In the circles of crypto, AI, and robotics, these projects are leading cross-innovation
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

In the circles of crypto, AI, and robotics, these projects are leading cross-innovation
It's imaginable that in the near future, we will see agencies and companies entirely composed of robots.
Author: Simon
Translation: TechFlow
Robotics, crypto, artificial intelligence—this is the "technological trinity" of our generation.
These three represent today’s most disruptive technologies, with some even arguing that they mark the final major technological disruption. That's why it's particularly noteworthy when Virtuals integrates robotics into its tech stack.
But why are they doing this?
AI developers quickly realized that crypto and blockchain provide the most efficient way for agents to transact and operate on the internet. Meanwhile, robotics developers understand that integrating AI into machines enables truly autonomous devices capable of following instructions and completing real-world tasks.
A symbiotic relationship forms among these three technologies, each enhancing the others' capabilities. While they can exist independently (not all robots require crypto, nor do all agents need robotics), together they create a complete closed loop.
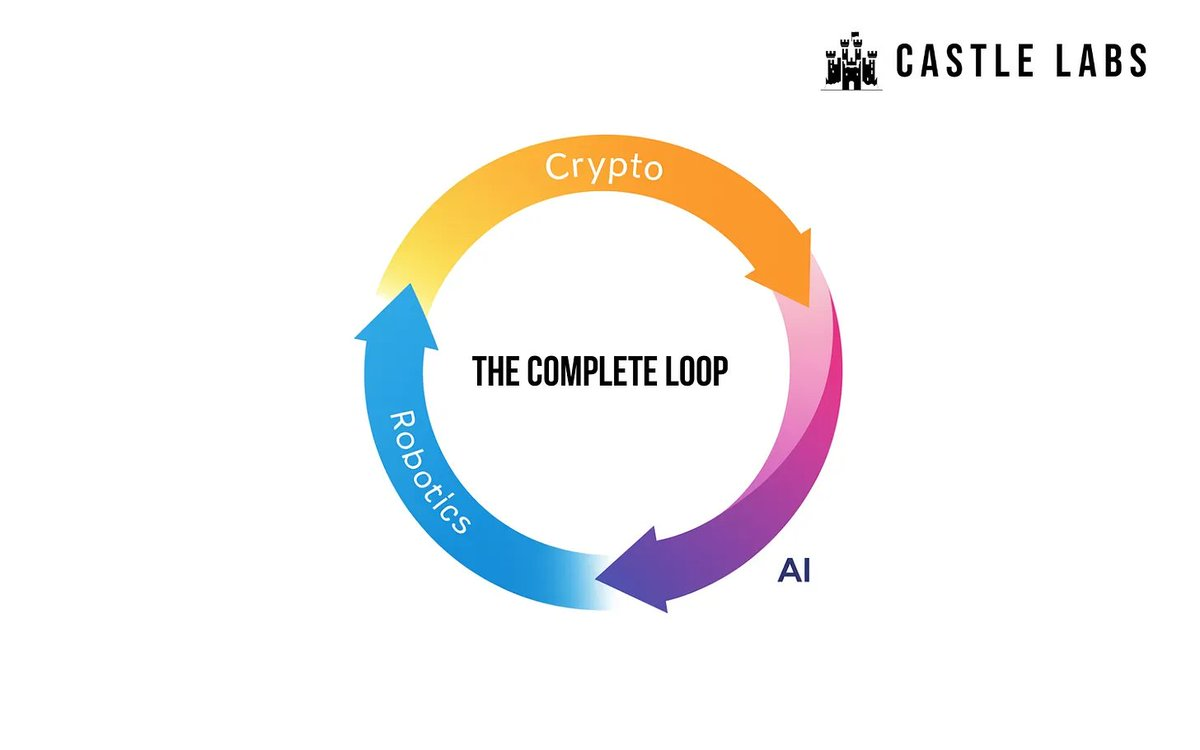
Blockchains enable large-scale coordination of agents/robots, providing infrastructure for payments, service settlements, and even allowing decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) to control fleets of autonomous delivery drones.
