Diving into NFT Market Data: Uncovering New Trends in NFT Market Evolution
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Diving into NFT Market Data: Uncovering New Trends in NFT Market Evolution
Insights into the Development of NFT Trading Markets: What Will Future Trends Be?
Written by: Henry Ang, Mustafa Yilham, Allen Zhao & Jermaine Wong, Bixin Ventures
Translated by: Evan Gu, Wayne Zhang, Bixin Ventures
As more new NFT marketplaces emerge, Opensea’s position as the leading player in the NFT marketplace space continues to be challenged. Intensifying competition has brought about waves of innovation across the sector—projects like X2Y2 and Magic Eden have directly announced they will no longer enforce royalties. Opensea previously collected royalties and even blacklisted NFTs that didn’t pay them. However, with the emergence of X2Y2, Opensea was forced to change its rules. Amid this industry-wide wave of innovation, changes around royalties are just one of many strategies used by NFT marketplaces to maintain price competitiveness. Other strategies include reducing trading fees and incentivizing NFT listings and trades through token airdrops.
As competition heats up, several key questions arise: What will the future of NFT marketplaces look like? Will Opensea continue to dominate the NFT marketplace landscape? First, this article examines the current landscape by comparing three major stakeholders—the direct marketplace represented by Opensea, the aggregator represented by Gem.xyz, and the new market model represented by Sudoswap. Then, we’ll explore existing gaps within NFT marketplace projects and discuss emerging trends that may shape the next generation of NFT marketplaces.
What Are Direct Marketplaces and Aggregators?
Direct Marketplaces
Opensea, X2Y2, Looksrare, and Magic Eden can all be considered direct marketplaces because NFTs are initially listed and traded here. The goal of direct marketplaces is to attract as many creators and users as possible to achieve high trading volume, since their primary revenue comes from transaction fees. Key problems direct marketplaces aim to solve include:
1. Balancing interests between creators and users when enforcing royalties. Marketplaces must maintain royalties to attract NFT creators, but risk alienating small yet active users.
2. Protecting users from malicious NFT projects and phishing sites. With many scammers attempting to steal user assets, direct marketplaces need safeguards in place.
3. Providing stable APIs for Web2 platforms and Web3 aggregators—direct marketplaces act as NFT trading infrastructure and need to integrate seamlessly with other platforms.
AMM NFT Marketplaces
Similar to how Uniswap helped solve liquidity issues in DeFi, new market models like Sudoswap allow users to buy and sell NFTs from liquidity pools instead of peer-to-peer trading. Compared to traditional order book models, AMMs offer several advantages—for example, they provide instant liquidity since trades execute automatically rather than waiting for matched orders on Opensea.
Another key selling point is that AMM-based platforms like Sudoswap are decentralized and fully on-chain, unlike most off-chain order book direct marketplaces. On the flip side, NFT AMMs may not work well with certain NFT categories (such as blue-chip or art NFTs where rarity matters), since sellers often want greater control over pricing. Another downside is that AMMs can be significantly more complex for average consumers, especially non-crypto-native users.
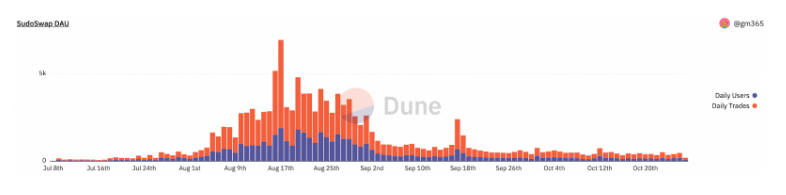
NFT Marketplace Aggregators
Much like DeFi aggregators such as 1inch—which emerged when users struggled to choose the best DEX among many options—NFT aggregators like Gem and Genie allow users to easily purchase NFTs across multiple marketplaces via a single interface. Aggregators also help prevent trade manipulation. As Delphi noted in this article: “Encouraging users to list NFTs at reasonable prices leads to tighter spreads. Tighter spreads mean traders and collectors experience optimal pricing, which creates sticky users and positive feedback loops.” One way to avoid fake or manipulated trading is using an aggregator. When using aggregators, users care about:
1. User Interface: Displaying the best prices across all markets.
2. User Interaction: Optimizing latency, gas fees, and API connections with underlying markets to show real-time price updates.
