A Brief Analysis of the Potential of Open-Source AI in Decentralized Networks
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

A Brief Analysis of the Potential of Open-Source AI in Decentralized Networks
By leveraging blockchain technology to add an economic layer to open-source AI code, developers around the world can compete in a more level playing field.
Author: Franklin Templeton Digital Assets
Translation: Alex Liu, Foresight News

Artificial intelligence (AI) will redefine internet experiences and the broader economy. The foundational AI models driving this revolution could either be closed-source and owned by a few entities, or open-source and collectively owned by thousands or even millions of people. Whichever path prevails will profoundly impact how value is created and distributed in an AI-driven global economy.
Centralized vs. Decentralized AI Infrastructure
Due to the high cost of training foundational models, the current AI landscape is dominated by a small number of major players. Hyperscalers—companies that operate large data centers and can rapidly scale infrastructure—are leading the charge. These firms, including Alphabet, Meta, Microsoft, and Amazon (the top tech companies by market capitalization), spend tens of billions of dollars each quarter building and maintaining their leadership in the field (see Figure 1). This level of investment by a few participants creates extremely high barriers to entry, potentially resulting in monopolistic pricing power, lack of transparency, and biased outputs.
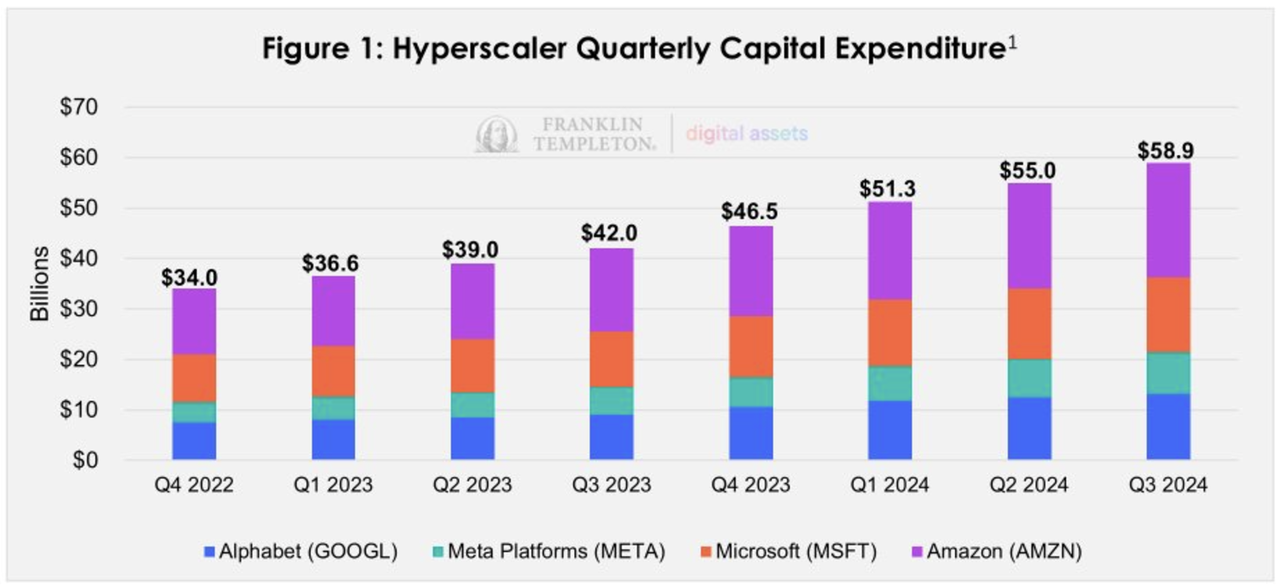
In contrast, decentralized ownership and governance offer solutions to these challenges. By leveraging crowd-sourced computing, decentralized AI enables diverse developers and contributors to train models, fostering an inclusive ecosystem with fairer value capture. This approach can mitigate monopolistic tendencies, encourage competitive innovation, and lower barriers to entry. Open-source models further enhance transparency, helping users understand AI logic, thereby building trust and enabling regulatory oversight.
