Can inscriptions under ecological empowerment carve out a new赛道?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Can inscriptions under ecological empowerment carve out a new赛道?
This article thoroughly explores the dynamics of the Bitcoin inscriptions space and examines the development of inscriptions empowered by the ecosystem.
Author: Stanley, Kernel Ventures
TL;DR
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the development trends and characteristics of various protocols within the Bitcoin inscription space.
-
Analyzes Bitcoin-based protocols such as Ordinals, BRC20, Atomicals, RGB, and Pipe, comparing them with other PoW chains like Dogechain and Litecoin, as well as Ethereum's Ethscriptions and Evm.ink, and Solana’s SPL20 protocol across dimensions including fees, divisibility, scalability, and user adoption—highlighting particularly the low fees and high scalability of the RGB protocol.
-
Examines market and product evolution in the inscription ecosystem, noting that with mature wallet infrastructure and the launch of AMM DEXs on Bitcoin, more advanced functionalities such as lending and derivatives may emerge. UniSat’s open API interface enables a wide range of tooling projects.
Overall, this article offers a comprehensive analysis of the dynamic developments in the Bitcoin inscription landscape, projecting future growth driven by ecosystem empowerment and providing readers with a thorough understanding and outlook.
Market Background of Inscriptions
Market Context
Since the emergence of the Bitcoin Ordinals protocol in January 2023, BRC20 and other Ordinals assets have sparked a wave on the Bitcoin blockchain, often referred to as the "retail investors' paradise." This is due to the Fair Launch model of inscriptions like BRC20, where all tokens are minted directly by retail users—no institutions, no project teams, and no insider allocations. For instance, Ordi had a minting cost of about $1 per inscription but surged to $20,000 after listing on Gate.io, fueling immense popularity for the BRC20 protocol. This attracted numerous Ordinals enthusiasts into BRC20, causing Bitcoin network gas fees to skyrocket, reaching peak confirmation fees as high as 400 s/vB—the highest level in over three years.
Starting from this point, this article explores the inscription ecosystems across various blockchains and their respective protocols, while also forecasting the developmental trajectory of inscriptions under ecosystem empowerment.
Data Overview
The three-year Bitcoin block fee chart clearly shows sharp spikes in May–June and November of this year, reflecting strong user enthusiasm for inscription protocols. Not only BRC20, but multiple protocols built on the Bitcoin network launched during these periods, contributing to a “Bitcoin Summer.”
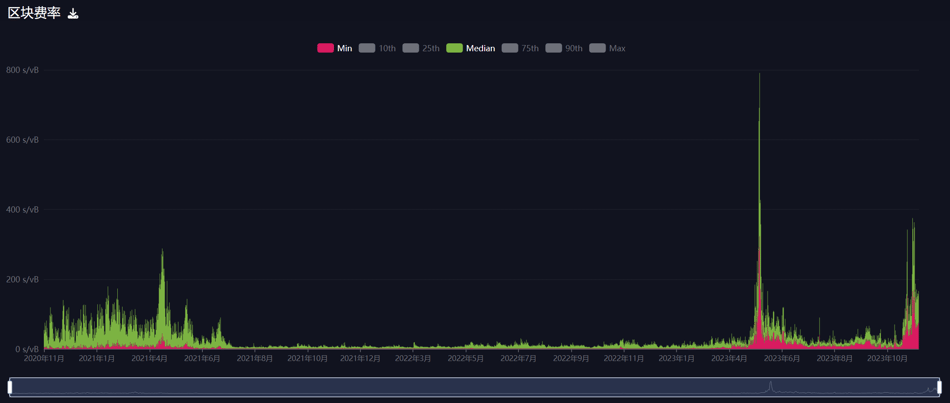
Bitcoin transaction fees over the past three years. Source: Mempool.space
From the data on inscription mints, the number of mints has stabilized at a high level.
