Hotcoin Research | Ethereum's Decade of Ups and Downs: From White Paper to Financial Restructuring Experiment as a Global Settlement Layer
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Hotcoin Research | Ethereum's Decade of Ups and Downs: From White Paper to Financial Restructuring Experiment as a Global Settlement Layer
Over the past decade since its launch in 2015, Ethereum has evolved from an initial smart contract platform into a global decentralized financial infrastructure, establishing its leadership in the blockchain industry through technological innovations (PoS, Layer2, etc.) and ecosystem growth (DeFi, NFT, DAO). Despite ongoing challenges such as scalability and competition, it has demonstrated the potential to become the foundational protocol of the future "Internet of Value."
1. Introduction
In 2013, 19-year-old programmer Vitalik Buterin unveiled a bold vision: he published a whitepaper titled "Ethereum," outlining a blockchain blueprint surpassing Bitcoin's capabilities. To turn this "world computer" vision into reality, he and his team raised approximately $18 million through an initial coin offering (ICO), officially launching the Ethereum network in 2015 and sparking a revolution in Web3 smart contracts and DApps. Over the past decade, it has weathered booms and busts, undergone technological evolution, witnessed the rise of financial applications, and overcome numerous internal and external challenges—reborn and strengthened through each upheaval. Today, Ethereum is no longer merely a daring idea but has grown into a cornerstone of the blockchain industry.
This article reviews Ethereum’s developmental milestones and technical evolution, analyzes its revolutionary role in DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs, and explores key themes such as Layer 2 scaling, competitive landscape, and future challenges. Through this analysis, we will trace Ethereum’s journey from its “world computer” vision to becoming a global decentralized financial infrastructure and explore potential directions for its next decade.
2. A Decade of Ethereum Development: Key Milestones

Ethereum’s ten-year journey represents one of the most significant storylines in blockchain history. Over the past decade, Ethereum has evolved from an early “hackers’ playground” into a new infrastructure supporting hundreds of billions in value. Each milestone not only advanced Ethereum itself but also reflected the broader crypto industry’s transformation and maturation.
- 2013–2015: Founding — Vitalik released the whitepaper; crowdfunding occurred in 2014; the genesis block launched on July 30, 2015, marking Ethereum mainnet’s official debut and the dawn of the smart contract platform era.
- 2016: Idealism and Crisis — The smart contract platform gained traction, but the “The DAO” security incident triggered a community hard fork, resulting in Ethereum Classic (ETC).
- 2017: Boom and Challenge — ICO mania exploded, with Ethereum becoming the dominant token issuance platform; ERC-721 standard introduced, enabling early NFT applications like CryptoKitties.
- 2018–2019: Winter and Hibernation — ICO bubble burst, ETH price plummeted from peak $1,448 to $84; Ethereum focused on technical upgrades (e.g., Byzantium, Constantinople hard forks) to lay foundations.
- 2020: Rise of DeFi — Decentralized finance surged, with “yield farming” igniting the DeFi Summer; protocols like Uniswap and Compound grew rapidly, while network congestion and high gas fees became prominent.
- 2021: Peak Performance — London upgrade implemented EIP-1559, introducing fee burning; Layer 2 solutions Arbitrum and Optimism launched mainnets; NFT boom (e.g., BAYC) drove ETH to an all-time high near $4,878.
- 2022: Turning Point and Transformation — “The Merge” completed, transitioning from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, reducing energy consumption by 99%; yet, the crypto market cooled (Terra collapse, FTX incident), with ETH briefly falling below $1,000.
- 2023: Revival and Upgrade — Shanghai/Shapella upgrade enabled staking withdrawals, completing PoS transition; Rollup ecosystems like Arbitrum matured; ZK Rollup solutions zkSync and StarkNet launched.
- 2024: Scaling and Integration — Cancun/Dencun upgrade (including EIP-4844) reduced Layer 2 fees by ~90%, improving data availability; U.S. approved ETH spot ETFs, attracting traditional institutions.
- 2025: Moving Forward — (Pectra upgrade, etc.) introduces account abstraction for more flexible wallets and contract accounts; Ethereum’s market cap approaches $500 billion, solidifying its role as a global decentralized financial infrastructure.
