When On-Chain Lending Systems Converge
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

When On-Chain Lending Systems Converge
On-chain lending saves time and reduces operational costs.
By: Prathik Desai
Translated by: Block Unicorn
Credit is the time machine of the economy. It enables businesses to bring future cash flows into today’s decision-making.
I believe this is one of the most underappreciated aspects of the financial world.
People rarely notice credit at work—yet it fundamentally shapes how businesses operate. An effective credit system allows retailers to restock shelves before they run empty, lets manufacturers upgrade aging equipment before it fails completely, and empowers founders to hire new staff before human-resource bottlenecks escalate into full-blown crises.
The gap between good ideas and actual execution often stems from limited access to credit—and banks promise to bridge that gap.
Banks accept customer deposits via bank accounts and extend credit to borrowers. They pay depositors relatively low interest rates while charging borrowers higher ones; the spread constitutes their profit. Yet bank credit faces numerous challenges—and mismatched supply and demand for credit stands out as one of the most significant.
Private credit fills some of the gaps left by traditional banking—but a substantial shortfall remains. This shortfall reflects investors’ current reluctance to lend in credit markets.
In March 2025, the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and the World Bank jointly published the report “SME Finance Gap,” estimating a financing gap of approximately $5.7 trillion across 119 emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs)—roughly 19% of their combined GDP.
Against this backdrop, I found last week’s developments in onchain credit especially encouraging. Onchain lending is not new. We experienced a frenzied cycle back in 2022—and people continue discussing it for various reasons even today. Yet this current cycle feels different.
In this article, I’ll dive deep into all the changes unfolding in the onchain credit market—and explain why I believe it may fundamentally transform the entire credit industry.
Let’s begin.
Money markets have existed on Ethereum for years. Over-collateralized lending, liquidation bots, interest-rate curves, and occasional cascading liquidations are nothing new. So what truly caught my attention about last week’s credit-related announcements wasn’t the money markets themselves—but rather the participants involved and how they’re re-packaging credit.
What excites me is that these seemingly isolated partnership announcements collectively signal a broader convergence trend. The fragmented DeFi landscape of summer 2022 is coalescing into a powerful force. Treasury infrastructure, non-custodial wrappers, specialized risk managers, and automated yield-optimization tools are now being integrated and scaled.
Kraken launched DeFi Earn—a platform targeting retail users that routes lenders’ deposits into vaults (in this case, Veda). Those vaults then deploy capital into lending protocols such as Aave. Chaos Labs serves as the risk manager, overseeing the entire engine. Kraken promises lenders up to 8% annual percentage yield (APY).
What do vaults change? They deliver self-custody and full fund transparency. Unlike traditional credit markets—where investors entrust funds to fund managers and wait for monthly disclosures—vaults integrate smart contracts that mint claims on deposited capital and display real-time fund deployment on-chain.
Almost simultaneously, Bitwise—the world’s largest crypto asset management firm—launched a non-custodial vault strategy on Morpho, an onchain lending platform.
This isn’t the first time onchain lending has received institutional recognition. In 2025, Coinbase launched USDC lending services, enabling smart contract wallets to connect and route deposits via onchain vaults to Morpho. Steakhouse Financial leverages this platform for cross-market capital allocation to optimize returns.
This development arrives just as the onchain lending market is poised for explosive growth—and the data confirms it.
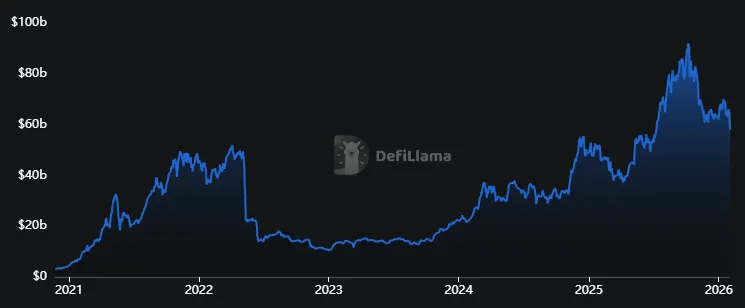
Total value locked (TVL) in lending protocols has reached $58 billion—a 150% increase over two years. Yet this figure is only 10% above the 2022 peak.
