Quick Overview: 2023 Annual Report on Blockchain Security and Anti-Money Laundering
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Quick Overview: 2023 Annual Report on Blockchain Security and Anti-Money Laundering
This report will review key regulatory compliance policies and developments in the blockchain industry in 2023.
Author: SlowMist AML Team
SlowMist Technology releases the "2023 Blockchain Security and Anti-Money Laundering Annual Report." We hope this report provides valuable insights to help industry practitioners and users better understand the current state of blockchain security and available solutions, contributing to the safety of the blockchain ecosystem. Due to space limitations, only key findings are presented here. For the full report, please click here.
I. Overview
2023 was a year of both excitement and turbulence for the blockchain industry. Against this backdrop, this report reviews major regulatory compliance developments in 2023, summarizes blockchain security incidents and anti-money laundering (AML) trends, analyzes certain money laundering tools, dissects typical security breaches and phishing scams, and offers prevention strategies and recommendations. Additionally, we invited Web3 anti-fraud platform Scam Sniffer to contribute content on Wallet Drainer groups, and we analyze the money laundering techniques and profits of the hacker group Lazarus Group.
II. Blockchain Security Landscape
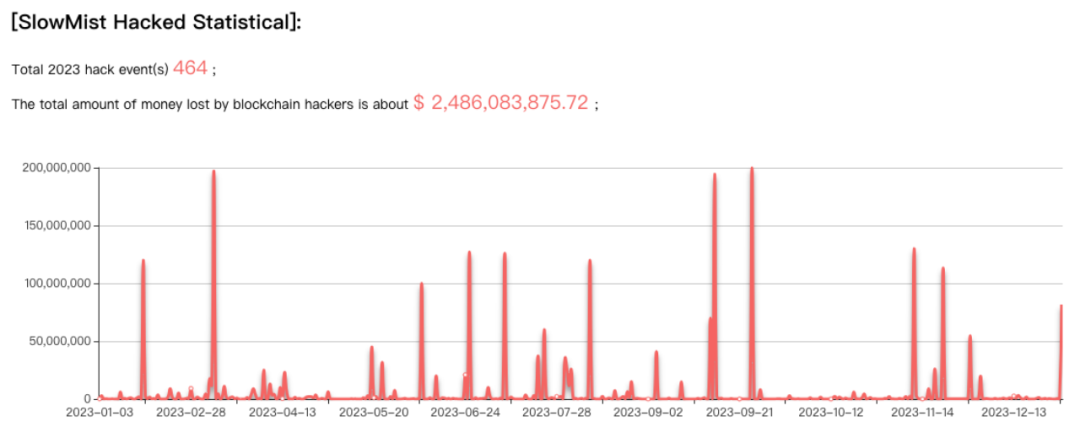
According to statistics from the SlowMist Hacked incident database, there were 464 blockchain security incidents in 2023, resulting in total losses of $2.486 billion. Compared to 2022 (303 incidents, ~$3.777 billion in losses), this represents a 34.2% year-on-year decrease in losses.
-
Overview of Blockchain Security Incidents
By sector, DeFi remained the most frequently targeted area. In 2023, there were 282 DeFi-related incidents, accounting for 60.77% of all incidents, with losses totaling $773 million. Compared to 2022 (183 incidents, ~$2.075 billion in losses), this marks a 62.73% decrease in losses.
