
Crypto Regulation Reversal: 2025 U.S. Crypto Policy Developments, Market Impact, and 2026 Outlook
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Crypto Regulation Reversal: 2025 U.S. Crypto Policy Developments, Market Impact, and 2026 Outlook
This article will provide an in-depth review of the cryptocurrency bills and policy measures that have been passed or are being advanced in the United States in 2025, analyze market performance before and after these initiatives were introduced, and forecast regulatory trends and industry impacts for 2026.
Author: Hotcoin Research

1. Introduction
2025 is seen as a watershed year for cryptocurrency regulation in the United States. Prior to this, U.S. regulators had long vacillated in their approach toward digital assets, and the lack of a clear regulatory framework led to rampant "enforcement-by-litigation," leaving the industry struggling to survive. However, in 2025, the U.S. federal government and Congress achieved a series of breakthroughs in crypto legislation and policy: Congress passed the first federal stablecoin bill (the GENIUS Stablecoin Act), the House advanced the Digital Asset Market Structure Bill (CLARITY Act), and successfully repealed inappropriate tax rules targeting DeFi. These measures not only clarified industry rules and boosted market confidence but also triggered significant price volatility and structural changes.
Changes in the U.S. political landscape paved the way for crypto-friendly policies: Donald Trump returned to the White House, explicitly stating his intention to make America the "global capital of crypto," issuing executive orders elevating digital assets to a national financial strategic priority, and appointing multiple officials supportive of crypto innovation to key positions. With improvements in legislative and regulatory environments, mainstream cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin entered a new bull market in 2024, reaching record highs in early 2025. Although prices retreated somewhat by year-end due to macroeconomic fluctuations, regulatory tailwinds were undoubtedly a major pillar behind this market recovery.
This article provides an in-depth review of the crypto bills and policies enacted or advanced in the U.S. during 2025, analyzes market performance before and after these developments, and looks ahead to regulatory trends and industry impacts in 2026. We will see that with greater policy clarity, both short-term sentiment and long-term structure of the U.S. crypto market have undergone profound shifts: prices react swiftly to policy news in the short term, while in the long run, compliant ecosystems gradually mature, institutional capital accelerates its entry, and the industry regains momentum. By examining this series of events, investors can gain clearer insights into how regulatory direction profoundly shapes the market.
2. The First Federal Stablecoin Law: GENIUS Act
Source:https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/senate-bill/1582/text
In June 2025, the U.S. Senate passed the Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins Act of 2025 (GENIUS Act) by a wide margin. This marked the first federal-level stablecoin regulation in U.S. history and became the first major crypto legislation passed by Congress. On July 17, the House of Representatives approved the bill overwhelmingly with 308 votes in favor and 122 opposed. The next day, President Trump signed the GENIUS Act into law. This swift legislative progress reflects bipartisan consensus on stablecoin regulation, signaling a shift in the U.S. stance on dollar-pegged stablecoins—from观望to proactive oversight.
1. Key Provisions of the Act
The GENIUS Act establishes a new federal regulatory framework for payment stablecoins. Under the law, a "payment stablecoin" is defined as a digital asset pegged to fiat currency value, usable for payments and settlements, redeemable at par value, and claiming to maintain price stability.
-
Issuer Requirements: Only qualified regulated entities may issue such stablecoins, including bank subsidiaries insured by the FDIC, non-bank institutions approved by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and state-regulated entities certified under specific standards. Issuer qualification ensures financial strength and compliance capability, allowing compliant firms like Circle a clear path to federal licensing while barring unqualified players from issuing stablecoins—preventing risks arising from disorderly innovation.