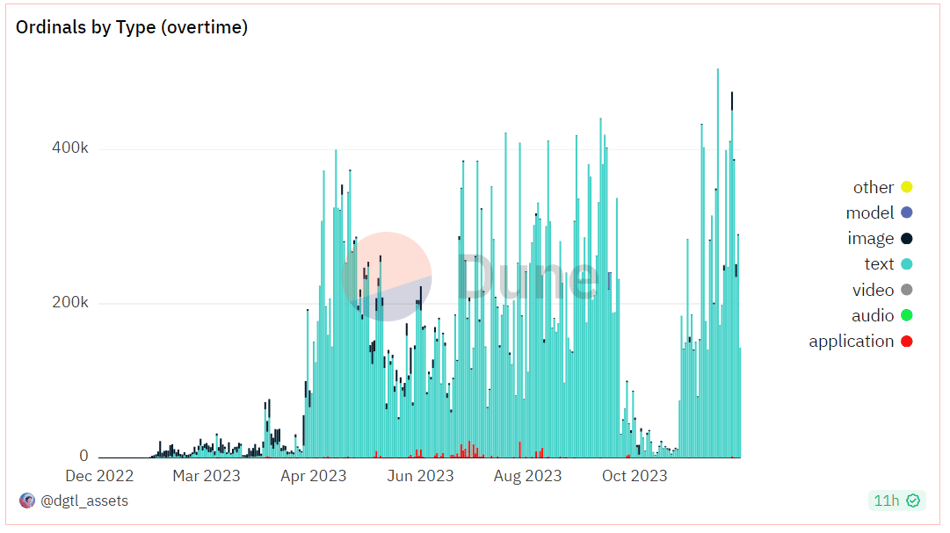
Ordinals inscription mint count. Source: Dune @dgtl_asserts
Sector Analysis
This article categorizes and analyzes inscription protocols by blockchain.
Bitcoin Chain
Ordinals / BRC20 Protocol
On January 21, 2023, Bitcoin developer Casey Rodarmor introduced the Ordinals protocol, enabling metadata to be inscribed onto the Bitcoin chain with sequential numbering. In March of the same year, Twitter user @domodata published the BRC20 protocol, which evolved token minting into string-based on-chain operations. On November 7, Binance listed the leading BRC20 token $ORDI, driving its price up nearly 100% in a single day.
As the first inscription protocol, Ordinals still faces several challenges:
-
BRC20 supports only four-character tickers, limiting flexibility
-
Ticker names are vulnerable to Sybil attacks, and mint transactions can be frontrun
-
The Ordinals protocol generates significant redundant data on the Bitcoin network
For example, after BRC20 minting concludes, tokens are transferred via inscription transfers, rendering the original mint inscription invalid—occupying substantial data space. This redundancy is one reason early Bitcoin purists oppose supporting Ordinals.
Atomicals Protocol
Atomicals’ ARC20 uses one satoshi to represent a deployed token and removes the four-character limit, enabling more diverse use cases. A notable project is Realm, where each registered name acts as a prefix, granting the owner pricing rights over all suffixes. At a basic level, Realms serve as payment addresses (payment handles); extended applications include community/DAO building, identity verification, and social profiles—fully aligning with our vision for DID (Decentralized Identity) development.
However, ARC20 and $ATOM remain in early stages, awaiting further development of wallets and markets.
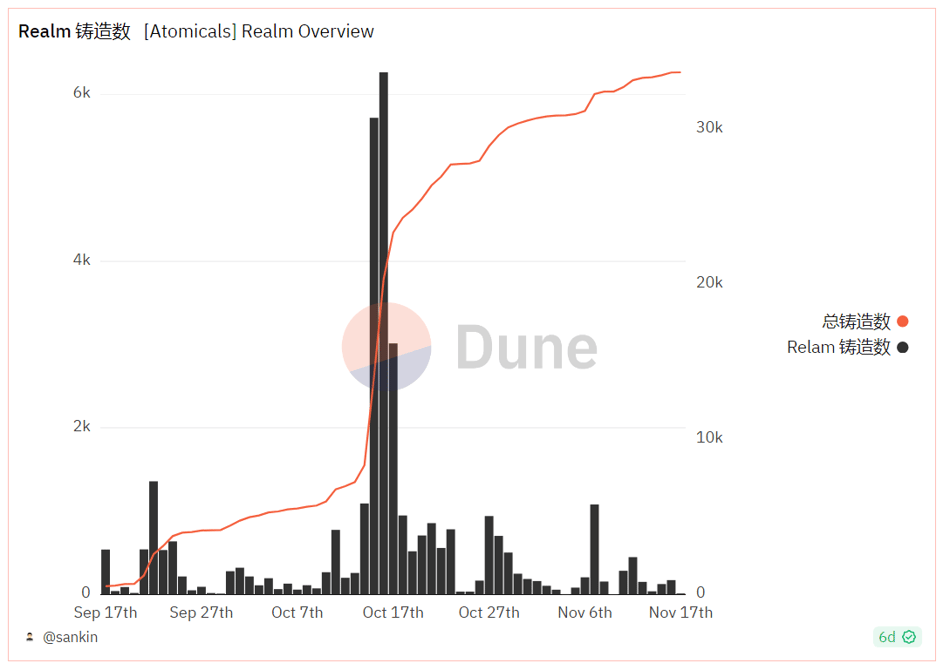
Realm mint count. Source: Dune @sankin
Pipe Protocol
Casey, the founder of Ordinals, proposed Rune—a dedicated method for issuing fungible tokens (FTs) through inscriptions—allowing direct embedding of token data (including Token ID, output, and amount) into UTXO scripts. Rune's implementation closely resembles ARC20, delegating token transfers directly to the BTC mainnet. The key difference lies in Rune writing token quantities directly into script data.