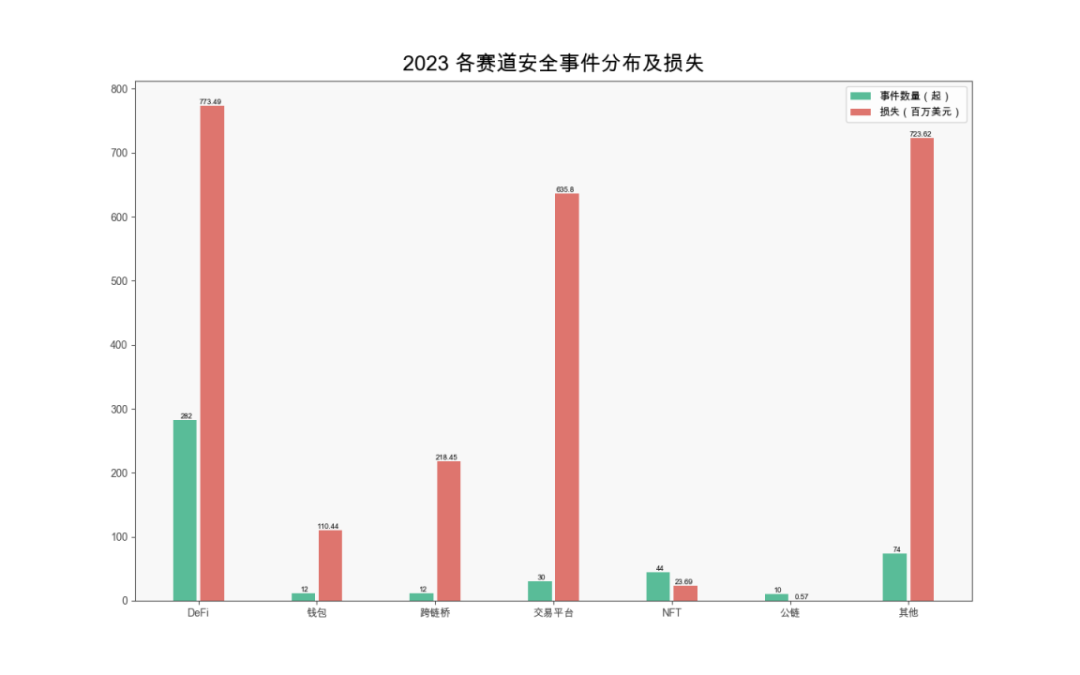
(Distribution and losses of security incidents across sectors in 2023)
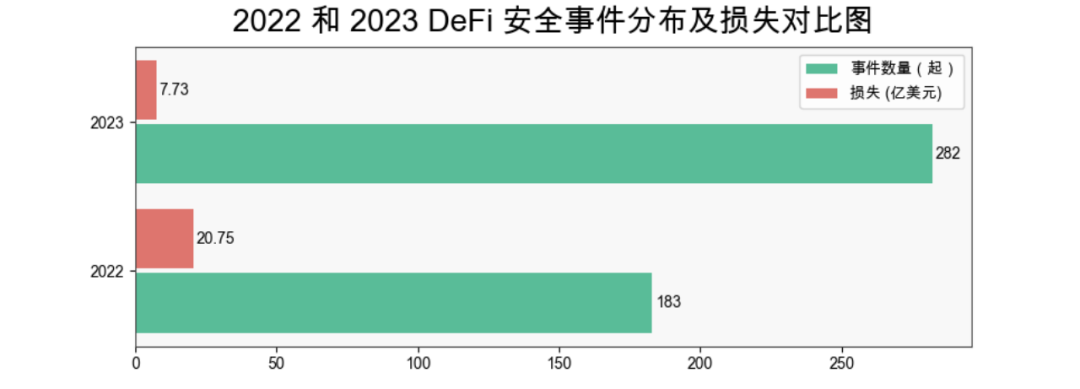
(Comparison of DeFi security incidents and losses between 2022 and 2023)
By ecosystem, Ethereum suffered the highest losses at $487 million, followed by Polygon at $123 million.