-
100% Reserves for Stablecoins: Must be backed at a minimum 1:1 ratio with safe, highly liquid assets. Eligible reserve assets include U.S. legal tender (including deposits at the Federal Reserve), short-term U.S. Treasury securities, high-credit-quality short-term repurchase agreements, and regulated deposits. The law also allows "tokenized forms" of these assets to count toward reserves—as long as the underlying assets meet regulatory requirements, their blockchain-based tokenized versions are acceptable. This provision creates space for future on-chain circulation of traditional financial assets. Additionally, the law prohibits interest payments to stablecoin holders to prevent “shadow banking” risks akin to deposit-taking. Issuers must disclose monthly on their websites the circulating supply of stablecoins and corresponding reserve composition, subject to independent audit by accounting firms, with CEO/CFO personally signing off on report accuracy.
-
Dual-layer Regulatory Oversight: Implementation of the GENIUS Act involves cooperation between federal and state regulators. Non-bank issuers must obtain OCC approval and submit to federal oversight, while smaller issuers opting for state-level regulation must still meet standards similar to federal ones. Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve is authorized to take enforcement actions against state-regulated stablecoin issuers in “extraordinary emergency situations” to mitigate systemic risk. This dual-layer model ensures central oversight over large-scale stablecoin issuers’ potential impact on the financial system, while allowing small innovators to develop within state regulatory sandboxes—balancing financial stability with innovation incentives.
-
Prohibition on Commercial Firms: The law specifically bars certain types of companies from issuing stablecoins. For example, non-financial commercial enterprises—especially big tech firms—are prohibited from issuing payment stablecoins. This aims to prevent platform giants with billions of users from bypassing financial regulation to directly issue money, thereby avoiding threats posed by “digital monopoly currencies” to financial sovereignty and competition. This clause serves as a direct response to Facebook’s former Libra (later renamed Diem) initiative, clearly delineating boundaries for tech giants in the digital currency arena.
-
Stablecoins Not Classified as Securities or Commodities: They fall outside SEC or CFTC jurisdiction and instead belong to the banking regulatory system. This resolves a long-standing uncertainty about regulatory classification: mainstream dollar stablecoins such as USDC and USDT will now be treated as prepaid payment instruments rather than securities, thus avoiding the inappropriate application of complex securities laws.
2. Market Impact of the GENIUS Act
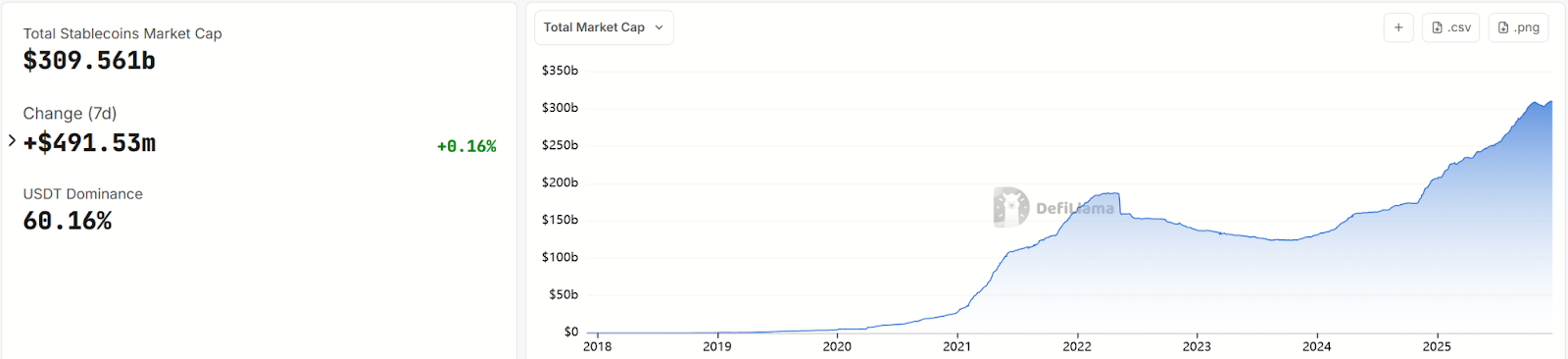
Source:https://defillama.com/stablecoins
The introduction of the GENIUS Act significantly enhanced market trust in stablecoins. After the announcement, the stablecoin market responded positively: as of December 2025, global stablecoin market capitalization exceeded $300 billion. While part of this growth stems from broader crypto market recovery, the primary driver has been investor expectations that regulation would legitimize stablecoins, making institutional investors more comfortable using and holding them for transactions and payments. Some traditional financial institutions have begun exploring stablecoin-related businesses.
