Steady Trading: Risk Management Strategies for the Crypto Derivatives Market
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Steady Trading: Risk Management Strategies for the Crypto Derivatives Market
This guide will help traders and investors carefully navigate market challenges, enhancing trading security and stability.
Key Takeaways
-
– Understand derivatives and risks: Cryptocurrency derivatives such as futures, options, and swaps offer profit opportunities but come with high volatility, leverage risks, and liquidity challenges.
-
– Implement effective risk management: Reduce liquidation risks from market fluctuations through position sizing, stop-loss orders, hedging strategies, and asset diversification.
-
– Ensure compliance and security: Stay informed about regulatory changes, choose compliant exchanges, and protect assets using cold wallets and secure trading practices.
-
– Maintain stable trading psychology: Avoid impulsive decisions driven by FOMO (fear of missing out) or panic, follow your trading plan, and keep a trading journal to refine strategies.
Cryptocurrencies are rapidly entering the mainstream, offering unique opportunities for investment, speculation, and hedging. In this emerging space, cryptocurrency derivatives—financial instruments based on digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum—have become a core part of the market. These include futures, options, swaps, and perpetual contracts, allowing traders to profit from price movements without owning the underlying assets.
However, high volatility, complex product structures, and unregulated markets can turn trading opportunities into significant risks. Therefore, effective risk management is crucial for all crypto derivatives traders. This guide provides:
-
– An overview of major derivative products
-
– Analysis of key risk factors
-
– Practical risk management strategies
To help traders and investors navigate market challenges with greater safety and stability.
Table of Contents
Understanding Cryptocurrency Derivatives
Main Risks in Crypto Derivatives
-
– Position planning and leverage control
-
– Stop-loss orders and risk/reward ratio
-
– Hedging strategies (options and arbitrage trading)
-
– Diversification of assets and trading strategies
-
– Collateral and margin management
-
– Continuous monitoring and adjustment
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Technology and Operational Risk Prevention
Trading Psychology and Emotional Control
-
– Avoiding FOMO (fear of missing out)
-
– Overcoming loss aversion bias
-
– Maintaining a trading journal
-
– Sticking to your trading plan
Understanding Cryptocurrency Derivatives
Cryptocurrency derivatives allow traders to gain market exposure or execute hedging strategies without directly holding Bitcoin or other digital assets. These tools can amplify profits but also carry higher risks. Below are the main categories:
Futures
Definition: Contracts requiring buyers and sellers to trade an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date.
Trading Platforms: Regulated exchanges (e.g., CME) and crypto exchanges (e.g., Binance, XT.COM).
-
– No expiry date: Price is kept close to the spot market via funding rates.
-
– Ideal for: Traders seeking long-term leveraged positions without rolling over contracts.
-
– Fixed expiry: Positions are settled in cryptocurrency or stablecoins upon expiration.
-
– Ideal for: Institutional investors or those who prefer defined settlement timing.
Stablecoin Margin vs. Coin-Backed Contracts
-
– Stablecoin-Backed (e.g., BTC/USDT): Uses stablecoins like USDT or USDC as margin, reducing volatility risk in leveraged positions.
-
– Coin-Backed (e.g., BTC/USD): Uses cryptocurrency as margin; both P&L and margin value fluctuate with market prices.
Options
Definition: Grants the holder the right—but not the obligation—to buy (call option) or sell (put option) cryptocurrency at a specified price before expiration.
Uses:
-
– Hedging: Protect large crypto holdings against market downturns.
-
– Income Generation: Earn premiums by selling options (e.g., covered calls).
-
– Speculation: Gain leveraged exposure to market direction without owning the asset.
Swaps
Definition: Contracts where two parties exchange financial obligations or returns.
Perpetual Swaps:
-
– No expiry date: Funding rates align contract prices with the spot market.
-
– Popular platforms: Commonly traded on Binance, OKX, Deribit, and others.
Structured Products
Structured products combine derivatives to create customized risk/return profiles, popular among institutional investors.
Dual Investment (Coming soon on XT.COM)
-
– No principal protection: Higher returns if the market price does not reach the target at maturity.
-
– How it works: If price is below target, investor receives original asset plus interest; if above, position converts to another asset (e.g., BTC → USDT), potentially missing further upside.
-
– Partial capital protection: Returns depend on whether price stays within a predefined range.
-
– Suitable for: Investors seeking steady returns while accepting moderate risk.
