MT Capital Research Report: The Current State and Future Prospects of the DeSci Sector
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

MT Capital Research Report: The Current State and Future Prospects of the DeSci Sector
DeSci development focuses on improving peer review, funding sponsorship, intellectual property management, and enhancing data transparency and scrutiny.
TL;DR
DeSci's integration with Web3 and blockchain: DeSci leverages blockchain technology to improve key aspects of scientific research, such as peer review, funding, intellectual property management, and data transparency.
How DeSci impacts scientific research: DeSci has the potential to enhance transparency, efficiency, and democratization in scientific research while creating new opportunities for addressing global challenges.
Challenges and future outlook: These include improving peer review mechanisms, securing funding, protecting data privacy, increasing diverse participation, and fostering integration between DeSci and traditional science.
What is DeSci?
The development of DeSci is closely tied to the rise of Web3 technologies, particularly blockchain. It represents a new approach to scientific research that uses blockchain to address fundamental issues in traditional research processes. DeSci focuses on enhancing peer review, funding, intellectual property (IP) management, and improving data transparency and auditability—key components of conventional scientific workflows.
Key characteristics of DeSci include:
-
Peer review and publishing process: Traditional scientific publishing is managed by journals and often involves lengthy peer review and editorial processes. Blockchain technology, especially smart contracts, can streamline this. Building decentralized communities and introducing reputation systems can increase efficiency and transparency. For example, VitaDAO applies blockchain in peer review and reputation systems.
-
Funding: Traditional grant models involve long application cycles and are susceptible to bias from review panels. Blockchain offers an alternative through direct crowdfunding of research. Molecule, for instance, is a blockchain-based funding marketplace connecting patients, biotech companies, investors, and scientists to promote open research markets.
-
Intellectual property management: In DeSci, IP-NFTs (Intellectual Property Non-Fungible Tokens) allow researchers to share ownership and future benefits of research projects. Molecule pioneers this approach, enabling easier access to funding and commercialization for scientists, biomedical researchers, and biotech firms via IP-NFTs.
-
Data transparency and auditability: Blockchain enhances data transparency by storing and accessing research data in a decentralized environment. This helps break down data silos and fosters collaboration across projects and institutions.
Impact and Prospects of DeSci
-
Simplified industry translation: Commercializing academic findings is often slow and complex due to institutional IP policies. DeSci creates new pathways for translating research into products by leveraging IP-NFTs and other innovations. It also helps VCs discover promising "under-the-table" projects before they gain mainstream attention.
-
Bridging traditional boundaries: DeSci extends beyond natural sciences—it applies equally to art, humanities, and indigenous knowledge systems. Cross-disciplinary collaboration and knowledge sharing are central to DeSci’s vision.
-
Enabling novel forms of collaboration: Leveraging decentralization, DeSci enables global cooperation, especially for projects requiring worldwide environmental data or multidisciplinary input. This positions DeSci to tackle urgent global challenges like climate change and public health crises.
Key Technologies and Applications in DeSci
-
Blockchain and Smart Contracts: Blockchain plays a core role in DeSci, particularly through smart contracts—self-executing code that automates steps in the scientific publishing workflow, such as peer review. These ensure transparency and efficiency while reducing time and costs associated with traditional publishing.
-
Decentralized Peer Review and Publishing: DeSci eliminates intermediaries like journal editors using blockchain, thereby increasing accessibility and transparency of research outputs. For example, Ants Review uses smart contracts to directly connect authors and reviewers, incentivized with tokens to improve the speed and quality of peer review.
-
Community-Based Research Funding: Blockchain enables crowdfunding, allowing scientists to directly engage with patients, biotech firms, or investors to fund open research. This model lets researchers bypass traditional funding channels. Molecule, for instance, raises funds for drug development using NFTs and DAOs.
-
Intellectual Property Management: In DeSci, NFTs manage and develop IP assets such as scientific datasets or publications. This improves the efficiency of IP sharing and monetization, offering scientists a new revenue stream. Molecule uses IP-NFTs to share project ownership and future outcomes.
-
Data Transparency and Auditability: Data hosted on blockchains increases transparency in research, enabling scientists to easily access and store databases related to their studies for more accurate decision-making. A unique feature DeSci leverages is the blockchain’s “permanent web”—once data is uploaded, it cannot be deleted or altered. This permanence is crucial for science, ensuring discoveries remain intact and accessible even under political or social pressure. It safeguards scientific integrity and resists censorship, preserving freedom and objectivity in research.