JPMorgan's research division forecasts that global stablecoin market cap could reach $500–750 billion in the coming years. Media outlets have dubbed 2025 “the true year one of stablecoins.” With regulatory support, dollar-pegged stablecoins are accelerating integration into mainstream finance. For instance, payment giants like Visa and Mastercard have started piloting stablecoin settlement for cross-border transactions; some banks are considering launching branded stablecoins or partnering with existing issuers to offer compliant digital dollar services to customers.
3. Digital Asset Market Structure Act: CLARITY Act
Source:https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/house-bill/3633/text
Following stablecoin legislation, Congress rapidly advanced broader legislative efforts targeting digital asset market structures. A centerpiece was the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act of 2025 (CLARITY Act), introduced and passed by the House of Representatives. Drafted jointly by the House Committee on Agriculture and the Committee on Financial Services, it is viewed as a comprehensive package to clarify regulatory boundaries for digital assets.
On July 17, 2025, the CLARITY Act passed the House with 294 votes in favor and 134 opposed. It was then sent to the Senate for consideration. However, just days after the House vote, the Senate Banking Committee introduced a competing draft bill on digital markets. The Senate Committees on Agriculture and Banking each held discussions on digital asset legislation within their respective jurisdictions and opened public consultations, planning to merge the two proposals into a unified Senate bill for a vote in 2026.
1. Core Framework: Three-Tier Regulatory Classification
The CLARITY Act seeks to resolve a longstanding industry dilemma—“Who regulates what?” To address this, the bill introduces a “three-tier” classification system dividing digital assets into three categories and clarifying the roles of the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) and CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission):
-
Digital Commodities: Defined as digital assets “inherently tied to a blockchain system itself, whose value depends directly on the functionality or services of that chain.” In simple terms, these are functional tokens used for payments, governance, service access, or incentives on decentralized networks—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. The bill explicitly excludes several items from this category, including securities and derivatives, stablecoins, bank deposits, fund shares, and collectibles. This classification recognizes the commodity nature of decentralized, non-income-generating tokens.
-
Investment Contract Assets: A new concept created by the bill, referring to “digital commodities issued or sold through investment contracts.” Colloquially, these are tokens sold to investors during fundraising—for example, via initial coin offerings (ICOs). Moreover, the bill establishes a “network maturity” certification mechanism, allowing project teams or decentralized communities to petition regulators to recognize that a blockchain network has matured, thereby confirming its tokens no longer qualify as securities. Criteria for maturity include: the blockchain having real-world utility and services, open-source core code, predetermined transparent rules that cannot be unilaterally altered, and no single entity controlling more than 20% of the token supply. This design mirrors lock-up periods post-IPO—projects face stricter securities regulation early on to protect investors, but once sufficiently decentralized, they exit strict oversight and tokens become freely tradable commodities.
-
Permitted Payment Stablecoins: Similar to definitions in the GENIUS Act, CLARITY separately categorizes fiat-pegged, payment-oriented stablecoins. These assets must be linked to a legal tender, issued by entities supervised at the state or federal level, and redeemable at par value. Under the CLARITY framework, stablecoins are neither securities nor commodities but treated as regulated payment instruments.
Through this classification, the CLARITY Act attempts to clarify jurisdictional boundaries between the SEC and CFTC. Specifically: digital commodities primarily fall under CFTC oversight; issuance of investment contract assets is regulated by the SEC; stablecoins remain under banking regulators. This arrangement promotes clear division of responsibilities: the SEC no longer treats nearly every token as a security, focusing instead on curbing misconduct in fundraising; the CFTC fills the prior gap in direct oversight of crypto spot markets, enabling active enforcement against market manipulation.