Case Study: OpenAI in Centralized AI
The top hyperscalers have become key contenders in the AI arms race, with OpenAI emerging as a frontrunner. This case study examines OpenAI’s journey as a pioneer in the AI industry and explores the ethical dilemmas associated with its growing influence and market dominance.
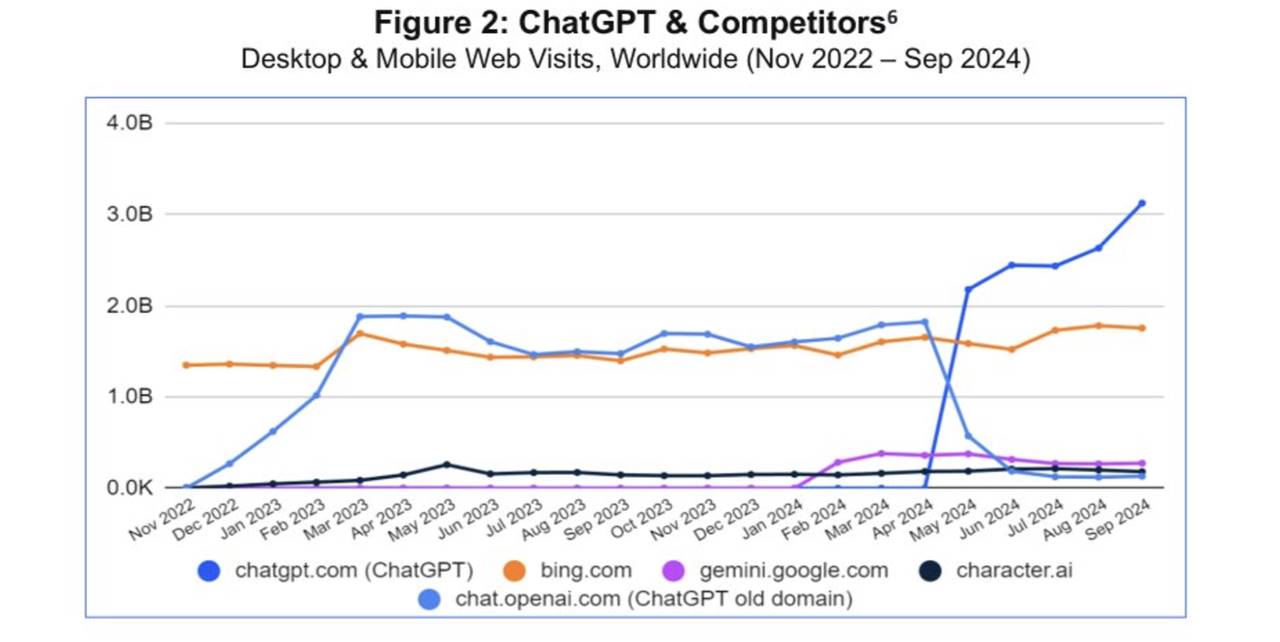
As the developer of ChatGPT, OpenAI has established a significant lead in this emerging space. Notably, ChatGPT reached 1 million users just five days after launch. By November 2024, the platform had grown to over 200 million weekly active users—double the number from November 2023. In October 2024 alone, ChatGPT attracted more than 3.7 billion visits, far surpassing all competitors combined. OpenAI is projected to generate $3.7 billion in revenue in 2024 and $11.6 billion in 2025. These figures highlight not only ChatGPT’s rapid growth but also the widening gap between OpenAI and its rivals (see Figure 2).
Founded in 2015 as a nonprofit AI research organization committed to open-source principles, OpenAI initially pledged to freely share its research, code, and data. However, in 2019, it shifted to a "capped-profit" model. In June 2020, OpenAI released GPT-3 as a closed-source model (with GPT-3.5 and later versions remaining closed-source). By September 2024, reports indicated that OpenAI would no longer be overseen by its nonprofit board as it moved toward becoming a fully for-profit company. Critics argue that OpenAI is drifting away from its founding mission of developing safe artificial general intelligence for humanity’s benefit, as well as its original emphasis on transparency and preventing concentration of power.
