Web3 Smartphone Market Overview: Mobile Accessibility Enhances Convenience, but Excessive Airdrop Marketing Lacks Technological Innovation
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Web3 Smartphone Market Overview: Mobile Accessibility Enhances Convenience, but Excessive Airdrop Marketing Lacks Technological Innovation
This report will examine the current state of Web3 smartphones and explore their future development directions.
Authors: Leo Park & Jay Jo & Yoon Lee
Translation: TechFlow
Key Takeaways:
-
Recently, Web3-enabled smartphones have been launched in large numbers and attracted attention. These phones are categorized into three types based on their level of Web3 integration: 1) Web3-supported, 2) Web3-focused, and 3) Web3-native smartphones.
-
Web3 smartphones hold promise for improving access to Web3 services and addressing high fees in the mobile market. However, current challenges include an excessive focus on airdrop marketing rather than technological innovation, as well as inadequate hardware performance.
-
Traditional smartphone manufacturers like Samsung have previously used Web3 technology for one-off promotional campaigns. Yet, the potential for broader Web3 integration on such devices continues to grow.
1. Introduction
Recently, Web3-enabled smartphones have drawn significant industry attention. Seen as the final link connecting users with new technologies, these devices are considered powerful tools for bringing Web3 into the mainstream. This report examines the current state of Web3 smartphones and explores their future trajectory.
2. Classification of Web3 Smartphone Projects
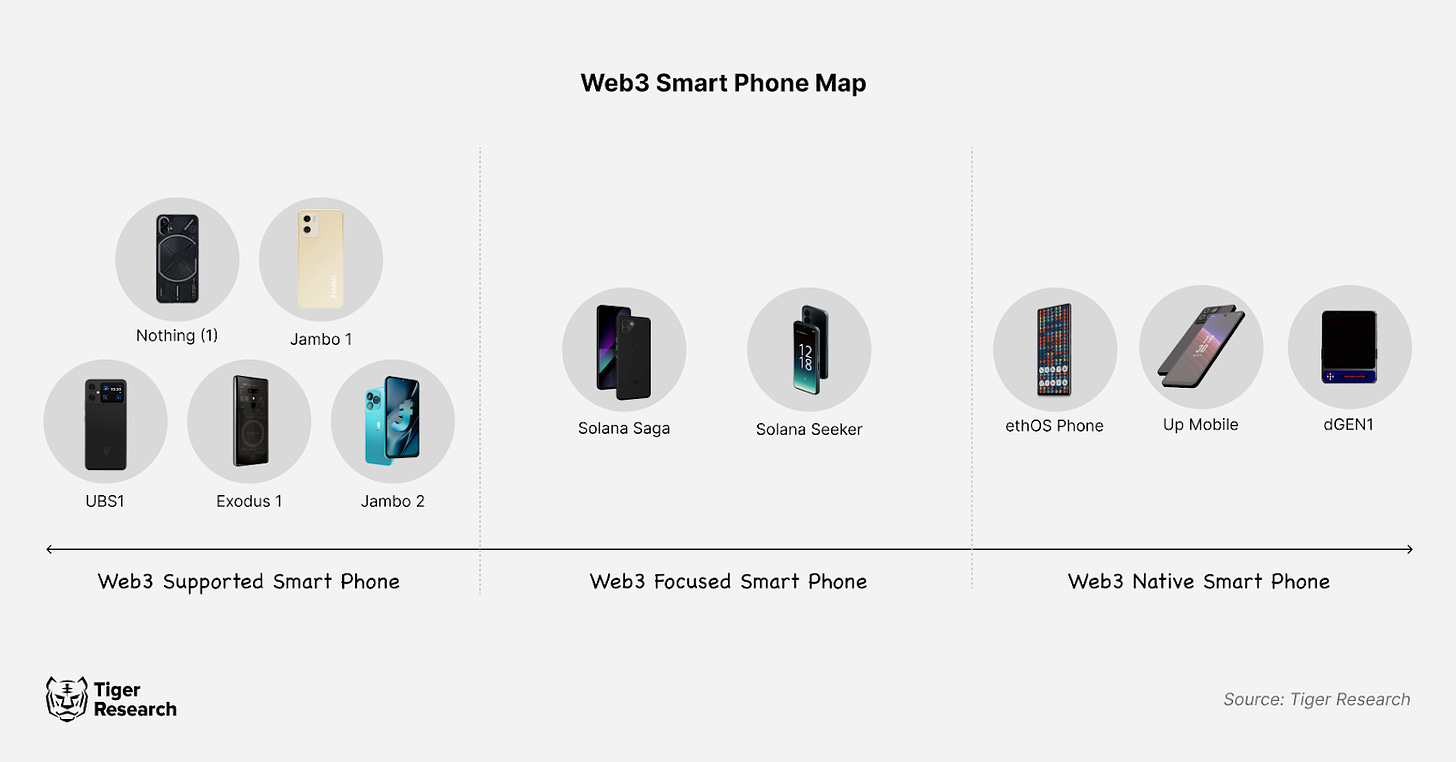
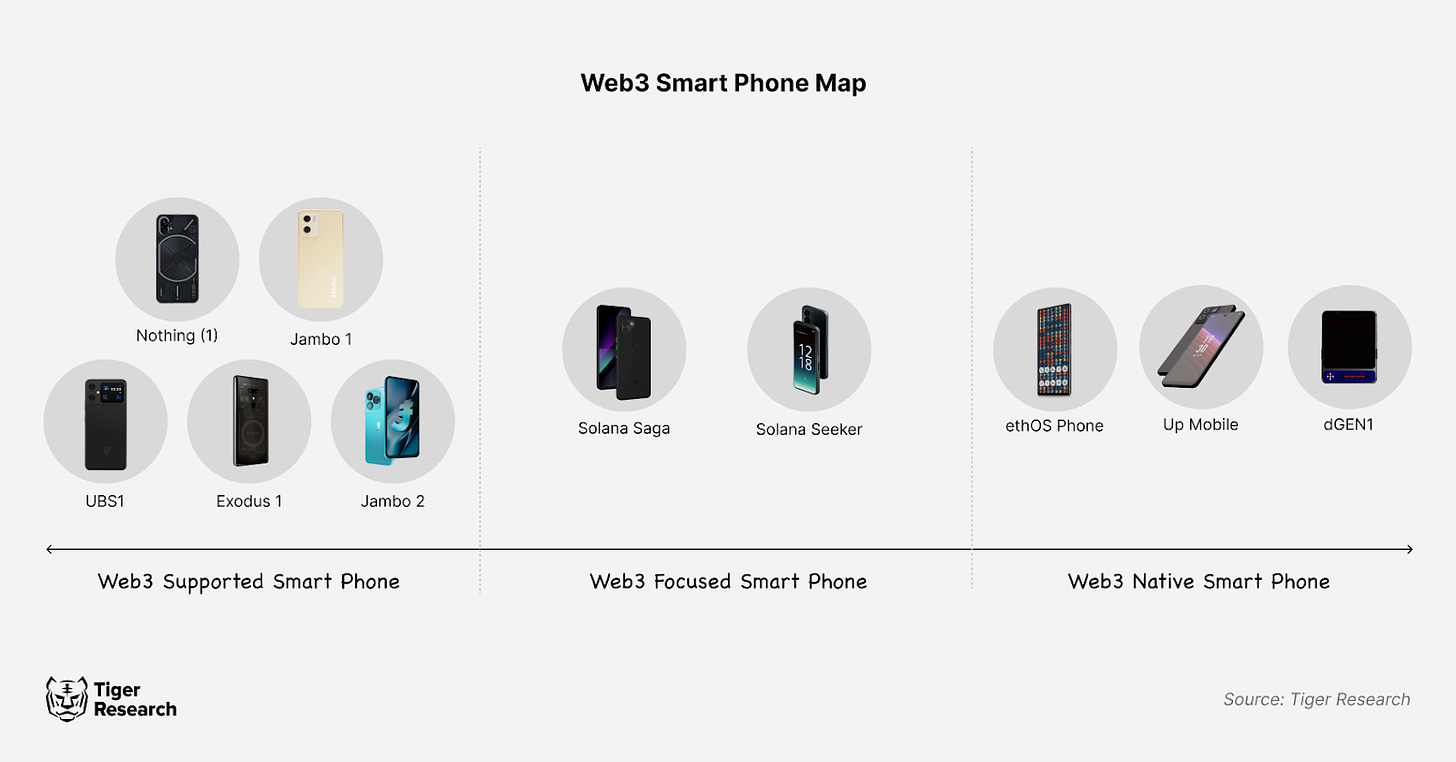
Web3 smartphone projects differ based on the extent of their adoption of Web3 technologies. As of October 2024, Tiger Research categorizes released Web3 smartphones into three groups: 1) Web3-Supported Smartphones, 2) Web3-Focused Smartphones, and 3) Web3-Native Smartphones, classified according to the depth of Web3 integration.