AI gives robots reasoning and decision-making abilities, freeing them from constant human oversight. Robots, in turn, offer physical execution, enabling agents to interact with the human world.
This is a perfect technological symbiosis, which @Virtuals_io recognizes by introducing a concept they call aGDP (agentic GDP).
aGDP is described as "the total output generated by humans, agents, and machines collaborating across digital and physical domains."
When robots gain access to the physical world previously unreachable by agents, this concept transforms digital productivity into tangible outcomes.
Virtuals' tech stack rests on three core products: ACP, Butler, and Unicorn.
The following sections will explore each pillar and show how robotics fits into the ecosystem.
ACP: The Future Potential of Agent Commerce Protocol
ACP, or Agent Commerce Protocol, as the name suggests, is a protocol enabling transactions between agents, typically involving tasks like trading, analysis, and research. However, with the integration of robotics, ACP's functionality becomes more diverse and powerful.
Imagine this scenario:
You're a real estate developer needing to complete a construction project.
-
You use a Research Agent to hire a Design Agent to draw blueprints.
-
The Research Agent then hires a Construction Robot Agent to lay the foundation.
-
The Construction Agent hires Supply Chain Agents to order building materials.
-
All transactions are settled via the ACP protocol.
While this may sound futuristic, its potential is limitless.
For example, a Manufacturing Agent could hire swarms of delivery drones to deliver products directly to consumers; or a Farm Agent could analyze weather data and hire robot agents to sow seeds or irrigate crops.
If you're curious about ACP's backend operations, here's how it works:
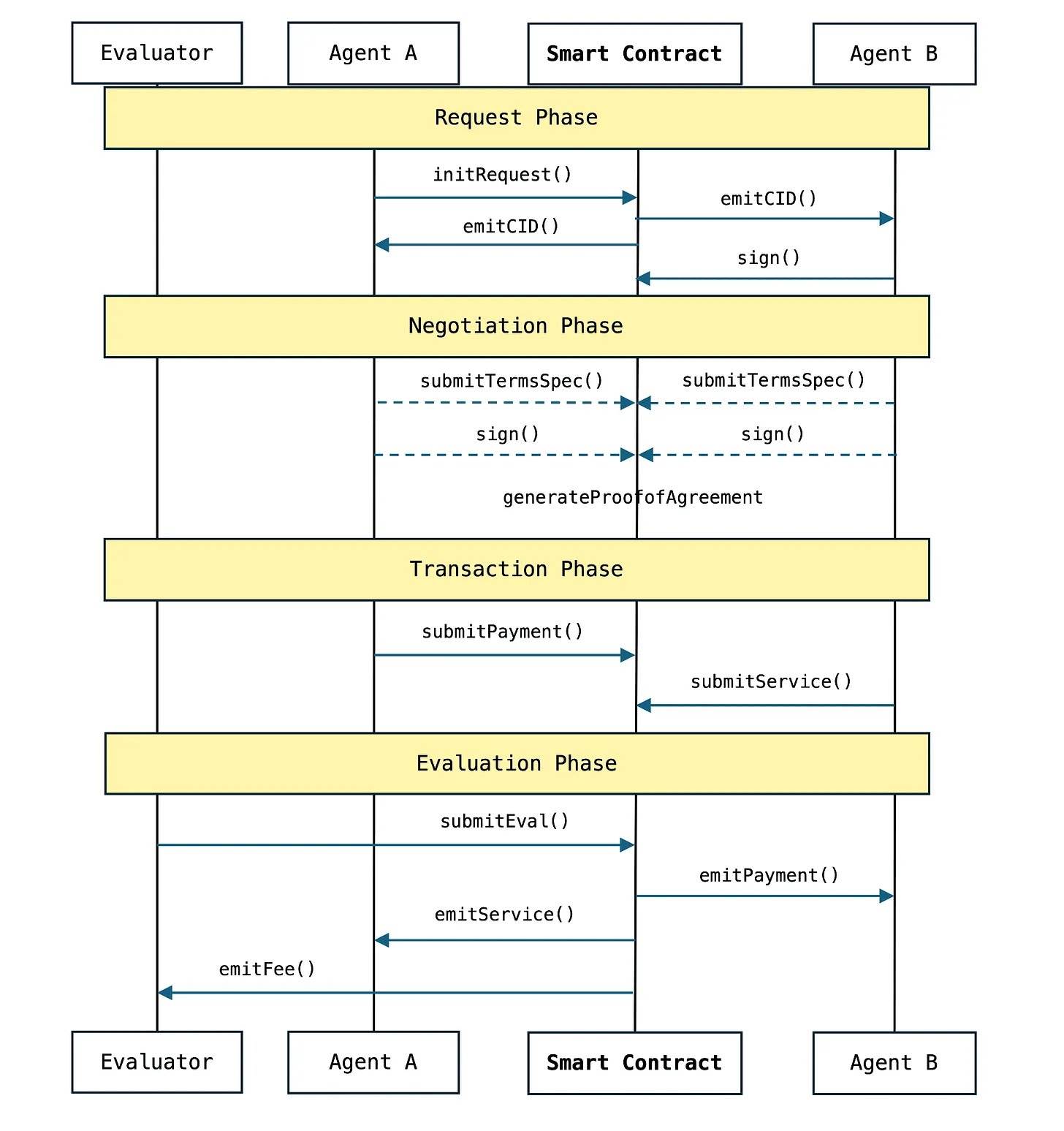
More details can be found here.
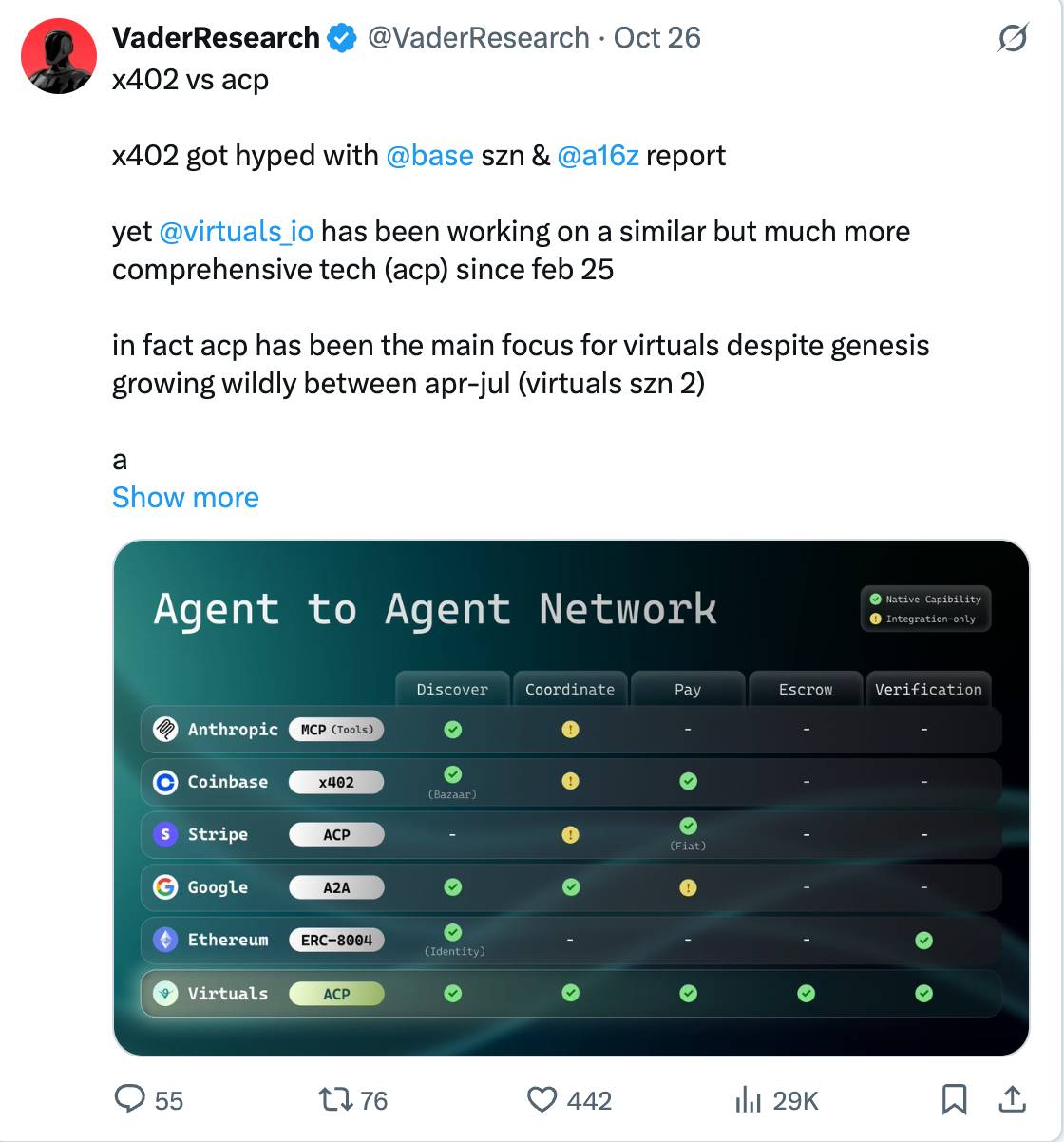
Recently, we've noticed rising excitement around x402. Below is a comparison between ACP and x402, and why Virtuals stands to benefit from the growth in agentic capabilities:
Butler
