Monad's Ambition: From Parallel Execution to Large-Scale Applications
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Monad's Ambition: From Parallel Execution to Large-Scale Applications
Before Monad TGE, decoding the breakthrough blockchain focused on "high performance + full EVM compatibility"
Jointly authored by K1 Research and Klein Labs
Key points:
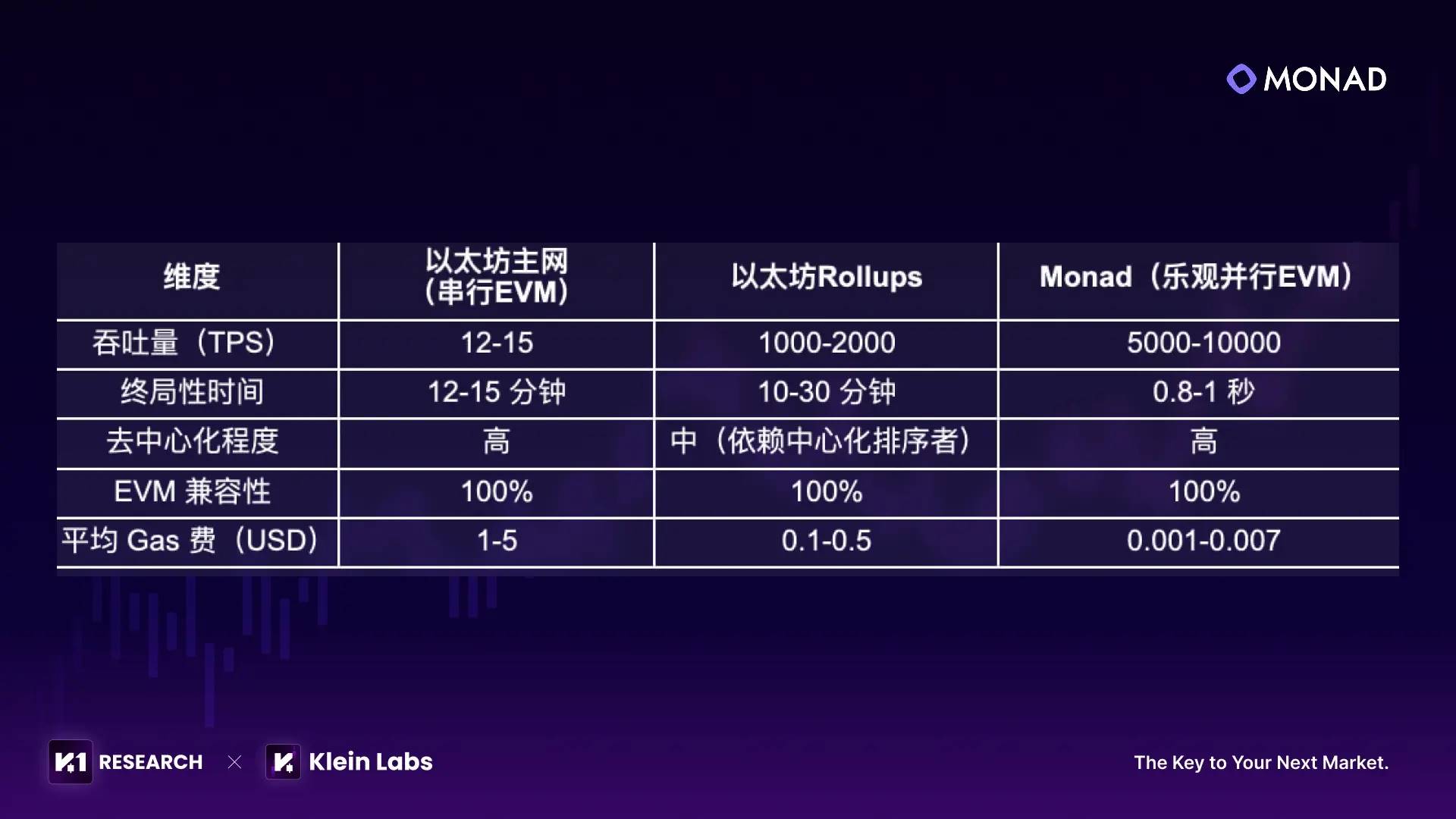
1. Monad is a Layer 1 blockchain focused on "high performance + full EVM compatibility", having raised over $240 million in funding. Its mainnet is expected to launch by the end of 2025, potentially breaking the long-standing trade-off between performance and compatibility in public blockchains. Its core technical breakthrough lies in its optimistic parallel EVM design.
2. Utilizing a "MonadBFT consensus + optimistic parallel EVM" architecture, Monad achieves 0.8–1 second speculative finality per round and enables 70%–80% of transactions to execute in parallel. However, performance stability under complex scenarios remains to be further validated after mainnet launch.
3. Compared with other parallel EVM projects in the same category, Monad differentiates itself through "independent Layer 1 architecture + full native EVM compatibility + over $240 million in funding reserves". During testnet phases, it has already demonstrated performance potential with a 0.5-second block interval.
4. The ecosystem has gathered over 280 projects, with total ecosystem funding reaching $1.32 billion. Through hackathons and specialized accelerator programs, Monad has driven ecosystem cold-start growth, with capital primarily flowing into DeFi infrastructure and core application layers.
5. With a core strategy of "Builders First", Monad attracts developers despite controversies around mainnet progress and validator decentralization. Its ecosystem friendliness and technological innovation provide long-term value support, though future success hinges on delivering promised performance and retaining user scale.
1. Rising Blockchain Star: Monad – Background and Development Milestones
1.1 The Game-Changer Monad: Positioning, Origins, and Vision
Looking back at blockchain evolution, Ethereum built the largest ecosystem thanks to EVM compatibility, yet its performance bottlenecks have always constrained scalability. Solana emerged as a symbol of "high-performance blockchains" with ultra-high TPS, but faced trust crises due to insufficient decentralization and technical instability. These experiences from two leading chains provide a clear reference point for Monad’s positioning.
Monad was created precisely to address the central dilemma in today’s blockchain landscape—“you can’t have both performance and compatibility.” Its core positioning is "a Layer 1 blockchain that combines extreme performance with full EVM compatibility." Unlike some blockchains that sacrifice EVM compatibility for speed or compromise performance for compatibility, Monad starts from the ground up in architectural design to break this “catch-22”—achieving high performance through innovative consensus mechanisms and execution layer optimizations while maintaining seamless compatibility with Ethereum's EVM. This allows developers to migrate applications without rewriting code, offering users low-latency, low-cost transaction experiences.
