Stanford HAI "Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2025" Highlights
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Stanford HAI "Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2025" Highlights
Artificial intelligence is more efficient, accessible, and cost-effective; in addition, people in Asia are more optimistic about AI.
Author: Stanford HAI (Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence)
Translation: Felix, PANews
Stanford HAI recently released its 456-page "Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2025." Below are some key highlights on AI trends:
1. AI is becoming far more powerful than imagined
On new benchmarks—MMMU, GPQA, and SWE-bench—AI performance has significantly improved, with scores increasing by 18.8%, 48.9%, and 67.3% respectively. Beyond benchmarks, AI systems have made major strides in generating high-quality video, and in some cases, large language models (LLMs) have even outperformed humans in time-constrained programming tasks.
Note:
MMMU is a carefully designed new benchmark tailored for university-level multidisciplinary multimodal understanding and reasoning, aiming to evaluate foundation models' expert-level multimodal comprehension across a wide range of tasks.
GPQA is a challenging dataset containing 448 high-quality, extremely difficult multiple-choice questions authored by domain experts. Domain experts holding or pursuing PhDs achieve only 65% accuracy, while skilled non-expert validators—with over 30 minutes on average and unrestricted internet access—achieve just 34% accuracy.
SWE-bench is a benchmark for evaluating large language models (LLMs) on real-world software engineering problems collected from GitHub.
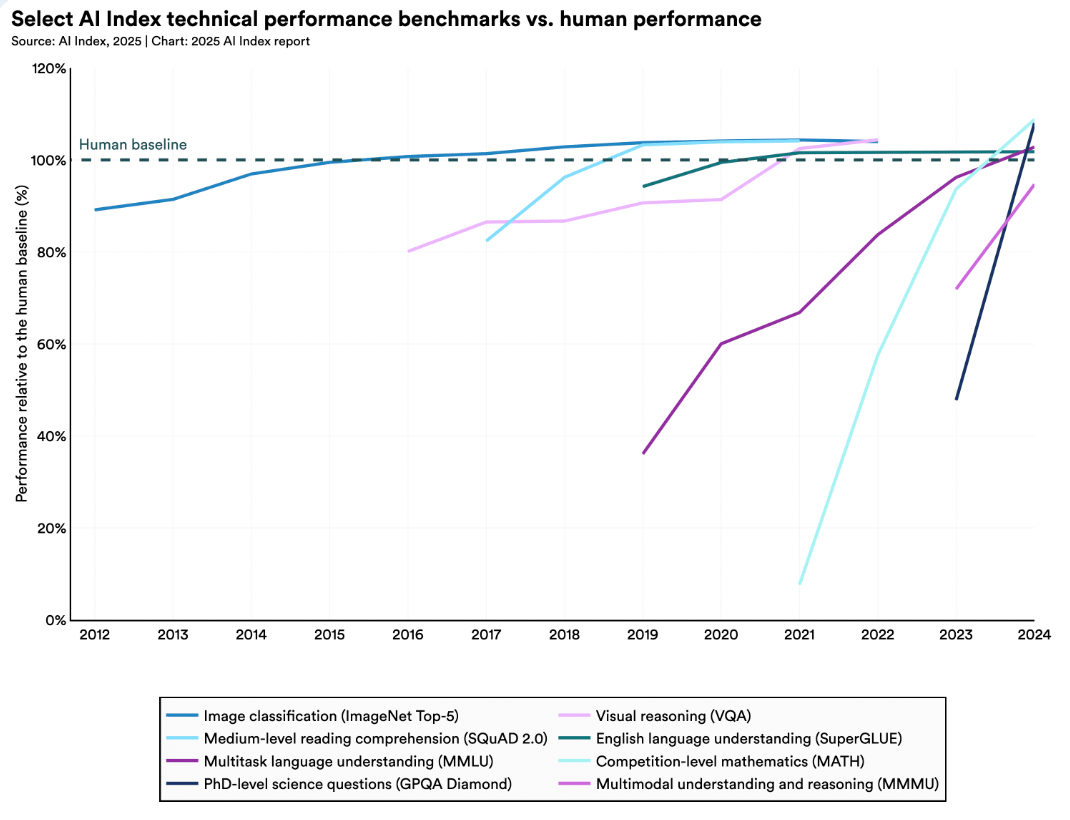
2. AI is becoming more efficient, accessible, and affordable
Smaller AI models with fewer parameters are growing increasingly capable: within just two years, parameter counts have dropped by roughly 100 times, yet their performance on the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) test still exceeds 60%.
The performance gap between open-source and closed-source models is also narrowing, shrinking from 8% to just 1.7% on certain benchmarks.
