2025 AI Implementation Playbook: Five Key Insights from Strategic Development to Scalable Operations
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

2025 AI Implementation Playbook: Five Key Insights from Strategic Development to Scalable Operations
Provide a tactical roadmap designed to transform the intelligence advantages of generative AI into sustainable business competitiveness.
Author: ICONIQ
Translation: Tim, PANews
Artificial intelligence has entered a new chapter—moving from heated discussions to practical implementation. Building scalable AI products has become the key battleground for competition. The 2025 State of AI Report, titled "The Builder's Guide," shifts focus from technology adoption to real-world execution, offering an in-depth blueprint for conceiving, launching, and scaling AI-powered products.
Basing on exclusive survey results from April 2025 involving 300 software company executives, combined with deep interviews with AI leaders within the ICONIQ community, this report delivers a tactical roadmap for transforming generative AI’s intelligence advantage into sustainable business competitiveness.
The report distills five key insights and explains how they empower teams to actively build AI applications.
1. AI Product Strategy Has Reached a New Level of Maturity
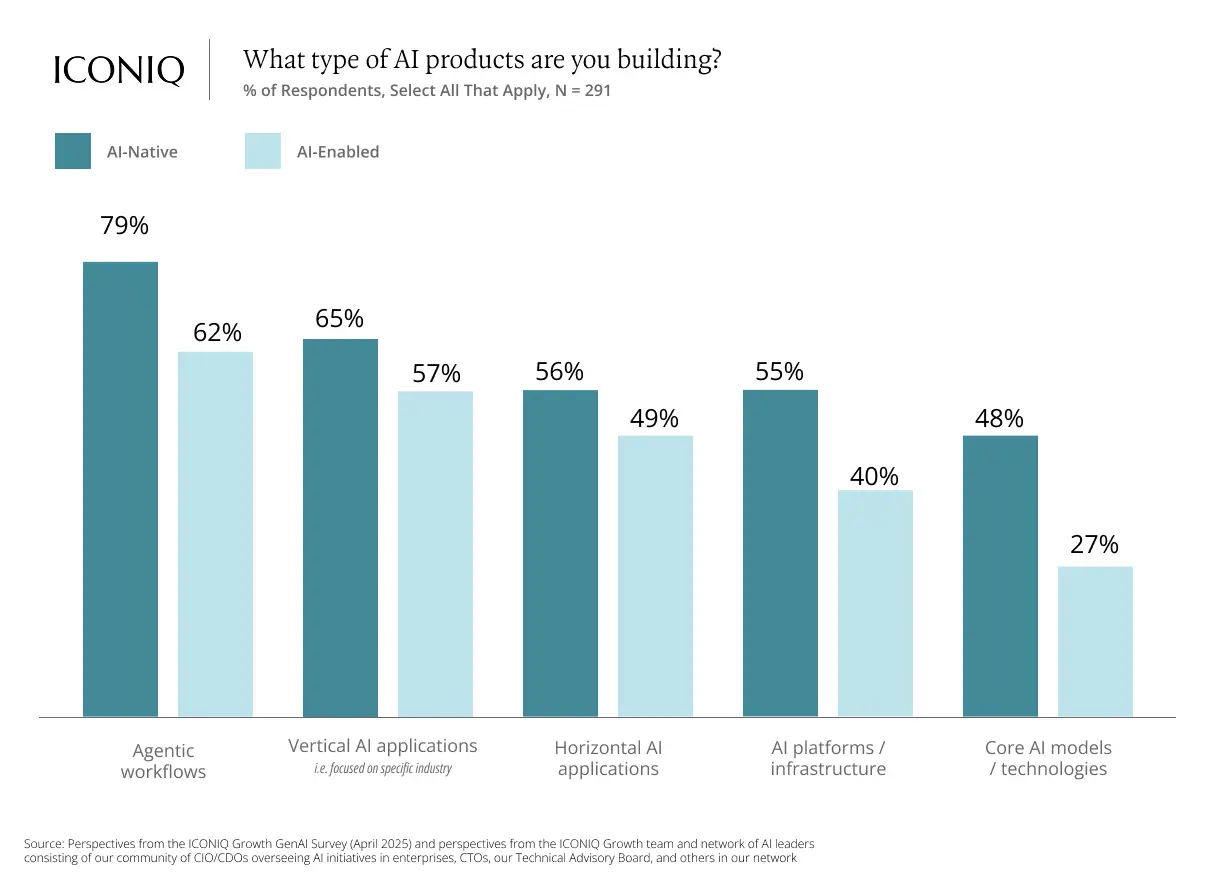
Companies built around AI are bringing products to market faster than those merely adding AI features to existing offerings. Data shows that nearly half (47%) of AI-native companies have achieved critical scale and demonstrated product-market fit, compared to just 13% of companies integrating AI into legacy products.