Rune was initially just a concept, but the founder of #Trac implemented it into the first working protocol and issued PIPE. Leveraging Casey’s reputation, PIPE inherited the hype from BRC20 and quickly completed its initial speculative cycle. While Rune holds greater legitimacy than BRC20, gaining acceptance from the broader BTC community remains challenging.
RGB Protocol
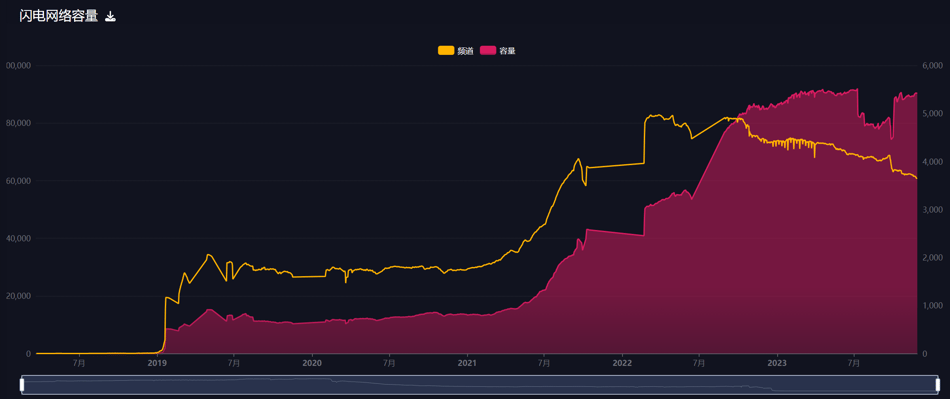
Lightning Network capacity. Source: Mempool.space
As the Ordinals protocol elevated Bitcoin’s ecosystem activity, increasing attention has turned toward the Lightning Network due to its near-zero fees and theoretical throughput of 40 million TPS.
RGB is a smart contract system built atop BTC and the Lightning Network, representing one of the ultimate scaling solutions—though progress is slow due to its complexity. RGB converts a smart contract’s state into a compact proof stored in the output script of a BTC UTXO. Users verify the contract state by checking this UTXO. When the state updates, a new UTXO stores the updated proof.
All smart contract data resides off-chain, managed by dedicated RGB nodes that maintain full contract records and handle computation. Users scan the entire BTC chain’s UTXOs to confirm the validity of state transitions.
RGB can be viewed as a Layer 2 for BTC, leveraging Bitcoin’s security while operating off-chain. However, as the number of contracts grows, demand for UTXO data encapsulation increases, inevitably leading to growing redundancy on the BTC blockchain.
Since 2018, RGB has remained in active development without speculative appeal. Tether, the issuer of USDT, is a major proponent and has expressed intentions to reissue large amounts of USDT on Bitcoin via RGB.
In terms of products, Bitmask is currently the dominant wallet, supporting Bitcoin and Lightning Network deposits and withdrawals, and handling RGB-20 and RGB-21 assets. It is the most widely used wallet available. Bitlight Labs is actively developing the RGB network, aiming to build its own wallet suite and write native smart contracts for a DEX. The project has already acquired BitSwap (bitswap-bifi.github.io) and plans to integrate it into the RGB network.
RGB’s greatest advantage lies in its extremely low transaction fees and exceptional scalability. Historically, smart contract development on Bitcoin was difficult and largely ignored. But with Ordinals boosting Bitcoin’s ecosystem visibility, more developers are beginning to experiment with RGB smart contracts—written in Rust and incompatible with Ethereum, resulting in higher learning curves and requiring technical evaluation over time.
For more technical details on the RGB protocol, Kernel Ventures previously published an article.
Other PoW Chains
When Bitcoin inscriptions gained massive traction, other PoW chains—sharing the same UTXO-based transaction model—also saw migration of Ordinals-like protocols. This section focuses on Dogechain and Litecoin, two chains with relatively high market adoption and development maturity.
Dogechain
Drc-20 is a Dogecoin-based protocol inspired by Ordinals, offering similar functionality to Bitcoin. Its appeal stems from low transfer costs and strong meme culture alignment, making it popular among users.
Litecoin
LTC20 follows the same principle—an Ordinals-inspired protocol on Litecoin. Backed by official Litecoin support and promoted by founder Charlie Lee, LTC20 enjoys strong credibility. Markets like Unilit and Litescribe, along with the Litescribe wallet, show high development maturity. The first token $Lite has already been listed on Gate.io.