2.1. Web3-Supported Smartphones
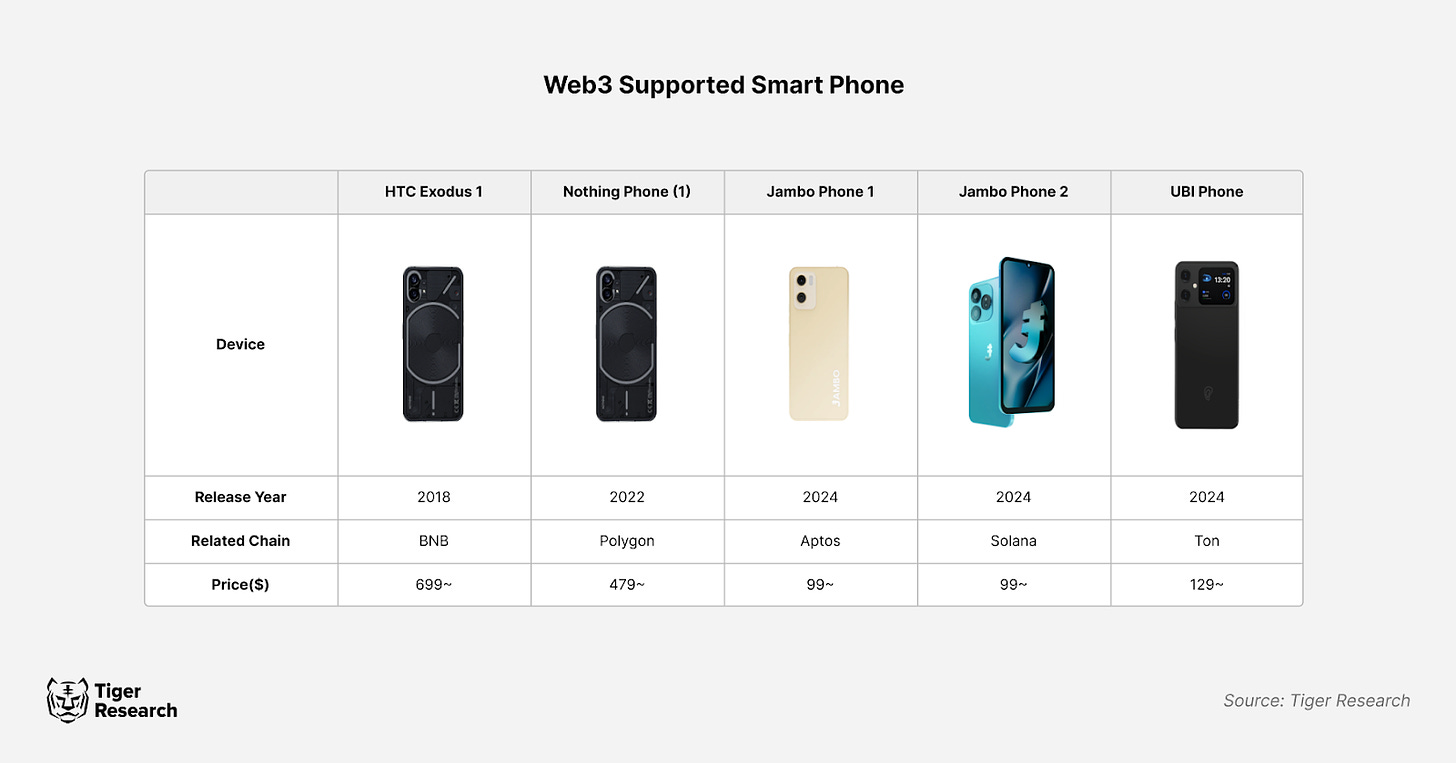
Web3-supported smartphones function similarly to traditional smartphones but offer basic-level support for Web3 technologies. They typically come preloaded with Web3 wallet apps such as Metamask and Petra, along with cryptocurrency exchange applications. Through experimental partnerships with blockchain mainnets, they introduce Web3 elements to expand their ecosystems. In most cases, however, these devices lack distinctive Web3 functionality. Users can achieve similar experiences by simply installing Web3 apps on regular smartphones. Consequently, these devices fail to deliver unique value, leading to rapidly declining user interest. A notable example is Nothing, a smartphone startup that partnered with Polygon to launch an NFT community and Polygon-based ID system, but has since discontinued most of these services.