What they’re doing: Agent workflows and vertical-specific applications are becoming mainstream. Nearly eight in ten AI-native developers are investing in agent workflows—AI systems capable of autonomously performing multi-step tasks on behalf of users.
How they’re doing it: Firms are converging on multi-model architectures to optimize performance, control costs, and align with specific use cases. In customer-facing products, each respondent uses an average of 2.8 models.
2. Evolving AI Pricing Models Reflect Unique Economic Characteristics
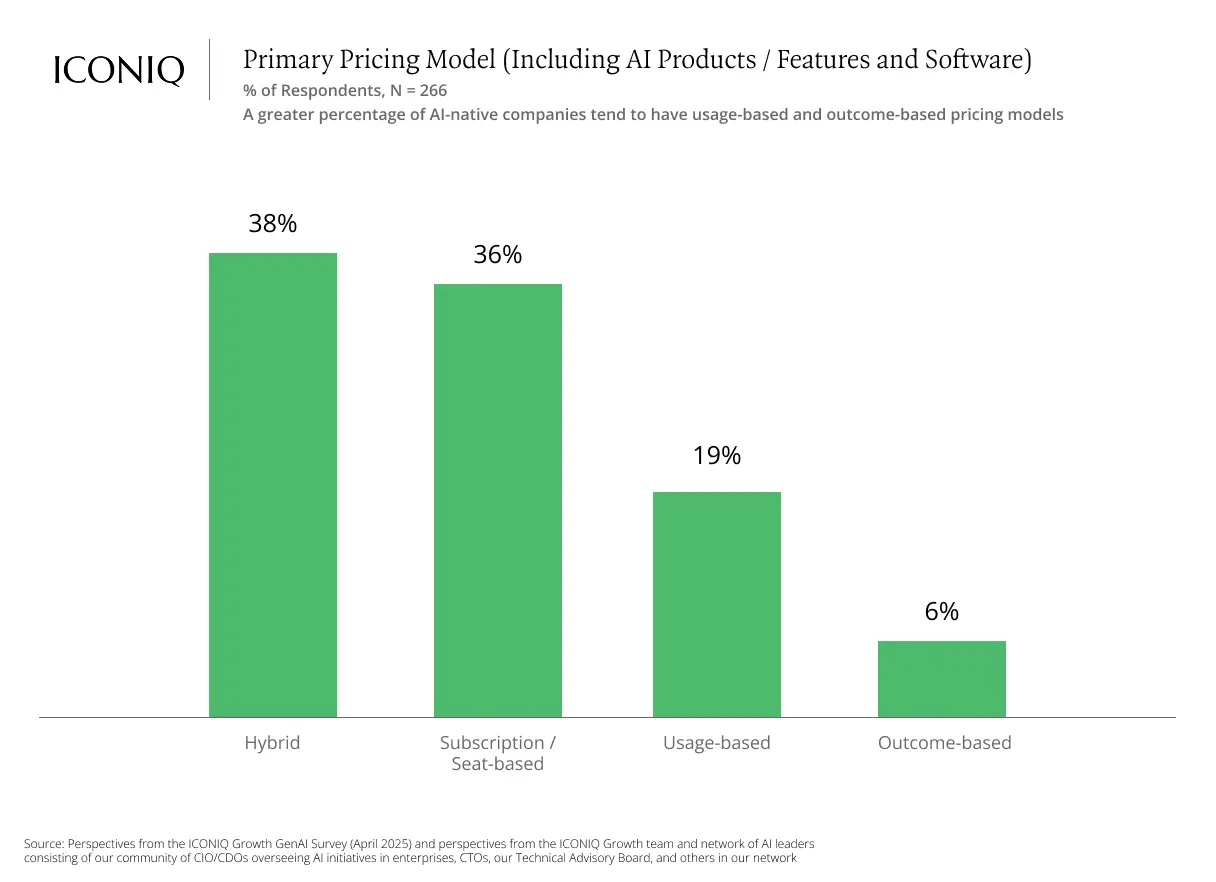
AI is reshaping how companies price their products and services. According to our survey, many firms are adopting hybrid pricing models, combining base subscription fees with usage-based charges. Others are exploring pricing models entirely tied to actual usage or measurable customer outcomes.