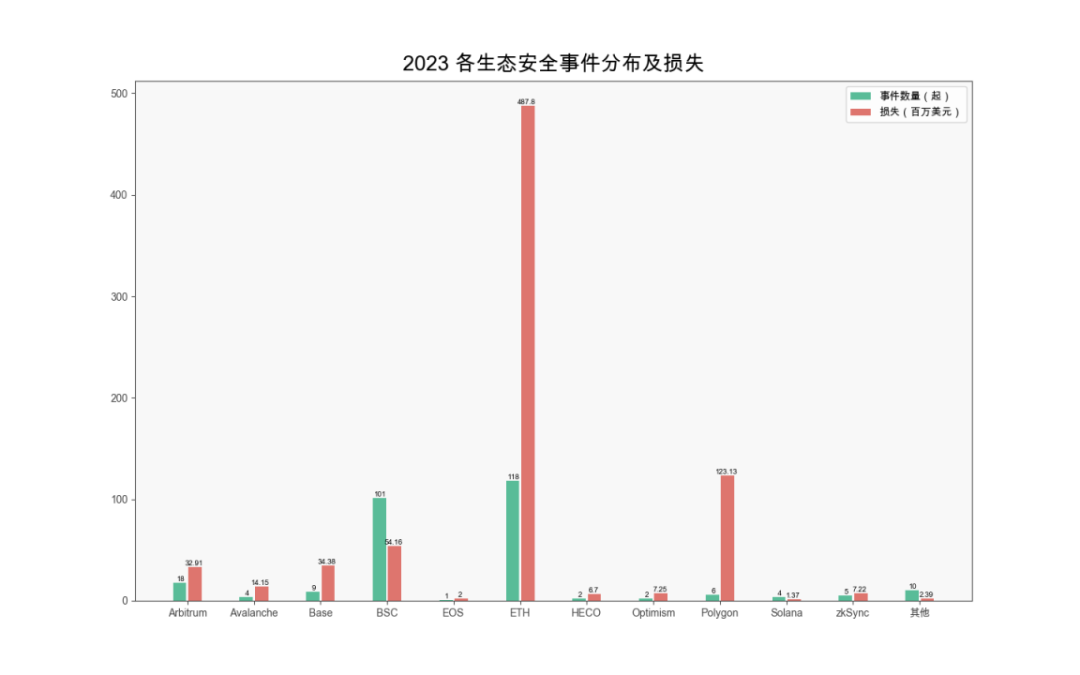
(Distribution and losses of security incidents across ecosystems in 2023)
By cause, rug pulls were the most common type of incident, totaling 117 cases with approximately $83 million in losses. Account compromises ranked second.
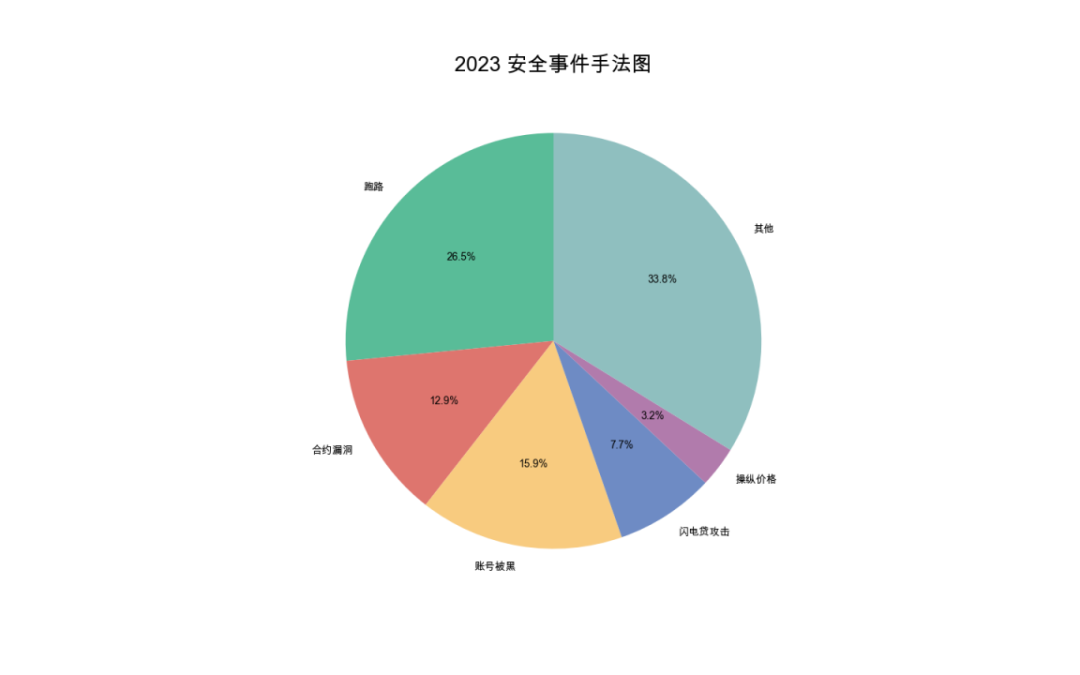
(Methods used in 2023 security incidents)
-
Notable Attack Incidents
This section highlights the top 10 highest-loss security incidents of 2023. Detailed information can be found in the PDF at the end of this article.