-
Decentralized Research Tools and Publishing Platforms: DeSci offers multifunctional decentralized platforms like DeSci Node and LabDAO, supporting research activities including seamless integration of reports, charts, code, and external APIs.
-
Reputation System Development: To build high-quality, trustworthy DeSci communities, platforms must implement robust reputation systems that track user interactions—likes, comments, posts—on decentralized networks to establish credibility and expertise. Using blockchain, scientists’ contributions—whether peer reviews, data sharing, or mentorship—can be recorded and verified via NFTs. These NFTs serve both as proof of contribution and as indicators of scientific reputation. Such systems encourage community engagement and knowledge sharing while providing a more objective, transparent way to evaluate and reward scientific work.
-
Social Platforms for Academia: While Web2 platforms like ResearchGate have raised over $100M, Web3 equivalents offer new ways for scientists, researchers, and stakeholders to communicate and collaborate. These social platforms enable researchers to share findings, find collaborators, and give VCs a channel to identify and invest in emerging research projects.
DeSci Ecosystem Projects
Molecule
Molecule is a decentralized fundraising platform for biotech research, currently hosting around 40 scientists seeking funding for their projects. Inspired by citizen science movements and the open development of therapeutics, Molecule originated from patient communities aiming to advance early-stage drug discovery. Built on Ethereum, Molecule comprises two main systems: Molecule Discovery and Molecule Finance, creating an active ecosystem for modular, decentralized drug development. By combining smart contracts with legal agreements, Molecule introduces Intellectual Property NFTs (IP-NFTs), a novel mechanism enabling anyone to co-own a research project and its future outputs—including IP rights, royalties, and data. Beyond basic website functions, Molecule builds a comprehensive ecosystem empowering patient collectives and drug development DAOs to maintain, manage, and interact with real-world IP.
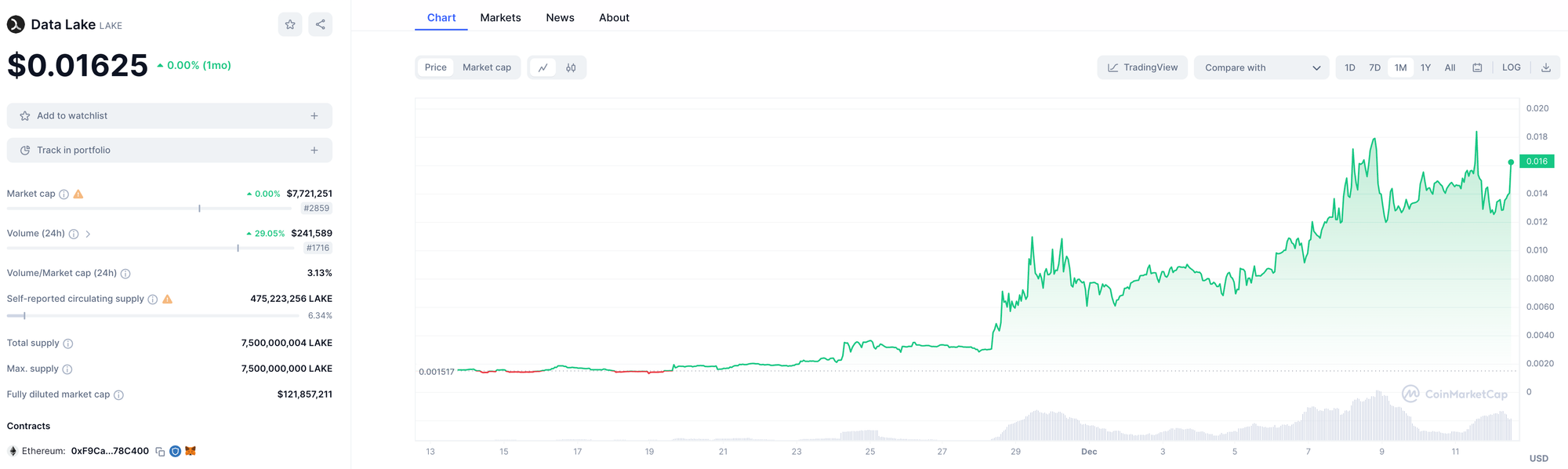
Data Lake
Data Lake is an innovative blockchain-powered medical data donation platform designed to support medical research and AI advancement. It bridges patients willing to donate health data with researchers needing such data, using Polygon and its native token ($LAKE). The platform aims to accelerate the discovery of treatments and therapies, ultimately improving healthcare services and patient outcomes.