3. One-stop Tools: Useful features enhancing the buying process, such as analytics, chat boxes, lending, and BNPL services.
Direct Marketplace Analysis: Why Is Opensea Still the King of the Market?
Overview of Top 3 NFT Marketplaces and Emerging Challengers
As an early industry pioneer, Opensea built a large user base from the start thanks to easy creation tools, diverse NFT project offerings, and a navigable directory system. Opensea further leveraged its initial user base by featuring prominent NFT projects and implementing popular features like multi-chain support.
To capture users from Opensea, Looksrare employed a “trade-to-earn” strategy and specifically allocated token airdrops for Opensea traders. In the short term, they captured between 26% and 37.2% of market trading volume. Looksrare also implemented a more decentralized revenue distribution model, allocating 100% of trading fees to $LOOKS stakers. While these incentives boosted trading volume, they also led to massive wash trading. Once incentives declined along with trading volume, Looksrare failed to retain its user base and now holds only about 0.7% of the entire industry’s users.
Similarly, X2Y2 initially attracted users with a “list-to-earn” model and lower trading fees compared to Opensea and Looksrare. This led to another set of problems, including many low-quality NFTs being listed solely to earn rewards. X2Y2 later shifted to a “trade-to-earn” model, again causing a surge in purely incentive-driven trading. Like Looksrare, despite redistributing 100% of revenue back to users, low trading volume and resulting fee earnings were insufficient to retain long-term engagement. At the time of writing, X2Y2 retains only 2.2% of the industry’s users.
Looksrare and X2Y2 weren’t the first to experiment with liquidity mining. Rarible, launched in early 2020, also attempted to attract traders with its $RARI token, but largely met the same fate.
Case Study: Why Rarible Lost Ground to Opensea
By the end of 2020, Rarible had nearly matched Opensea with over 4 million monthly trades.
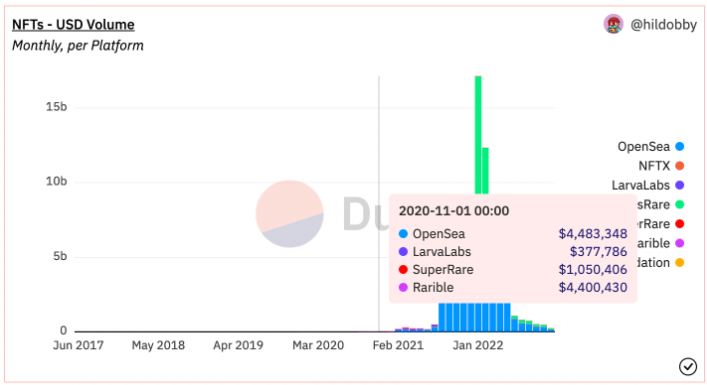
Afterward, the gap between Opensea and Rarible widened significantly, with Rarible losing 75% of its trading volume by the end of Q1 2021. Unlike Opensea, whose proposed IPO route sparked community backlash, Rarible chose to decentralize itself by launching the $RARI token. Following a strategy similar to X2Y2, Rarible’s token incentives drove both trading volume growth and significant wash trading during its early stages. Beyond this, Rarible fell behind due to lack of partnerships with well-known IPs, resulting in lower deployed liquidity, and an inability to handle counterfeit IP NFTs. Meanwhile, Opensea acted faster against fraud, introduced timed auctions, and partnered with multiple IPs, positioning itself as a trusted marketplace. The data below highlights the disparity in popularity: from December 2020 to November 2022, the blue-chip NFT BAYC traded 27,442 times on Opensea versus only 72 times on Rarible.