However, prior to index implementation, the protocol lacked proper indexing. After introducing indexing, an inflation bug emerged—but it has since been fixed. As shown below, LTC20’s launch caused a sharp spike in Litecoin network fees.
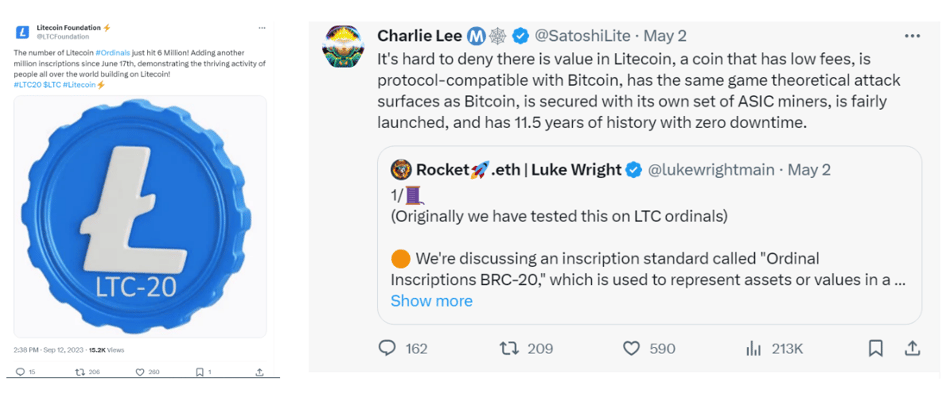
Source: Twitter, Charlie Lee @SatoshiLite
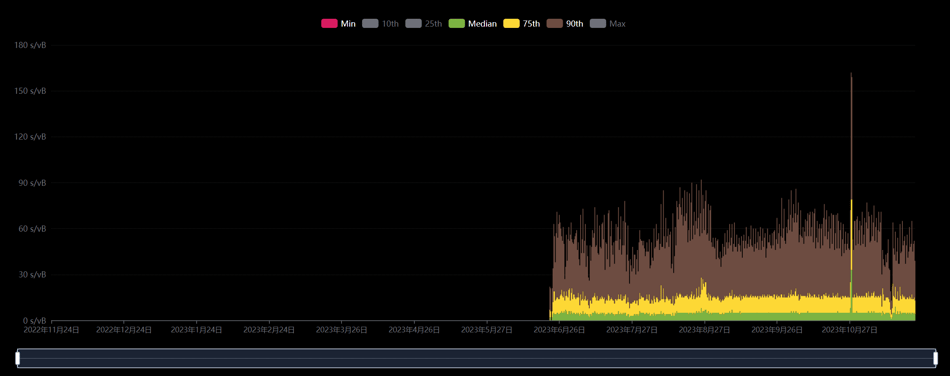
Litecoin fees over the past year. Source: Litecoinspace
Ethereum Chain
Ethscriptions
To date, the Ethscriptions marketplace Etch has achieved trading volume of 10,500 ETH. The first token, Eths, has a floor price of $4,300—up from less than $1 at initial minting on June 18. Early adopters who held throughout have realized returns exceeding 6,000x.
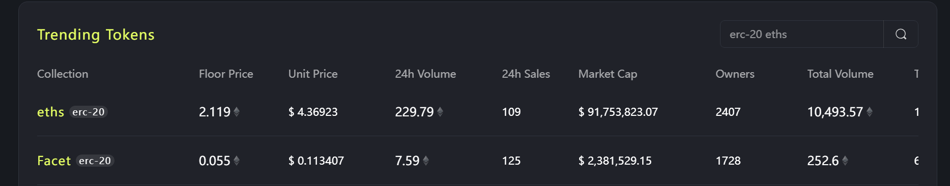
Eths trading data. Source: ETCH Market
Tom Lehman proposed a novel Ethereum scaling solution on August 8, utilizing Calldata expansion and an Ordinals-like inscription technique to drastically reduce mainnet gas fees while enabling rich application layers—this is Ethscriptions.
At the core of Eths is the Ethscriptions Virtual Machine (ESC VM), analogous to Ethereum’s EVM. ESC VM features “Dumb Contracts”—simple, non-upgradable contracts—that free Eths from being limited to NFT speculation and enable functional, practical use cases. This positions Eths as a foundational layer competing directly with traditional Layer 2 solutions.