Data Lake works by obtaining access to donors’ medical records from healthcare providers, then anonymizing the data for secure use by researchers. Additionally, hospitals and data donors can share in the economic value generated from the data, incentivizing broader participation in data sharing. In this way, Data Lake protects privacy while advancing medical research.
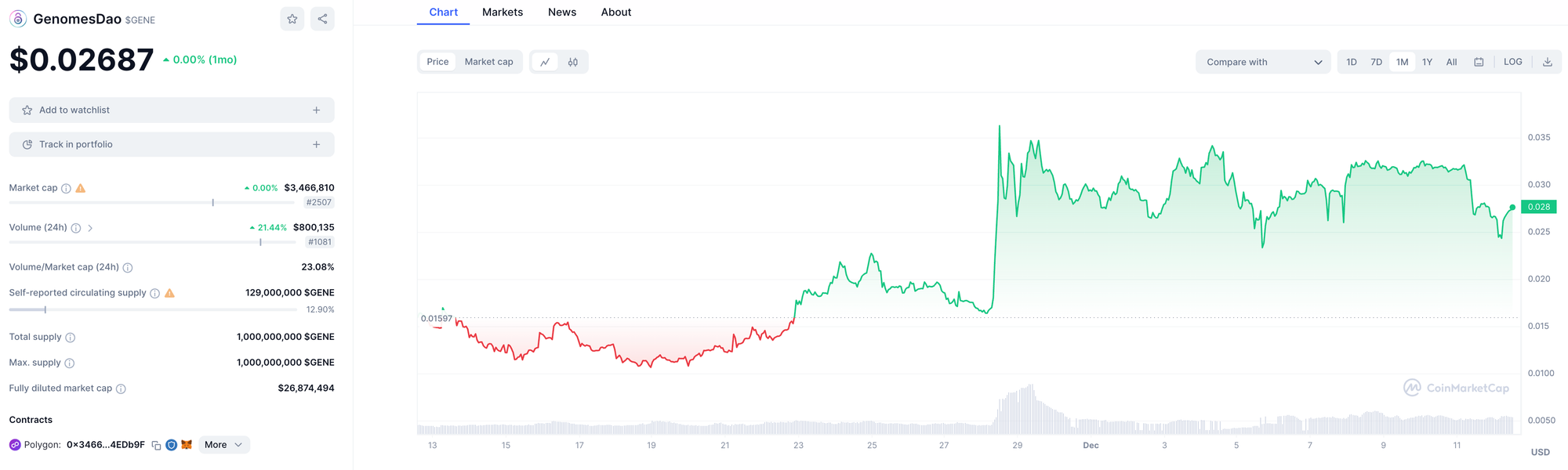
GenomesDAO
GenomesDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) focused on monetizing genomic data, integrating concepts from decentralized finance (DeFi) to ensure security, privacy, and auditability. Key features of GenomesDAO include:
GenomesDAO aims to advance genomics research and drug innovation while safeguarding individual privacy. Its platform transforms personal genetic data into valuable resources without compromising data security.
-
Target Users: GenomesDAO serves individuals and organizations. Individuals receive whole-genome sequencing, personalized genome reports, and secure DNA vault storage. Organizations gain technical support to create secure, participant-owned genomic databases.
-
Research Support: Provides researchers access to high-quality genomic datasets to understand disease mechanisms and develop new drugs.
-
Token Utility: Uses the GENE token to pay for whole-genome sequencing and incentivizes queries within its encrypted DNA data vault.