While many companies still offer AI features for free, over one-third (37%) plan to adjust their pricing within the next year to better reflect customer value and usage levels.
3. Talent Strategy as a Source of Differentiation
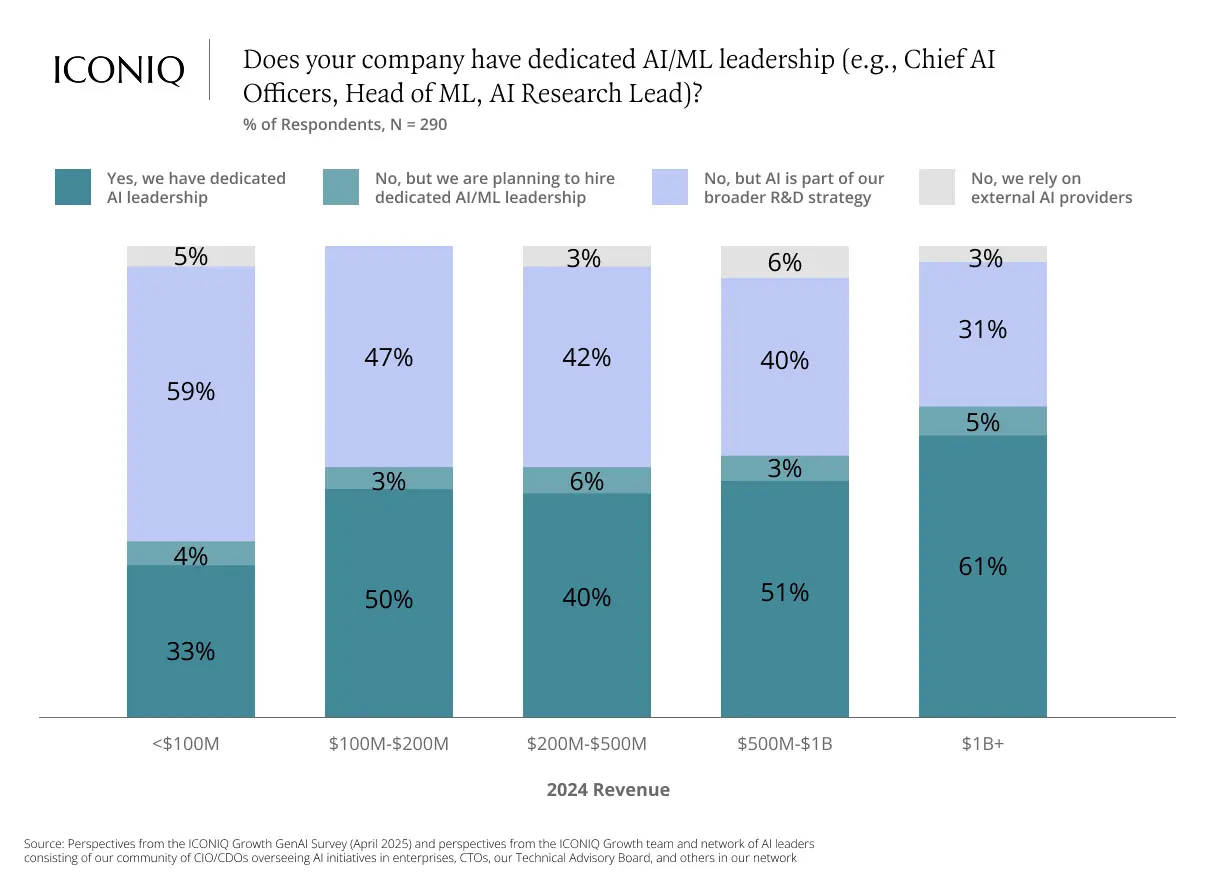
AI is not just a technical challenge—it's an organizational one. Most leading teams today are building cross-functional squads composed of AI engineers, machine learning engineers, data scientists, and AI product managers.