Here, the outstanding loan balance dashboard offers a more accurate picture.
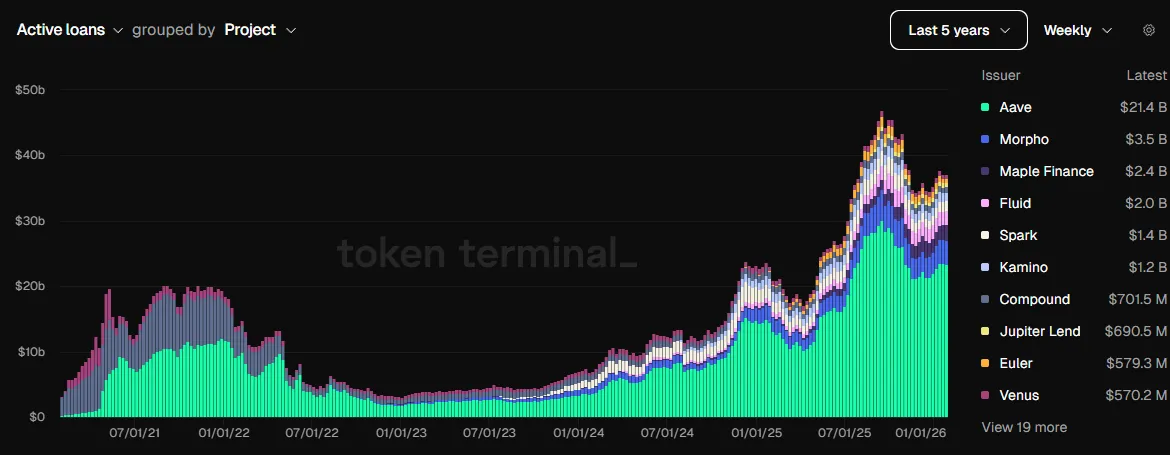
The dashboard shows that the foundation laid by leading protocols—including Aave and Morpho—is exceptionally solid: active loans have recently surpassed $40 billion—more than double the 2022 high.
The dashboard shows that existing institutions—including Aave and Morpho—have built a robust foundation, with active loans exceeding $40 billion over recent months—more than double the 2022 peak.
Today, Aave and Morpho each generate six times the revenue they did two years ago.
While these charts reflect investor confidence in lending protocols, I find the sustained growth in vault deposits even more compelling.
In October 2025, total vault deposits crossed $6 billion for the first time. Today, they stand at $5.7 billion—more than double the year-ago level of $2.34 billion.
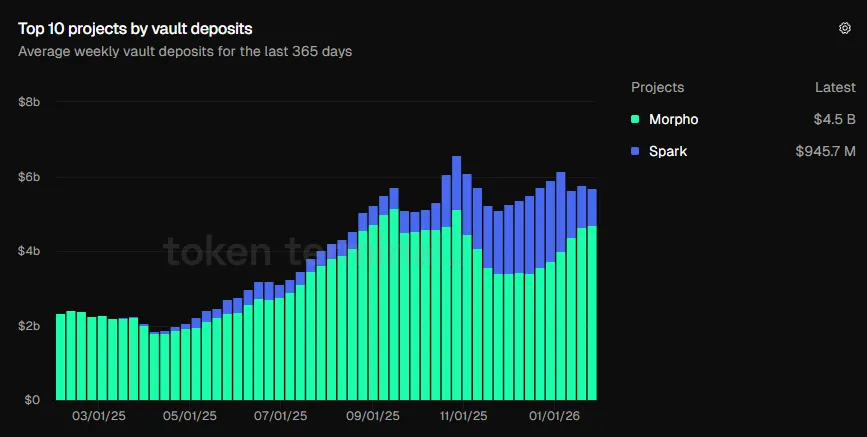
These charts indicate users are gravitating toward products offering comprehensive ecosystems—including vaults, yield-optimization strategies, risk allocation frameworks, and professional management.