From pioneering smart contract platforms to embracing proof-of-stake consensus, Ethereum has repeatedly transcended its limits at critical junctures. The experience and lessons accumulated through these developments have strengthened the network’s resilience and guided future technological evolution.
3. Technical Evolution: From “World Computer” to Sharding and Rollups
At inception, Ethereum was dubbed the “world computer,” with its core innovation being a Turing-complete smart contract platform that expanded blockchain into a programmable, decentralized computer. Developers could deploy smart contracts on Ethereum to support complex applications beyond simple transfers. Since the 2015 mainnet launch, tens of millions of smart contracts have been deployed globally, powering a thriving ecosystem. However, early Ethereum used proof-of-work (PoW) consensus, which ensured decentralization and security but limited performance. As the 2017–2018 ICO boom and apps like CryptoKitties gained popularity, network congestion and soaring fees exposed throughput bottlenecks. With single-chain capacity limited to just over a dozen transactions per second, demand outpaced supply—gas fees sometimes exceeded $50 during peaks. This performance and cost crisis prompted the Ethereum community to initiate the ambitious “Ethereum 2.0” upgrade roadmap, aiming to dramatically enhance scalability and sustainability without compromising decentralization and security.
1. Consensus Evolution: From PoW to PoS
After years of research and preparation, Ethereum underwent the historic “Merge” upgrade in 2022. Prior to this, the Ethereum team had launched a standalone PoS Beacon Chain in 2020 as a testbed and repeatedly delayed the PoW chain’s “difficulty bomb” to allow time for transition. Finally, on September 15, 2022, the Ethereum mainnet successfully merged without downtime, transitioning from energy-intensive PoW to efficient proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus. This shift reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by 99.95% and introduced staking: ETH holders can stake to earn ~4% annual yield, participate in network validation, and secure the network. This made ETH a “productive asset” and enhanced network security. As of July 31, 2025, over one million validators have participated in staking, locking approximately 36.11 million ETH (about 29.17% of circulating supply) to protect the network. The PoS mechanism also reduced Ethereum’s new coin issuance rate by about 90%, and combined with fee burning, has led to net deflationary periods during high activity.
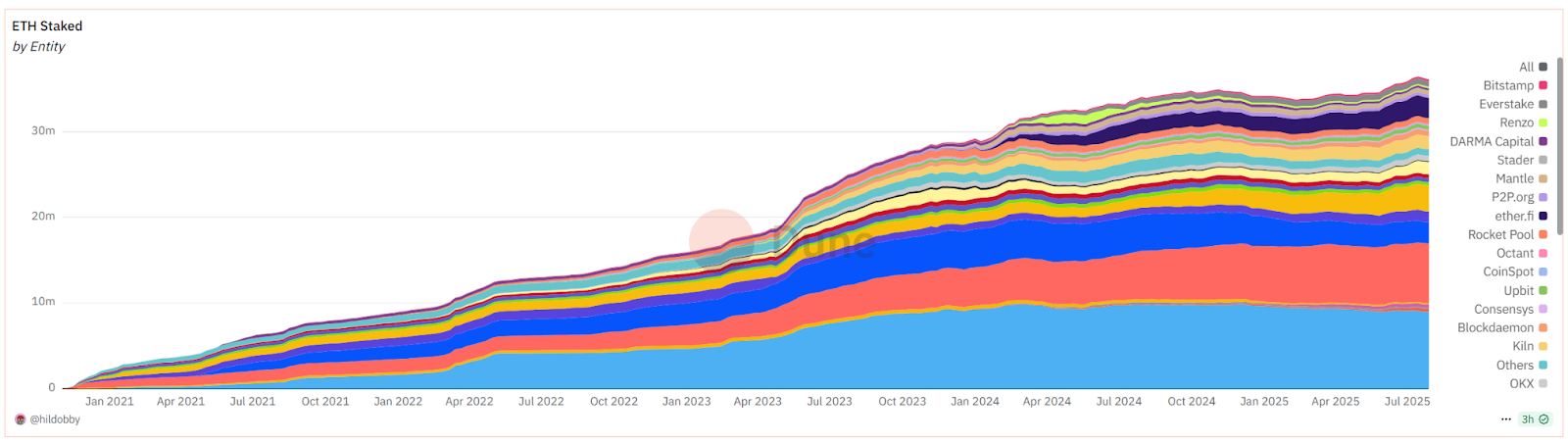
Source: https://dune.com/hildobby/eth2-staking
2. Key Proposals and Protocol Upgrades
Alongside consensus changes, a series of Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) were implemented, shaping the network’s economic and performance characteristics. The most impactful was EIP-1559: introduced during the August 2021 London upgrade, it implemented base fee burning, destroying part of each transaction fee. Since launch, over 4 million ETH have been burned, optimizing the fee market and reducing ETH supply growth, contributing to deflationary expectations. Additionally, EIP-4844, deployed in March 2024, significantly improved Ethereum’s data throughput. By introducing “blob” transactions, it lowered data submission costs for Layer 2 Rollups—reducing Rollup gas costs by more than half. These EIPs not only improved user experience but also laid the groundwork for future large-scale scaling.