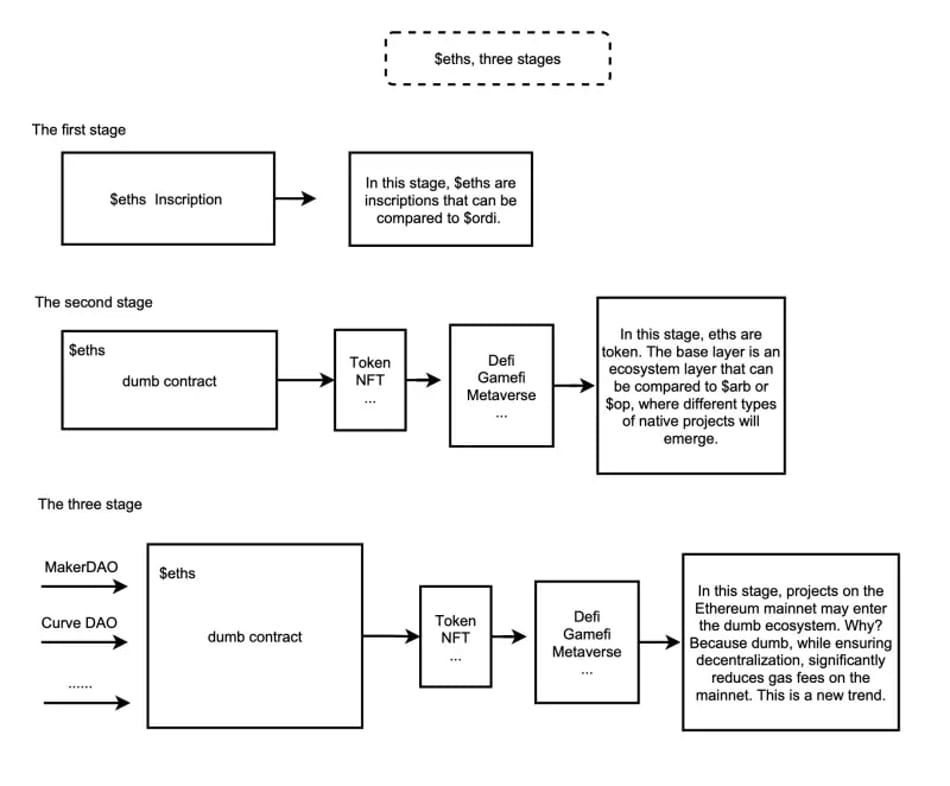
Dumb Contract execution logic. Source: Ethscriptions ESIP-4 Proposal
“Eths represents another approach to Ethereum Layer 2—whereas L2s are separate chains that could potentially have backdoors, Eths operates directly on the Ethereum mainnet with fees as low as L2s. All mainnet functionalities—Swaps, DeFi, GameFi—can be implemented on Eths. Most importantly, because it runs natively on the mainnet, it cannot be censored or shut down, making it more secure and decentralized than conventional L2s.” — From the Eths community.
However, this new L2 narrative is still incomplete. Token splitting is still under development—current inscriptions remain NFTs and cannot yet be divided into fungible tokens (FTs).
As of the latest update, FacetSwap has launched a split function on its website. However, testing reveals that mainstream marketplaces do not yet support split inscriptions—compatibility will require future upgrades. Currently, split inscriptions can be swapped and added to liquidity pools on FacetSwap. All actions are parsed by a virtual address (non-existent) 0x000...Face7. Users simply embed messages in IDM and send hexadecimal data to the Face7-ending address to perform approve, transfer, and other operations. Given its early stage, ongoing monitoring is advised.
Other EVM Chains
Evm.ink
Evm.ink ports the Ethscriptions standard to other EVM-compatible chains, enabling inscription minting and index construction across alternative EVM ecosystems. Recently trending tokens like POLS and AVAL rely on Evm.ink (i.e., Ethscriptions) standards for indexing and recognition.
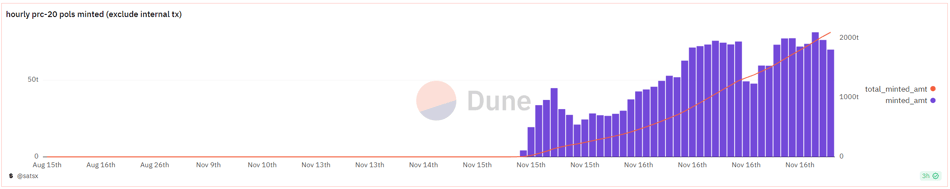
POLS mint data. Source: Dune @satsx
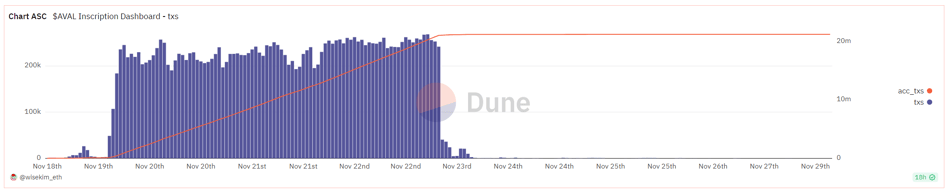
AVAL mint data. Source: Dune @helium_1990
Both POLS and AVAL have a total supply of 21 million. POLS has over 80,000 holders, AVAL over 23,000. Minting was completed within 2–3 days, indicating strong participation interest in low-cost Layer 2 inscriptions due to high ROI. This trend has led to gas spikes not only on these chains but also on Heco and Fantom, all linked to inscription activity.