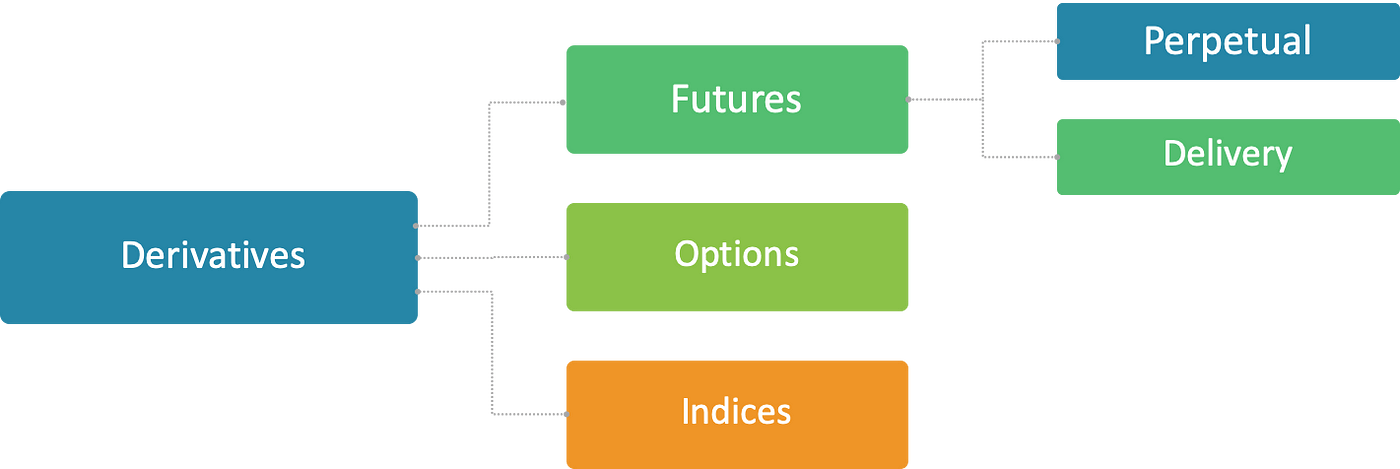
Image Credit: Medium
Main Risks in Crypto Derivatives
Risks in the crypto derivatives market are interconnected. Understanding them helps traders build effective protective strategies.
Volatility Risk
-
– Cryptocurrency prices are extremely volatile; daily swings exceeding 80% are not uncommon.
-
– Leverage amplifies market moves—unfavorable price action can quickly trigger forced liquidation (margin call).
Counterparty Risk
-
– Traders rely on the financial health and security measures of exchanges.
-
– If an exchange suffers a hack or bankruptcy, traders may lose margin and unrealized profits.
Liquidity Risk
-
– Market liquidity is fragmented, especially for low-cap assets; shallow depth can cause execution issues.
-
– Low liquidity leads to slippage; during sharp moves, closing positions becomes harder and losses can increase.
Regulatory and Legal Risk
-
– Global crypto regulations change frequently, with varying policies across regions.
-
– Regulatory shifts may affect leverage limits, margin requirements, or even ban derivatives trading in certain jurisdictions.
Technology and Operational Risk
-
– Exchanges may suffer hacks, system failures, or server overloads, impacting trading and fund security.
-
– High-frequency trading strategies may fail due to API latency or outages, affecting performance.
Identifying these risks and their potential severity is key to building robust risk management strategies.

Image Credit: Insurance Risk Services
Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management combines quantitative tools, disciplined trading, and market analysis. Key strategies include:
Position Planning and Leverage Control
Position Sizing
-
– Allocate only a portion of capital per trade to manage volatility and limit individual exposure.
-
– Over-committing funds can lead to rapid portfolio drawdowns, especially during extreme market moves.
Leverage Management
-
– High leverage (e.g., 20x, 50x) magnifies gains but also increases loss potential.
-
– Experienced traders often use moderate to low leverage to reduce liquidation risk.
Stop-Loss Orders and Risk/Reward Ratio
Stop-Loss Orders
-
– Set automatic exit points to close positions when price hits a predefined level, limiting losses.
-
– A well-placed stop-loss helps maintain discipline and prevents small losses from turning into large ones.
Risk/Reward Ratio
-
– Aim for a favorable risk/reward ratio (e.g., 1:3) to ensure long-term profitability.
-
– Even with losing trades, consistent winners can offset losses and generate net gains.