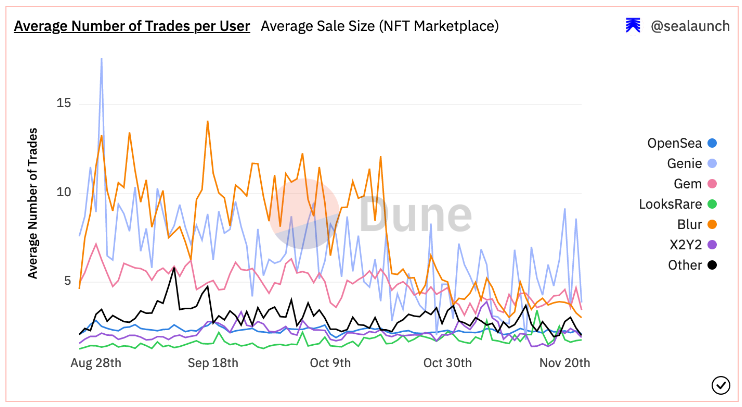
Newer entrants like Blur and Atomic0 are attracting users with zero trading fees, optional royalties, and airdrop incentives. Notably, Blur functions not only as a native direct marketplace but also as an aggregator—a hybrid model we’ll examine in depth later. Blur also uses a “list-to-earn” strategy to incentivize participation. Blur stated that users attempting to game the system—such as listing at unrealistic prices or re-listing “dead NFTs”—will be ineligible for airdrops. Other ways to qualify for $BLUR airdrops include paying royalties and listing blue-chip collections. The actual airdrop will occur in January 2023, and only time will tell if their strategy avoids the pitfalls faced by earlier competitors. From a product perspective, platforms like Blur differentiate themselves through superior UX—real-time display of offers, sales, and metadata; much faster scrolling and loading speeds; and advanced portfolio analytics enabling informed decision-making across multiple NFT marketplaces. Unlike previous rivals, Blur does not follow Opensea’s UI/UX design patterns.
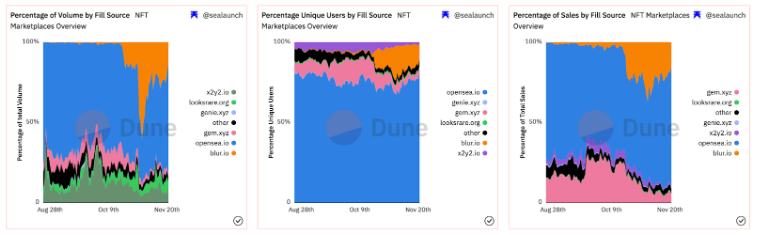
Nevertheless, as of this writing, Opensea remains the dominant platform, holding approximately 72%, 82.7%, and 75.7% of shares in trading volume, unique buyers, and number of transactions, respectively.
How Has Opensea Retained Users Despite New Competitors?
Although Opensea’s market share has declined, it still controls over two-thirds of total trading volume. Over the years, Opensea has undoubtedly built a strong brand moat in the NFT space. For instance, most NFT projects launch officially on Opensea for legitimacy, simply because people recognize and trust the brand. Whether on Twitter or Discord, most projects direct their users to Opensea to purchase NFTs. This results in more projects being listed, which attracts more users, encouraging even more projects to list—creating a flywheel effect.
Ultimately, the battle comes down to liquidity—the marketplace with the most listings wins. Even with poor UX and no token incentives, people still choose to list and buy on Opensea because it's where you'll find the most projects and traders. We believe token incentives are not a sustainable solution, as they attract opportunistic traders without building brand loyalty or product stickiness. Users trade on these platforms not because they believe it’s a good exchange, but merely for incentives. Once those incentives inevitably dry up, they leave. Token incentives may help gain initial traction, but ultimately only solid products and great user experiences can retain users long-term. Historically, this pattern has repeated multiple times—not only in NFT marketplaces, but also in crypto exchanges that adopted similar strategies but eventually collapsed.