From an origin perspective, Monad directly addresses real-world limitations within the Ethereum ecosystem. As applications like DeFi, NFTs, and GameFi experienced explosive growth, Ethereum frequently hit peaks of fewer than 15 TPS during congestion, with gas fees soaring to tens or even hundreds of dollars and transaction confirmations delayed beyond 10 minutes. For example, during the 2021 bull market, gas fees for a single NFT transaction on OpenSea reached a peak of $196, forcing ordinary users out of high-frequency trading. DeFi protocol liquidations often failed due to network congestion, resulting in user losses. Although Ethereum’s Layer 2 scaling solutions alleviated some pressure, interaction costs between Layer 2 and the mainnet, along with cross-chain complexity, remain unresolved. The Monad team consists of engineers with years of experience in blockchain infrastructure development, who previously contributed deeply to Ethereum core protocol optimization and Solana performance tuning. They recognized that achieving mass blockchain adoption requires simultaneously solving the three major challenges—performance, compatibility, and decentralization—at the Layer 1 level. This insight became the foundational motivation behind launching Monad.
Monad’s long-term vision isn’t simply to replace an existing chain, but to build a universal platform for next-generation blockchain infrastructure. On one hand, it aims to meet demand for use cases currently unfeasible on Ethereum—such as high-frequency trading, large-scale gaming, and real-time data interactions—through ambitious performance targets of 10,000 TPS, 1-second finality, and average gas fees below one cent. On the other hand, leveraging full EVM compatibility, it seeks to inherit Ethereum’s developer base and project resources, creating a closed-loop ecosystem where migration is seamless and operations efficient. Ultimately, through dynamic validator mechanisms and distributed storage solutions, Monad will preserve decentralization, enabling regular nodes to participate in network maintenance. From a broader perspective, Monad aims to shift blockchain technology from “niche experimentation” to “mass adoption,” providing foundational support for digital transformation across traditional industries such as finance, logistics, healthcare, and social networking—fulfilling the industry-wide vision of "empowering the real economy with high-performance blockchains."
1.2 Timeline Overview: Monad’s Rapid Growth Journey
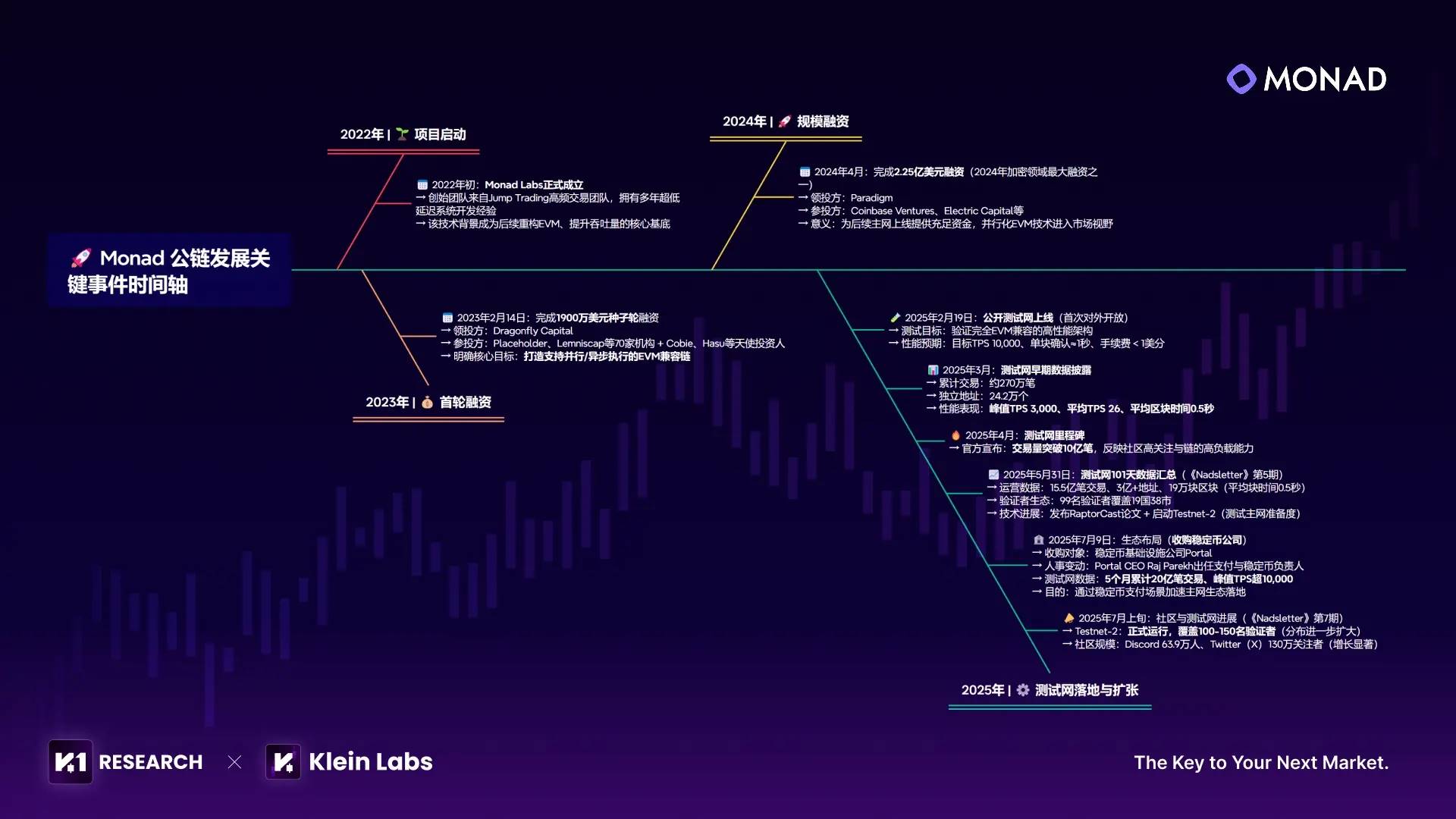
This timeline clearly shows that Monad’s “star power” is no accident—it results from the synergistic combination of capital backing, talent strength, and technical execution capability:
In terms of fundraising, Monad secured continuous support from top-tier industry investors due to its clear technical direction and promising outlook. It raised $19 million in seed funding led by Dragonfly Capital in 2023, followed by $225 million in funding led by Paradigm in 2024. Combined, these rounds exceed $240 million, with notable backers including Coinbase Ventures and Electric Capital. The project’s valuation rose concurrently to $3 billion, laying a solid financial foundation for technical R&D, team expansion, and ecosystem development.
On the team side, core members come from elite financial and tech institutions such as Jump Trading and Goldman Sachs, bringing deep expertise in distributed systems design and low-latency transaction optimization. Some were also heavily involved in Ethereum core protocol upgrades and Solana performance debugging. Their professional background provides critical assurance for overcoming the industry’s persistent trilemma of “performance-compatibility-decentralization.”
Technically, testnet performance further validates its potential—peaking at 5,200 TPS, processing over 334 million RPC requests within 12 hours, and surpassing 300 million unique on-chain addresses. These figures not only confirm the feasibility and stability of core technologies like parallel EVM and MonadBFT but also demonstrate strong appeal to users and developers alike.
