Interpreting Injective (INJ): A Comprehensive SWOT-Based Assessment of the DeFi Project
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Interpreting Injective (INJ): A Comprehensive SWOT-Based Assessment of the DeFi Project
Researcher Andrey Didovskiy will conduct a SWOT analysis of Injective (INJ), a blockchain built for DeFi using the Cosmos SDK.
Author: Andrey Didovskiy
Compiled by: TechFlow
Note: SWOT analysis is an evaluation of operations/fundamentals, not a model for technical or trading purposes. (NFA, DYOR)
The SWOT analysis framework consists of four elements: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It provides excellent high-level insight into assessing a project's health. It can help make decisions about which areas need more attention, set performance goals, and organize fundamental understanding of the project’s direction.
Although SWOT analysis is rarely (if ever) used in the cryptocurrency space, now is the time to apply this time-tested evaluation method to the digital asset domain.
Today, researcher Andrey Didovskiy will conduct a SWOT analysis on Injective (INJ), a blockchain built specifically for DeFi using the Cosmos SDK.
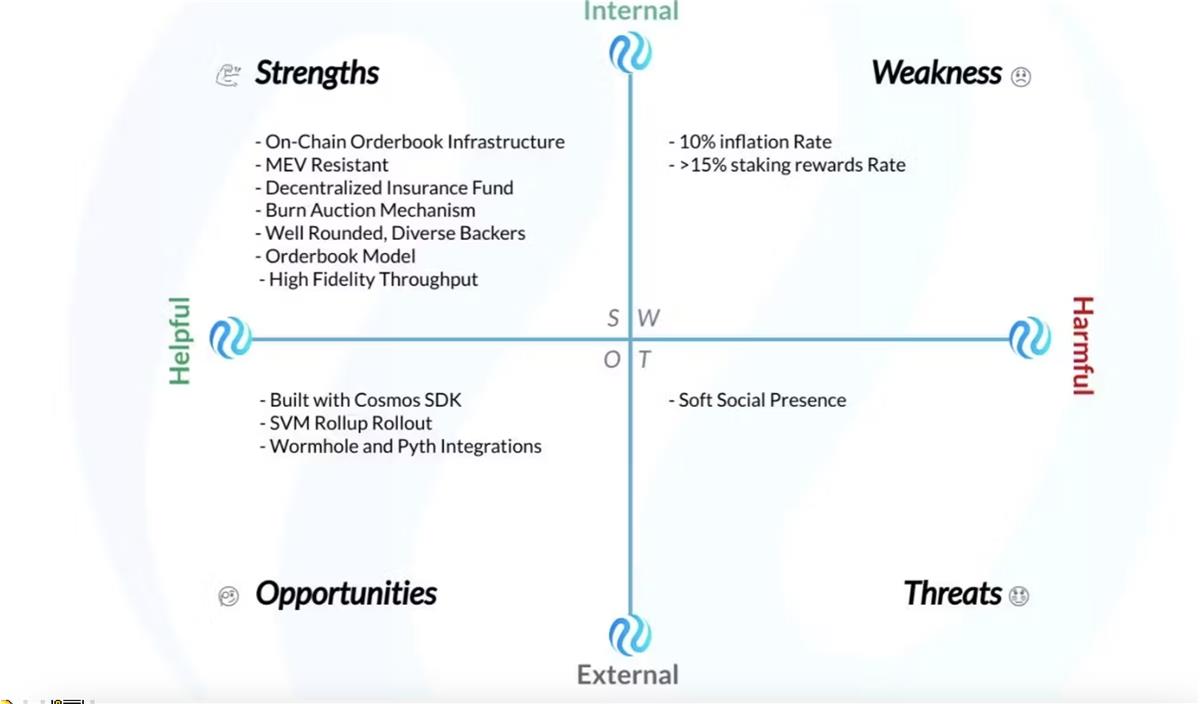
Strengths (Internal)
Fully On-Chain Order Book Infrastructure
While many DEX projects boast about their decentralization, they often fail to disclose the extent of it. In reality, most DEXs are decentralized only at the asset custody level—meaning users retain control over their funds, but the exchange itself processes all activities within a closed, centralized environment. Injective takes a more radical approach by deploying key application infrastructure of the order book (order creation, acceptance, and matching) fully on-chain.
MEV Resistance
MEV is one of the biggest challenges in on-chain finance. Injective combats MEV on its chain through two features: FBA (Frequent Batch Auctions) and the Skip protocol. Injective has long used FBA, whose effectiveness against MEV rests on three principles. First, activity is published in batches rather than individual transactions, eliminating the possibility of transaction reordering or sandwich attacks. Second, there is a uniform clearing price, which removes priority by enforcing trades at a hard-coded settlement price set by the protocol. Third, all submissions undergo a sealed-bid auction after submission, solving front-running issues. The Skip protocol is an open-source solution that allows a round of bidding before batches/transactions are finalized, redistributing profits to users and stakers instead of searchers, sequencers, and miners.