Case Study: First-Mover Advantage Isn't Everything—Magic Eden
Given that Opensea was the first NFT marketplace, one might assume its leadership stems solely from first-mover advantage. To assess the value of timing, consider the Solana NFT ecosystem. Magic Eden is currently the leading NFT marketplace on Solana—but contrary to popular belief, it was actually the third marketplace launched on the chain. The first two were Solanart and Digital Eyes in 2021, which initially dominated trading volume. Eventually, Solanart lost community trust following incidents involving fake listings and stolen digital assets, prompting users to shift to Digital Eyes. Magic Eden surpassed Digital Eyes primarily due to its superior UI/UX and overall user experience. It continued strengthening its moat by launching features like a dedicated launchpad for new NFT series and integrating with all wallets on Solana. This is why Magic Eden became the dominant force in the Solana ecosystem, commanding nearly 98% of daily active users at the time of writing.
Product Innovation Drives Growth
From these case studies, we conclude that product-led growth is a sustainable path to capturing long-term market share. Common complaints about Opensea’s UX include high gas and trading fees, high latency, slow interface loading, etc. We believe unless these issues are addressed and better UX delivered, Opensea’s brand equity will continue eroding as platforms like Blur innovate. As mentioned, Blur not only aggregates liquidity from other marketplaces but also enhances convenience. In contrast, while competitors like X2Y2 and Looksrare offer lower trading fees, their general user experience differs little from Opensea. For example, the snapshots below clearly show which marketplace offers a differentiated interface for the BAYC collection. Ultimately, the marketplace offering the best user experience will attract the most listings and traders, building a lasting brand moat.
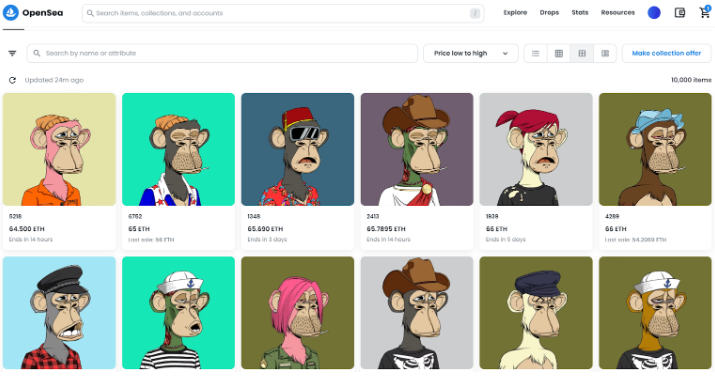
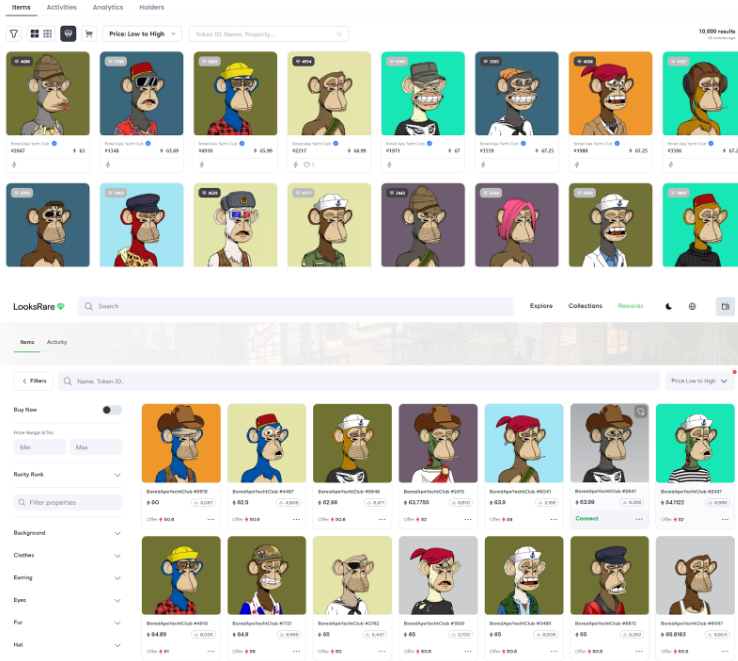
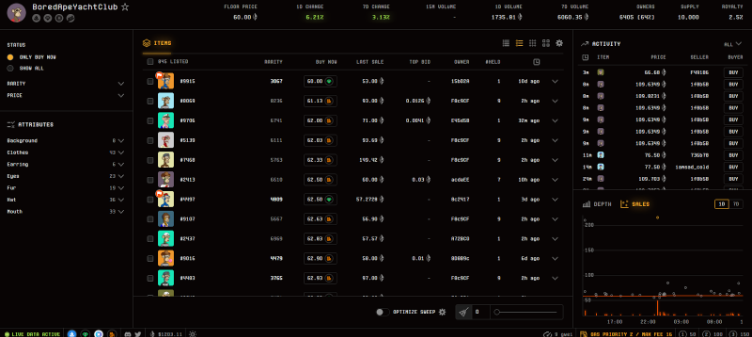
Below is a comparison of key service metrics across several NFT marketplaces:
Opensea (First) |
X2Y2 |
Looksrare |
Magic Eden |
Blur |
Atomic0 |
|
Supported Blockchains |
6 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
User Acquisition Strategy |
First Mover |
List-to-earn Low Fees |
Trade-to-earn Airdrop |
Product Innovation |
Airdrop |