The integration of capital, talent, and technical execution forms the core engine driving Monad’s rapid advancement in the competitive blockchain landscape, allowing it to stand out among peers.
1.3 Uncertainties and Future Outlook
Although Monad faces certain challenges during its development, these very issues present opportunities to refine its technology and grow its ecosystem. Current uncertainties mainly revolve around mainnet release timing, fluctuations in user activity, and the efficiency of fund utilization. However, as the testnet continues to operate, the gradual rollout of the mainnet will clarify the project’s progress and potential. Community skepticism largely stems from differing expectations and typical early-stage concerns rather than fatal flaws in the project itself.
Going forward, when tracking Monad’s development, we must closely monitor whether its promised high-performance goals are delivered on schedule, alongside progress in technical delivery, effectiveness of decentralization, and tangible outcomes in ecosystem building. As the mainnet launch approaches, these factors will determine Monad’s true competitiveness in the blockchain space.
The following sections will conduct an in-depth analysis of Monad from multiple dimensions—network data and operational metrics, technical breakdown, competitive landscape and advantage analysis, ecosystem development, and community culture and builder incentives—to comprehensively assess its growth potential and long-term risks.
2. Network Data and Operational Metrics
2.1 Performance Metrics
Transaction Throughput and Success Rate: According to the Monad Testnet Overview Dashboard, as of the end of August 2025, the testnet had processed approximately 255 million successful transactions, with a 90-day average success rate of 98.18%. Institutional validator Twinstake achieved 100% block production rate and 100% block proposal rate on Testnet-2, with network-wide average block production rate at about 98.75%, indicating stable consensus efficiency even under high-performance targets.
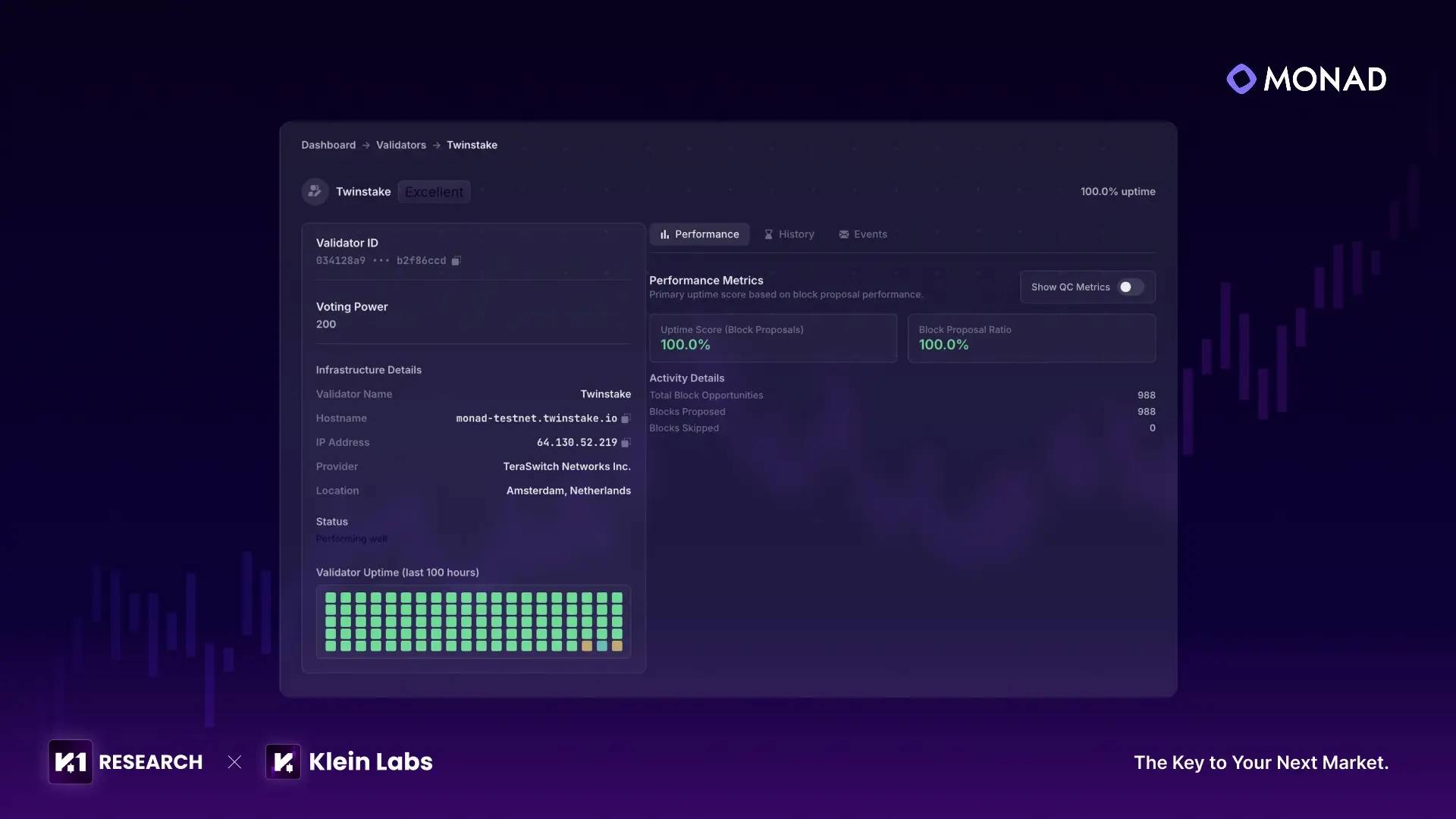
Source:Twinstake | Monad in the Wild: Institutional Insights from Testnet Deployment
● TPS and Fees: The dashboard shows peak TPS reached 300–350 TPS (weekly average ~100 TPS) between March and April 2025, still far below the official claim of a theoretical 10,000 TPS. Median transaction fee over the past 90 days was around 0.0028 MON.
● Block Latency: While average block time isn't directly shown, steady throughput between June and July 2025 without widespread failures suggests sub-second block intervals, validating the stability of the testnet’s parallel execution architecture.
2.2 On-Chain Data
● Addresses and Wallet Activity: The Monad Foundation dashboard reports 310,630,141 unique addresses. BlockRaptor defines "active wallets" as those that have made at least one successful transaction, calculating approximately 309,903,696 active wallets, averaging about 7 transactions per wallet.