OpenAI's shift to closed systems has been mirrored by other leading foundational models, including Google Gemini, Claude AI, and Perplexity, with only Meta’s LLaMa offering an open-source alternative.
While the move toward closed systems was initially justified by concerns over misuse and safety, it has raised significant questions about accessibility, transparency, and the broader ethical implications of an internet driven by closed models controlled by a few centralized entities.
Empowering Open-Source AI Development Through Blockchain Economics
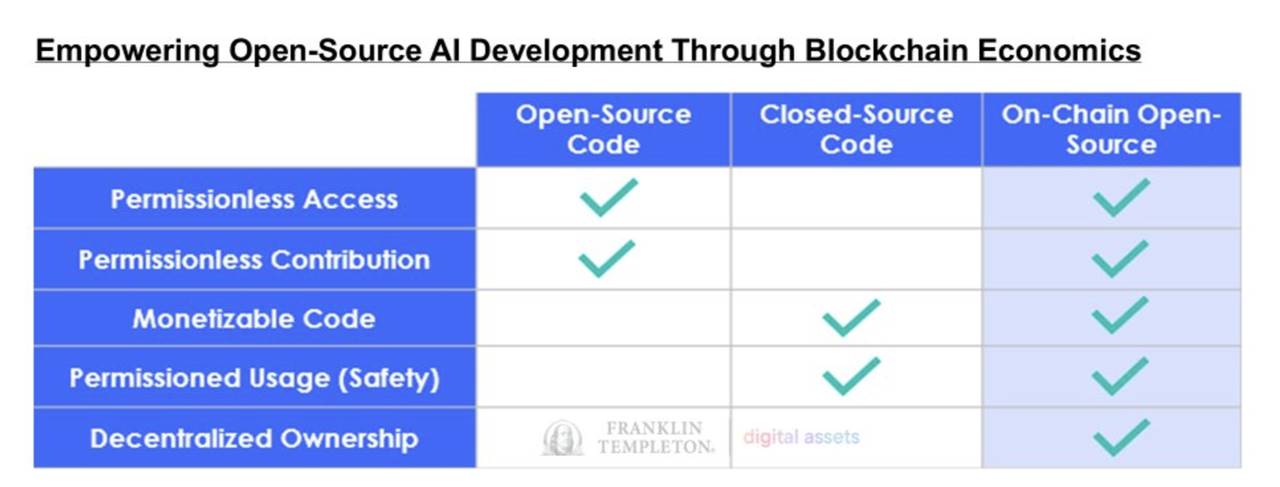
The early dominance of leading firms like OpenAI, Microsoft, Alphabet, and Amazon in developing AI foundation models is concentrating control and economic benefits in the hands of a few organizations. By applying blockchain technology to add an economic layer to open-source AI code, developers worldwide can compete on a more level playing field. This novel approach allows open-source contributors to monetize their models, data, and innovations—for the first time combining the collaborative advantages of open-source development with the monetization and security benefits typically associated with closed-source software.
Beyond enabling monetization of open-source code, blockchain-based decentralized protocols also allow individual developers and smaller organizations to crowdsource critical data and computing resources. Without such access, many developers would be blocked before they even begin. Yet, if developers around the world can obtain the necessary data and computational power, they will undoubtedly produce innovations that complement those developed by hyperscalers.
In summary, blockchain-powered coordination protocols for AI development enable developers to benefit from open collaboration and shared resources while also enjoying the ability to monetize their contributions and secure their work through cryptographic integrity. Individual developers and small organizations can meaningfully participate in AI advancement, receive economic incentives, retain ownership, and ultimately become key stakeholders in the AI-powered internet.
Conclusion
By unlocking the potential for millions of people to contribute to AI in an open and economically sustainable way, blockchain-enabled platforms have the power to shape how value is generated and distributed in the emerging AI-native internet. Beyond promoting collaboration, monetization, and sharing of critical data and computing resources, these protocols support community governance, ensuring that decisions regarding AI development, usage, and safety are made collectively. This paradigm shift could lead to a more diverse, equitable, and innovative economy.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