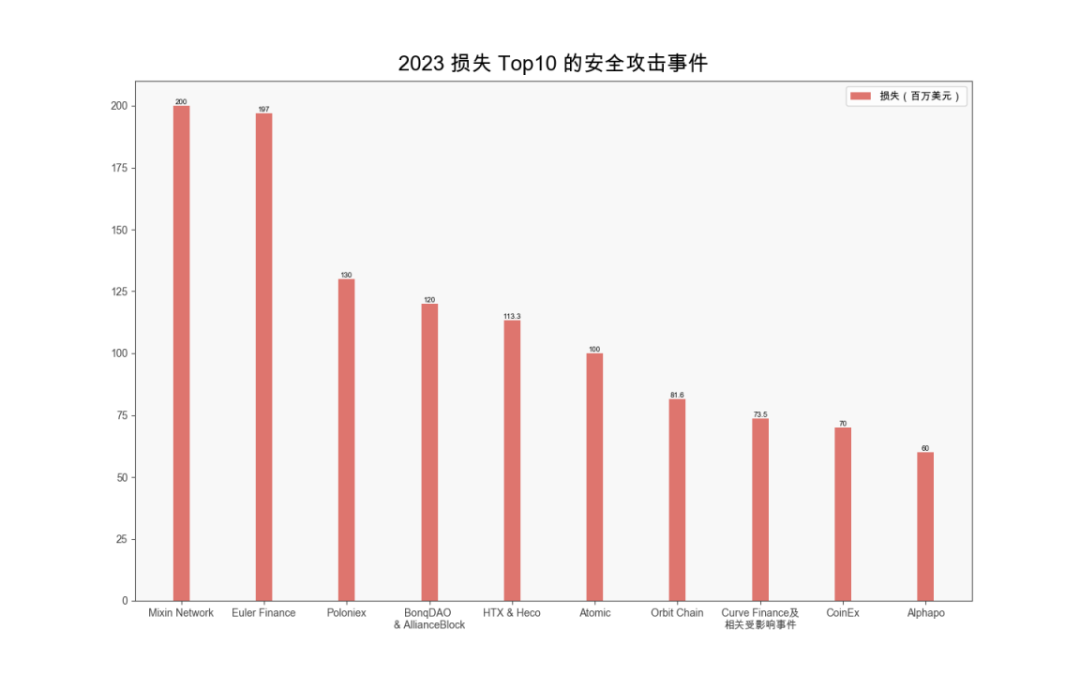
(Top 10 highest-loss security incidents in 2023)
Rug Pull
According to the SlowMist Hacked database, there were 117 rug pull incidents in 2023, causing around $83 million in losses. The Base ecosystem incurred the highest losses ($32.5 million), followed by BSC ($23.05 million).