Hedging Strategies
Using Options
-
– Buy put options to hedge against market crashes when holding large crypto positions.
-
– If bearish but concerned about upside risk, buy call options to cap potential losses.
Arbitrage Trading
-
– Arbitrage reduces risk by holding offsetting positions (e.g., long and short simultaneously).
-
– This strategy minimizes broad market exposure and focuses on relative price differences.
Diversification
Asset Diversification
-
– Hold multiple cryptocurrencies or stablecoins to reduce impact from a single asset's decline.
-
– For example, if Bitcoin crashes but Ethereum remains stable, overall losses are reduced.
Strategy Diversification
-
– Use varied strategies (e.g., trend following, mean reversion, volatility arbitrage) to adapt to changing markets.
-
– Some strategies work in trending markets but fail in sideways conditions; combining them improves long-term consistency.
Margin Management
Over-Collateralization
-
– Deposit extra margin to avoid forced liquidation during sharp price swings.
-
– However, keeping too much capital on one exchange increases exposure to platform failure or hacks.
Stablecoin Margin
-
– Using stablecoins (e.g., USDT, USDC, DAI) as margin reduces additional risk from margin value fluctuations.
-
– Ensures risk is tied only to the position, not to volatility in the margin itself.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Dynamic Risk Adjustment
-
– Markets evolve; adjust leverage and stop-loss levels based on current volatility.
-
– For instance, during high volatility, reduce leverage and tighten stop-losses to minimize exposure.
Risk Analysis and Stress Testing
-
– Use simulation tools to stress-test worst-case scenarios like market crashes or exchange failures.
-
– Adjust position size, hedging, and margin plans based on test outcomes.
These strategies form a foundational risk management framework. True success, however, depends on disciplined execution and adaptive adjustments.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
The regulatory landscape for crypto derivatives is constantly evolving, affecting how they're traded and accessed. The U.S. allows regulated Bitcoin futures (under CFTC oversight) but restricts retail leverage, while some countries fully ban or heavily limit crypto derivatives trading.
Jurisdictional Compliance
-
– Understand local laws governing exchanges to avoid fines, frozen assets, or legal actions.
-
– Regulations vary widely; stay updated on policy developments.
Exchange Due Diligence
-
– Verify if the exchange holds valid licenses and is under regulatory supervision.
-
– Assess financial stability, ensuring sufficient liquidity and strong security protocols.
-
– Review security history—check for past breaches or fund losses.
Tax and Recordkeeping
-
– Maintain full transaction records (entry/exit prices, profits/losses).
-
– Many jurisdictions treat crypto gains as taxable income; accurate reporting avoids legal complications.
KYC and AML Requirements
-
– Compliant exchanges require identity verification (KYC) and transaction monitoring to prevent illicit activity.
-
– Adhering to KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) rules helps prevent account freezes or regulatory scrutiny.
Proactive compliance reduces legal risks and supports sustainable, long-term trading.

Image Credit: Financial Crime Academy
Technology and Operational Security
Crypto trading relies on robust security and operational resilience to protect funds and ensure smooth execution.
Fund Security
-
– Major exchanges store most user funds in cold wallets to prevent hacking.
-
– Multi-signature systems enhance security by requiring multiple approvals for large withdrawals.
Platform Stability
-
– Exchanges should have backup servers and failover mechanisms to maintain uptime.
-
– Algorithmic traders must verify API reliability to prevent failed executions due to delays or outages.
Operational Risk Management
-
– Well-managed exchanges respond swiftly to hacks or outages and restore service quickly.
-
– Transparent platforms provide proof of reserves and undergo third-party audits to build trust.
Understanding an exchange’s security and operations is as vital as any trading strategy—because a single breach or outage can result in catastrophic losses.
Emotional Management in Trading
Even with strong technical skills and solid strategies, emotional influences can lead to significant losses. Crypto markets are often driven by hype and fear, triggering poor decisions based on greed or panic. Maintaining emotional discipline ensures traders follow their plans rather than act impulsively.
Avoiding FOMO
-
– During rapid price surges, traders may enter impulsively, ignoring risk controls and over-leveraging after optimal entry points have passed.
-
– Stick to predefined rules and position limits to avoid FOMO-driven mistakes.
Overcoming Loss Aversion
-
– Many traders hold losing positions too long, hoping to break even, which blocks better opportunities.
-
– Cutting small losses early preserves capital for more favorable trades.