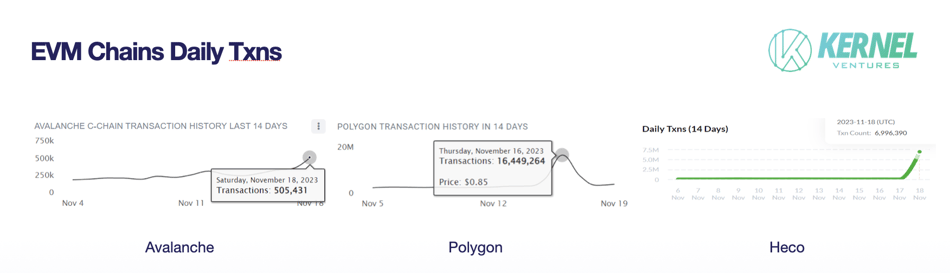
Daily transactions on EVM chains. Source: Kernel Ventures
Solana Chain
SPL20
Solana inscriptions began at 4 AM on November 17 and were completed by 8 AM, with a total of 21,000 inscriptions. Unlike other networks, the inscription entity here is an NFT, while Index Content constitutes the actual inscription. NFTs can be created on any platform, and indexing depends on the hash of the associated image/file. Additionally, embedded text must match—only entries matching both hash and text are considered valid inscriptions. Images are stored off-chain, while text is on-chain. Major minting platforms use IPFS, though some employ AR.
Like Eths, Solana inscriptions’ biggest flaw is lack of divisibility. Without splitting capability, they remain essentially NFTs—lacking the liquidity and operational convenience of fungible tokens, let alone supporting future visions like DEX swaps.
The protocol was founded by the creator of TapPunk on the Tap protocol. The leading minting platform, Libreplex, is highly active—since launch, the team has rapidly developed features including hash indexing, immutable attribute modification, and even live-coding sessions and Q&As in their Discord. The marketplace Tensor is already integrated, and development velocity is extremely fast.
The first inscription, $Sols, had a mint cost of ~$5, reached a secondary market high of 14 SOL, and as of writing, sits at a floor price of 7.4 SOL (~$428). Daily volume exceeds 20,000 SOL (~$1.2M), showing strong trading activity and turnover.
Core Comparison
Comparison of Core Protocols
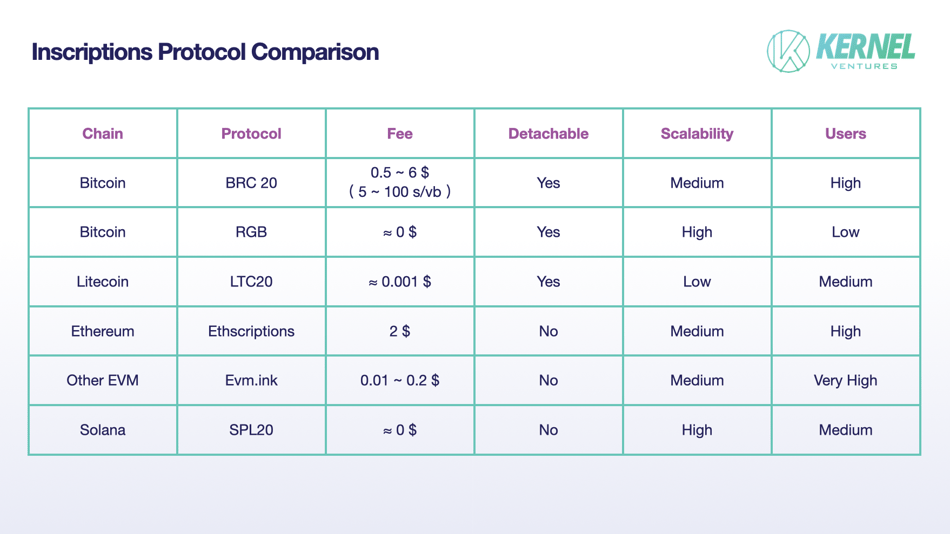
Comparison of major inscription protocols. Source: Kernel Ventures
This chart compares major inscription protocols across four dimensions: fees, divisibility, scalability, and user count. As shown, RGB leads in fee efficiency—leveraging the Lightning Network’s near-zero fees, enabling virtually costless transactions.