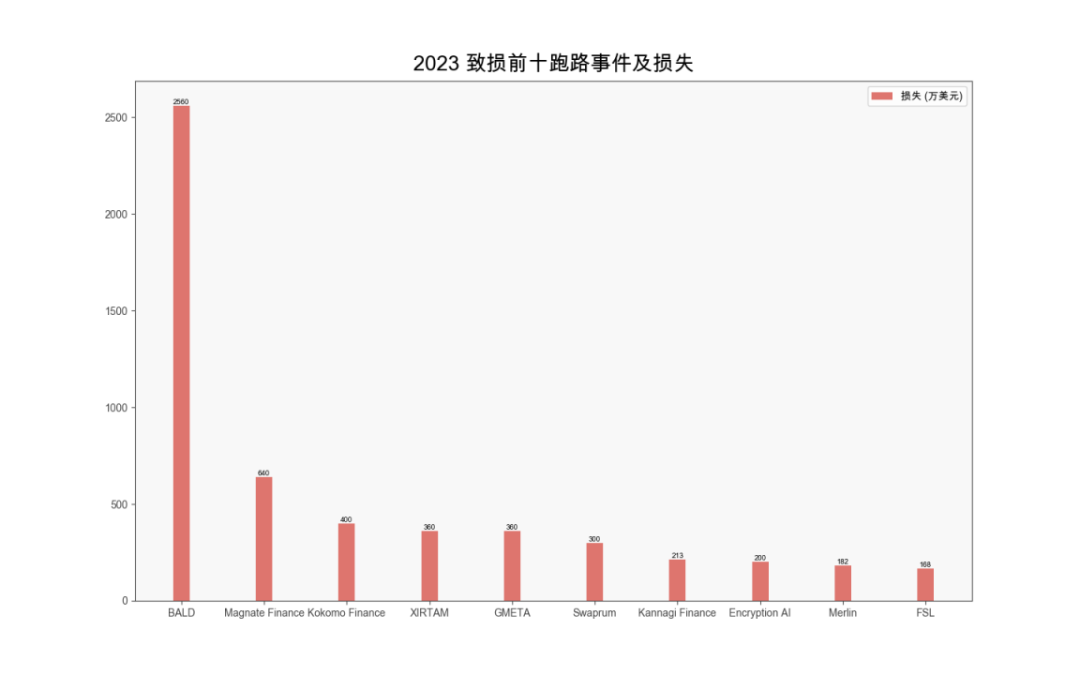
(Top 10 loss-causing rug pulls and associated losses in 2023)
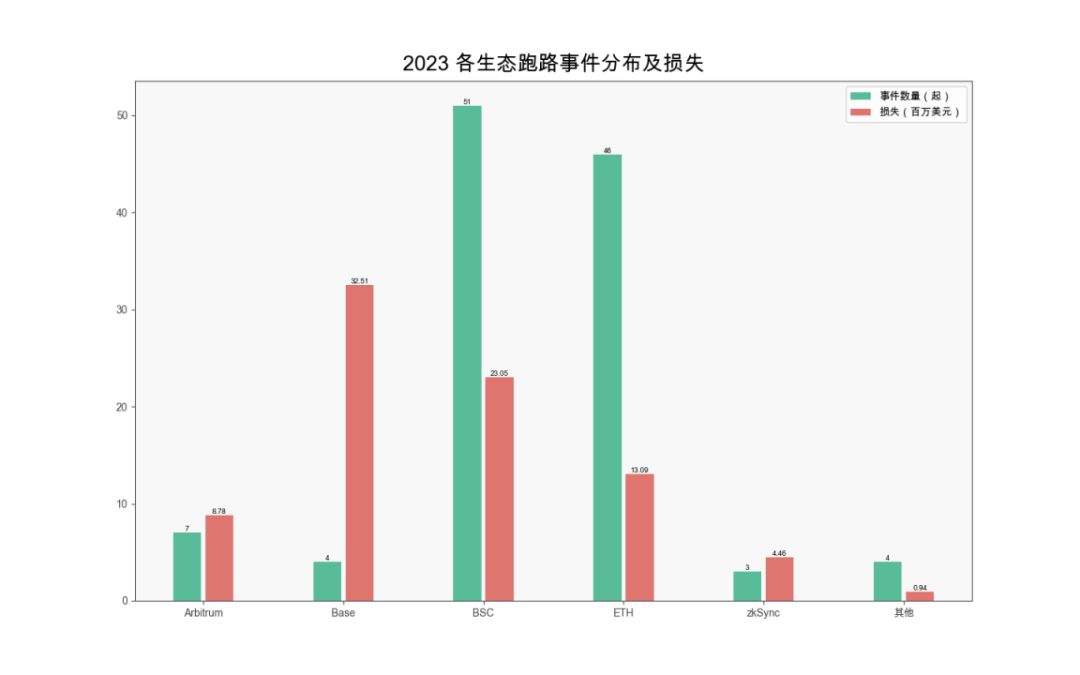
(Distribution and losses of rug pulls across ecosystems in 2023)
A rug pull is a scam typically orchestrated maliciously by project teams through various means: initiating liquidity and then withdrawing it after inflating prices; launching a crypto project, attracting investments via marketing, and suddenly absconding with funds or dumping tokens; launching a website, collecting hundreds of thousands in deposits, then shutting it down; or leaving backdoor code within the project. Regardless of the method, all types of rug pulls result in investor losses.