3. Toward Sharding and Modular Architecture
To fundamentally overcome performance bottlenecks, Ethereum planned a “sharding” (Sharding) technology roadmap. Sharding splits blockchain state and transaction load across multiple parallel shard chains, enabling parallel scaling. Ethereum’s consensus layer coordinates these shards, sharing security while processing transactions independently. This approach could boost Ethereum’s TPS into the hundreds of thousands, reducing per-transaction costs to fractions of a cent. Full sharding is expected to be gradually introduced between 2025 and 2026. While full sharding isn’t live yet, its principles are partially realized in current Rollup scaling solutions. Rollups are Layer 2 networks built atop Ethereum, executing many transactions off-chain and batching results back to the main chain to reduce load. In recent years, both Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup technologies have advanced, spawning Layer 2 networks like Optimism, Arbitrum, zkSync, and StarkNet. Ethereum mainnet is increasingly evolving into a settlement layer for these L2s: securing finality and data availability, while Rollups handle high-throughput transaction processing. This synergy transforms Ethereum from a single-layer chain into a multi-layer modular network.
4. Leap in Performance and Scalability
Through PoS upgrades and Layer 2 scaling strategies, Ethereum’s technical evolution over the past decade has consistently focused on enhancing performance and lowering usage barriers. Today, a collaborative structure between mainnet and Layer 2 networks is established: mainnet securely processes around 1.8 million transactions daily while maintaining high decentralization; meanwhile, total Layer 2 transaction volume exceeds mainnet by multiples, with over 5 million transactions executed daily across Ethereum L2s. Thanks to Layer 2 offloading, mainnet congestion has greatly eased—typical user gas fees have dropped from dozens of dollars at peak times to mere cents on mainnet and less than a cent on L2s. As a result, Ethereum’s on-chain interaction experience now approaches the speed and cost of Web2 applications. From consensus upgrades and virtual machine optimizations to sharding and Rollup scaling, each technological leap has made Ethereum stronger and more efficient while preserving decentralization.
