Understanding AminoChain: a16z's First Foray into DeSci, Leading a $5M Investment, Enabling Patients to Earn by Contributing Biological Samples
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Understanding AminoChain: a16z's First Foray into DeSci, Leading a $5M Investment, Enabling Patients to Earn by Contributing Biological Samples
AminoChain belongs to the pure DeSci sector, leveraging blockchain's traceability and transparency for processes in the medical and scientific research fields, including the collection, contribution, usage, and compensation of biological specimens.
Author: TechFlow
The crypto market is about more than just memes—efforts to apply economic incentives and data ownership in practical ways have never ceased.
Among these, DeSci (Decentralized Science) has long been a focal point—leveraging blockchain’s transparency and incentive mechanisms to enable data owners to contribute data, track its usage, and receive appropriate compensation.
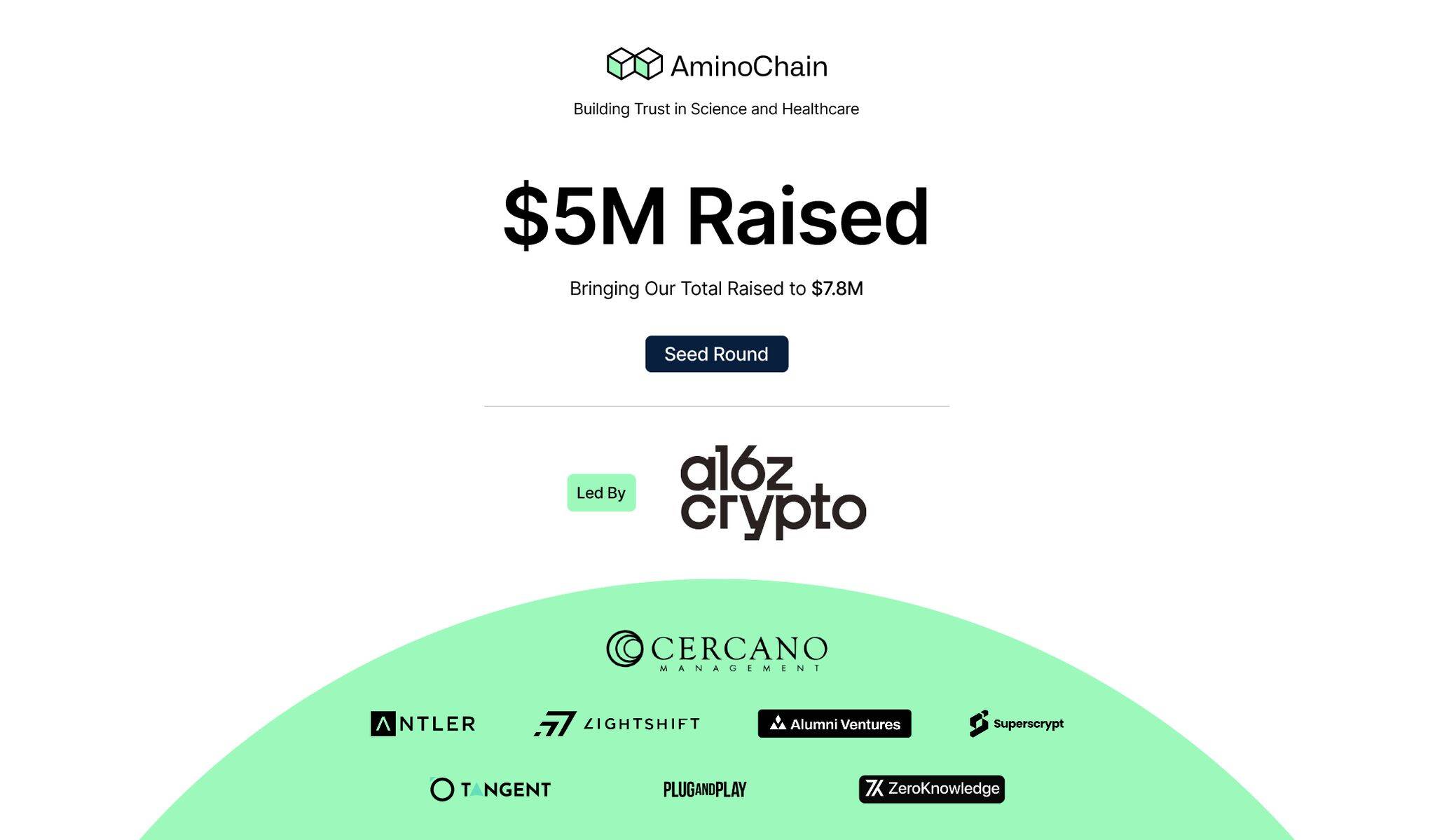
Recently, a new project called AminoChain announced on its official X account that it has secured $5 million in seed funding led by a16z. With additional investments from private funds such as Cercano, the project's total funding has reached $7.8 million.