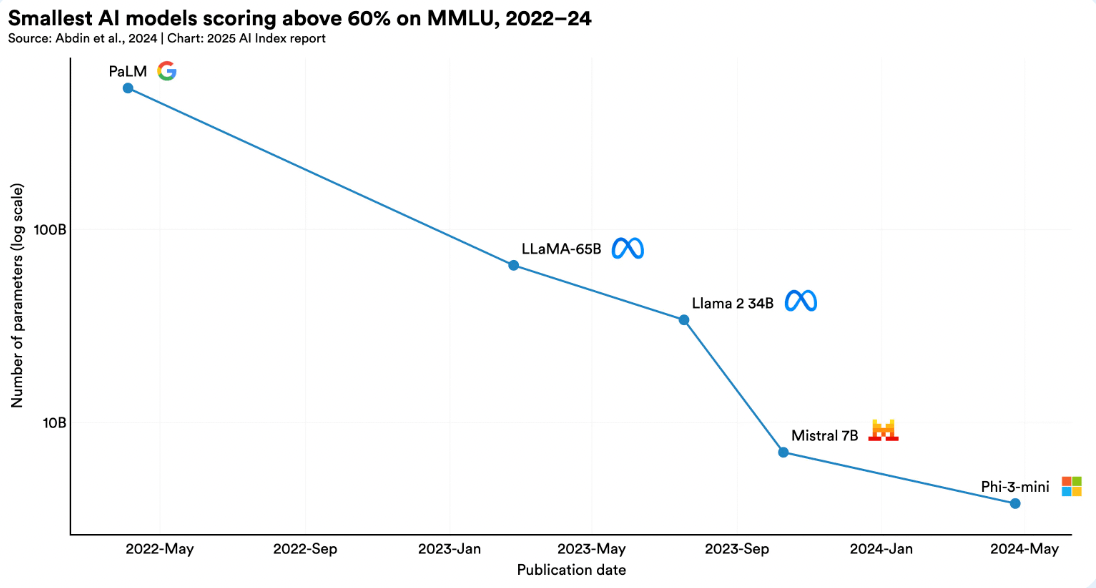
Moreover, from November 2022 to October 2024, the inference cost for systems at GPT-3.5 level dropped by over 280 times. At the hardware level, costs are decreasing by 30% annually, while energy efficiency improves by 40% per year.
The barrier to advanced AI is rapidly lowering. Not to mention developments like sparse models such as DeepSeek, which under a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture activate only relevant parameters to respond to user queries, making the entire process more efficient.
Indeed, as smaller yet more capable AI models emerge, the requirements for AI model training are decreasing, and cost-effective distributed training is expected to become mainstream in the next decade. Several cutting-edge projects are currently conducting research based on different theoretical frameworks.
3. AI is increasingly integrated into daily life
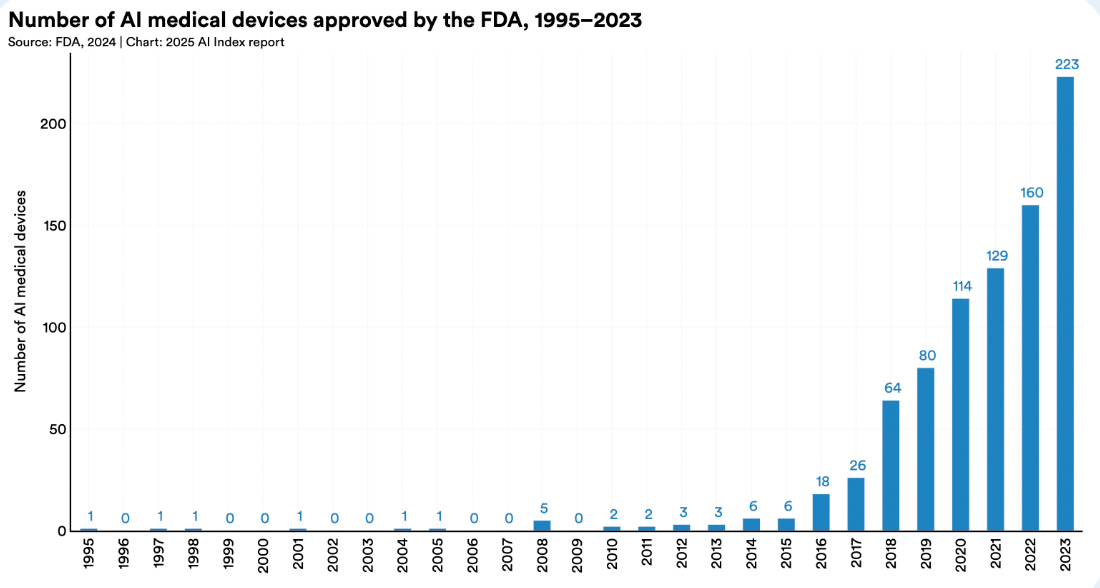
In 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 223 AI-assisted medical devices, compared to only 6 in 2015. On roads, autonomous vehicles are no longer experimental: Waymo, one of the largest operators in the U.S., now provides over 150,000 driverless rides weekly, while Baidu’s Apollo Go robotaxi fleet is already operating across multiple Chinese cities.