Source:
https://dune.com/monad_foundation/monad-testnet-overview-dashboard
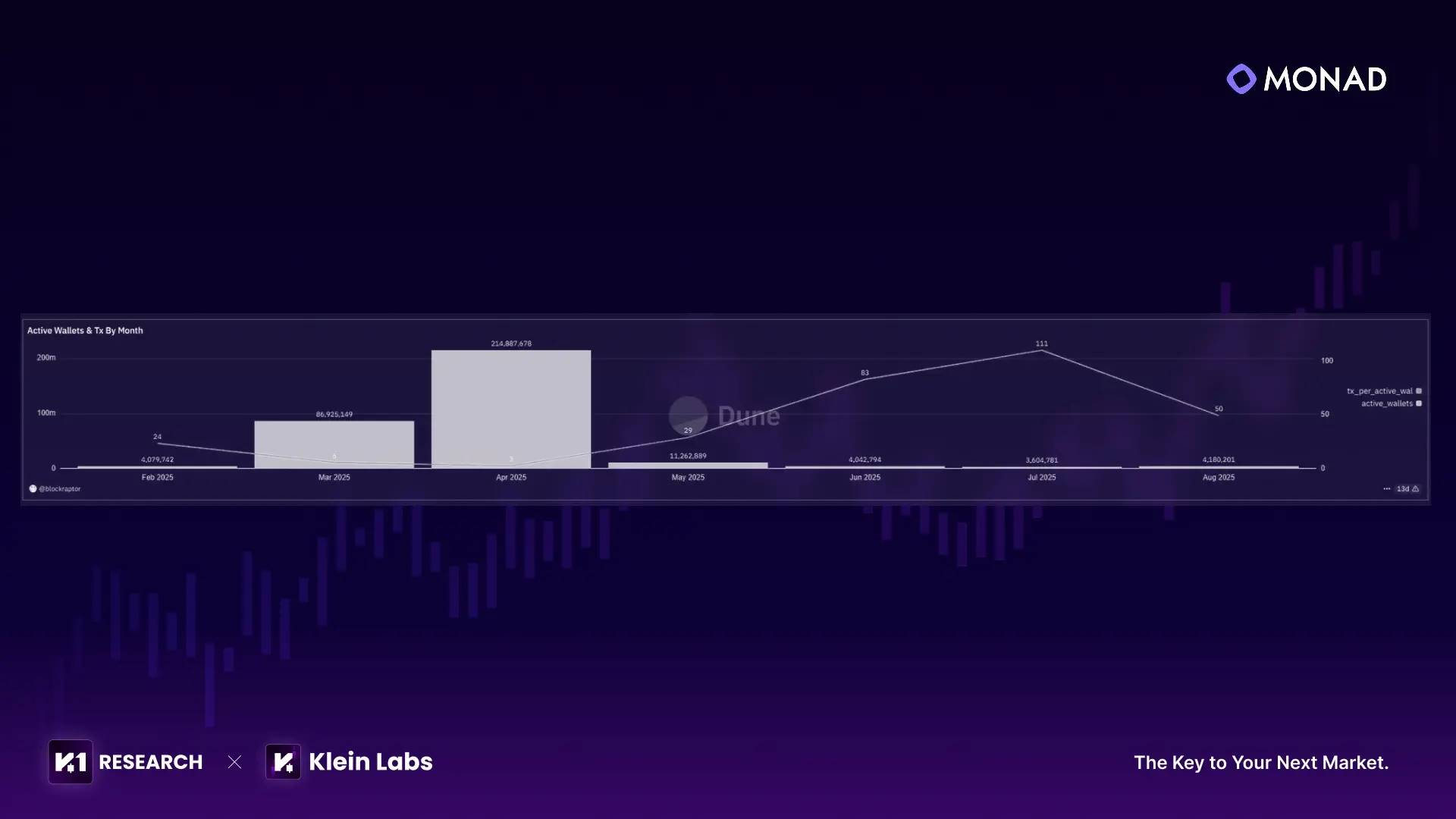
● Transaction Distribution and Temporal Evolution: The BlockRaptor "Active Wallets & Tx By Month" chart reveals a distinct "surge-and-fall" pattern in user growth: 86.92 million active wallets in March, spiking to 215 million in April, then dropping to 11.28 million in May, stabilizing around 4 million from June to August. Correspondingly, average monthly transactions per wallet dropped from 6 in March to 3 in April, then rebounded to ranges of 29, 83, and 111 afterward. This indicates that the initial surge driven by "airdrop anticipation" did not translate into sustained engagement.
● Smart Contracts and Creators: The official dashboard shows 36,108,124 contracts deployed by 2,975,837 contract creators as of late August. Monthly statistics from BlockRaptor show contract creation peaked between March and April (60k–80k new per month), declining afterward but continuing to grow cumulatively.
● Wallet Behavior Distribution: The BlockRaptor dashboard breaks down active wallets by number of transactions per month: In April, 209.5 million wallets conducted only one transaction, accounting for 97.5% of total monthly active wallets; only 0.9% executed more than 10 transactions in a month. Overall, by August, 293,597,158 active wallets had conducted just one transaction, about 89%, further confirming that most testnet users are short-term "participation-driven."
2.3 Decentralization Status
● Validators and Contract Creators: There are currently approximately 186 active validators on the Monad testnet. The validator list shows all staking amounts uniformly set at 200 units, with near-universal success rates approaching 100%, indicating strong consistency. Validators are located in countries including Romania, Germany, Ireland, South Korea, and Singapore. This demonstrates that Monad has achieved an initial balance between performance and decentralization, leaving room to expand validator count ahead of mainnet.