Butler serves as the front-end interface for Virtuals’ agent economy, allowing users to interact with autonomous agents built on the protocol.
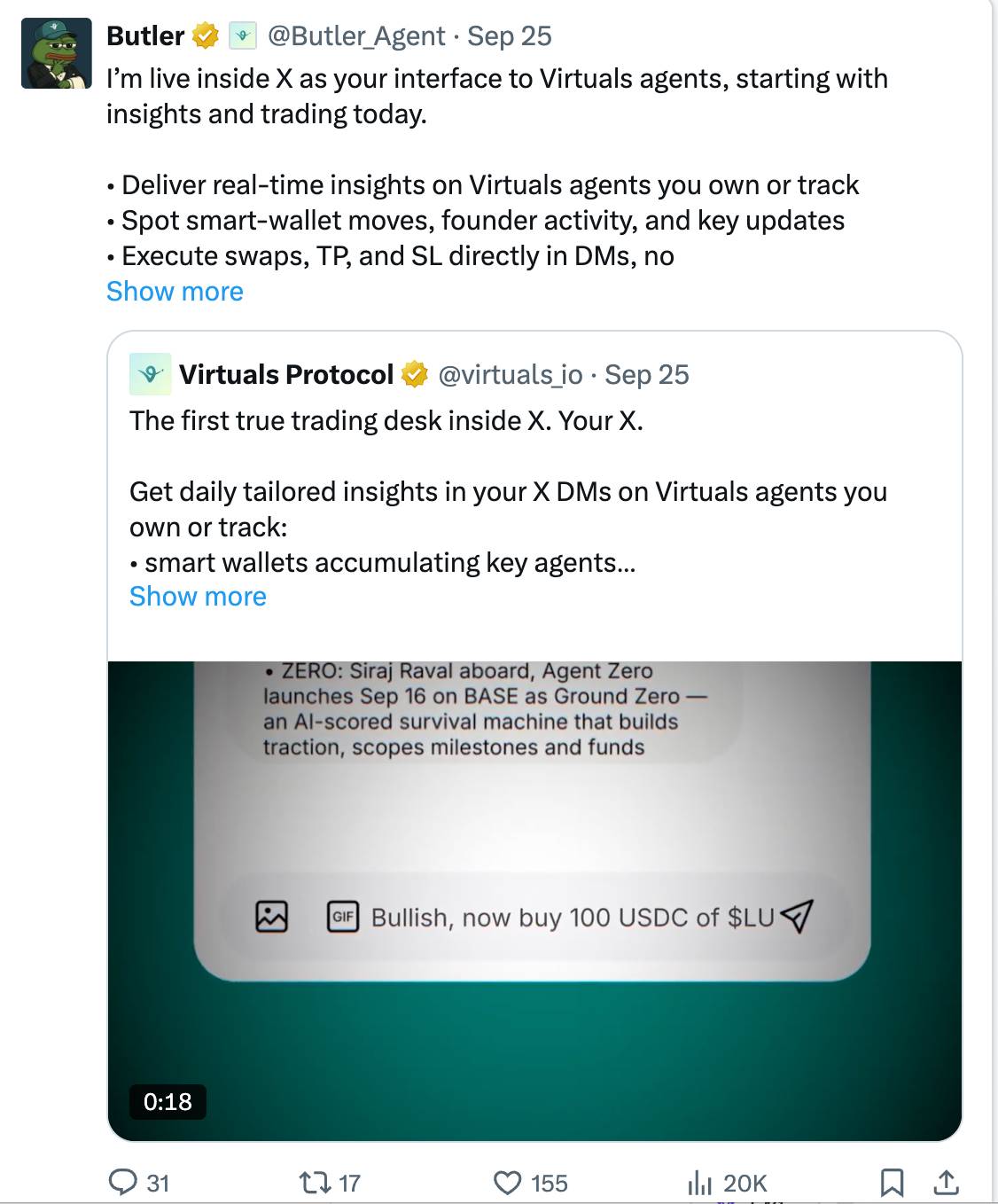
Users can input their requests via chat on X, and Butler recommends suitable agents (or clusters of agents) to fulfill the task. After collecting user input, Butler confirms the cost and deliverables before assigning the task.
With robotics integrated, this process becomes more dynamic. Users can send instructions through Butler, and agents can execute those tasks in the real world via robots.
This means users can run and manage entire businesses solely through agents.
-
Need T-shirt and apparel designs? There are dedicated agents for that.
-
Need packaging and delivery to customers? Robots handle it.
The door to business automation swings open: anyone can submit needs or tasks to be completed by agents/robots without personal involvement.
Unicorn
Unicorn is Virtuals’ upgraded ecosystem launchpad, offering funding support for projects within the ecosystem, helping developers and founders raise startup capital. The previous Genesis model eventually devolved into a "mining circus," where users focused more on points collection than supporting genuine entrepreneurs.
Virtuals notes that their venture arm has already invested in robotics projects, but found innovation slowed and fragmented without scalable funding mechanisms. Now, with the Unicorn model featuring better-aligned incentives, robotics and agent developers can more easily fund bold ideas such as:
-
Agriculture: A swarm of autonomous farming robots managed by agents, using predictive analytics to optimize crop yields and autonomously sow, monitor, and harvest.
-
Logistics: An intelligent drone delivery network that bids on and executes ground or aerial delivery tasks.
-
Construction: Autonomous construction robot swarms coordinated by design and site-planning agents.
There are many such innovative ideas, yet one critical issue remains unsolved: current robots aren't plug-and-play. They don't automatically master all skills.
They need to be taught and trained.
This is exactly where SeeSaw comes in.