Airdrop |
Trading Fee |
2.5% |
0.5% |
2% |
2% → 0% |
Optional |
Optional |
Strengths |
1. NFT minting tool 2. iOS App 3. Deeper liquidity 4. Fraud and phishing warnings 5. Strong brand
|
1. Powerful analytics dashboard 2. P2P lending |
Discounts on NFT collections |
1. Launchpad 2. iOS App 3. Whitelist tracking 4. Fraud and phishing warnings 5. Creator-focused tools 6. Strong brand |
1. NFT status filters 2. Gas caps 3. Optional royalties 4. Floor sweeping 5. Portfolio tracking |
Flexible/optional royalties |
Weaknesses |
High latency Lack of analytics |
Token utility Business partnerships |
Mispricing Lack of analytics Token utility |
Standardized listings |
Not suitable for retail users |
Not yet launched |
Market Share (Ethereum) |
42% |
40% |
18% |
N.A. |
N.A. |
N.A. |
Users (Ethereum) |
89% |
10% |
1% |
N.A. |
N.A. |
N.A. |
Aggregator Analysis: Why Hasn’t the Aggregator Model Truly Taken Off?
With multiple direct marketplaces available, aggregators make sense by providing consolidated cross-market information. Instead of manually checking Opensea, Looksrare, and X2Y2 for the best price, users can conveniently use an aggregator. However, data shows most trades still occur on Opensea. Although aggregators like Gem and Genie saw initial spikes in volume, their activity has since declined relative to Opensea. Several reasons may explain this. Before diving deeper, it helps to identify two major user segments:
(1) NFT community members who know exactly which collection they want. Their journey typically begins by clicking an official link on Twitter or Discord.
(2) Opportunistic speculators looking for good deals—such as undervalued blue-chip collections or mispriced NFTs.
First, since most NFT projects use Opensea links for legitimacy, community users tend to go directly to Opensea. Second, speculative traders are more likely to use aggregators, as they prioritize finding value over specific collections.
While volumes on Gem and Genie have declined, another aggregator—Blur—has seen a resurgence in trading activity. Of course, it’s too early to say whether Blur has pioneered a successful aggregator model.
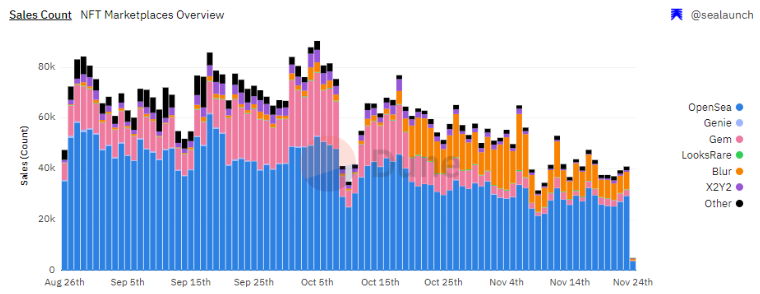
Case Study: How Gem Surpassed Genie to Become the Leader
Genie was the pioneer in the aggregator space but failed to address key product optimizations such as UI/UX layout and high gas costs. Gem, on the other hand, helped users save up to 40% on gas fees.

