Starting with Oracles, But Not Limited to Oracles: Chainlink's Ambition Through CCIP
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Starting with Oracles, But Not Limited to Oracles: Chainlink's Ambition Through CCIP
See how Chainlink is revolutionizing the $30 trillion global trade market.
Author: Chianlink Blog
Translation: Weng Hao
When Maersk tracked and analyzed the documentation involved in a shipment of avocados and roses from Kenya to the Netherlands, it found that over 100 people and 200 transactions were involved. More surprisingly, out of the 34-day transportation process, as many as 10 days were spent waiting for document processing.
Although blockchain and IoT technologies have shown immense transformative potential in global trade, their adoption has been surprisingly slow. The primary obstacles are how to seamlessly and securely connect supply chain systems and how to access data from internet-connected devices.
Chainlink, through its decentralized computing platform, has successfully addressed these interoperability and connectivity challenges, ushering in a new era for global trade.
01 Seven Challenges Facing Global Trade
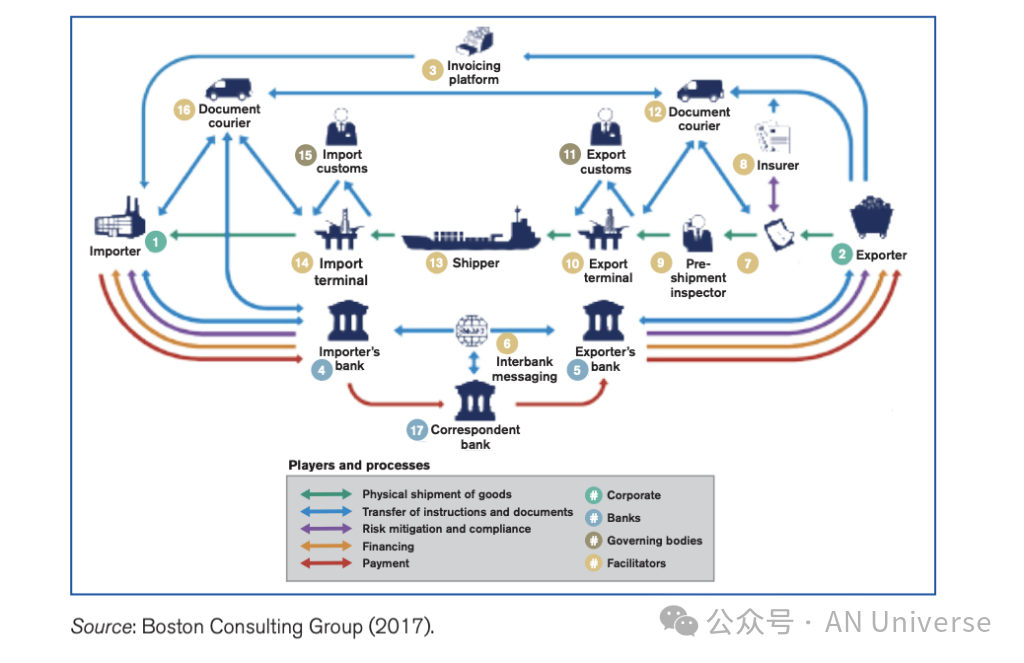
Global trade systems rely on fragmented operational systems
1. Interoperability
The inherent isolation of blockchains prevents them from connecting with existing trade platforms or other blockchain-based applications used by companies and regions. A universal blockchain interoperability standard is needed to connect all supply chain systems and access real-world data.
2. Financing
According to data from the World Trade Organization (WTO), up to 80% of global trade requires financing support, as buyers typically prefer to pay only after goods are delivered. Whether through letters of credit or other supply chain financing tools, paper-intensive processes and multiple stakeholders often lead to high costs, time-consuming procedures, and exposure to various risks.
3. Documentation
Paper-based processes not only increase administrative costs but are also prone to errors, fraud, and limited visibility. Despite advances in digital technology, the industry still relies heavily on paper documents such as packing lists, letters of credit, bills of lading, certificates of origin, import/export licenses, and customs declarations.