2. Compliance Pathways for Exchanges and Participants
Beyond defining asset classifications, the CLARITY Act also provides clear compliance guidance for market intermediaries and participants.
-
Crypto Exchanges: The bill requires digital commodity trading platforms to register with the CFTC as “Digital Commodity Exchanges” and adhere to core principles, including establishing listing criteria (ensuring issuers provide necessary disclosures such as open-source code, issuance volume, and economic models), implementing trade surveillance, preventing conflicts of interest, safeguarding funds and systems. Exchanges must segregate customer assets from proprietary funds, ensure customer holdings are stored with qualified digital asset custodians, provide full risk disclosures, and join self-regulatory organizations like the Futures Industry Association. The bill even places limits on innovative services—for example, exchanges may offer staking to enhance blockchain security, but cannot mandate user participation or mix it with their own trading activities to avoid conflicts of interest.
-
Brokers/Dealers: The bill breaks down current barriers between digital asset and securities businesses, encouraging compliant brokers and exchanges to integrate digital assets into their operations. Entities engaging in digital commodity brokerage must register with the CFTC as Digital Commodity Brokers and meet capital, reporting, and customer protection requirements. The SEC is required to allow registered brokers, exchanges, or alternative trading systems (ATS) to handle trading and custody of digital commodities and stablecoins, without rejecting registration or exemption applications solely because the platform offers both securities and digital assets. The SEC is also granted discretion to apply existing exemptions to certain DeFi activities, preventing inappropriate regulation from stifling innovation.
-
Technology Developers: According to reports, the final version of the CLARITY Act explicitly states that individuals engaged in non-custodial activities such as blockchain development, node operation, and wallet creation do not require state or federal licenses. This provision is vital for the U.S. blockchain development ecosystem, meaning pure technology providers will not bear heavy regulatory burdens due to financial activities conducted by users on-chain—removing prior legal uncertainties facing miners, nodes, and smart contract developers.
3. Market Impact: Positive Expectations Amid Heightened Volatility
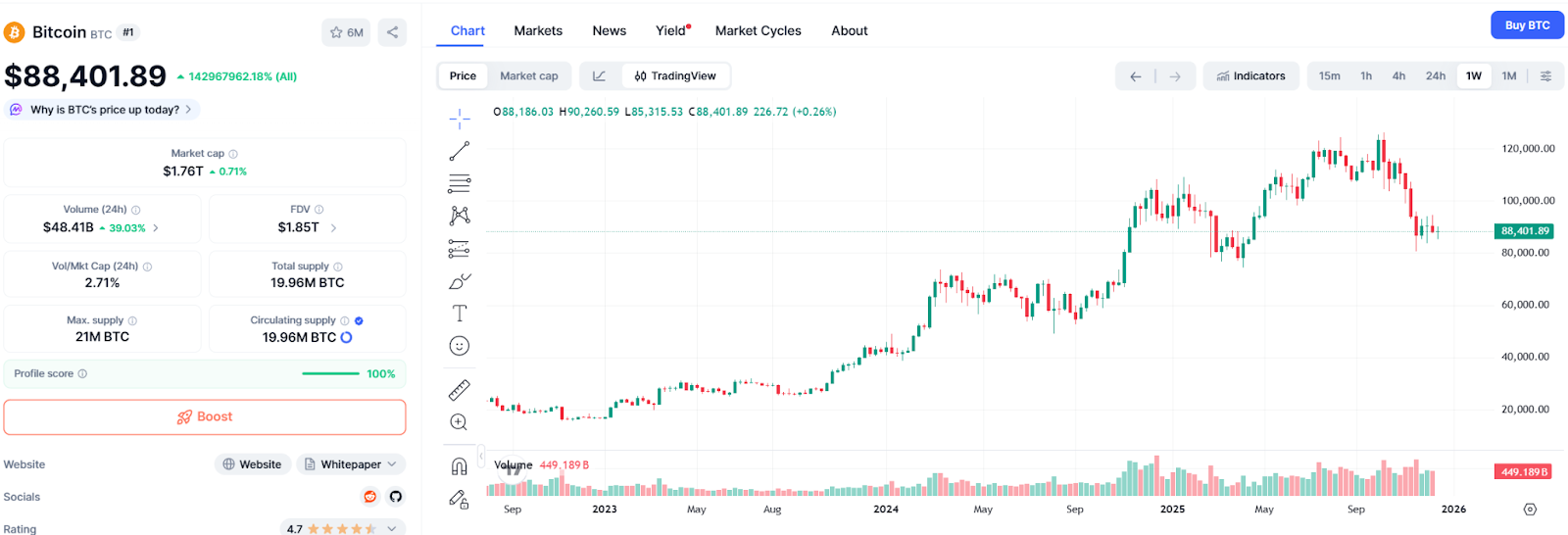
Source:https://coinmarketcap.com/currencies/bitcoin/
When the House announced mid-July 2025 as “Crypto Week,” preparing votes on the CLARITY Act, anti-CBDC provisions, and the stablecoin bill, market optimism surged. Indeed, favorable headlines served as a key catalyst for strong mid-year crypto market performance: Bitcoin reached rebound highs in July, its market dominance rose, and many U.S.-listed blockchain stocks recorded gains. After passage, the industry widely believed that long-pending issues in U.S. crypto were finally nearing resolution, increasing institutional willingness to enter. Previously stalled digital asset trading or custody plans at platforms like the New York Stock Exchange and Nasdaq began reevaluating launch possibilities.