Currently, Gem has become the largest traffic gateway for direct marketplaces including Opensea, X2Y2, Looksrare, and Larva Labs.
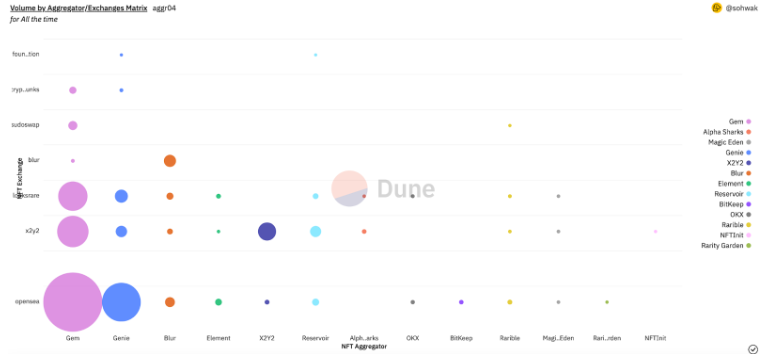
Why Hasn’t Gem Captured a Larger Share?
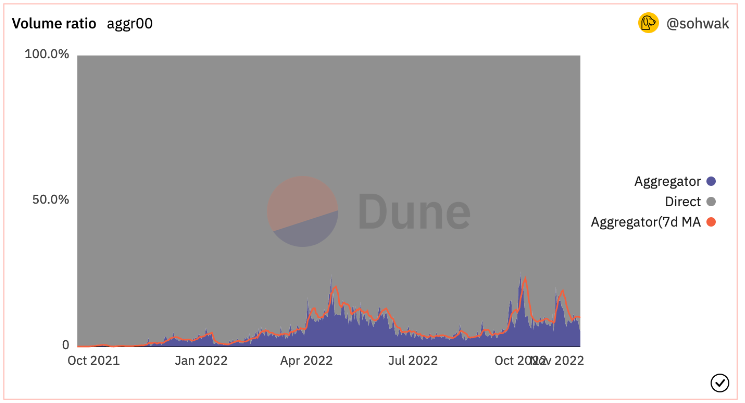
Data below shows that roughly 33% of NFTs are purchased via aggregators. Prior to Blur’s launch, Gem accounted for about 70–80% of all aggregator volume.
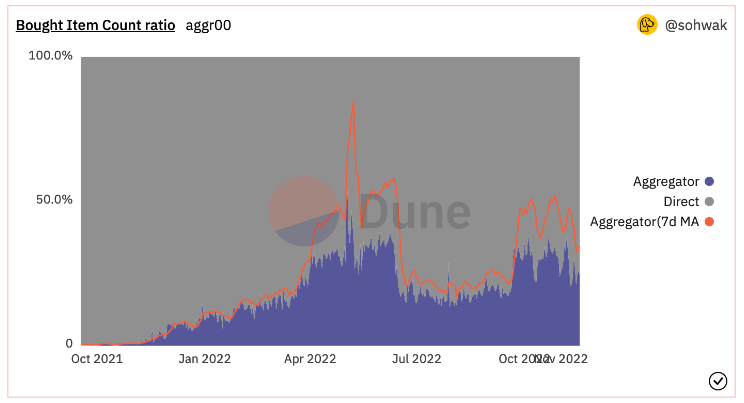
Despite 33% of NFTs being traded through aggregators, interestingly, 90% of transaction value occurs on direct marketplaces. This suggests users prefer trading high-value blue-chip NFTs on direct platforms while using aggregators mainly for lower-value NFTs.