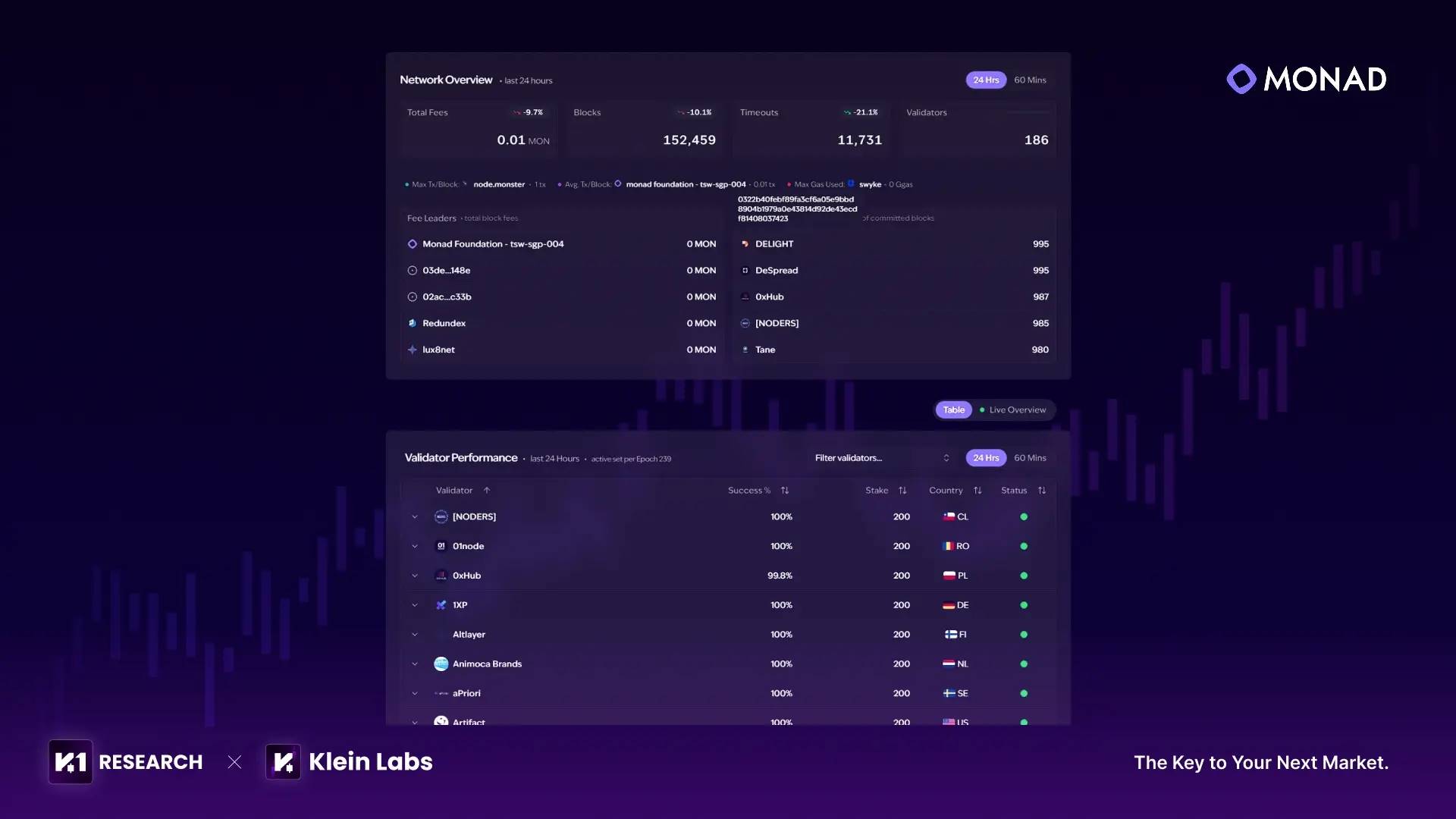
Source:
https://www.gmonads.com/validators
Overall, Monad testnet data across performance, user participation, and developer activity shows billions of cumulative transactions and over 300 million active wallets reflect strong early interest, but low user stickiness and genuine engagement. Only a small fraction of users maintain high-frequency trading monthly, while transaction success rates remain above 98% with extremely low fees—indicating the core architecture can handle high loads, though still in early ramp-up phase.
3. Technical Breakdown
3.1 Consensus Layer: MonadBFT—Making High-Performance Consensus More Reliable
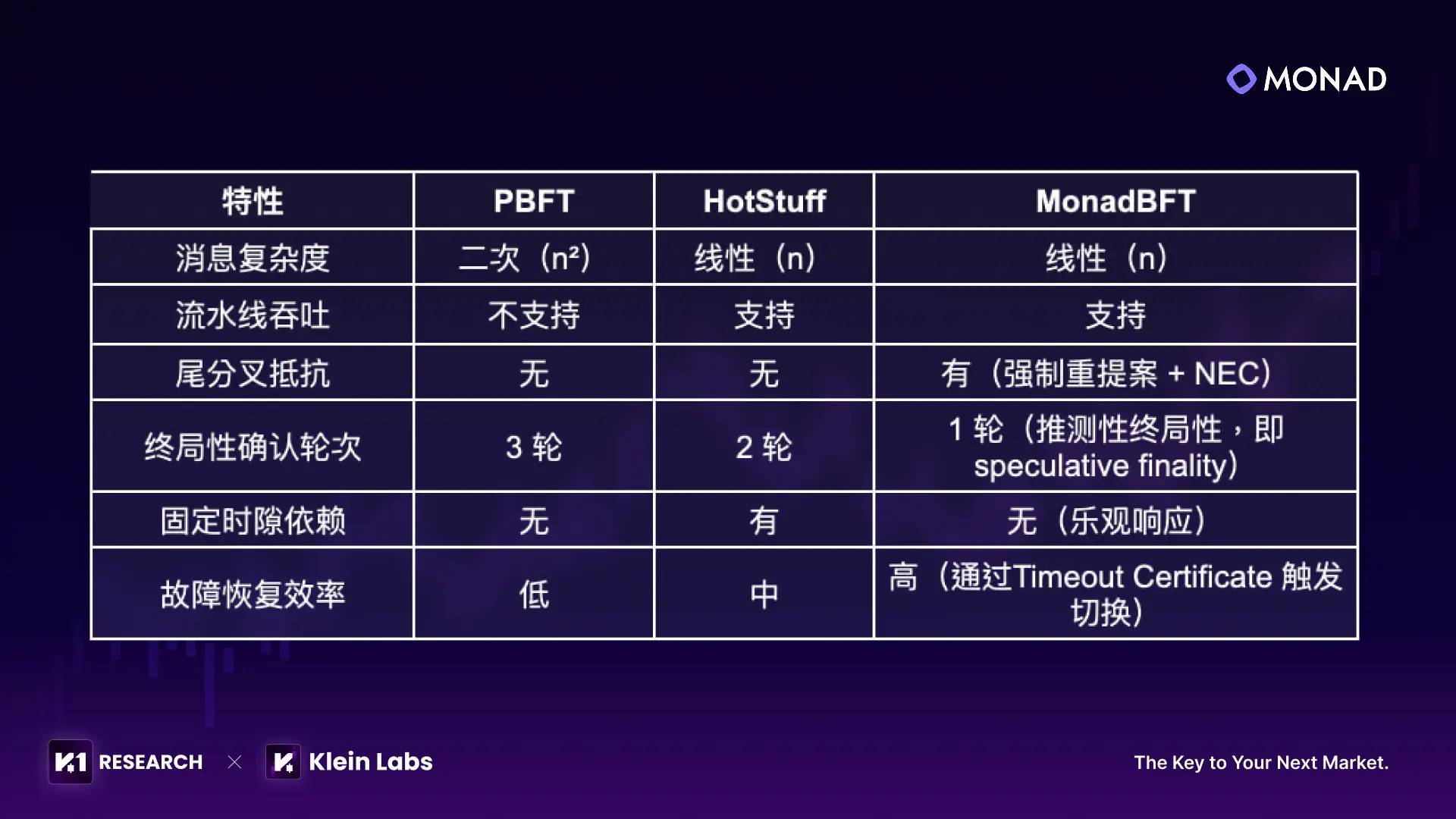
One key to Monad’s high performance is its proprietary MonadBFT consensus mechanism. Based on improvements to the 2018 HotStuff consensus, it solves message congestion issues common in traditional BFT protocols (like PBFT) and fixes the frequent “tail forks” found in HotStuff, laying the groundwork for high-performance chain operation.