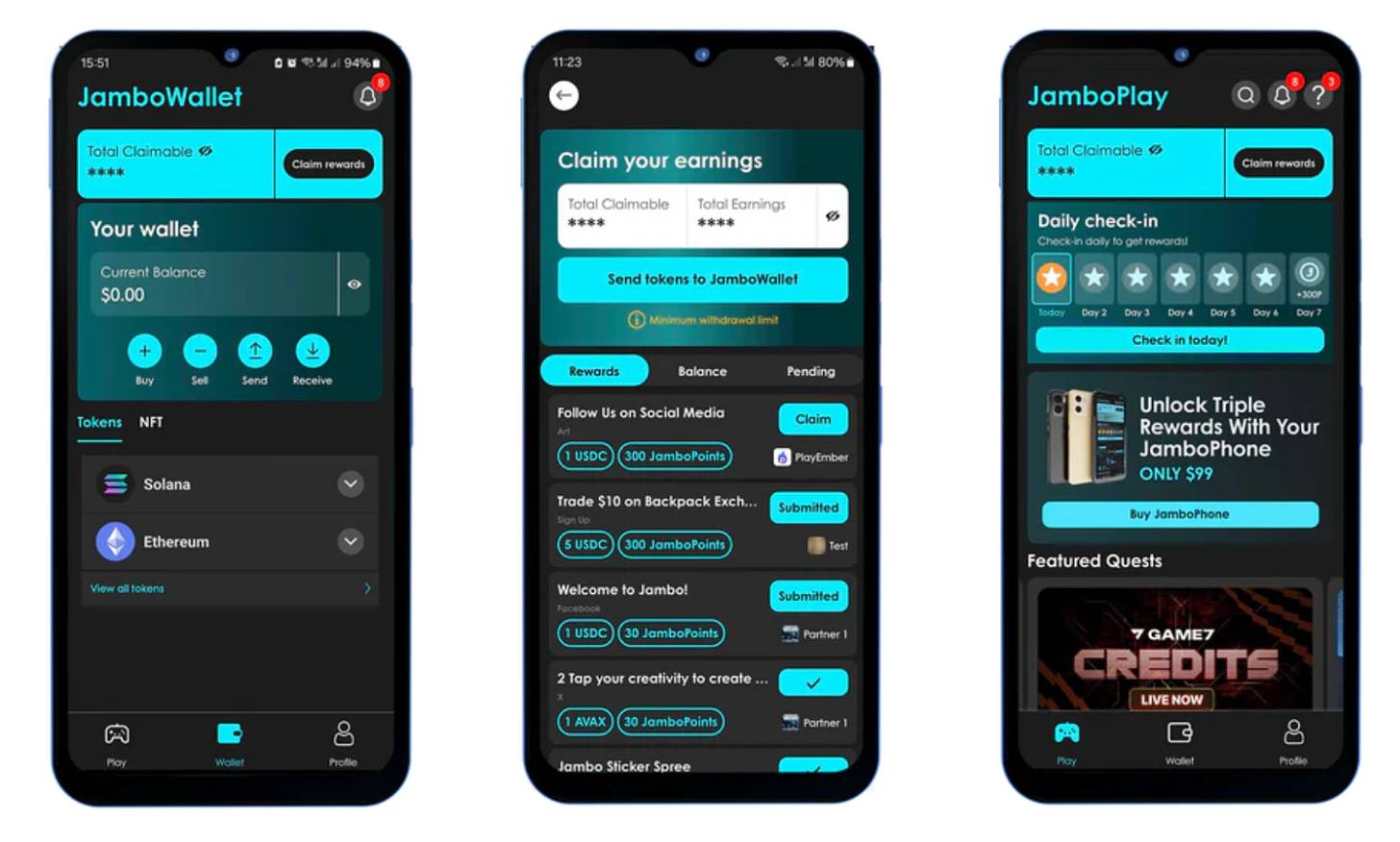
Source: Jambo Phone
More recent examples show more proactive adoption of Web3 features. For instance, Jambo Phone comes with preinstalled apps including the Web3 wallet Petra and the crypto exchange OKX. It also introduces users to the Web3 ecosystem via its proprietary app, Jambo Play, which allows participation in Web3 project tasks and earning cryptocurrency rewards. This approach serves as a lightweight testing platform and collaboration model. We expect to see more such cases in the future.