4. Corporate investment in AI has surged, driving record levels of funding and adoption
AI adoption in business is accelerating: in 2024, 78% of organizations are using AI, up from 55% the previous year. Meanwhile, growing evidence confirms that AI boosts productivity and helps narrow skill gaps across the workforce.
In fact, as AI drives exponential growth in customer expectations, existing solutions can appear outdated overnight, leaving incumbent companies little room to adapt—resulting in product-market fit breakdowns occurring more frequently.
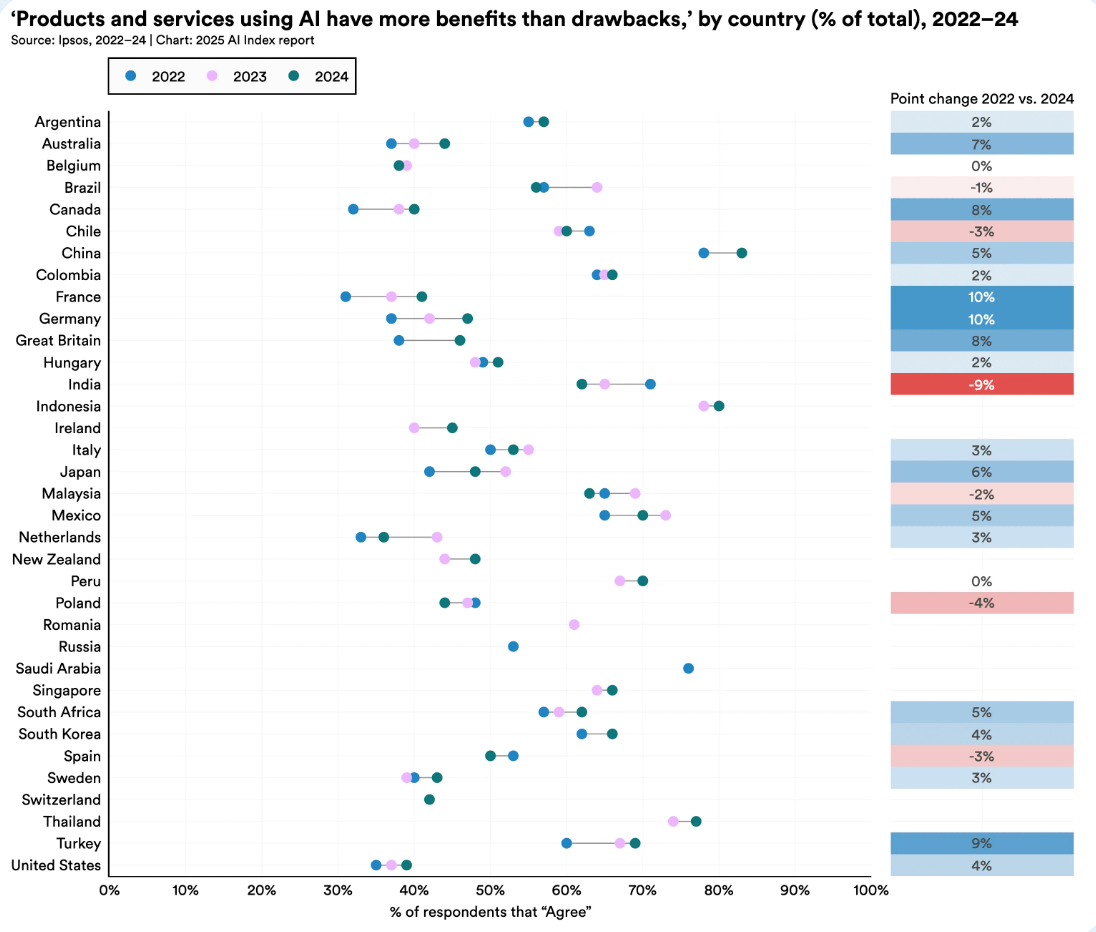
5. While global optimism about AI is rising, people in Asia are notably more optimistic
In countries such as China (83%), Indonesia (80%), and Thailand (77%), most people believe AI products and services do more good than harm. In contrast, optimism remains much lower in Canada (40%), the United States (39%), and the Netherlands (36%).
However, attitudes are shifting: since 2022, optimism has grown significantly in several previously skeptical countries, including Germany (+10%), France (+10%), Canada (+8%), the UK (+8%), and the United States (+4%).
6. AI's impact in scientific research is growing, becoming a key driver of scientific advancement
AI's rising importance is reflected in major science awards: two Nobel Prizes were awarded—one in Physics for contributions to deep learning, and another in Chemistry for its application to protein folding—while the Turing Award recognized pioneering work in reinforcement learning.
Clearly, AI is advancing at an exponential and unexpected pace, profoundly impacting most people. Consequently, AI safety is becoming increasingly critical. While AI makes forgery easier, cryptography makes it harder. We look forward to crypto projects leveraging blockchain’s native attributes—verifiability and transparency—to build practical solutions in this space.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News