AminoChain is a pure-play DeSci project, applying blockchain’s traceability and transparency to the collection, contribution, use, and compensation of biological specimens in medical and scientific research.
Notably, public reports indicate this marks **the first time top-tier VC a16z has invested in a DeSci project**.
In a market where VCs avoid each other’s tokens and memes dominate, if crypto can do some real good for traditional industries—and if VCs can seriously back projects that benefit other sectors—it would represent a positive and refreshing shift.
Building a Dedicated Biobank on an L2
Public information shows that AminoChain is building a decentralized “biobank” on an L2 network.
This biobank can be understood as an on-chain platform connecting one end to patients and volunteers who can upload their biological samples for use and study by medical and research institutions, and the other end to those institutions, enabling them to securely share and process medical data within the biobank network.
Thanks to public blockchain design features, researchers can easily discover and access samples, while patients retain control and receive compensation when their data is used.
It remains unclear whether AminoChain will build its decentralized biobank on an existing L2 or launch its own dedicated L2 to handle “transactions” related to medical data and biological specimens.
Judging from the project name, the latter seems more likely.
Regardless of specific technical choices, what’s the motivation behind building a decentralized biobank?
As AminoChain’s founder wrote in a blog post:
“Every year, thousands of people provide medicine with their blood, saliva, and cancer tissue samples to help researchers develop life-saving new drugs for humanity... Unfortunately, today data collected from these highly sensitive personal samples flows in one direction only.
Donors are asked whether their samples can be used for scientific research, they sign a consent form, researchers collect the biological sample, and then both parties go their separate ways, never to interact again. The donation process is a black box for donors, and current institutional consent rates are as low as 25%.”
Therefore, in this largely opaque domain of biological sample contribution, at least two problems exist:
-
Data is centrally controlled and stored, creating major barriers to scientific progress and improved patient outcomes
-
Inability to effectively trace sample origins and manage user consent
To put it bluntly, patients or volunteers who contribute biological samples may not receive proper compensation—even if their contributions are significant—or know the full impact of their donation.
Thus, AminoChain is a technology connecting corporate medical institutions, enabling healthcare applications to be built on top of it, and offering patients transparency so they finally understand where their societal contributions lead.
Installing a Node Inside Traditional Institutions’ Databases
How exactly does AminoChain work?
The key lies in AminoNode, a software package developed by the project.
Traditional medical or research institutions are unlikely to be well-versed in crypto or blockchain, and their information systems are often highly customized and closed.
Therefore, AminoChain’s approach is to install its own software package, AminoNode, into existing institutional systems without altering them. While the name suggests it functions as a node on the Amimo network, its functionality differs from typical nodes that validate transactions:
Instead, it acts more like a data collector embedded within traditional systems, standardizing data formats.
AminoNode can integrate with hospitals' or research institutions’ own EMR, inventory management, and data collection software. Data remains stored on each institution’s private servers, while the node software standardizes the data into a universal format, enabling interoperability across partner networks.
Thus, the Node software aggregates data from all providers, bringing trusted neutrality to the network. On this foundation, developers can access data from multiple medical institutions and build any number of patient-centric applications.
Currently, AminoChain’s first self-developed application is called "Sample Hub," a peer-to-peer biological sample marketplace.