3.1.1 Four Core Innovations of MonadBFT
1. Tail-Fork Prevention: A new leader must re-propose the previous valid block unless a majority of validators haven’t seen it, ensuring valid blocks aren’t lost;
2. Fast Confirmation: One vote achieves “basic confirmation” of a transaction, completed within hundreds of milliseconds and irreversible unless the proposer misbehaves;
3. Responsive Flexibility: No fixed block interval; consensus completes in 200–300ms, with fast leader switching upon failure;
4. Scalability: Validators communicate unidirectionally only with the leader, so performance remains unaffected even with hundreds of nodes.
3.1.2 Comparison with HotStuff Family Protocols
3.2 Execution Layer: Optimistic Parallel EVM—Achieving Both Compatibility and Performance
Monad employs an optimistic parallel EVM at the execution layer, fully compatible with the Ethereum EVM ecosystem while overcoming performance bottlenecks through parallel processing.
3.2.1 Core Positioning: Leveraging “Full Compatibility” to Capture Ecosystem Momentum
Supports the latest Ethereum opcodes and precompiles, allowing existing contracts to deploy without modification. Common tools (e.g., Hardhat, MetaMask) integrate seamlessly, significantly reducing developer migration costs.
3.2.2 Technical Breakthrough: Optimistic Parallel Execution and Conflict Rollback Mechanism
Monad improves efficiency via an “execute first, verify later” optimistic parallel model: grouping unrelated transactions for parallel processing, rolling back and re-executing sequentially if they modify shared data. Testing shows 70%–80% of transactions can run in parallel, with DeFi scenarios running 8–10x faster than Ethereum.
3.2.3 Differentiation from Ethereum Rollups
3.3 Technical Synergy Value: Balanced Perspective on Advantages and Realities
Monad attempts to overcome the blockchain trilemma of “performance, compatibility, decentralization” through synergy between its consensus and execution layers. However, its actual value must be objectively assessed considering both technical strengths and implementation challenges.
3.3.1 Verified Core Advantages: Addressing Clear Industry Pain Points
Based on testnet performance and technical design, Monad’s technology stack delivers targeted improvements:
● User Experience: Transaction confirmation reduced from “minutes” to “milliseconds,” with gas fees just 1/20–1/30 of Ethereum’s, balancing speed and stability;
● Developer Friendliness: Zero migration cost, enabling applications like high-frequency trading and on-chain gaming that Ethereum struggles to support;
● Ecosystem Continuity: Direct access to Ethereum’s $52 billion TVL and vast developer resources, accelerating ecosystem maturity.
3.3.2 Pending Challenges: Uncertainties in Real-World Implementation
● Performance in Complex Scenarios: Efficiency in handling multi-dependent transactions needs validation on mainnet;
● Validator Decentralization: Balancing accessibility for ordinary nodes with consensus efficiency;
● Ecosystem Differentiation: Attracting Ethereum Layer 2 developers and strengthening scenario-specific advantages.
4. Competitive Landscape and Advantage Analysis
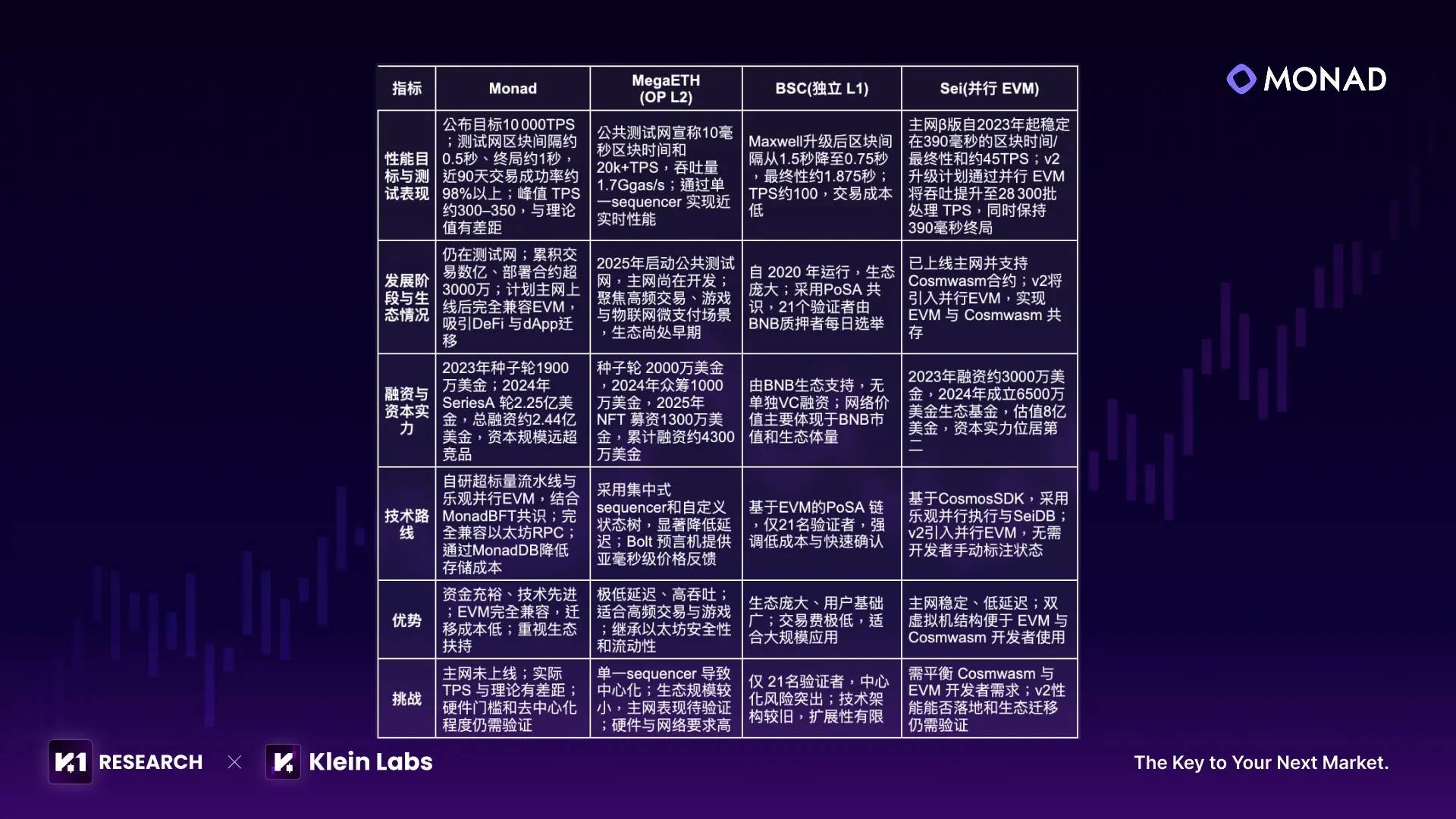
4.1 Core Blockchain Performance and Ecosystem Comparison: Monad & MegaETH & BSC & Sei
4.2 Comprehensive Assessment: Monad’s Core Competitiveness and Challenges in the High-Performance EVM Race
In the competitive landscape of high-performance EVM blockchains, Monad holds clear advantages in capital strength, technical roadmap, and ecosystem compatibility, forming a solid foundation for rapid growth.