Additional data highlights user segmentation in NFT marketplaces. It shows that less than 5% of users who visit Opensea go on to visit other marketplaces. Conversely, 74.76% of Gem visitors later visit Opensea, and similarly for Blur and Genie (43.76% and 40.55%, respectively).
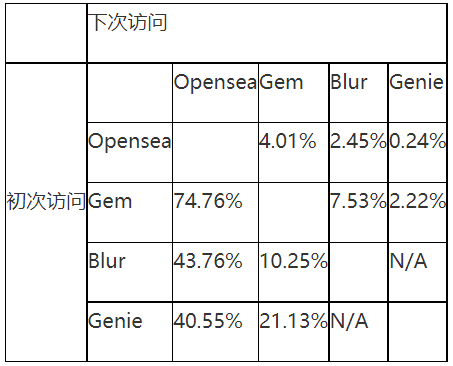
Source: similarweb.com
Can Uniswap’s New Marketplace Compete With Other Aggregators?
Genie was acquired by Uniswap in June 2022 and has recently been integrated into the Uniswap ecosystem. Users can now trade NFTs across various marketplaces—including Opensea, X2Y2, and Sudoswap—via Uniswap. Uniswap’s NFT interface is fully open-source and claims to save users up to 15% in gas costs compared to other NFT aggregators.

Visually, the interface is clean and simple, resembling most existing marketplaces. A notable difference is the ability to toggle between ETH and USD pricing, which may be friendlier for non-crypto-native users.
As an aggregator, Uniswap’s NFT marketplace offers fewer features than some competitors. Most notably, it lacks advanced analytics like floor depth, trade history, and price charts. Some argue that in today’s low-gas environment, gas savings alone may not be enough to attract users.
On the other hand, we believe Uniswap’s moat lies in its Universal Router, which enables seamless FT and NFT interoperability. With Universal Router, users can execute multiple token swaps across Uniswap V2 and V3 and purchase NFTs from multiple marketplaces—all within a single transaction. For example—users previously had to manually convert USDC, ETH, and DAI into WETH across multiple transactions before buying an NFT. Uniswap can now do this in one transaction, as shown below:
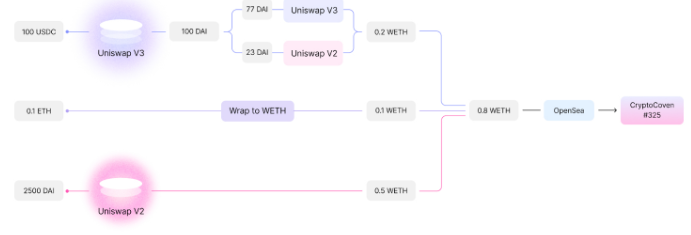
This is critical because Uniswap hosts the deepest FT liquidity in DeFi and attracts massive crypto-native traffic. The natural fusion of FTs and NFTs provides significant convenience during the purchasing process. This is truly a game-changer—it drastically reduces friction, especially in multi-asset environments. The inability to use ERC-20 tokens to buy NFTs remains a major pain point for many NFT aggregator users.
Building on their AMM expertise and breakthrough innovations like Universal Router, future developments could include consumer-facing products independent of current NFT aggregators. Unlike Sudoswap’s single-token, single-pool model, Uniswap could enable mixed payments and AMM-like multi-currency trades powered by Universal Router. Uniswap could also deploy new AMM pools—offering NFT project owners more liquidity options beyond ETH. These capabilities differentiate Uniswap from other aggregators. Uniswap’s NFT integration is still early, and only time will tell whether users adopt it.
Blur |
Gem.xyz |
Genie.xyz → Uniswap |
|
Supported Direct Marketplaces |
X2Y2, Looks Rare, Opensea |
X2Y2, Looksrare, Opensea, XMarket, NFTx, Larva Labs, Sudoswap |
X2Y2, Looksrare, Opensea, Larva Labs, Rarible, Coinbase, Sudoswap |
User Acquisition Strategy |
Airdrop |
Very low gas fees Potential airdrop rumors Product innovation |
First mover |
Features |
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News |