However, due to slow and uncertain policy progress, the market also experienced news-driven swings. For example, after the House passed the CLARITY Act and sent it to the Senate, investors initially expected rapid follow-through, leading Bitcoin to hit a new all-time high near $126,000 in early October. But in mid-October, a surprise presidential announcement of new tariffs on China triggered global risk-off sentiment, causing Bitcoin to crash alongside equities—the largest single-day liquidation in crypto history ($19 billion in leveraged positions). Subsequent macro headwinds kept crypto markets under pressure. Bitcoin recorded its worst monthly drop since 2021 in November and remains below $90,000. This shows that as risk assets, cryptos remain heavily influenced by macro conditions and broad market sentiment—Bitcoin’s correlation with the S&P 500 rose to 0.5 in 2025, far above 0.29 in 2024.
4. Other Representative Crypto Policies
Besides major legislative initiatives, the U.S. government took important steps in other crypto-related policies in 2025, further improving the compliance environment for the crypto ecosystem.
1. Anti-CBDC Legislation: Protecting Financial Privacy
After taking office, the Trump administration underwent a 180-degree shift in attitude toward central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). In January 2025, President Trump signed an executive order directly prohibiting any federal agency from advancing, issuing, or promoting CBDCs. This stance was later reinforced legislatively: the House added Title VI, the “Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act,” to the CLARITY Act. Its core provision legally blocks the Federal Reserve from launching consumer-facing CBDC accounts or products, emphasizing privacy and freedom, and preventing government use of CBDCs to access citizen transaction data. During “Crypto Week” in 2025, the House separately voted and passed this bill. Though the Senate has yet to complete its review, given the clear opposition from the new administration and House leadership, the door to a U.S. CBDC is effectively closed.
Supporters argue that banning CBDCs helps defend financial privacy and private-sector innovation. Once launched, a CBDC could enable real-time government monitoring—or even restriction—of personal spending, contradicting American values of free markets and privacy rights. In this context, the Fed noticeably slowed its digital dollar research in 2025, focusing only on wholesale CBDCs (for interbank settlement). This means privately issued stablecoins will dominate the digital dollar landscape, aligning with the GENIUS Act’s policy direction of encouraging banks and compliant institutions to issue stablecoins.