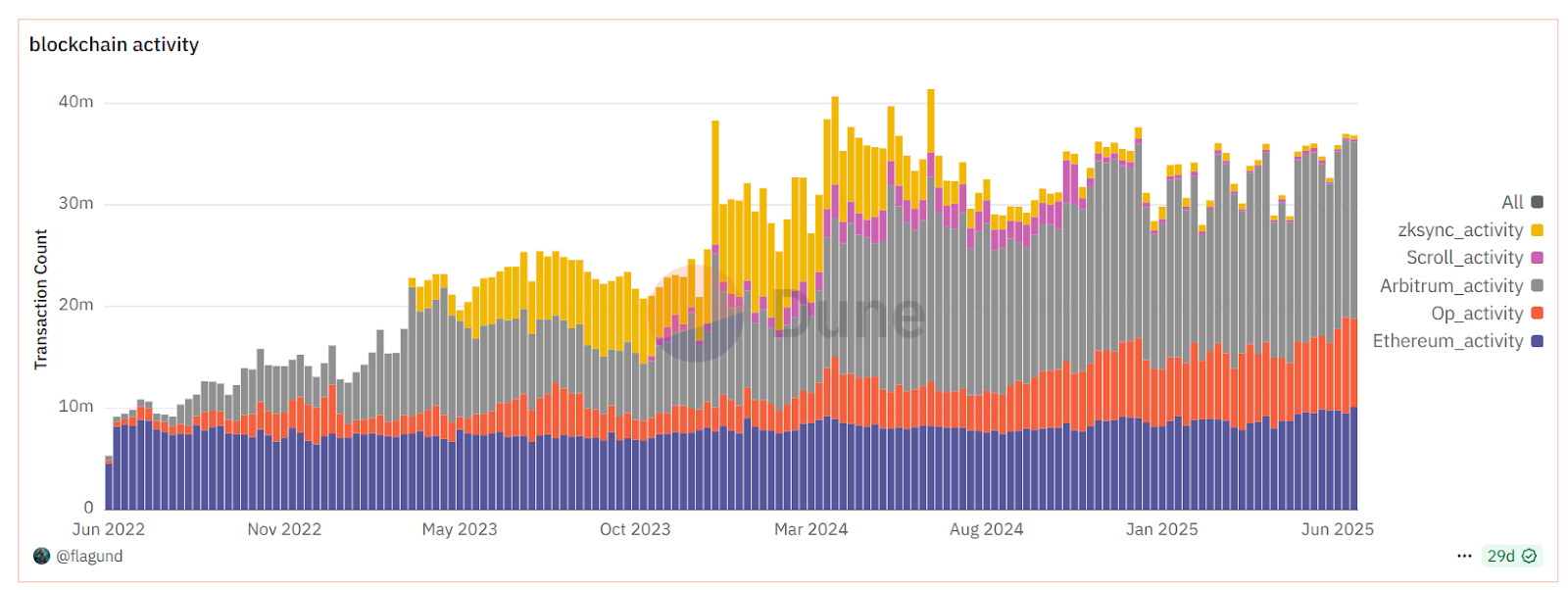
Source: https://dune.com/flagund/l2-stats-vs-ethereum
4. Ethereum Ecosystem and Application Development
Technical advancements have laid the foundation for a flourishing application ecosystem. Over the past decade, Ethereum has given rise to an unprecedented world of open finance and digital assets, experiencing explosive growth across DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs.
1. DeFi Revolution: Ethereum’s New Financial System
In 2017, early DeFi applications emerged on Ethereum. MakerDAO launched the over-collateralized stablecoin DAI, laying the groundwork for crypto lending. In 2018, the decentralized exchange Uniswap introduced the automated market maker (AMM) model, enabling trustless token swaps via code, revolutionizing trading. Between 2019 and 2020, protocols like Compound and Aave expanded on-chain lending markets. The real explosion began in 2020’s “DeFi Summer”: Compound’s governance token launch sparked yield farming, driving users to deposit assets for rewards. Total Value Locked (TVL) on Ethereum surged from under $1 billion to tens of billions within months, accompanied by spikes in transaction volume and fees. By end-2021, the DeFi landscape reached an all-time high, with aggregate TVL surpassing $100 billion. Though the market later adjusted, by mid-2025, the DeFi ecosystem had regained momentum, with global TVL rebounding to ~$150 billion—nearly 60% (~$85 billion) on Ethereum, cementing its position as the leading DeFi public chain.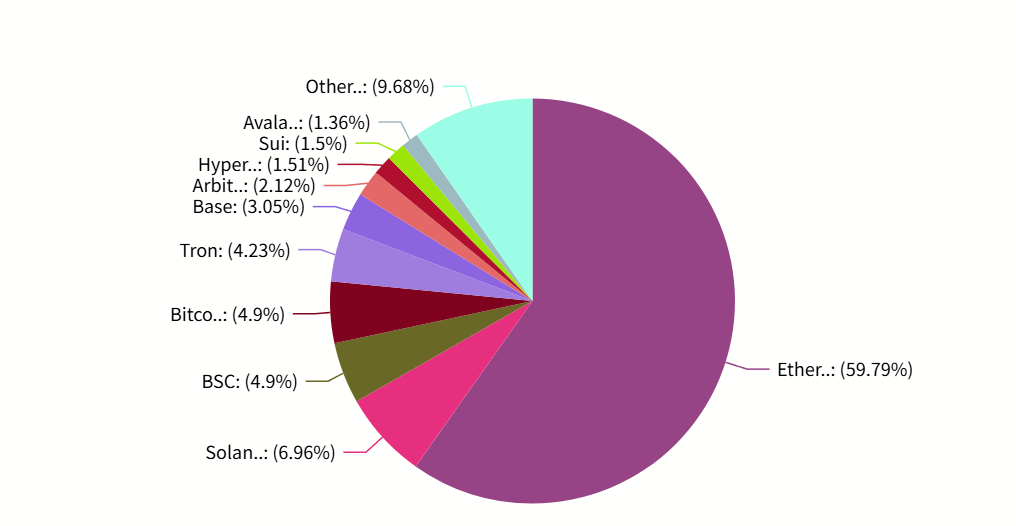
Source: https://defillama.com/chains
Several landmark DeFi projects emerged on Ethereum, pioneering new financial models:
- Uniswap Decentralized Exchange: Pioneered the AMM model using a constant product formula to automatically match trades without order books or centralized intermediaries, enabling peer-to-peer asset swaps—once surpassing many traditional exchanges in trading volume.