Core Barriers in Competitive Positioning
1. Dual Moat of Capital and Ecosystem Migration: With approximately $244 million raised, Monad far exceeds MegaETH (~$43 million) and Sei in funding, strongly supporting technical development and ecosystem launch. More importantly, Monad’s 100% bytecode-level compatibility with Ethereum enables nearly zero-cost contract migration: developers don’t need to rewrite code, and users don’t need to change wallets or habits. This dramatically lowers the barrier for ecosystems to move from Ethereum to Monad, giving it strong potential to quickly gather DeFi and dApp projects.
2. Performance Advantages of Independent L1 Architecture: As an independent L1, Monad uses its proprietary MonadBFT consensus and optimistic parallel EVM to target 5,000–10,000 TPS throughput and 0.8–1 second finality, aiming for high performance without sacrificing decentralization. In contrast, MegaETH pursues sub-millisecond latency via a single sequencer but faces significant centralization concerns; BSC’s PoSA model relies on only 21 validators, limiting decentralization; Sei v2 claims 28k+ TPS batch throughput but awaits mainnet validation. Monad’s positioning makes it more attractive for applications requiring independent security boundaries.
In summary, Monad establishes a clear edge in the high-performance EVM race through ample capital, full EVM compatibility, and high-performance standalone L1 positioning. If it successfully delivers on performance promises, enhances decentralization, and cultivates a vibrant application ecosystem, it could become the benchmark for “high-performance + full compatibility” independent blockchains.
5. Ecosystem Development
5.1 Ecosystem Funding Trends: Top Projects Attract Tier-One Investors
As a next-gen Layer 1 blockchain with over $240 million raised and a valuation exceeding $3 billion, Monad’s own capital appeal extends to its ecosystem. Leading ecosystem projects have received intensive investments from top-tier institutions like Pantera Capital and Binance Labs, injecting strong momentum into ecosystem bootstrapping.
Currently, most Monad ecosystem projects are in seed or angel stages, with investor interest concentrated in areas demonstrating strong technical fit and clear use-case applicability. Below, we outline representative projects across sectors to illustrate its diversified ecosystem layout.
5.2 Ecosystem Expansion: Portal Acquisition and Stablecoin Strategy
In July 2025, the Monad Foundation completed the acquisition of Portal, marking a pivotal step in its strategic layout for stablecoins and payment infrastructure. Portal is a company offering cross-chain stablecoin wallets and payment solutions, already capable of supporting daily settlements worth millions of dollars in stablecoin volume.
The strategic significance of this acquisition includes:
1. Rapid entry into the stablecoin market, reducing reliance on external stablecoins;
2. Strengthening foundational financial infrastructure to reliably support DeFi, payments, and trading;
3. Sending a clear signal to the ecosystem—via direct foundation investment—about prioritizing stablecoin and payment use cases.
Overall, the Portal acquisition represents not just a capital investment, but a forward-looking strategic move by Monad to build financial infrastructure and stablecoin capabilities before mainnet launch, laying a robust foundation for future DeFi and payment applications.
5.3 Ecosystem Scale: Pre-Mainnet Blueprint and Growth Potential
According to official 2025 statistics from Monad, its ecosystem directory lists nearly 280 projects spanning DeFi, infrastructure, AI, gaming, payments, and DePIN, forming a “full-spectrum coverage with key areas emphasized” layout.
Notably, despite the mainnet not yet launching, Monad has attracted numerous high-quality startup teams due to its technical advantages of “high performance (high throughput, low latency) + full EVM compatibility,” amplified by endorsements from top-tier investors. The ecosystem is transitioning from early “concept incubation” to a critical preparation phase of “application testing and use-case refinement”—for instance, multiple core DeFi applications have completed testnet iterations, and infrastructure projects have begun preliminary integration, setting a strong foundation for rapid growth in user base and transaction volume post-mainnet launch.
5.4 Ecosystem Composition: Multi-Track Project Matrix and Key Examples
Monad’s ecosystem follows a structure of "DeFi at the core, extended collaboratively across tracks": DeFi leads with 12 projects, making it the most active sector. Wallets, as key user gateways, host 4 projects. Foundational tracks such as Identity, Analytics, and Infrastructure, along with innovative areas like AI and Prediction Markets, are also represented—reflecting an expansion logic from “core financial use cases” to “foundational support + diverse applications.”
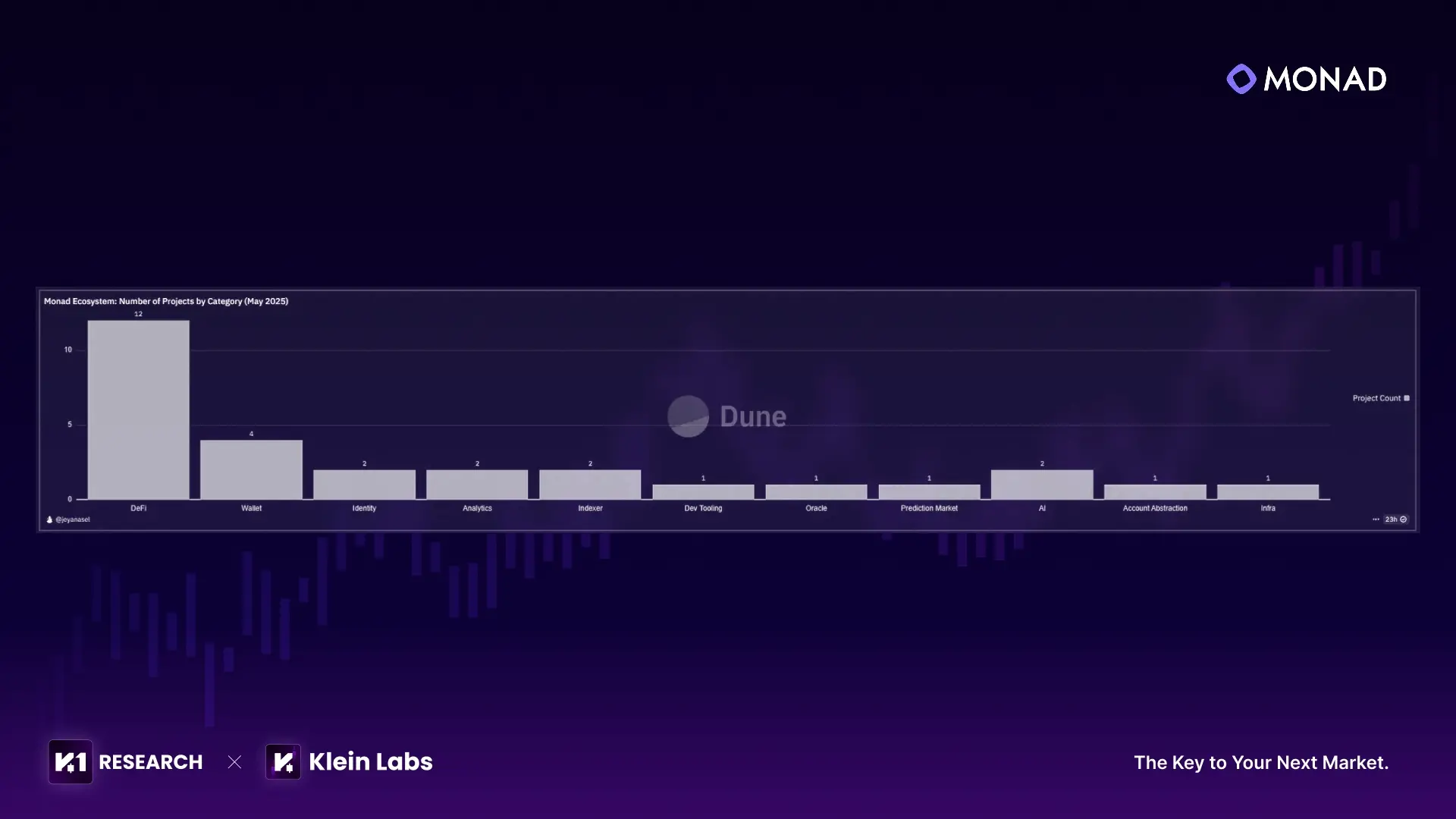
Source:Monad
Combining funding trends and official priorities, the following section focuses on core projects with dense funding and strong foundation backing, analyzing their potential and progress across sectors.