Looking ahead, most companies expect 20–30% of their engineering teams to focus on AI, with high-growth firms projecting this share to reach up to 37%. However, talent acquisition remains a bottleneck. Among all AI-specific roles, hiring AI and machine learning engineers takes the longest—averaging over 70 days to fill.
There is divergence in hiring progress. While some recruiters report positive momentum, 54% of respondents say they are behind schedule, with the most common reason being insufficient pipeline of qualified candidates.
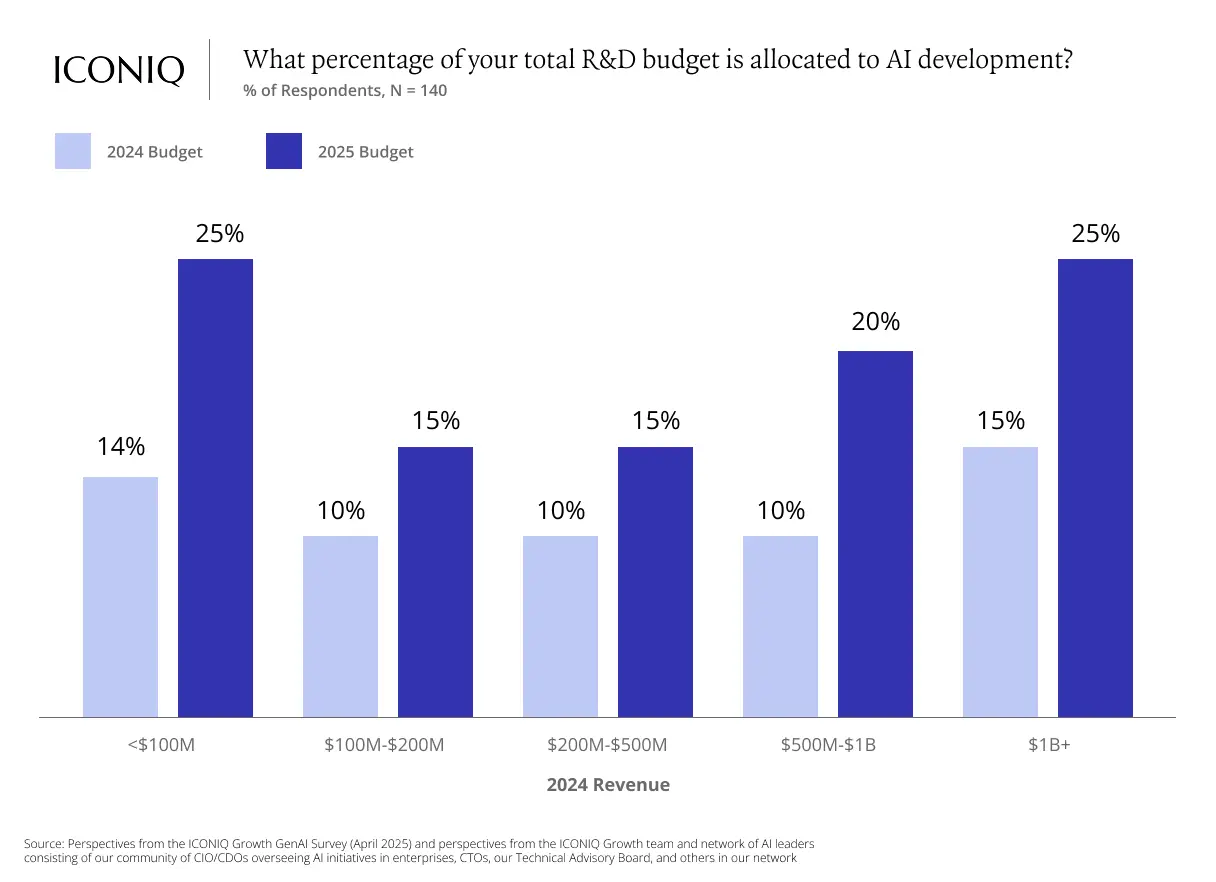
4. Surging AI Budgets Are Now Visible on P&L Statements
Enterprises adopting AI are allocating 10%–20% of their R&D budgets to AI initiatives, with consistent growth across all revenue bands in 2025. This strategic shift underscores that AI has become a core driver in product strategy planning.