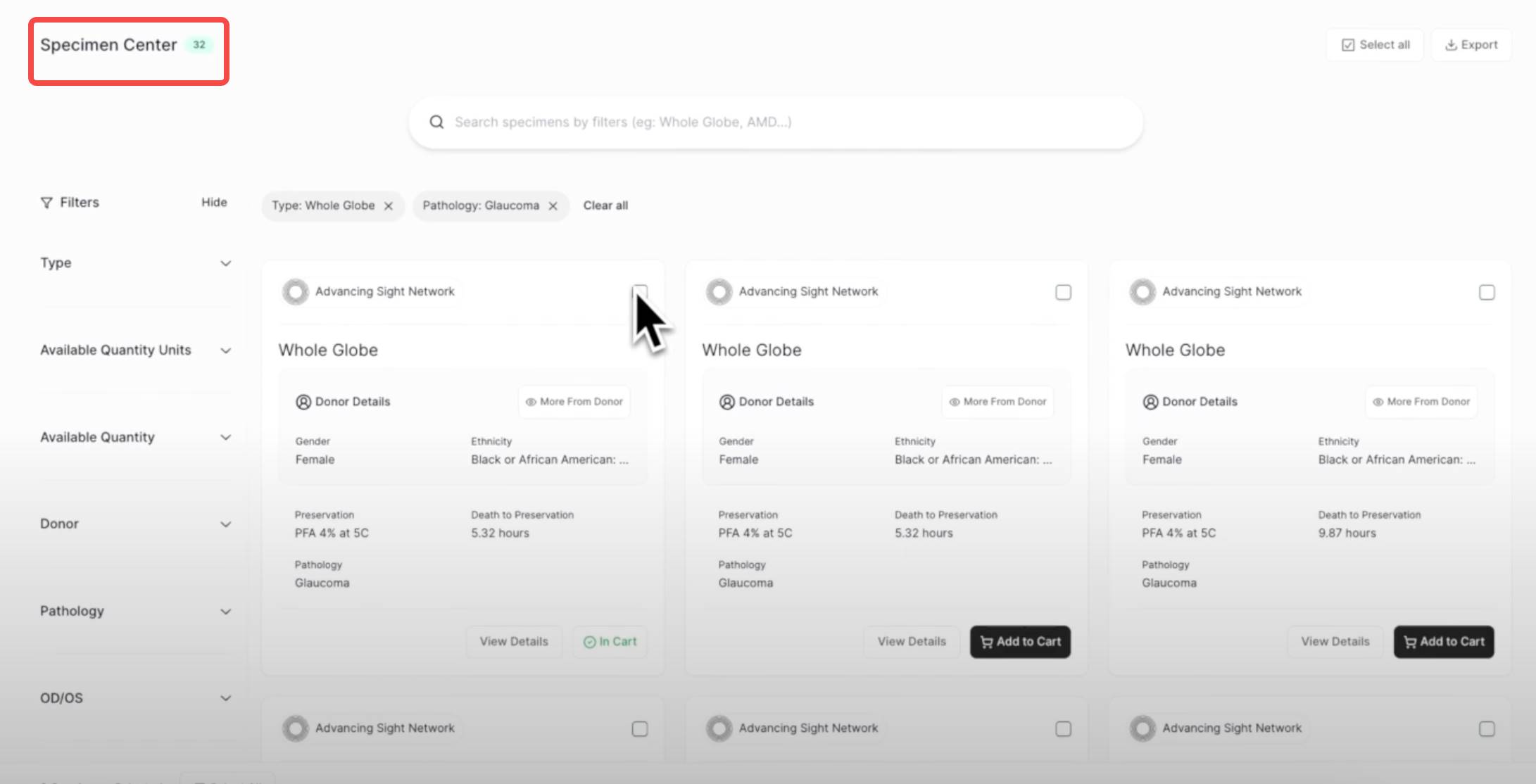
In this marketplace, researchers and collaborators can query available biological sample collections and research assets accessible to them. Between institutions, users can streamline licensing agreements, track sample and data usage, and maintain complete provenance of biological samples within an interoperable biobank network.
Thanks to market transparency and traceability, efficiency in sample use and communication clearly improves. Whereas researchers previously needed an average of eight weeks of back-and-forth emails to locate samples, sign licenses, and arrange shipments, now it could be done with a single click.