2. Repealing Harsh DeFi Reporting Rules
Back in 2021, the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) included a controversial provision requiring broad “digital asset brokers” to report user transaction data to the IRS. This definition was overly expansive and could have classified DeFi miners, validators, and smart contract developers as “brokers,” forcing them to comply with burdensome KYC and tax reporting obligations. In 2025, both chambers of Congress passed Joint Resolution 25 (H.J. Res. 25), which President Trump signed into law on April 10, 2025 (Public Law 119-5). This law formally revoked the Treasury Department’s implementation rules for Section 80603 of the IIJA (Digital Asset Broker Information Reporting).
After repeal, the IRS clarified: purely automated DeFi platforms operating on-chain without fiat on/off ramps are not required to file Form 1099-DA transaction reports or collect user identity information. Centralized exchanges and service providers (holding customer assets and offering fiat conversion) still bear reporting obligations: starting January 1, 2025, they must record user digital asset transactions and issue Form 1099-DA to users and the IRS by early 2026. This means licensed U.S. exchanges like Coinbase and Kraken must continue filing, while decentralized protocols like Uniswap are exempt. Meanwhile, payment processors and entities frequently issuing or redeeming their own tokens remain classified as “brokers” and must fulfill reporting duties—primarily targeting centralized stablecoin issuers.
3. Regulatory Personnel and Enforcement Shifts
Beyond legislation and macro policy, the improvement in the U.S. crypto regulatory environment in 2025 was also evident in personnel reshuffles and shifts in enforcement style. After taking office, the new administration appointed several crypto-friendly officials to key roles. Most notably, former SEC commissioner Paul S. Atkins was named Chairman of the Securities and Exchange Commission. Upon appointment, Atkins immediately launched an internal initiative codenamed “Project Crypto” to establish formal token classification standards and guidance, and formed a “Crypto 2.0” task force. The new team’s mission is to help the commission develop a “comprehensive and clear regulatory framework” and use enforcement resources more judiciously.
Accompanying personnel changes was a swift shift in SEC enforcement posture. Since Trump took office in early 2025, the SEC has paused or dropped around 60% of its crypto-related investigations and lawsuits. High-profile cases, such as litigation against Ripple and enforcement actions against Binance, showed significant de-escalation. For example, the SEC reached a settlement with Ripple in July 2025, dropping charges against its executives; investigations into Binance reportedly ceased active pursuit. Even the four-year probe into decentralized lending platform Aave concluded without penalties. These changes greatly eased industry pressure, allowing firms to refocus from legal defense to business operations. This contributed to the 2025 market recovery and reduced exodus of U.S.-based projects.
Meanwhile, banking regulators previously hostile to crypto involvement began moderately loosening restrictions. Newly appointed Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent expressed openness to digital assets. Acting FDIC Chair Travis Hill issued a public statement in January, pledging a “more transparent approach to fintech collaboration and digital asset tokenization” and considering additional guidance on bank participation in digital asset activities. The Federal Reserve, OCC, and others withdrew earlier restrictive statements on bank crypto activities in 2025, shifting instead to case-by-case reviews. As a result, some U.S. regional and community banks reconsidered providing banking services to crypto firms, reviving bank-crypto partnerships. After the collapse of several “crypto-friendly banks” like Signature and Silvergate left crypto companies struggling to access basic banking, this situation now appears poised for improvement.
4. Executive Orders and Exploration of Bitcoin Reserves
On January 23, President Trump signed an executive order titled “Strengthening American Leadership in Digital Financial Technology,” declaring it national policy to “support responsible growth and use of digital assets, blockchain technologies, and related innovations across economic sectors.” The order established the President’s Working Group on Digital Asset Markets, composed of over a dozen senior officials including the SEC Chair, CFTC Chair, Treasury Secretary, Commerce Secretary, and Attorney General, with invitations extended to private-sector digital asset leaders for consultation. The President directed the group to submit a report within 180 days proposing a comprehensive federal digital asset regulatory framework and assessing the feasibility of establishing a national “digital asset reserve.”