- Sky (formerly MakerDAO) Stablecoin System: Introduced over-collateralization to issue decentralized stablecoin DAI, allowing users to borrow stablecoins against crypto collateral—creating a bankless lending and stablecoin issuance model, providing a foundational value anchor for the DeFi ecosystem.
- Aave Lending Protocol: Offers permissionless lending markets with algorithmically adjusted interest rates; users can deposit assets to earn yield or borrow other assets. Aave also introduced innovative features like flash loans, allowing uncollateralized borrowing and repayment within a single transaction, vastly expanding DeFi use cases.
Through these protocols, traditional financial services (trading, lending, derivatives, etc.) have been reimagined on-chain. This open financial boom proves blockchain can support high-value financial activities with 7×24 global access. Ethereum’s robust smart contract foundation and security enable seamless composability among protocols, accelerating financial innovation like Lego blocks. It’s no exaggeration to say DeFi has triggered a paradigm shift in finance—from centralized monopolies to decentralized collaboration, from manual approvals to automated execution. In this process, Ethereum has become the foundational layer of the global “internet of value.”
2. NFT Boom: A New Frontier for Digital Assets
Late 2017 saw the Ethereum game CryptoKitties introduce the world to NFT-based digital collectibles: users could own and breed unique virtual cats. The game unexpectedly went viral, clogging the Ethereum network due to high transaction volume. NFTs are blockchain tokens (commonly ERC-721) representing ownership of unique assets, turning digital art, collectibles, and gaming items into distinct, tradable assets.
After an exploratory phase, the NFT market exploded in 2021: Ethereum hosted breakout projects like CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC). These pixelated avatars and cartoon apes became sought-after “digital streetwear,” selling for hundreds of ETH, with celebrities and institutions rushing in. In March 2021, digital artist Beeple sold an NFT artwork for $69.3 million at Christie’s, marking digital art’s entry into mainstream auctions. As the primary platform, Ethereum dominated NFT trading volume, bringing blockchain into art, entertainment, and fashion. OpenSea, the leading marketplace, briefly topped Ethereum DApp revenue charts in 2021. Brands and sports leagues embraced NFTs for fan engagement—NBA launched “Top Shot” highlight NFTs, game studios experimented with tradable in-game items. However, NFT surges worsened Ethereum congestion—during popular mint events, gas fees soared, often pricing out regular users.
After years of development, the NFT market has cooled from its frenzy and matured toward practical utility. Though the 2022 crypto winter caused prices and volumes to dip, the space persisted, evolving toward real-world use. For example, more NFTs are now used as game assets, giving players true ownership of tradable gear; others serve as digital identities or membership passes granting special privileges; brand NFTs emphasize interactive fan value. Currently, Ethereum’s daily NFT trading volume remains around $10 million, making “digital collectibles” an indispensable part of the blockchain landscape.