Additionally, this section presents an extremely stealthy rug pull case: where attackers drained pool funds using a large volume of unrecorded minted tokens despite no official token minting history.
Fraud
In recent years, the cryptocurrency market has become fertile ground for scammers. Common tactics include impersonating celebrities via fake accounts, romance scams ("pig butchering"), promoting fraudulent trading platforms, Ponzi schemes, and increasingly, leveraging AI software to make scams more convincing. This section examines JPEX, a major crypto fraud case primarily affecting Hong Kong. According to reports, JPEX's collapse may become the largest financial fraud in Hong Kong's history.
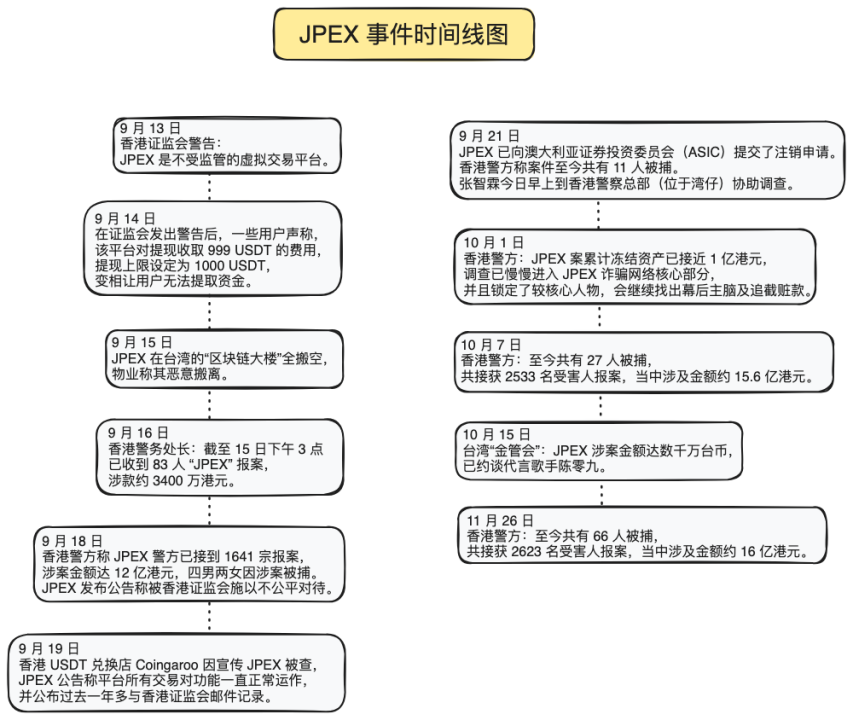
(JPEX incident timeline)
-
Phishing / Scam Techniques
This section covers selected phishing and scam techniques disclosed by us in 2023:
1. WalletConnect Phishing Risks
4. Phishing URLs Disguised as Transfer Addresses
5. Telegram Targeted Fraud Attacks
6. Create2 Phishing Risk (https://drops.scamsniffer.io/post/wallet-drainers-starts-using-create2-bypass-wallet-security-alert)
III. Anti-Money Laundering Landscape
This section is divided into four parts: AML and regulatory developments, AML related to security incidents, hacker group profiles and activities, and money laundering tools.