This evolution—my source of optimism—is fundamentally different from what we observed during DeFi Summer.
Back then, the lending market resembled a closed loop. Users deposited collateral, borrowed against it, used proceeds to buy more collateral, and redeposited—all to chase higher yields. Even if collateral prices fell, users could still earn platform incentives for participating in lending protocols. But when those incentives vanished, the loop collapsed.
Even today’s cycle rests on the same foundational element—over-collateralized lending—but it’s built atop a radically different—and far sturdier—foundation. Vaults have evolved into wrappers that transform protocols into automated asset-management tools. Risk managers now play a central role, establishing guardrails and safety mechanisms.
This shift reshapes the appeal of onchain lending for both investors and lenders.
During DeFi Summer, lending protocols were merely another fast-money vehicle. That model worked—until the incentives disappeared. Users signed up for Aave accounts, deposited funds, borrowed against collateral, repeated the process—until incentives dried up. We saw this clearly in Aave’s Avalanche deployment: incentives attracted deposits and kept the loop running early on. But as subsidies tapered off, the loop unraveled. As a result, Avalanche’s outstanding debt dropped 73% quarter-on-quarter in Q3 2022.
Today, lending has matured into a fully-fledged ecosystem with dedicated participants handling risk management, yield optimization, and liquidity management.
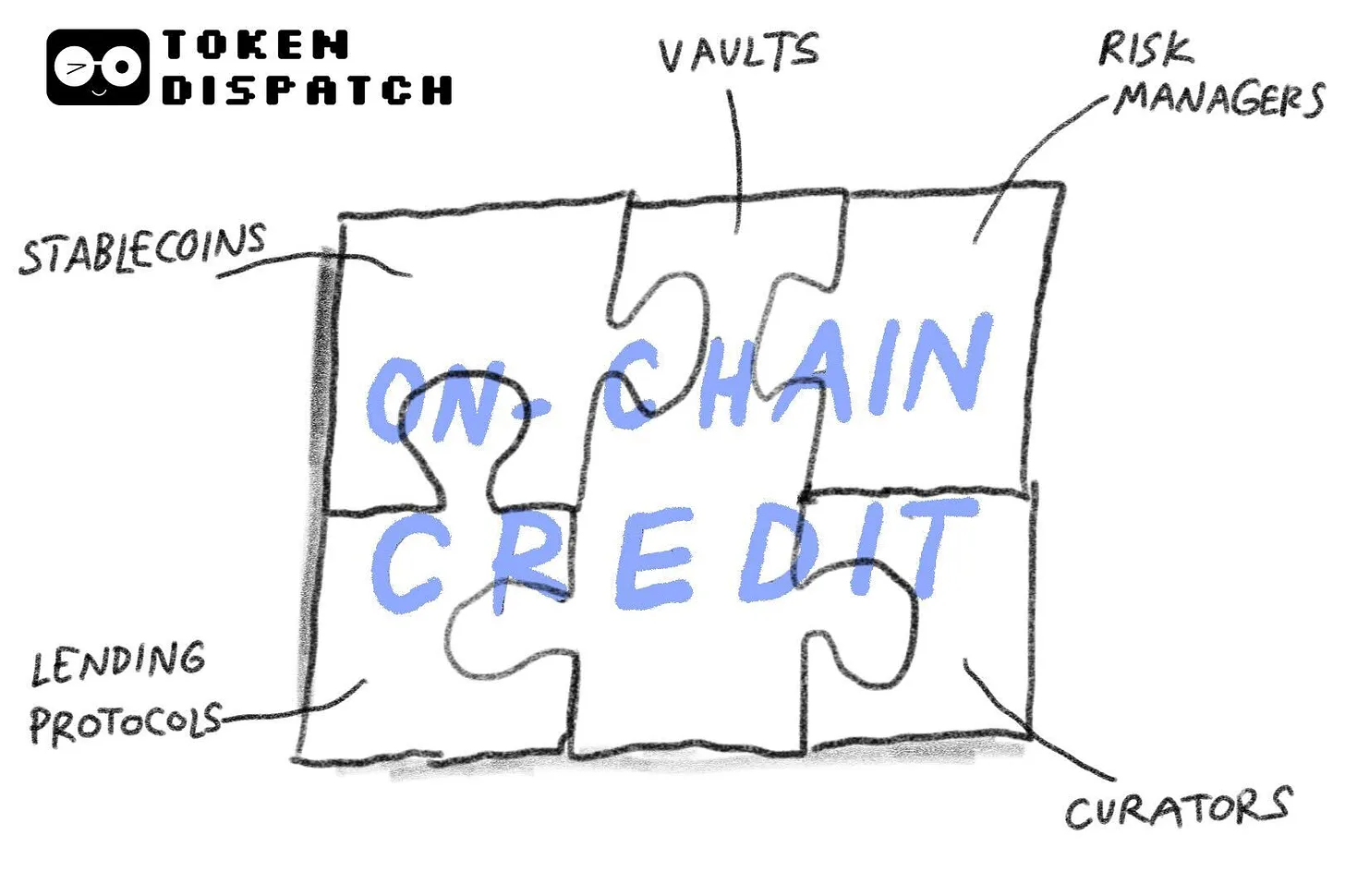
Here’s how I conceptualize the full stack.
At the base lies settlement capital—in stablecoin form. It can be transferred instantly, held anywhere, deployed on demand, and—critically—measured with precision.
Above that sits the familiar money market layer—protocols like Aave—where lending is enforced by software code and collateral requirements.
Next comes the world of wrappers and routers—aggregating capital and routing it from lenders to borrowers. Vaults act as wrappers, packaging the entire lending product into a format easily digestible for retail investors. For example: “Deposit $X to earn up to Y% APY”—exactly what Veda Wallet does on Kraken’s Earn platform.
Custodians sit atop these protocols, determining which collateral types to accept, setting liquidation thresholds, defining concentration limits for risk exposure, and specifying when to unwind positions as collateral values decline. Consider Steakhouse Financial’s approach on Morpho—or how asset managers like Bitwise embed their judgment directly into vault rules.