Decentralized Insurance Fund
As a permissionless protocol, Injective allows users to create their own on-chain derivatives markets. However, derivatives markets are generally considered highly risky, and building them in a decentralized environment is tricky because full liquidations could leave profitable traders unable to withdraw profits. Recognizing this, Injective has implemented decentralized insurance funds deployed per individual market. These funds provide settlement guarantees and mitigate the impact of potential liquidations.
Burn Auction Mechanism
Token burning is a widely adopted module in crypto tokenomics, yet most implementations are fairly basic forks. Injective designed its own novel "burn auction" mechanism, where 60% of all transaction fees are collected and deposited into a vault (a basket of various assets). Once a week, this vault is auctioned off to members of the Injective community in exchange for INJ tokens. The winning bidder receives the vault’s assets, while the INJ tokens used in the bid are permanently burned.
Broadly Diversified Backers
Injective has received significant credibility and financial backing from some of the industry’s most prominent names, including Pantera Capital, Binance, Jump, and Mark Cuban.
Order Book Model
Unlike the vast majority of DEXs that use the heavily hyped AMM trading model, Injective employs the traditional order book matching model. While AMMs do have certain advantages, the order book offers users infinitely higher granularity and gives them greater control over their assets. Given institutional and enterprise familiarity with order books in traditional finance, they are likely to prefer operating in environments built on models they already know work effectively.
High-Fidelity Throughput
Leveraging a PoS mechanism capable of handling ~10,000+ TPS and processing blocks in approximately 1.1 seconds, Injective achieves exceptional operational efficiency and transaction throughput.
Weaknesses (Internal)
10% Inflation Rate
Given that this inflation rate is not permanent and INJ caps maximum supply at 100,000,000 tokens, this is certainly not a dealbreaker. Currently, circulating supply is around 80,000,000, so we can expect the remaining ~20,000,000 INJ tokens to enter the market over the next 2–2.5 years; afterward, the inflation rate will be suspended. This doesn’t indicate negative project development, but it may exert potential downward pressure on price appreciation.
15% Staking Reward Rate
Consistent with the high inflation rate, the elevated staking reward rate could affect upward price momentum, as stakers/network participants might engage in large-scale sell-offs. While current staking participants appear to be experienced long-term holders who won’t jeopardize the project’s economic well-being for short-term gains, contingency plans must account for unexpected scenarios—if any major staker coordinates an exit from the Injective network, their oversized INJ holdings could trigger adverse price action.
Opportunities (External)
Built Using Cosmos SDK
As part of the Cosmos IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) ecosystem, Injective holds immense future potential to become a highly interoperable network capable of seamless, fluid cross-chain activity. Additionally, by using the Cosmos SDK, Injective inherits the Tendermint consensus protocol, resulting in instant transaction finality.
SVM Rollup Rollout (Cascade)
Injective is the first project to launch an IBC-compatible environment enabling data sharing between the Cosmos ecosystem and Solana’s Sealevel Virtual Machine. This will enable cross-chain computation and potentially enhance scalability for both chains through shared parallel processing.
Wormhole and Pyth Integration
Injective is the first protocol in the IBC ecosystem to integrate both Wormhole and Pyth. Wormhole is a cross-chain bridge connecting the Solana network and facilitating asset transfers to and from Solana. Pyth is one of the leading oracle networks, providing secure data feeds from some of the world’s largest markets (CBOE, Binance, OKX, Jane Street, etc.). The presence of these two technologies on Injective unlocks theoretically unlimited market potential by enabling Solana-based assets (via Wormhole) and RWA tokenization (via Pyth).
Threats (External)
Low Social Presence
Compared to the strong traditional social media presence of most crypto projects, Injective does not focus on cultivating a robust degenerate community. Although they’ve recently begun expanding their social outreach (e.g., introducing NFTs), simple observational experience suggests their engagement rate is several orders of magnitude lower than comparable-tier projects. I expect this to change, but honestly, it doesn’t matter much—Injective’s primary strategic focus appears to be serving enterprise-grade clients.
Conclusion
Injective is severely undervalued. Within the DeFi space, few innovative leaders offer such a powerful architecture and genuinely differentiated technology while maintaining such a low social profile. This is my first deep dive into Injective’s fundamentals, and after thorough examination and research, I will be adding INJ to my personal portfolio. I’m not yet sure whether I’ll use their technology, but I definitely want exposure to their network.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