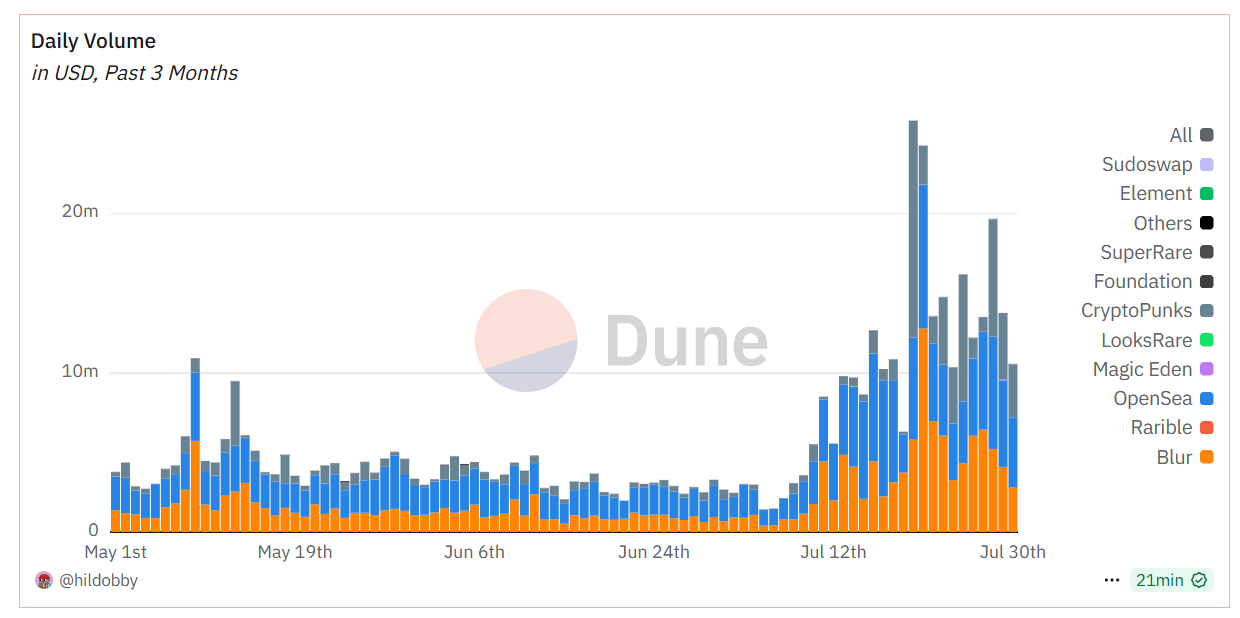
Source: https://dune.com/hildobby/ethereum-nfts
3. DAO Governance: Reshaping Organizational Collaboration
Ethereum has not only fostered new asset forms but also nurtured new organizational models: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). DAOs are structures governed by smart contracts and token voting, aiming to let participants collectively make decisions and manage funds without centralized leadership. As early as April 2016, Ethereum hosted its first major DAO experiment—“The DAO,” a decentralized venture fund that raised over $150 million in ETH to let token holders vote on funding startups. However, The DAO suffered a hack due to a code vulnerability, losing ~$60 million. This led to Ethereum’s famous hard fork—the new chain retained the Ethereum name to recover funds, while the original chain became Ethereum Classic (ETC). Despite The DAO’s failure, its self-governance concept endured. In recent years, numerous projects adopted DAO governance: MakerDAO holders vote on stability fees, Uniswap community proposes protocol upgrades, investment-focused LAO, rare-item collector PleasrDAO, and even ConstitutionDAO in 2021, where thousands pooled funds via Ethereum to bid on a U.S. Constitution copy. Ethereum’s own development process embodies open governance: anyone can submit EIPs, and upgrades proceed after community discussion and client implementation. This collaborative, transparent model has deeply influenced countless crypto projects, setting a benchmark for “community governance.”
Ethereum provides reliable infrastructure for DAO operations: on-chain multisig wallets hold funds, governance tokens enable voting, smart contracts execute outcomes—all processes are public and verifiable. This transparent mechanism drastically reduces trust costs in large-scale collaboration, enabling strangers to form “digital communities” around shared goals. While DAOs challenge traditional organizational boundaries, they face real hurdles. For instance, voter turnout in many DAOs remains low, posing challenges for broad participation; decision-making is often slow and public, making rapid response difficult. Moreover, large token holders (“whales”) wield disproportionate influence, raising concerns about governance centralization—a key area for future exploration.