5.4.1 DeFi Infrastructure and Core Applications (Funding Hotspots)
1. aPriori (@apr_labs)
● Funding: Raised over $30 million in seed and strategic rounds (led by Pantera Capital, with Yzi Labs participating).
● Positioning: MEV-optimized LSD derivatives platform focusing on Monad-native staking.
● Highlights: Reduces gas costs by over 30% via MEV capture, supports issuance of multiple staking derivatives; a flagship DeFi project receiving priority support from the Monad Foundation’s "Fundraising & Foundry Program."
2. Fastlane Labs (@0xFastLane)
● Funding: $6 million in strategic round (co-led by Figment Capital and DBA); $2.3 million seed round (led by Multicoin Capital).
● Positioning: Provider of low-latency transaction execution optimization.
● Highlights: Compresses transaction confirmation to sub-millisecond levels, optimized for high-frequency quant and derivatives trading; custom-optimized transaction bundling logic for MonadBFT, serving as a “performance backbone” infrastructure.
3. Kintsu (@KintsuFinance)
● Funding: $4 million in seed round (led by Castle Island Ventures).
● Positioning: Liquid staking service platform.
● Highlights: Supports staking of Monad-native tokens and multi-chain assets, tightly integrated with Monad’s consensus for security and yield efficiency; a core project in Monad’s “Staking Layer.”
4. Curvance (@Curvance)
● Support: Awarded Monad’s official “Ecosystem Pioneer” label during testnet, ranked Top 3 in community热度.
● Positioning: Cross-chain lending market (focused on Monad mainnet).
● Highlights: Supports lending/borrowing of over 15 assets, leverages Monad’s low gas fees to offer borrowing rates 40% lower than Ethereum L2s; surpassed 100,000 users on testnet, poised to become the ecosystem’s “lending hub” post-launch.
5. Perpl (@perpltrade)
● Funding: ~$9.25 million in strategic/seed rounds (led by Dragonfly).
● Positioning: Decentralized perpetual futures exchange (perps DEX) built on Monad using EVM architecture, planning to implement on-chain central limit order book (CLOB).
● Highlights: ① Plans testnet launch by year-end for early user testing and bug discovery; ② Leverages Monad’s low latency and EVM compatibility to enhance trading experience and compliance speed (e.g., faster token listings); ③ Concentrates all liquidity into perpetual contracts instead of spreading across multiple expiries (unlike options), improving depth and user experience.
6. Modus Finance (@Modus_Finance)
● Positioning: High-capital-efficiency, composable DeFi lending protocol supporting LST, LRT, LP tokens, and stablecoins.
● Highlights: Offers up to 95% LTV borrowing, enhancing leverage and asset utilization; modular markets reduce systemic risk, supports auto-leverage strategies (Looping Vault) to maximize returns, especially suited for Monad reward-bearing assets.
5.4.2 Infrastructure and User Access Points
1. Monorail (@monorail_xyz)
● Positioning: DEX aggregator (combining AMM and CLOB liquidity).
● Highlights: First “full-type DEX aggregator” supporting Monad, routing optimal prices from sources like Kuru, CrystalExch, and AMMs, reducing slippage by 20% vs. single DEXs; processed over 50,000 transactions daily on testnet.
2. Kuru Exchange (@KuruExchange)
● Funding: $11.6 million Series A (initial $2M seed led by Electric Capital, later $9.6M Series A led by Paradigm).
● Positioning: Shifted business model with Kuru Flow smart aggregator, retains orderbook with integrated AMM, connects all major liquidity sources on Monad, aiming to become the best spot trading venue on Monad.
● Highlights: Dual architecture of “custodial accounts + Uniswap-style Lite mode” caters to both pro traders and beginners; one of the highest-volume DEXs in the ecosystem.
3. Clober (@CloberDEX)
Requirement: Preserve all HTML tags and technical terms exactly as they appear - When "深潮" and "TechFlow" appear together (e.g., "深潮 TechFlow"), translate them as just "TechFlow" - Apply the glossary terms if provided below We are translating from Chinese to English, and the text contains instances of "深潮 TechFlow", which should be translated as just "TechFlow". However, in the provided text, there are no instances of "深潮" alone or combined with "TechFlow" in a way that violates the rule. The images are hosted on "techflowpost.com", but that's part of the URL and not the content to be translated. Therefore, we proceed with the translation as is. Note: The last project in section 5.4.2 is incomplete in the original text. We must preserve the structure and not add anything. But note: The original text ends abruptly at:
3. Clober (@CloberDEX)
● Positioning: Based on LOBSTER mechanism, a cross-chain order book DEX (Monad native).
● Highlights: Uses Segment Tree-based LOBSTER matching engine and self-developed Octopus Heap data structure to greatly reduce matching gas costs and improve efficiency; asynchronous settlement decouples transactions from funds, optimizing on-chain execution performance.
Then it jumps to:5.4.3 Innovation Scenarios and Niche Tracks
So we continue accordingly. Also, note that in the original text, the image tag for 3.2.3 is malformed: it hasaround the img tag. We preserve it exactly. Let's now output the entire translation as required, without any additions or omissions.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News