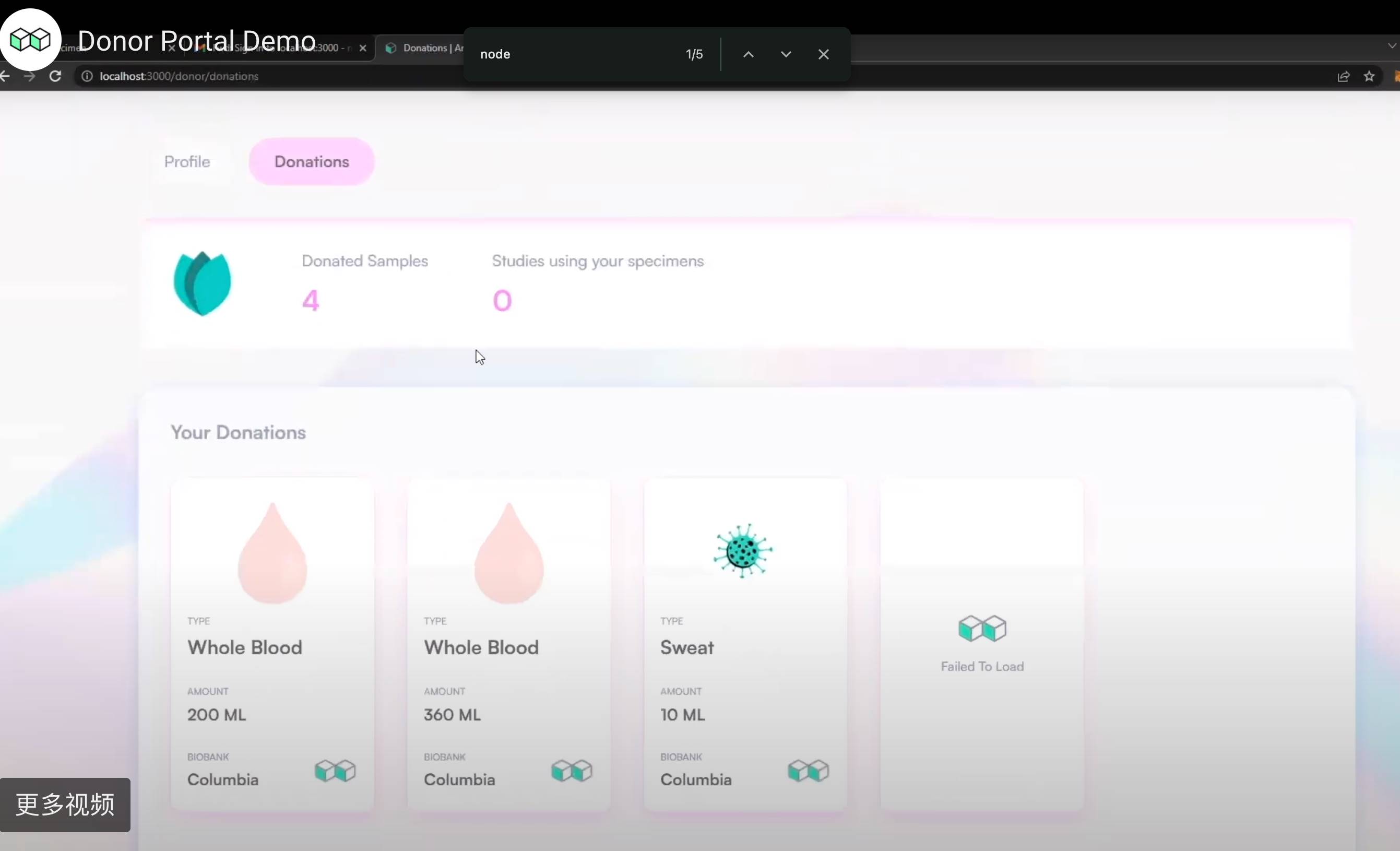
Meanwhile, patients/sample donors can track where their samples go across the network, learn from generated insights, and earn money when their samples are commercialized or sold.
For example, in the demo below, a patient’s blood and sweat data contributed at different times can all be viewed from a single dashboard, with sample usage and flow traceable on the blockchain (L2).
More Than Just Biological Samples
This marketplace use case demonstrates patients’ control over their contributed data and the benefits they can derive. But the potential applications extend far beyond this.
Medical institutions within the AminoChain network will benefit from multiple decentralized applications including clinical recruitment, clinical trial management, decentralized AI, and federated learning.
Ultimately, the project aims to build the healthcare industry’s first blockchain compliant with HIPAA and GDPR standards—enabling any company, network, nonprofit, or independent scientist to access and build upon compliant healthcare data on this platform.