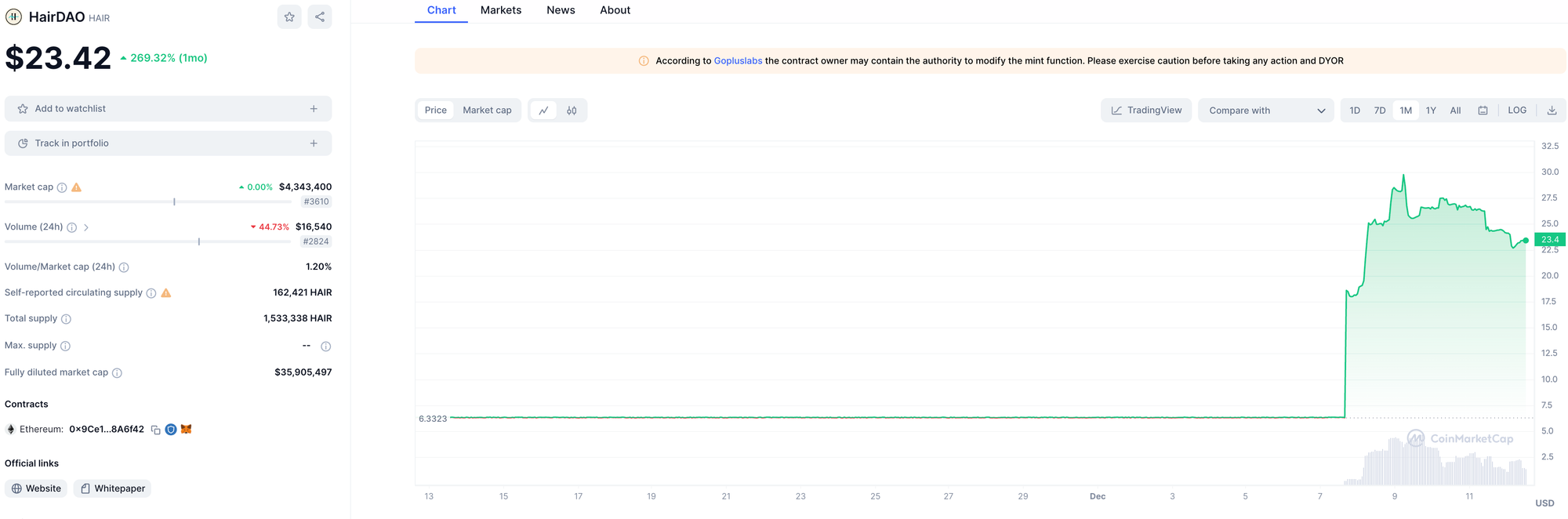
HairDAO
HairDAO is a decentralized organization dedicated to curing hair loss using open-source investment and operational models. It aims to democratize research and development in hair loss treatment and provide early-stage funding for relevant research and startups.
Key features of HairDAO include:
-
Diverse Participation: HairDAO encourages people with various skills—technical or domain-specific—to join.
-
Reward Mechanism: Through its $HAIR token, HairDAO rewards contributors. Users earn $HAIR by uploading anonymized, encrypted genomic data.
-
Cultural Identity: Despite its scientific focus, HairDAO adopts a lighthearted, humorous tone on its website and Twitter, contrasting sharply with traditional research projects. Its content and design are unconventional, even evoking a silent film-era comedic flair.
- Meme Culture: Within the DeSci space, HairDAO stands out with its baldness theme and playful branding. Its Twitter even uses salon emojis, reinforcing its meme coin identity.
VitaDAO
VitaDAO is a decentralized biotech DAO initiated by Molecule, leading in longevity research and development. As the world’s first biotech DAO, VitaDAO’s primary mission is to advance longevity science and extend human healthspan and lifespan.
Core features of VitaDAO include:
To incentivize early funding for longevity biomedicine, VitaDAO combines innovative governance frameworks and financial tools such as DAOs, NFTs, and AMMs. Operating on Ethereum, VitaDAO not only jointly funds research but also digitizes results into IP NFTs. The VITA token is earned by contributing work, capital, or resources (like data and IP) to VitaDAO. Token holders participate in democratic governance, guiding research directions, profiting from data repositories, and managing IP portfolios. This model fosters innovation and democratization in science while giving community members direct influence and benefit from scientific progress.
-
Community Governance: Governed by $VITA token holders, VitaDAO focuses on funding early-stage longevity research.
-
Funded Projects: Has funded over 20 research projects totaling more than $6 million, covering age-related diseases and novel therapies.
-
Research Scope: Supports both basic and preclinical research.
-
Voting Rights for Token Holders: $VITA holders participate in decision-making, including project selection, fund allocation, and governance activities.