-
AML and Regulatory Developments
The cryptocurrency world remained turbulent throughout 2023. During the previous bull market, every move by industry giants like SBF and CZ seemed to significantly impact the market. However, in November, a federal jury found SBF guilty on charges of fraud and conspiracy related to FTX’s collapse. Just weeks later, Binance accepted penalties, paying $4.3 billion in fines, while CZ agreed to relinquish control of Binance. As the crypto industry continues to navigate a volatile “winter” and bear market, governments and international organizations have adopted increasingly cautious stances, with national crypto regulations still evolving. See the full PDF for detailed policy and enforcement actions.
-
Security Incident-Related Money Laundering
1. Fund Freeze Statistics
With strong support from InMist intelligence network partners, SlowMist assisted clients, partners, and public incident responses in freezing over $12.5 million in illicit funds in 2023.
2. Fund Recovery Statistics
In 2023, there were 31 incidents where victims recovered some or all stolen funds. Across these incidents, approximately $384 million was stolen, with $297 million returned—representing 77% recovery. Ten protocols fully recovered their stolen assets.
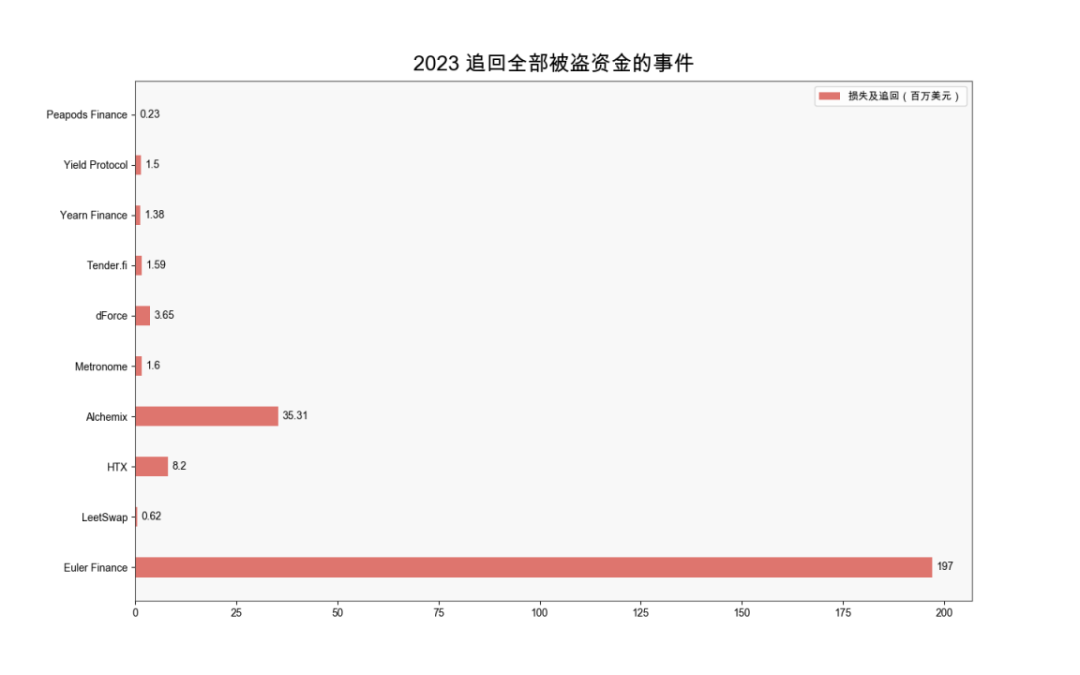
(Incidents in 2023 with full recovery of stolen funds)
-
Hacker Group Profiles and Activities
1. Hacker Group: Lazarus Group
Based on publicly available information in 2023, no major cryptocurrency theft had been attributed to North Korea’s Lazarus Group by June. On-chain activity shows that Lazarus primarily focused on laundering crypto stolen in 2022, including around $100 million from the June 23, 2022 attack on the Harmony cross-chain bridge. Beyond laundering past proceeds, the group remained active in conducting covert APT-style attacks during this period—leading directly to what became known as the crypto industry’s “Dark 101 Days” starting June 3.