5. Ethereum’s Competition and Challenges
Currently, over 4,000 decentralized applications (dApps) run on Ethereum, spanning lending, trading, payments, gaming, social media, and more. Its developer ecosystem remains the largest among public blockchains. More apps and users strengthen Ethereum’s status as the “internet of value” and deepen its “ecosystem moat.” Yet beneath this prosperity, Ethereum faces unprecedented competition and internal challenges.
1. Competitive Landscape: Ethereum Among Rivals
Over the past decade, several so-called “Ethereum killers” emerged briefly. EOS, launched in 2017, claimed superior performance and set an ICO record by raising $4.2 billion. However, post-launch, EOS exposed governance centralization issues—its nodes sparked controversy days after launch by freezing accounts, followed by sharp declines in developer activity and economic vitality. Binance Smart Chain (BSC), rising in 2020, attracted users and DeFi projects with ultra-low fees. But BSC uses a Proof-of-Authority consensus with only 21 validators—selected daily by 11 super nodes on Binance’s chain—raising concerns over concentrated control. Solana, emerging in 2021, boasts thousands of TPS and sub-second finality, positioning itself as a “high-speed chain” for mass consumer apps. During NFT and Meme coin booms, Solana’s transaction volume surged, challenging Ethereum’s dominance. Yet Solana’s high performance comes at the cost of reduced decentralization, with multiple network outages (some lasting hours) disrupting user access and raising reliability concerns.
Competitors continue iterating rapidly—Solana’s meme-driven wealth effect once pushed its gas fees above Ethereum’s; modular blockchain concepts are gaining traction, with Celestia focusing on data availability and EigenLayer proposing “restaking” to reuse Ethereum’s trust layer. These new narratives expand blockchain’s frontiers while challenging Ethereum’s role: in a multi-chain, layered future, how can Ethereum maintain its core status while coexisting and collaborating with other chains? This remains a critical question.
2. Challenges Facing Ethereum and Responses
After a decade, Ethereum holds industry leadership, but still faces significant internal hurdles—including technical bottlenecks and market and governance tests.
- Long-standing Scalability Bottleneck: Ethereum mainnet’s limited throughput and high gas fees frustrate ordinary users and hinder mainstream adoption. This directly fueled the rise of scaling solutions, especially Layer 2 networks. However, Layer 2s bring new challenges: isolated ecosystems lack direct interoperability, fragmenting liquidity across Rollup networks—undermining the very UX improvements they aim to deliver.
- Performance vs. Decentralization Trade-off: Blockchain’s famous “impossible trinity” suggests decentralization, security, and scalability cannot coexist perfectly. Ethereum has prioritized decentralization and security since inception—keeping node operation accessible to ensure global participation—but at the cost of constrained block size and speed, limiting throughput and confirmation times.
- Security Risks: As a programmable blockchain, Ethereum’s smart contracts have repeatedly suffered exploits, reminding developers and users that immutable on-chain code demands rigorous auditing and risk management.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: As DeFi integrates with traditional finance and NFTs enter mainstream culture, regulators increasingly scrutinize on-chain compliance risks. Some Ethereum applications—like decentralized exchanges and stablecoin issuance—may fall under existing financial regulations. Compliance pressure could drive major players to exit or shift to permissioned chains, affecting talent and capital flows in Ethereum’s ecosystem.
- Governance and Roadmap Execution: As a decentralized open-source protocol, Ethereum upgrades via EIP proposals requiring broad community consensus and multi-client implementation. This transparent model ensures inclusivity but leads to lengthy decision-making and high coordination costs. Major upgrades (e.g., Berlin, London, Paris hard forks) have faced delays and disputes. Meanwhile, the rise of “staking-as-a-service” platforms has concentrated staking power—entities like Lido, Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance now control over half of staked ETH, raising concerns about governance centralization and transaction censorship.