4. Coordination
Global trade depends on independent processes across numerous participants, lacking trust and coordination. Research by Boston Consulting Group found that in a single trade finance transaction, more than 20 different entities and approximately 5,000 data interactions are involved, with 85%-90% of these interactions adding no value. This problem is especially pronounced in emerging markets that lack access to financial services comparable to those in developed economies.
5. Fraud
Malicious activities such as counterfeit goods and double financing remain prevalent in global trade due to the lack of necessary verification, tracking, and transparency mechanisms to prevent fraud.
6. Errors
Real-time detection of lost shipments, duplicate payments, and inventory tracking errors is nearly impossible. Even when detected, correcting these issues is extremely difficult because it's hard to determine which ledger entries correspond to which transactions—especially given the large scale at which many supply chain companies operate.
7. Visibility
Order, shipment, and payment information are difficult to track across the entire supply chain. They are also often unsynchronized in back-end systems, as one order may be split into multiple shipments or multiple orders consolidated into one. Although audits can help verify transactions and ensure contract fulfillment, they often lack the detailed information needed to improve decision-making and business operations.
02 How Chainlink Helps Solve Supply Chain Challenges
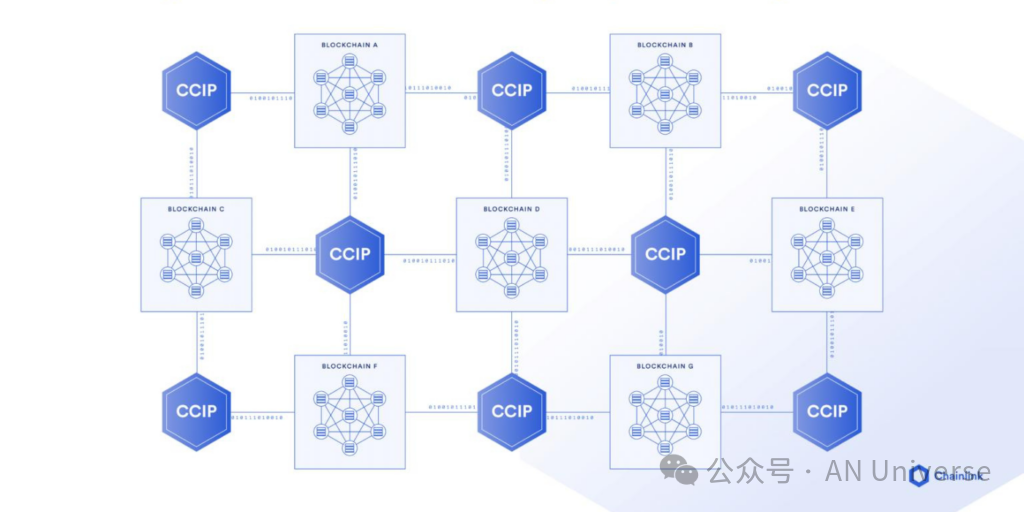
Chainlink CCIP connects fragmented blockchains
Blockchain technology can significantly improve global trade by enabling faster, more efficient, and verifiable delivery of goods, enhancing end-to-end traceability, improving coordination among partners, and expanding access to financing. The Chainlink platform enables supply chains to fully realize the benefits of blockchain and IoT technologies by reliably, securely, and decentralizing connecting trade systems with real-world data.
Chainlink assists supply chains in achieving:
1. Seamless Interoperability
Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) provides a universal interoperability standard, enabling secure transfer of value and data between blockchains and connecting with existing platforms and systems.
2. On-chain Trade Finance
Chainlink supports on-chain financing systems by providing accurate market data, identity information, and proof of reserves, helping improve trade efficiency and expand access to global trade in emerging markets.
3. Digitization and Automation
— By converting paper-based documents into dynamic NFTs and leveraging Chainlink automation and function features, digitized documents automatically update as they move through the supply chain.
4. Ecosystem Alignment
Unified records on the blockchain allow multiple stakeholders to automate invoice financing, payments, and other processes, reducing manual errors and saving backend management costs.
5. Anti-Fraud Protection
By enabling load tracking and verification across the entire supply chain via blockchain and IoT technologies, Chainlink provides end-to-end validation to establish product authenticity, thereby reducing counterfeits and fraudulent activities.