Trump himself expressed strong interest in creating a national Bitcoin reserve, hoping to leverage the government’s existing Bitcoin holdings (from law enforcement seizures) to explore diversifying national reserves into digital assets. On March 6, he issued Executive Order 14233, directing the establishment of a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve and a U.S. Digital Asset Inventory.
In essence, the U.S. government’s formal embrace of Bitcoin is less an economic decision than a geopolitical strategy: ensuring dollar dominance in the future digital economy and guarding against rising foreign digital currencies or gold. While this idea remains controversial among traditional financial officials, by 2025, it had moved from science fiction to reality.
In sum, the policy moves of 2025 demonstrate a comprehensive U.S. embrace of crypto innovation: establishing rules through legislation, changing regulatory tone via personnel appointments, and setting strategic direction through executive orders. This top-down design and strong execution send a clear signal to the global crypto industry: the U.S. intends to actively participate in and lead this financial revolution. While a more regulated market may dampen speculative bubbles, in the long run it will attract larger-scale, more rational capital, positioning crypto assets as a standard component of global portfolios rather than gray-market alternatives.
5. Outlook for 2026: New Rules and Industry Transformation
Looking ahead to 2026, U.S. crypto regulation will continue deepening and refining along the trajectory set in 2025. Here are several key areas to watch:
1. Legislative Finalization and Rulemaking
Digital asset market structure legislation is expected to achieve final passage in 2026. The two Senate committees plan to consolidate their drafts by year-end and push for a full chamber vote in early 2026. Given the House version already secured strong support and executive backing, industry observers believe Senate passage is highly likely.
Once both chambers agree on final text, the CLARITY Act and related provisions (such as anti-CBDC clauses) could be signed into law in the first half of 2026. Following enactment, the SEC and CFTC will enter a busy rulemaking phase. During this period, industry associations and major corporations will engage in negotiations to shape favorable regulations.
The specifics of final rules will determine how market participants adjust their business models. For example, if exchange registration processes are relatively straightforward and transparent, we may see U.S.-based platforms like Coinbase apply for CFTC registration, and even overseas exchanges consider applying for U.S. licenses.
2. Formation of a Compliance Ecosystem and Institutional Acceleration
With a clear regulatory framework and gradual implementation of supporting rules, the U.S. crypto compliance ecosystem will begin to take shape. Legally operating exchanges, custodians, brokers, and stablecoin issuers will progressively obtain formal registration or licensing from regulators, significantly boosting institutional participation.
Major asset managers (e.g., BlackRock, Fidelity) have already brought some traditional capital into the market via ETFs. With clearer regulations in 2026, these institutions may expand into more diverse offerings—launching crypto hedge funds, providing custody and derivatives trading. Wall Street banks like Goldman Sachs might roll out digital asset trading and custody services. In the stablecoin space, qualified bank subsidiaries like JPMorgan Chase could issue payment stablecoins, while non-banks like PayPal gain pathways to issue stablecoins via OCC approval.
Large-scale institutional entry will bring incremental capital and more sophisticated risk management, helping reduce crypto market volatility and improve market depth and pricing efficiency over time.
3. Industry Competition and Consolidation
The dawn of a compliance era also means industry reshuffling. Companies willing and able to meet regulatory standards will prevail, while those resisting or failing to comply will be phased out. For example, compliance pioneers like Coinbase are likely to further expand market share; meanwhile, unlicensed platforms with opaque business models will struggle to serve U.S. clients.
Similarly, among crypto projects, high-quality ventures will increasingly prefer compliant U.S. token launches. If the SEC successfully establishes a token registration exemption regime in 2026, we might witness the first batch of SEC-registered token offerings available to the public under regulatory oversight—a revolutionary change. This would mean crypto startups can raise funds legally like IPOs, with investors enjoying transparency and legal protections.