As AI products scale, cost structures often shift significantly. In early development stages, human capital typically represents the largest expense—covering recruitment, training, and upskilling. As products mature, cloud infrastructure, model inference, and compliance costs become dominant line items.
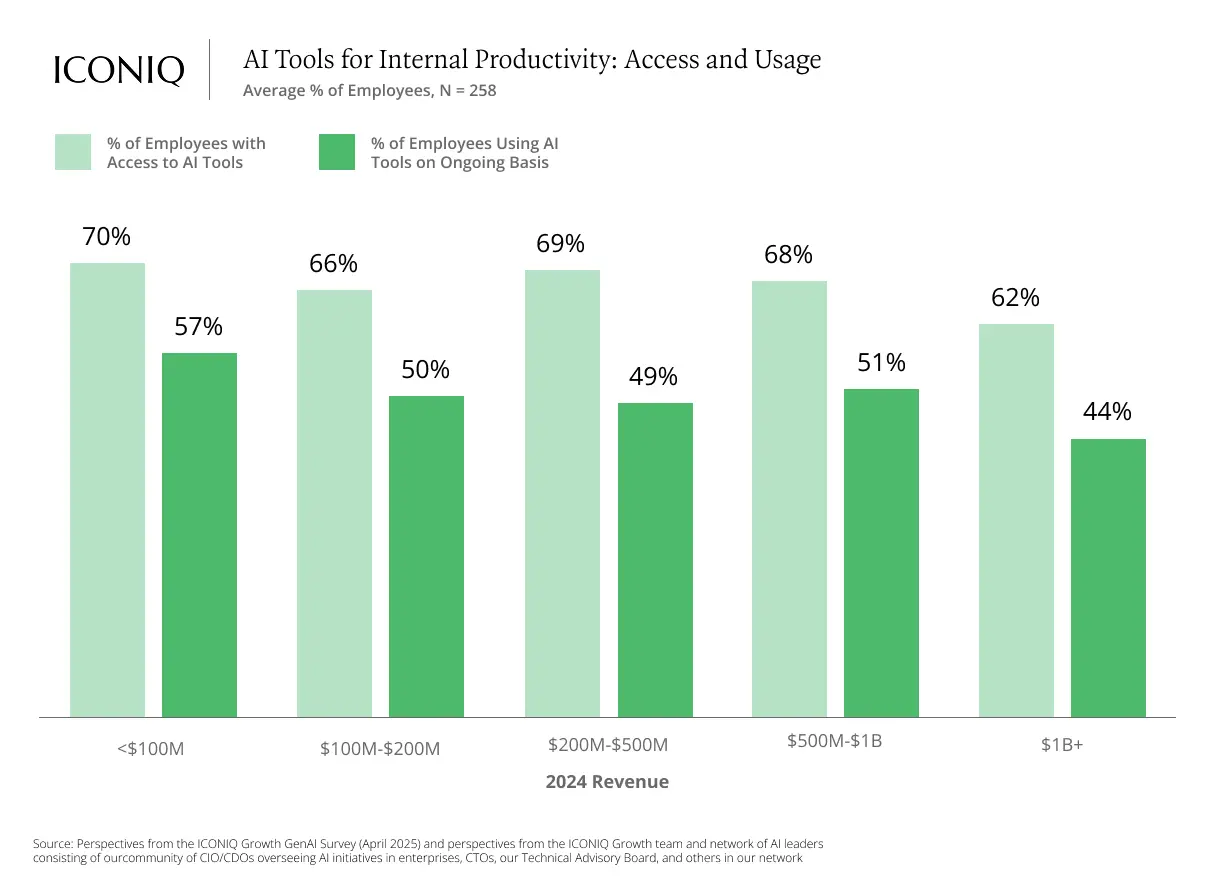
5. Internal AI Adoption Is Expanding, But Unevenly Distributed
While most surveyed companies grant about 70% of employees access to internal AI tools, only around half actually use them regularly. Larger, more established organizations face particular challenges in driving employee-level AI adoption.
High-adoption companies—where more than half of employees use AI tools—deploy AI across seven or more internal use cases on average. These include coding assistants (used by 77%), content generation (65%), and document search (57%). In these areas, productivity gains range from 15% to 30%.