During the “Dark 101 Days,” five platforms were compromised, with over $300 million stolen—most being centralized service providers.
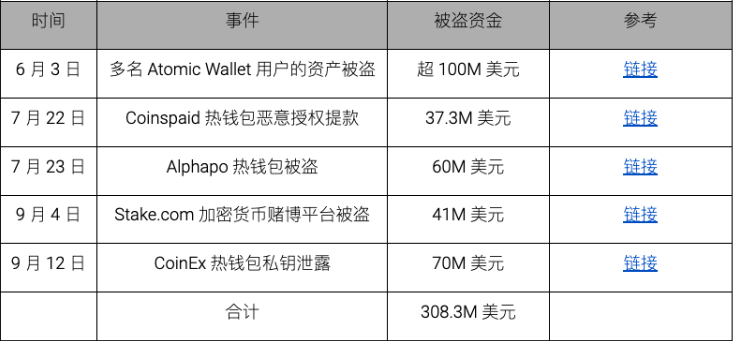
Our analysis indicates that Lazarus Group’s money laundering methods continue to evolve, with new techniques emerging periodically. Refer to the full PDF for a timeline of their laundering evolution.
2. Phishing Group: Wallet Drainers
Note: This subsection is contributed by Scam Sniffer. Our sincere thanks.
Wallet Drainers, a type of crypto-focused malware, achieved notable success over the past year. Deployed on phishing websites, they trick users into signing malicious transactions, draining wallet assets. These campaigns continuously target ordinary users in various forms, leading many to unknowingly sign harmful transactions and suffer significant financial losses. Over the past year, Scam Sniffer observed these Wallet Drainers stealing nearly $295 million from approximately 320,000 victims.
Notably, nearly $7 million was stolen on March 11 alone—mostly due to USDC price fluctuations and fake Circle phishing sites. Another surge occurred near March 24 following the Arbitrum Discord breach and subsequent airdrop.
Each spike coincided with specific mass events—such as airdrops or hacking incidents.
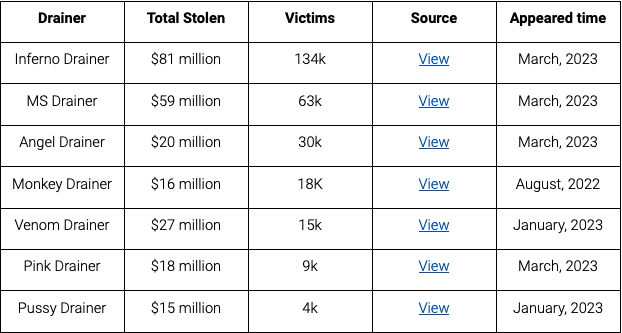
After ZachXBT exposed Monkey Drainer, the group retired after six months of operation, with Venom taking over most of its clients. Subsequently, MS, Inferno, Angel, and Pink emerged around March. When Venom ceased operations around April, most phishing groups shifted to alternative services. Based on a 20% drainer fee, these operators earned at least $47 million in revenue from service sales.
-
Money Laundering Tools
1. Sinbad Mixer
2. Tornado Cash
3. eXch
4. Railgun
IV. Conclusion
This report summarizes key regulatory compliance policies and developments in the blockchain industry in 2023, including global regulatory attitudes toward cryptocurrencies and major policy changes. It also reviews blockchain security incidents and AML trends, analyzes select money laundering tools, explains typical security breaches and phishing scams, and proposes corresponding preventive and responsive measures. We hope this report delivers valuable information, helping readers gain a comprehensive understanding of the current state of blockchain security and anti-money laundering efforts, benefiting every participant in the ecosystem and contributing to the advancement of blockchain security.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News