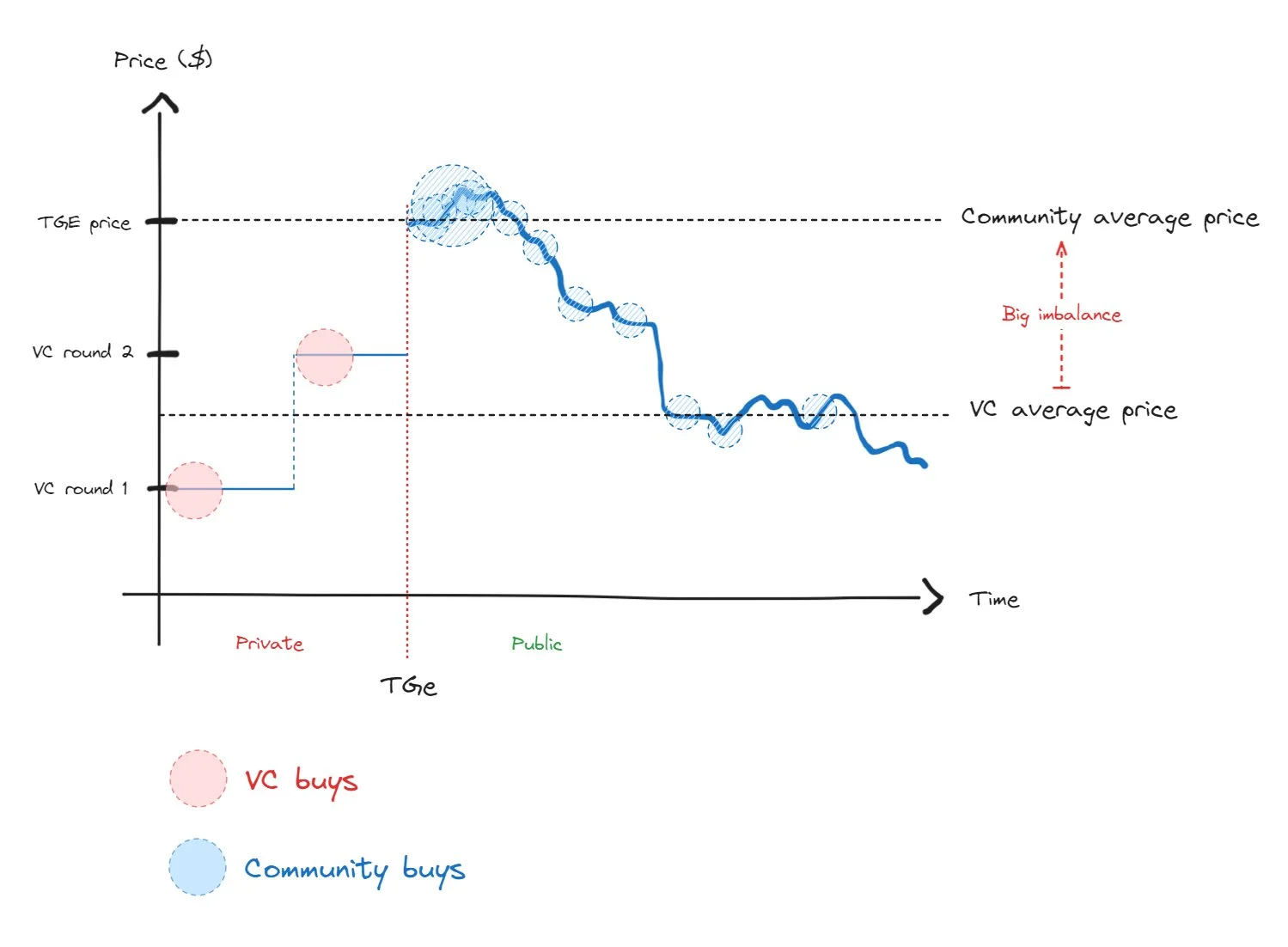
Hypothetical token performance across funding rounds via OTC
Another way to promote secondary market appreciation is allowing private market prices to decline before TGE. This reduces valuation gaps between funding rounds. The chart above shows a simplified comparison of two hypothetical projects, illustrating the potential benefits of OTC trading on post-TGE performance. If a down round occurs between Series A and TGE, where existing investors sell holdings below cost basis, it signals to the team that the planned TGE price should be lowered. Such adjustments help bring project valuations closer to market expectations.
If a project ultimately succeeds and reaches its intended post-TGE price level, having more profitably positioned holders from liquid markets can provide longer-term support.
Deep Dive into Crypto OTC Desks
While allowing more price declines in private markets may seem ideal, the process isn’t straightforward due to legal barriers and the complexity of transaction types. OTC trades mainly fall into two categories: pure principal buying and funding rate arbitrage.