Behind the scenes, AI systems run continuously—managing onchain credit risk and acting as the nervous system of the lending ecosystem when humans are offline. Manual risk management doesn’t scale. Constrained risk oversight increases credit risk during market volatility. Best-case outcome: subpar returns. Worst-case: liquidations.
AI-powered optimization engines track borrowing demand, oracle deviations, and liquidity depth to trigger timely withdrawals. When vault risk exposure breaches preset thresholds, alerts fire. Moreover, they recommend de-risking actions and assist risk teams in decision-making.
It’s precisely this combination—24/7 optimization, systematic de-risking, auditable vaults, carefully curated strategies, institutional backing, and professional risk management—that makes today’s market feel safer and lower-risk.
Yet none of these measures eliminate risk entirely. Liquidity risk—among the most overlooked—is one key example.
Although vaults offer superior liquidity compared to isolated protocols, they still operate within the same underlying markets. In low-volume markets, vaults can inflate unwinding costs—making exits difficult.
Additionally, curator discretion poses its own risks.
When users deposit funds into vaults, they implicitly trust certain institutions to make investment decisions based on market conditions—select appropriate collateral—and set corresponding redemption thresholds. Credit operations vary widely, but lenders must understand: non-custodial does not mean risk-free.
Despite these challenges, onchain lending is already reshaping the crypto landscape—and, by extension, the broader economic landscape.
The operating cost of credit markets depends on time and operational overhead.
Massive investments in verification, monitoring, reporting, settlement, and transaction execution make traditional credit expensive. Much of the interest charged to borrowers is avoidable—and often unrelated to the “time value of money.”
Onchain credit saves both time and operational cost.
Stablecoins minimize settlement latency; smart contracts reduce execution time; transparent ledgers cut auditing and reporting time; and vaults simplify user complexity. These cost savings become especially impactful when addressing SME credit gaps.
Onchain credit won’t close the credit gap overnight—but lower credit costs will streamline verification and democratize access. And that could reshape the economic landscape.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News