-
Regarding divisibility, recent protocols on Solana and EVM chains currently lack splitting capabilities, pending future development.
-
In scalability, RGB’s smart contract functionality grants it immense extensibility. Solana’s scalability remains to be seen, though both the team and Solana Foundation express support—suggesting room for positive development.
-
In terms of users, EVM chains benefit from naturally low gas fees, lowering user trial barriers and attracting larger communities. BRC20, as the first inscription token, holds top legitimacy and thus maintains a large user base.
Protocol Token Data Comparison
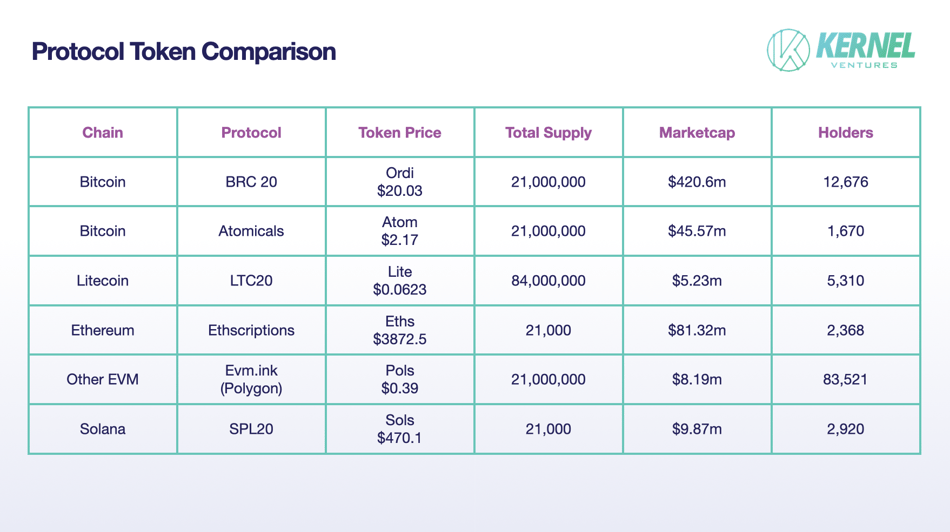
Protocol token comparison. Source: Kernel Ventures
Analyzing major protocol tokens, we see current market caps hovering around $600 million (excluding smaller-cap tokens). $ORDI alone accounts for 80% of total value, indicating vast growth potential for other protocols. Moreover, RGB and others are still under development and have not yet issued tokens.
In terms of holder count, Pols and Ordi lead, while others lag. Since Eths and Solana inscriptions haven’t been split yet, holder analysis should await future developments.
Innovation and Risk Analysis
Currently, the primary use of inscriptions is Fair Launch, allowing equitable access to project participation. However, the sector cannot remain stagnant at fair launches alone.
Recent developments in the inscription space demonstrate remarkable vitality and innovation, fueled by key Bitcoin technological advancements—SegWit, Bech32 encoding, Taproot upgrade, and Schnorr signatures—which have enhanced transaction efficiency, scalability, and programmability.
For example, RGB’s smart contracts—if implemented on Bitcoin’s Lightning Network—could achieve extremely high TPS (40 million) while benefiting from Bitcoin’s massive security and ecosystem.
On the risk side, caution is needed regarding certain launchpads. Following the success of MUBI and TURT, many new launchpads have emerged, some of which executed rug pulls immediately after IDO. Always read whitepapers carefully, research backgrounds thoroughly, and avoid FOMO-driven decisions based solely on influencer endorsements.
Future Outlook for the Inscription Ecosystem
Market Projection
Galaxy Research and Mining predicted that by 2025, the Ordinals market cap would reach $5 billion—with only 260,000 inscriptions at the time. Today, inscription counts have soared to 33 million—an increase of 126x in just six months. Meanwhile, $Ordi’s market cap has reached $400 million, and $Sats has hit $300 million. Clearly, earlier market forecasts were vastly underestimated.
Product Projection
Currently, BRC20 trading activity is concentrated on OKX and UniSat. OKX’s Web3 wallet, heavily promoted this year, offers excellent user experience for BRC20 asset trading. With robust wallet infrastructure, the onboarding path for casual investors (“mama-tier speculators”) has become smoother and shorter, enabling easier entry into this new market. As new protocols emerge, each brings its own marketplaces and wallets—such as for Atomicals, Dogechain, Litecoin, etc. However, most existing wallets are modified versions of UniSat, forked from its open-source code. Comparing Bitcoin (PoW) with Ethereum, we can view different protocols as different chains—whose fundamental distinction lies only in Chain ID. Therefore, future products may involve UniSat integrating multiple protocols, allowing seamless switching between them within a single wallet—similar to MetaMask’s chain-switching feature.