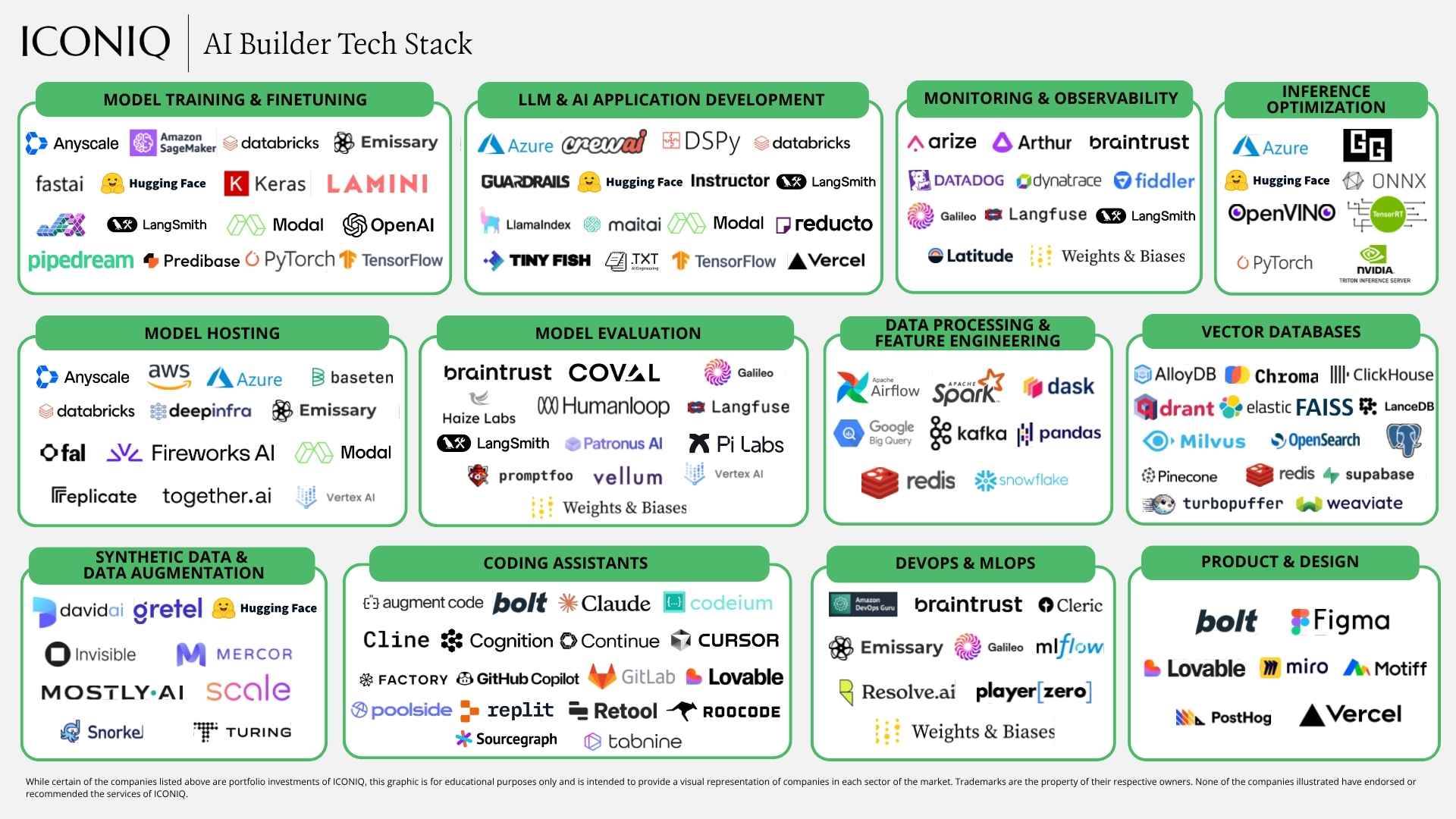
The AI Tool Ecosystem Remains Fragmented but Is Maturing
We surveyed hundreds of enterprises to understand which frameworks, libraries, and platforms are actually running in production environments today. This report does not rank tools—it reflects the real-world landscape of developer tool adoption across domains.
Below is a brief alphabetical overview of the most commonly used tools:
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