ResearchHub
Founded by Coinbase co-founder Brian Armstrong, ResearchHub aims to transform traditional academic journal publishing. The platform recently closed a $5 million Series A funding round on June 15. ResearchHub creates an alternative “Hub” system to traditional journals, allowing scientists and scholars to publish and discuss academic content directly, bypassing traditional gatekeeping and accelerating information dissemination, with peer review occurring post-publication.
Users on ResearchHub earn ResearchCoin (RSC), an ERC-20 cryptocurrency on Ethereum designed to incentivize the sharing, reviewing, and curation of scientific knowledge. RSC rewards are available for:
Additionally, users can set RSC bounties for peer reviews, paper summaries, or new lab methods. They can also raise cryptocurrency through “pre-registration” posts to fund research before starting. According to ResearchHub, platform activity grows steadily over time, with peer review being one of the most active and promising areas.
-
Sharing PDFs of research papers (provided copyright isn’t violated)
-
Commenting and discussing scientific research
-
Conducting peer reviews of scientific papers
-
Receiving RSC tips from other users
-
Developing open-source features
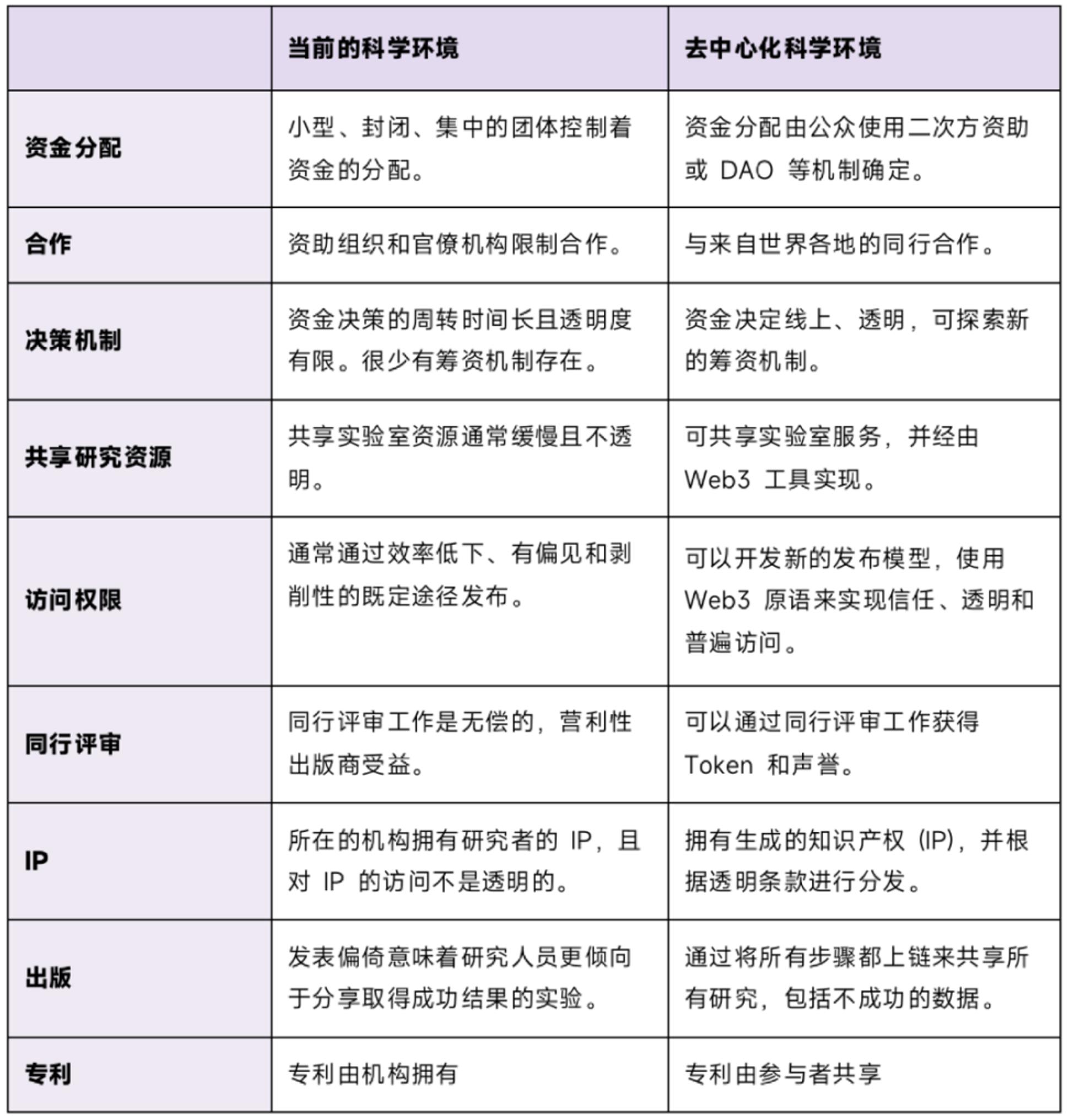
DeSci vs. Traditional Scientific Environments
DeSci offers a more decentralized, transparent, and collaborative research environment, contrasting sharply with the traditional, centralized, and closed-door nature of conventional science.