6. High-Accuracy Data
By using various IoT and RFID devices to verify cargo delivery and conditions, recorded statuses reflect actual product conditions, accelerating business response times and helping identify critical supply chain issues. For example, container temperatures transporting fresh food can be monitored; if they exceed preset ranges, an on-chain insurance smart contract can be triggered to automatically release compensation.
7. End-to-End Transparency
Blockchain technology not only provides tier-by-tier visibility but also offers participants a broader perspective with all necessary information while protecting commercial secrets and personal data.
03 Chainlink and Vodafone DAB Jointly Transforming Global Trade

Chainlink and Vodafone DAB are jointly transforming global supply chains
Chainlink and Vodafone’s Digital Asset Broker (DAB) demonstrate how CCIP can enable seamless exchange of trade documents across different platforms and blockchains. This collaboration could allow supply chain applications to securely exchange data and tokens across public and private blockchains and access IoT device data via the DAB platform. For instance, an IoT device detecting a fire on cargo could automatically initiate an on-chain insurance process. By securely linking IoT data to blockchains, CCIP unlocks numerous exciting use cases for trade finance.
“Vodafone DAB and Chainlink are demonstrating how their platforms can work together to solve these compatibility issues by bridging traditional markets with advanced decentralized platforms. This ensures seamless and secure exchange of data and services within the global trade ecosystem, valued at over $30 trillion last year.” — Jorge Bento, CEO of Vodafone DAB
04 Enabling the Economy of Things (EoT)
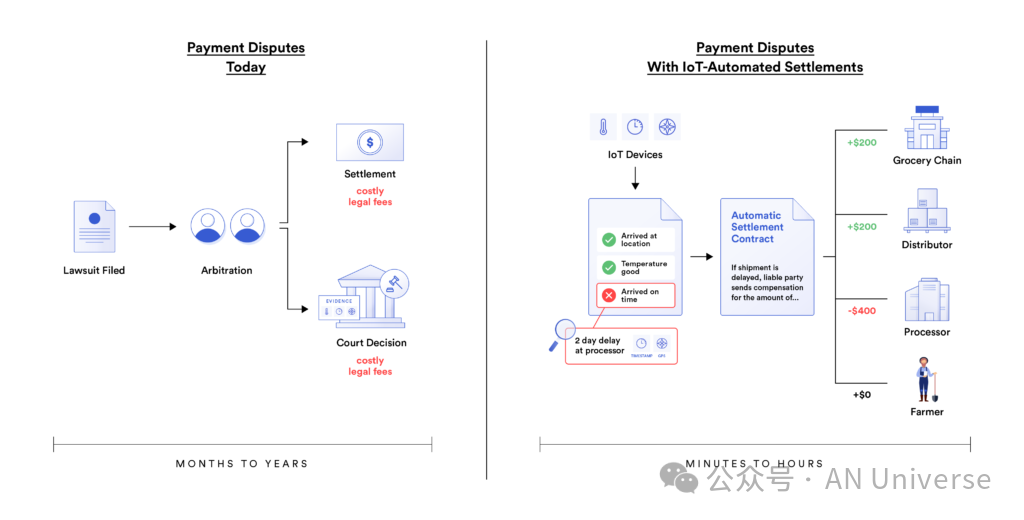
Combining IoT with tamper-proof value transfer enables fair end-to-end dispute resolution.
The Economy of Things (EoT) represents the next evolutionary stage of the Internet of Things (IoT). In EoT, real-world devices not only send and receive information—they also conduct transactions. Electric vehicles can pay at charging stations, refrigerators can automatically purchase groceries, and homes can automatically trigger insurance contracts.
Blockchain, smart contracts, and oracles are key enablers of EoT, providing real-world devices with immutable records, determinism, programmable protocols, and connectivity to real-world information and other systems.
With the support of Chainlink and Vodafone DAB, EoT will completely redefine how supply chains operate. Instead of relying on paper-based processes, manual updates, audits, and inefficient financing methods, the entire supply chain will become automated, highly verifiable, and efficient.
CCIP is not just for finance or global trade—it applies to the entire global economy. Whether connecting to IoT devices or private banking chains, CCIP is becoming the universal standard for secure transfer of value and data for any blockchain-enabled application.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News