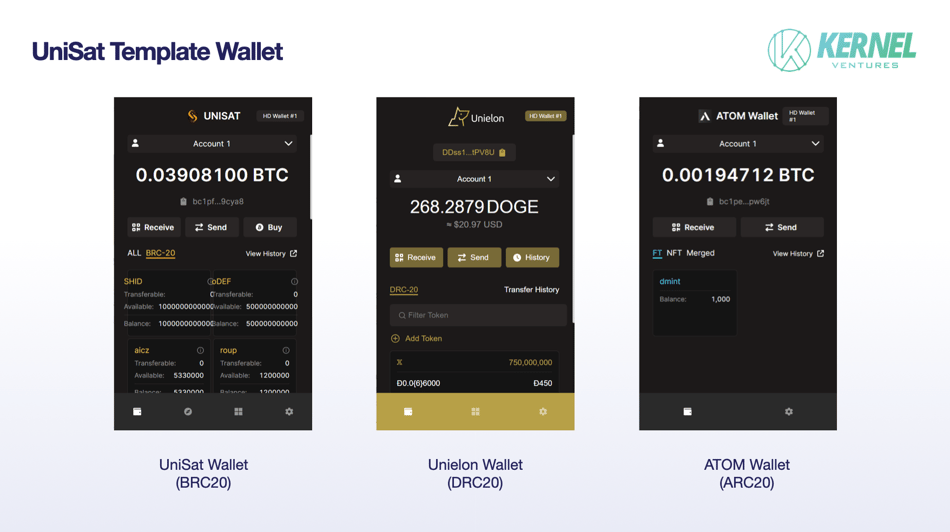
Comparison of protocol wallets. Source: Kernel Ventures
Sector Projection
As capital flows into the inscription market, users are moving beyond meme speculation and turning toward inscription-based applications. UniSat has introduced innovations for BRC20—via BRC20-Swap, users can now exchange BRC20 tokens as easily as on an AMM DEX. As the first product enhancing liquidity in the Ordinals ecosystem, it unlocks Bitcoin’s DeFi potential. More advanced features like lending and derivatives may follow. Recently, UniSat opened its API, greatly benefiting small developers by enabling functions such as automated batch buying, inscription monitoring, and auto-minting—spawning numerous tooling projects.
Bitcoin’s transaction fees are relatively high. While Stacks and RIF offer lower fees as Bitcoin Layer 2s, they suffer from small user bases and immature infrastructure. Hence, a Bitcoin EVM presents a compelling narrative.
Take BEVM, for example—a Bitcoin Layer 2 built on Ethereum—with BTC as its native token. Users can bridge BTC from the mainnet to BEVM via an official cross-chain bridge. BEVM’s EVM compatibility drastically lowers the barrier for building applications, allowing easy migration of DeFi, Swap, and other dApps from other EVM chains.
However, Bitcoin EVMs face critical questions: Can bridged assets maintain decentralization and non-inflation? How is node sequencing consensus achieved? And how are transactions synchronized back to the Bitcoin network (or decentralized storage)? Given the low entry barrier of EVM chains, security risks rise accordingly—this should be the top concern for anyone exploring Bitcoin EVMs.
Source: BEVM Bridge
Conclusion
This article provides an in-depth examination of trends and protocol characteristics in the Bitcoin inscription space. By analyzing Bitcoin-based protocols such as Ordinals (BRC20), Atomicals, RGB, and Pipe alongside PoW chains, Ethereum’s Ethscriptions and Evm.ink, and Solana’s SPL20, we compare their differences in fees, divisibility, scalability, and user adoption. We conclude that divisibility remains a bottleneck, while among Bitcoin-based protocols, RGB stands out as the most comprehensive and promising.
In reviewing the market context, starting with the Ordinals protocol, inscription protocols like BRC20 triggered a wave dubbed the “retail investors’ paradise.” Through analysis of Bitcoin block fee charts and Ordinals minting data, we gain insight into the evolutionary trajectory of the inscription ecosystem.
In sector analysis, comparisons of core attributes—fees, divisibility, scalability, and user count—reveal key similarities and differences among leading protocols. Finally, through comparative analysis of protocol token metrics and core protocols, we assess market caps and user distributions. The discussion concludes with insights into innovation and risks, emphasizing the vibrancy and creativity within the inscription space.
Looking ahead, the inscription field is poised to witness continuous technological innovation, enabling increasingly complex real-world applications. Market growth is expected to remain robust, offering abundant opportunities for investors and participants. Meanwhile, more creative projects and protocols are likely to emerge, further enriching the inscription ecosystems across Bitcoin and other public blockchains. Miners may also see increased revenues, as the inscription space opens new income streams for them.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News