Challenges and Future Outlook for DeSci
Current Technical and Operational Challenges in DeSci
-
Peer Review Mechanisms: In DeSci, peer review remains a critical quality control step. For example, Ants-Review proposes a blockchain-based incentive protocol to address the cost, inefficiency, and centralization of traditional peer review. However, challenges remain—such as determining reviewer qualifications and preventing malicious behavior or cheating.
-
Funding Research Projects: While blockchain enables new “crowdfunding” models, financing large-scale research projects remains challenging. Small projects may use NFR (non-fungible rights) models, but major initiatives typically require national-level investment.
-
Privacy Protection: DeSci must balance transparency and collaboration with data confidentiality. Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology plays a key role here.
-
Diverse Participation: The composition of DeSci communities reflects existing demographics in crypto and science, where women and other underrepresented groups are lacking. This includes disparities in gender, race, geography, and socioeconomic background. Lack of diversity may introduce bias and limit research scope. To improve inclusivity, DeSci projects must actively attract and support broader participation—through education, partnerships, and ensuring diverse voices in decision-making.
Long-Term Impact and Potential Development Paths
-
Innovative Fundraising Models: Platforms like Gitcoin use new mechanisms such as quadratic funding to support projects.
-
Intellectual Property Management: Projects like Molecule pioneer new IP management models through IP-NFTs.
-
Data Market Development: Open data markets will foster new collaboration models. Innovative database structures like DBDAO allow individuals to benefit from their own data.
-
Importance of Emergency Funding: DeSci’s ability to rapidly fund research during emergencies—such as the COVID-19 pandemic—is crucial. Traditional government funding follows annual budget cycles, which lack flexibility in crises. In contrast, DeSci’s decentralized nature allows rapid mobilization of resources toward critical research. This speed and agility make DeSci a potentially vital tool for responding to global health emergencies in the future.
Promoting Integration Between DeSci and Traditional Science
-
Transparent Fund Management: Drawing from DeFi experience, DeSci can achieve more efficient use of research funds.
-
Optimized Resource Sharing: Smart contracts can facilitate easier sharing of research equipment and other resources, promoting efficient utilization.
-
Global Collaboration: Decentralized science leverages blockchain to foster international cooperation, especially for projects requiring global environmental data.
-
Application of AIGC Technology: Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) can boost productivity in scientific writing and improve the presentation of research findings.
-
Promoting Open Science and Interdisciplinary Collaboration: DeSci supports and strengthens the concept of open science—making research and data accessible to all, increasing transparency and reach. This improves research quality and impact. DeSci encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration by breaking down traditional barriers using blockchain and smart contracts. Such collaboration is essential for solving complex global problems like climate change and public health crises.
Conclusion and Recommendations
-
For research institutions and investors, DeSci offers a novel approach to fundraising and project management. The case of VitaDAO shows how research projects can receive funding from specialized DAOs and be governed through member voting. This model provides researchers with transparency in fund allocation and allows funders direct involvement in decision-making.
-
DeSci’s current focus is on solving issues of funding, organization, and transparency in scientific research. By leveraging blockchain’s transparency and immutability, DeSci introduces a new model for funding and managing research. This could foster closer collaboration between research institutions and private funders, helping bridge the so-called “valley of death” between basic and clinical research. It may also offer young scientists greater support for non-traditional research paths.
-
DeSci significantly improves the efficiency of academic publishing. Through decentralized peer review and publishing, it reduces publication time and complexity, accelerating the dissemination of scientific knowledge. By providing an open, transparent platform, DeSci alleviates monopolistic tendencies in traditional academic publishing, increasing publishing diversity and offering more researchers opportunities to publish—thus promoting pluralism and democratization in science.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News