Principal buyers are typically valuation-sensitive investors seeking direct exposure to the underlying asset. This involves taking over SAFT/SAFE agreements from prior investors or purchasing tokens directly from the project team. When acquiring SAFT/SAFE contracts from early investors, transactions are usually priced at par or include a 25–30% premium before TGE.
Funding rate arbitrageurs care less about valuation. Their profit depends on the difference between the spot discount and hedging costs, which is influenced by perpetual contract funding rates during the token vesting period. According to STIX reports, these buyers typically acquire tokens at 60–65% below spot price, executing a market-neutral strategy. However, this opportunity requires three conditions: first, there must be a perpetual contract for the underlying asset; second, sufficient market liquidity to execute trades; and third, hedging costs (i.e., opportunity cost of collateral) must not exceed gains from the spot discount. To avoid liquidation when shorting perps, these buyers must post substantial collateral, as any short squeeze could render the trade unprofitable.
Given the diverse nature of OTC buyers, large OTC deals announced by foundations should be viewed with caution. These transactions may reflect arbitrage opportunities rather than genuine long-term demand at current price levels.
Challenges in the OTC Market
A complex issue facing OTC trading is the presence of anti-assignment clauses in contracts. These clauses restrict investors from transferring shares to third parties (i.e., new OTC buyers) without founder approval. According to STIX, such clauses exist in 30%–45% of SAFTs.
If foundations block OTC transfers, buyers must assume additional counterparty risk. Without the legal protections offered by "formalized" transactions, buyers have limited recourse against seller misconduct. This risk is particularly pronounced for smaller funds, which may not face the same reputational consequences as larger, well-known VC firms.
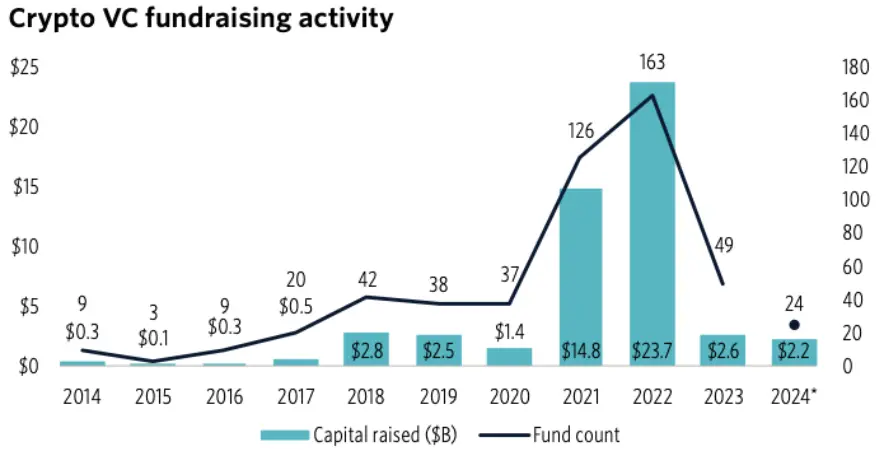
Crypto venture capital fundraising activity
Source: Pitchbook
In 2021 and 2022, fundraising reached record highs, fueled by pandemic stimulus policies and strong returns from prior investments. During this period, abundant and eager VC capital led to rapid deal-making. However, the bear markets of 2022 and 2023 brought significant changes. Down rounds became more common, investor risk appetite declined, and TGE delays became standard. Shifting market dynamics and high-profile collapses like Terra, FTX, and 3AC caused fund performance stagnation and reduced capital inflows into crypto VCs.
PitchBook’s report shows declining investor interest in venture capital, with new funds taking longer to raise—increasing from 6 months in 2021 to 21 months in 2024. Furthermore, VC funds structured with a 4+2 lifecycle raised in 2021 and 2022 are now entering their harvesting phase, creating structural sellers in the secondary market.
Due to underperformance, crypto VC funds are exploring alternative strategies such as investing in liquid tokens or engaging in OTC trading. Although OTC investments still involve lock-ups and vesting terms, their typical holding periods are shorter than traditional VC investments, making them more suitable for time-sensitive investors. If OTC trading becomes more widespread in the industry, platforms like STIX could benefit significantly by offering comprehensive services that address market fragmentation.
The Future Direction of Venture Capital
The current trend of shrinking capital in crypto venture faces significant challenges. One potential path forward is adopting active investment strategies. Rather than chasing the next “zero-to-one” opportunity, funds can focus on acquiring liquid tokens and leveraging their expertise and networks to scale projects from “one to ten.”
If you're interested in this active investment strategy, STIX is actively seeking more venture funds to join. For more information, please visit STIX.co or contact taran_ss on X.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