Maintaining a Trading Journal
-
– Record each trade’s rationale (entry/exit prices, reasoning, emotional state) to identify recurring mistakes.
-
– Regular review improves strategy and strengthens discipline.
Sticking to Your Trading Plan
-
– Before entering, define profit targets and stop-loss levels to ensure every trade has clear risk parameters.
-
– Avoid impulsive changes due to short-term noise; adjustments should stem from analysis, not emotion.
Emotional control separates consistently profitable traders from chronic losers. Staying calm, executing plans rigorously, and overcoming psychological barriers are essential for long-term survival and success in crypto markets.
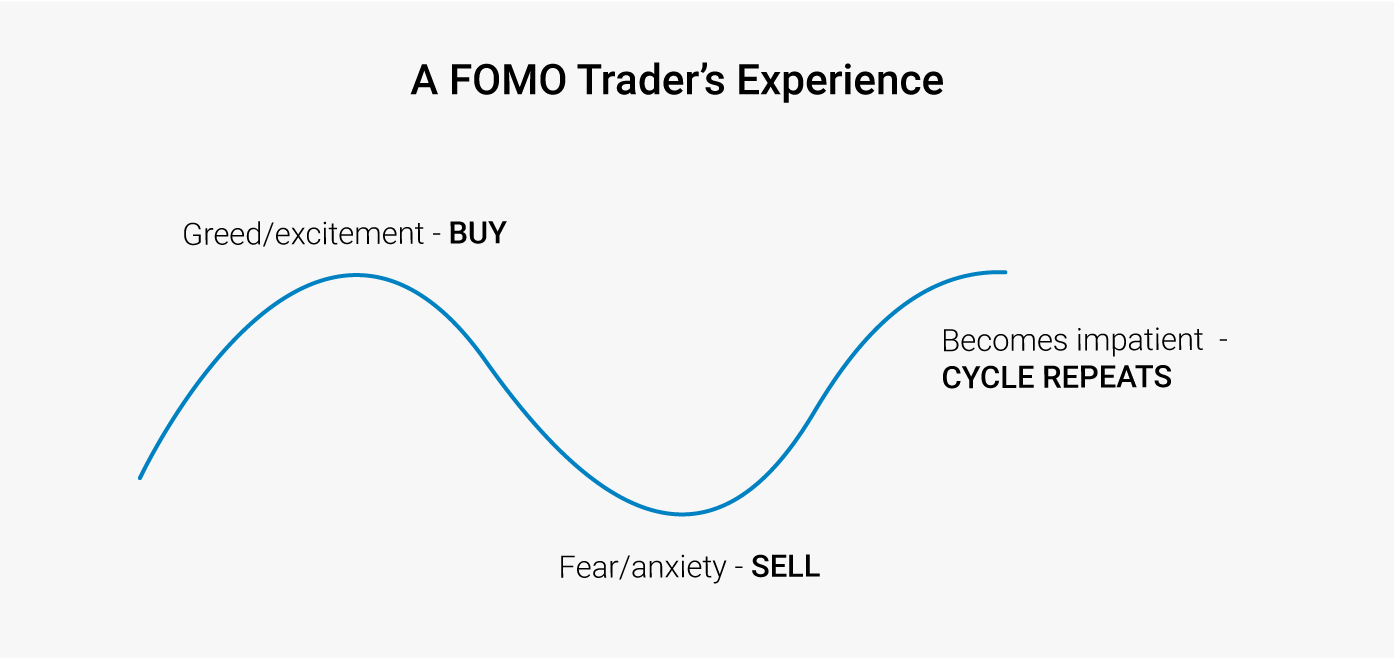
Image Credit: Carl Fajardo
Conclusion
Crypto derivatives offer high-return potential but come with high volatility and complexity. Successful traders must manage risk effectively across key areas:
-
– Product Knowledge: Fully understand how futures, options, and swaps work before trading.
-
– Risk Control: Use stop-losses, appropriate leverage, and hedging to minimize losses.
-
– Trading Security: Choose secure, reputable platforms to reduce counterparty risk.
-
– Regulatory Compliance: Stay updated on KYC, AML, and tax requirements.
-
– Emotional Discipline: Follow your trading plan strictly and avoid impulsive reactions to market sentiment.
As the market evolves, traders must continuously learn and adapt. While no strategy eliminates risk entirely, disciplined execution and sound risk management greatly improve the odds of long-term success in crypto derivatives trading.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News