To address these challenges, the Ethereum community is pursuing a multi-pronged strategy:
- Rollup-Centric Roadmap: Short-term scaling via Rollups (e.g., Optimism, Arbitrum); long-term sharding to boost data processing by an order of magnitude, further reducing Rollup costs.
- Preserving Decentralization: Maintain high decentralization standards by shifting scaling to Layer 2. Post-Merge, efforts focus on light clients, state expiry, and data sampling to lower node resource requirements, enabling home computers or phones to run Ethereum nodes.
- Enhancing Security and Developer Support: Implement bug bounty programs and improve smart contract development frameworks to reduce vulnerabilities; host annual DevCon conferences and hackathons to foster global collaboration and innovation.
- Regulatory Engagement and Innovation Protection: Industry groups, including the Ethereum Foundation, are actively engaging regulators to shape innovation-friendly, user-protective rules. For example, developers are exploring on-chain audit tools for AML and sanctions compliance without sacrificing privacy.
- Improving Governance: The community is experimenting with diverse staking clients, trustless staking pools (e.g., Rocket Pool, SSV Network), and economic penalties for censorship in extreme scenarios.
6. Latest Developments and Future Outlook
On July 30, 2025, Ethereum celebrated its 10th anniversary. In today’s market landscape, as the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency and top smart contract platform, Ethereum is becoming an essential component of global investment portfolios—its influence spans the intersection of crypto and traditional finance, holding potential to drive the next wave of innovation.
- Market Cap and Institutional Adoption: The institutional era for Ethereum has arrived, with massive inflows into ETH spot ETFs; publicly traded companies like Bitmine and SharpLink are adopting ETH treasury strategies, treating ETH as a long-term value reserve and strategic asset.
- Regulatory Progress and Mainstream Recognition: Regulatory conditions have improved compared to five years ago. U.S. Congress is advancing legislation recognizing ETH as a commodity, not a security; “on-chain dollar” stablecoins are being regulated—removing barriers for institutional participation. Companies like Visa have used Ethereum to settle USDC since 2021; banks like JPMorgan are piloting tokenized deposits on Ethereum-compatible networks—signaling Ethereum’s integration into mainstream finance.
- RWA On-Chain: Since 2024, “real-world asset tokenization” has emerged as a trend, with firms like Blackstone and Franklin issuing tokenized funds on Ethereum. Over 70% of on-chain RWA issuance now occurs on Ethereum and its Layer 2s. In the future, more bonds, equities, and traditional assets may achieve digital circulation via Ethereum, expanding blockchain’s applicability.
- Technology Roadmap Outlook: In coming years, Ethereum’s focus will shift from theoretical research to real-world impact. Technically, beyond sharding and “100x scaling,” emphasis will be on UX: account abstraction will eliminate private key management hassles, social recovery wallets will roll out; privacy tech (e.g., ZK-EVM) will enhance transaction confidentiality—lowering barriers for everyday users.
Looking back at Ethereum’s first decade, we see a story of repeated rebirth amid skepticism—each time facing constraints, the community’s wisdom and perseverance found breakthroughs. If the past decade reshaped digital finance’s foundations, the next ten years could see this “world computer” evolve into public infrastructure, playing pivotal roles in finance, commerce, governance, and beyond—enabling true interconnectedness and free value flow. From a whitepaper vision to a globally operating network, Ethereum’s story continues. The next chapter is one we eagerly await.
About Us
Hotcoin Research, as the core investment research hub of the Hotcoin ecosystem, is dedicated to providing professional, in-depth analysis and forward-looking insights for global crypto investors. We build a three-in-one service system of “trend analysis + value discovery + real-time tracking,” delivering precise market interpretations and practical strategies to investors at all levels through deep dives into crypto industry trends, multidimensional assessments of promising projects, round-the-clock market monitoring, biweekly《Hotcoin Select》strategy livestreams, and daily《Blockchain Today》news briefings. Leveraging cutting-edge data analytics models and industry networks, we continuously empower novice investors to build cognitive frameworks and help professional institutions capture alpha returns, jointly seizing value growth opportunities in the Web3 era.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and investing inherently involves risk. We strongly advise investors to fully understand these risks and invest strictly within a sound risk management framework to ensure capital safety.
Website:https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
Mail:labs@hotcoin.com
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News