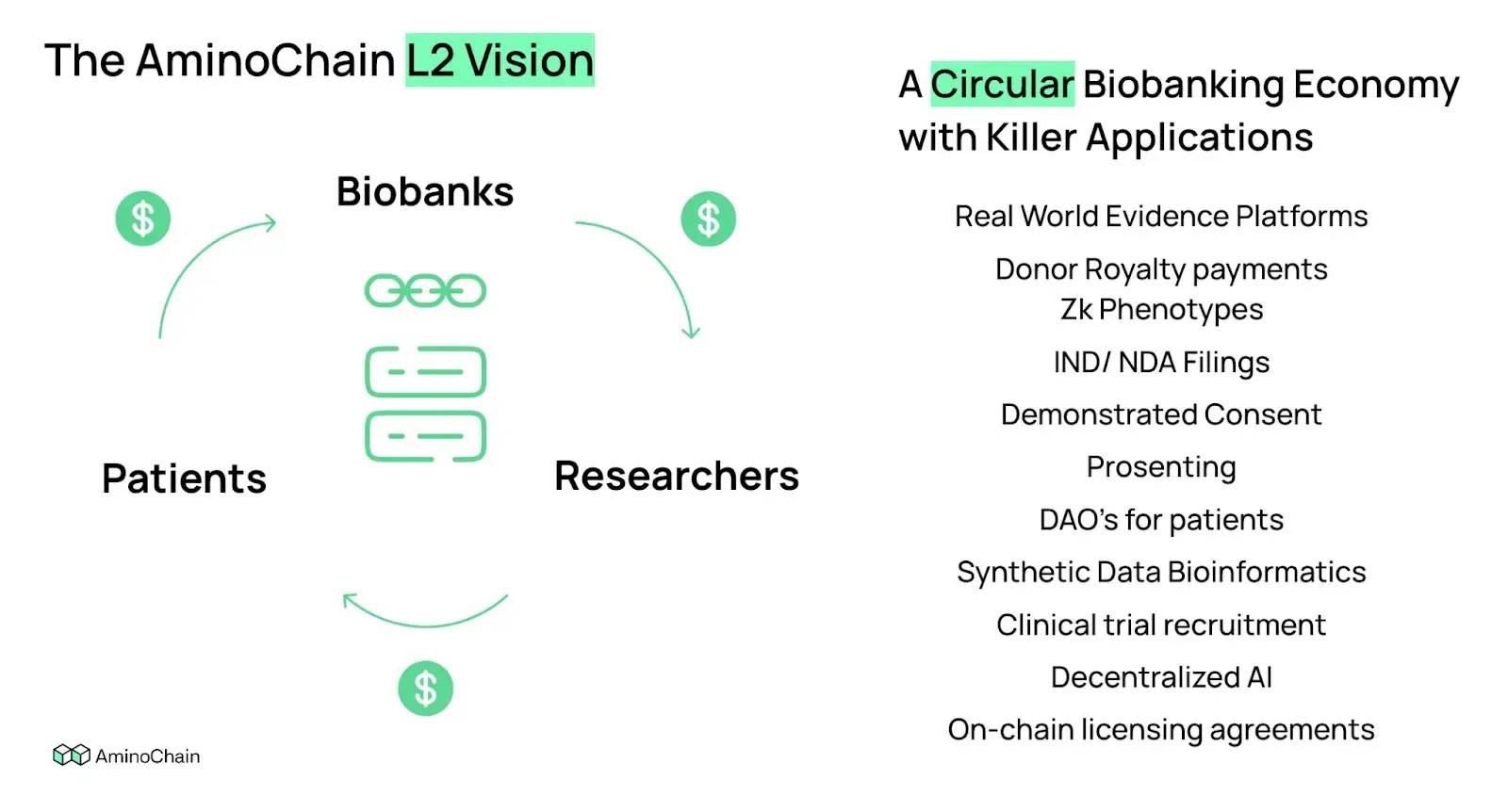
Given the sensitivity and privacy of medical data, on-chain storage and tokenization will inevitably incorporate privacy-preserving technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs, allowing data owners to assert control, grant varying usage rights, and earn revenue according to predefined rules.
If anything, the DeSci narrative aligns well with the ethos of the crypto community and degens—the maximization of individual rights. Patients no longer occupy the weakest link in the value chain but become the first to benefit from participating in scientific research.
Additionally, we’ve recently seen more projects emerging around RWA, clean energy, and DeSci.
As deeper integration with traditional industries becomes a trend, the perception of crypto as merely a casino may gradually change.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