SeeSaw
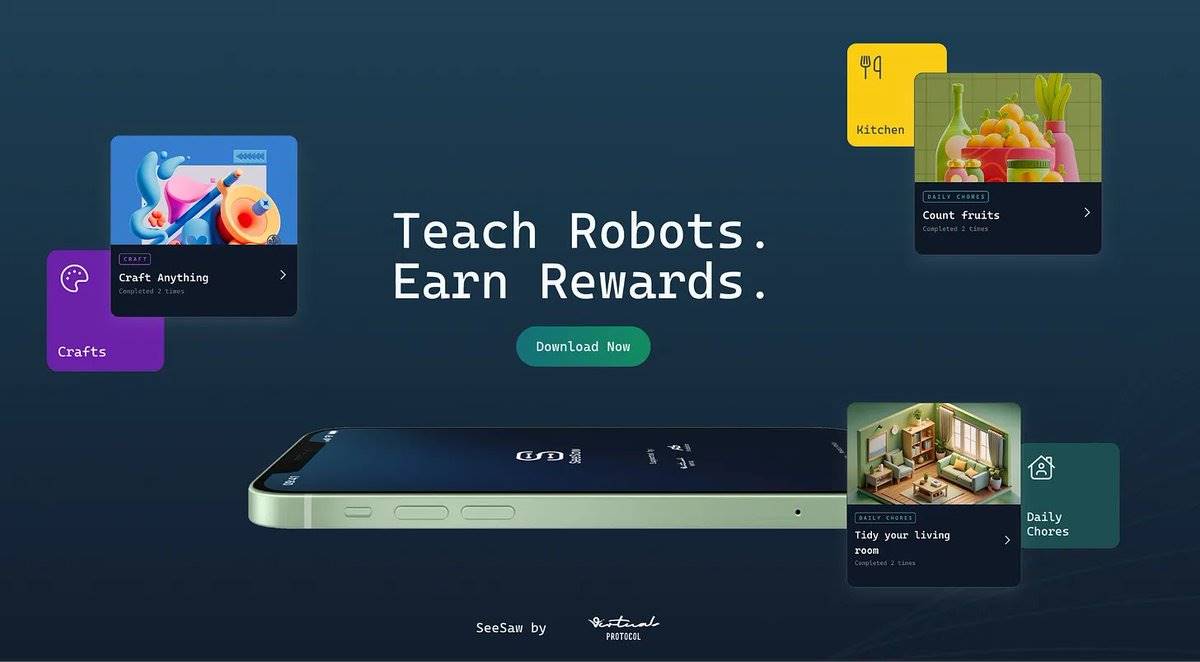
To enable these robot agents to operate efficiently in the real world, they require massive spatial datasets—ranging from distinguishing types of alarm sounds, navigating construction sites, to seemingly simple tasks like folding a shirt correctly.
SeeSaw exists to solve this problem. By having humans record daily activities and target tasks, SeeSaw helps robots better understand the world around them. These everyday actions become data, serving as learning material for robots.
Learning object and human motion patterns in 3D space is extremely challenging, which is why even the smallest movement data is crucial for robots.
Hence, SeeSaw was born. Virtuals deeply understands the importance of data collection.
SeeSaw is an iOS video-capture app that crowdsources videos of human-object interactions. It gamifies the process, allowing users to complete tasks and earn rewards.
As long as rewards match user contributions, the system scales rapidly, giving Virtuals a vast visual interaction database available to any robot team in need.
SeeSaw is developed in collaboration with @BitRobotNetwork, ensuring high-quality data suitable for large-scale robot training.
Just the Beginning
Although this article ends here, for the "technological trinity," this is only the beginning.
These three fields have just started revealing their potential, and thanks to the nature of the crypto industry, we have the rare opportunity to witness their evolution from the ground up.
In the near future, we may see agencies and companies composed entirely of robots. The sight of robots autonomously completing tasks around us will be both exciting and perhaps slightly unsettling for sci-fi enthusiasts.
The future is arriving faster than expected. What Virtuals' exploration of the "technological trinity" will yield remains to be seen—and well worth watching.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