At the same time, emerging decentralized models will grow stronger, protected by safe harbor provisions. Decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and derivatives protocols may thrive further after gaining clear regulatory boundaries and gradually integrating with traditional finance.
4. Government Strategy and Global Competition
From a governmental perspective, the Trump administration will continue pursuing its strategic goal of making America the “global leader in crypto and blockchain innovation,” securing influence in international standard-setting bodies such as FATF digital asset regulations and cross-border payment frameworks. In 2026, the U.S. may seek closer dialogue and cooperation with advanced regulatory economies like Europe, the UK, and Japan, aiming for partial regulatory equivalence or mutual recognition. This would facilitate cross-border operations, enabling compliant crypto firms to operate seamlessly across major markets.
Additionally, the U.S. may increasingly incorporate crypto into its financial diplomacy agenda, promoting dollar-pegged stablecoins in developing countries to reinforce dollar supremacy. In late 2025, newly appointed Treasury Secretary Bessent praised the liquidity of U.S. Treasury markets and noted that stablecoin growth is expanding demand for Treasuries. This indicates official recognition of the potential benefits of stablecoins and other crypto products to U.S. financial markets.
5. Risks and Challenges
Of course, despite promising prospects, 2026 is not without risks. Macroeconomic factors such as shifts in interest rate cycles or geopolitical conflicts could still deliver external shocks to crypto markets.
Moreover, regulatory goodwill does not imply complacency. Should a major crypto security incident occur in 2026, regulators may swiftly tighten rules and punish offenders as examples. This raises higher demands for industry self-discipline: firms must strengthen security and risk controls even as they benefit from favorable policies.
Lastly, the U.S. political cycle warrants attention. 2026 is a congressional midterm election year, and should political dynamics shift again, the current crypto-friendly stance could reverse. Yet at least within the 2025–2026 cycle, bipartisan consensus appears solid on supporting reasonable regulation and fostering innovation.
6. Conclusion
Reviewing 2025, the U.S. underwent a transformation in crypto regulation—from chaos to clarity, from passive reaction to proactive leadership. This year, Congress and the government jointly delivered landmark measures including the stablecoin bill and market structure legislation. In the short term, these policy announcements significantly influenced market sentiment and price movements. When combined with macro headwinds, markets remained volatile. Yet deeper impacts lie in fundamental shifts to industry ecology and structure: clear rules removed obstacles to compliant operations, enabled traditional financial institutions to enter confidently, freed innovators from regulatory uncertainty, and restored the U.S. as a magnet for crypto entrepreneurship and capital.
As regulatory clarity improves, the industry itself must place greater emphasis on compliance and risk control to uphold regulators’ trust. Only through positive interaction between regulators and the industry can crypto technology truly integrate into the socioeconomic fabric and realize its transformative potential. For investors, closely tracking policy directions is crucial, as regulation has become a key driver of crypto market trends. Policy tailwinds not only boost prices but, more importantly, reduce long-term risk premiums, enhancing asset intrinsic value and sustainability.
Looking forward, the U.S. regulatory journey will offer valuable lessons globally: how to maximize digital financial innovation under the premise of maintaining financial stability and security. It is foreseeable that in 2026, the crypto industry will continue advancing on a firmer legal foundation, with the U.S. consolidating its position as a global hub for crypto capital and technology. There may still be setbacks, but the direction is clear: crypto assets are stepping out of the shadows, entering the mainstream to actively shape the future of finance.
About Us
Hotcoin Research, as the core research arm of Hotcoin Exchange, is dedicated to turning professional analysis into practical tools for your trading success. Through our “Weekly Insights” and “In-Depth Reports,” we decode market trends; with our exclusive column “Top Picks” (powered by AI + expert screening), we identify high-potential assets and reduce trial-and-error costs. Every week, our analysts go live to interact with you directly, explaining hot topics and forecasting trends. We believe that informed guidance paired with human-centered support empowers more investors to navigate market cycles and capture value opportunities in Web3.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News