2.2. Web3-Focused Smartphones
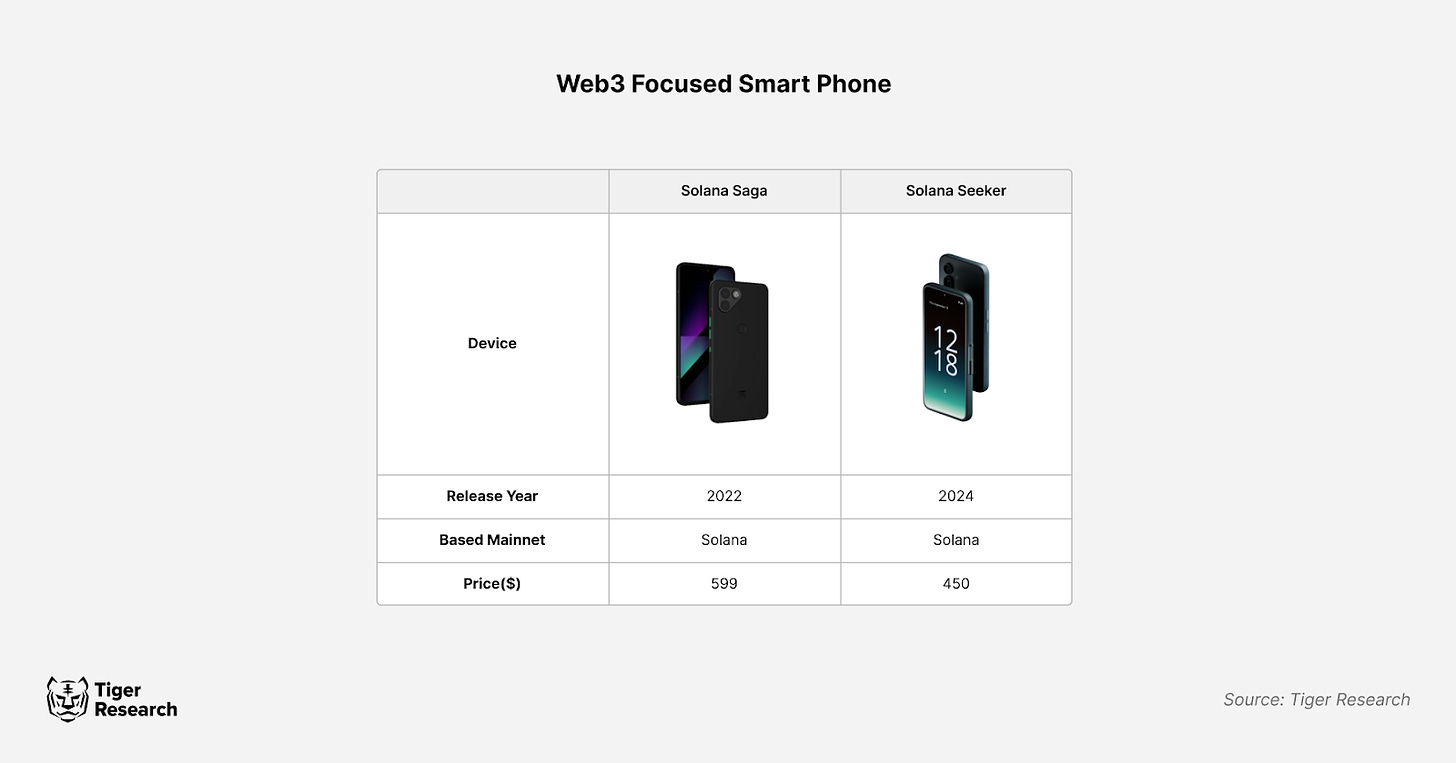
Web3-focused smartphones integrate Web3 technology partially into the device system. These phones run conventional mobile operating systems while adding Web3 capabilities, offering moderate integration rather than full Web3 functionality. Examples include Solana’s first-generation Saga and the recently announced second-generation Seeker.
These Web3-focused smartphones connect the traditional mobile environment with the Web3 ecosystem through dedicated interfaces. Solana provides the Solana Mobile Stack (SMS) to help developers build Web3 services. The phones feature Web3-optimized tools such as the Solana Pay system, which leverages Android’s NFC functionality and QR codes, along with a secure key vault for enhanced security.

Solana Seeker, Source: Solana Mobile
However, these Web3-focused smartphones still fall short of delivering a fully native Web3 experience. Users must install standalone Web3 wallets or use specific browsers like Brave to access Web3 services. Seeker, developed in partnership with Solflare, will feature built-in Seed Vault Wallet functionality. Many features remain undisclosed, potentially positioning it closer to a true Web3-native smartphone in the future.
2.3. Web3-Native Smartphones

This is achieved either by using a proprietary Web3 operating system or by providing native support for core Web3 technologies such as peer-to-peer distributed file systems (IPFS), Web3 messaging protocols (XMTP), and blockchain-based naming systems (CNS). These smartphones also include lightweight node clients, enabling users to independently verify transactions.
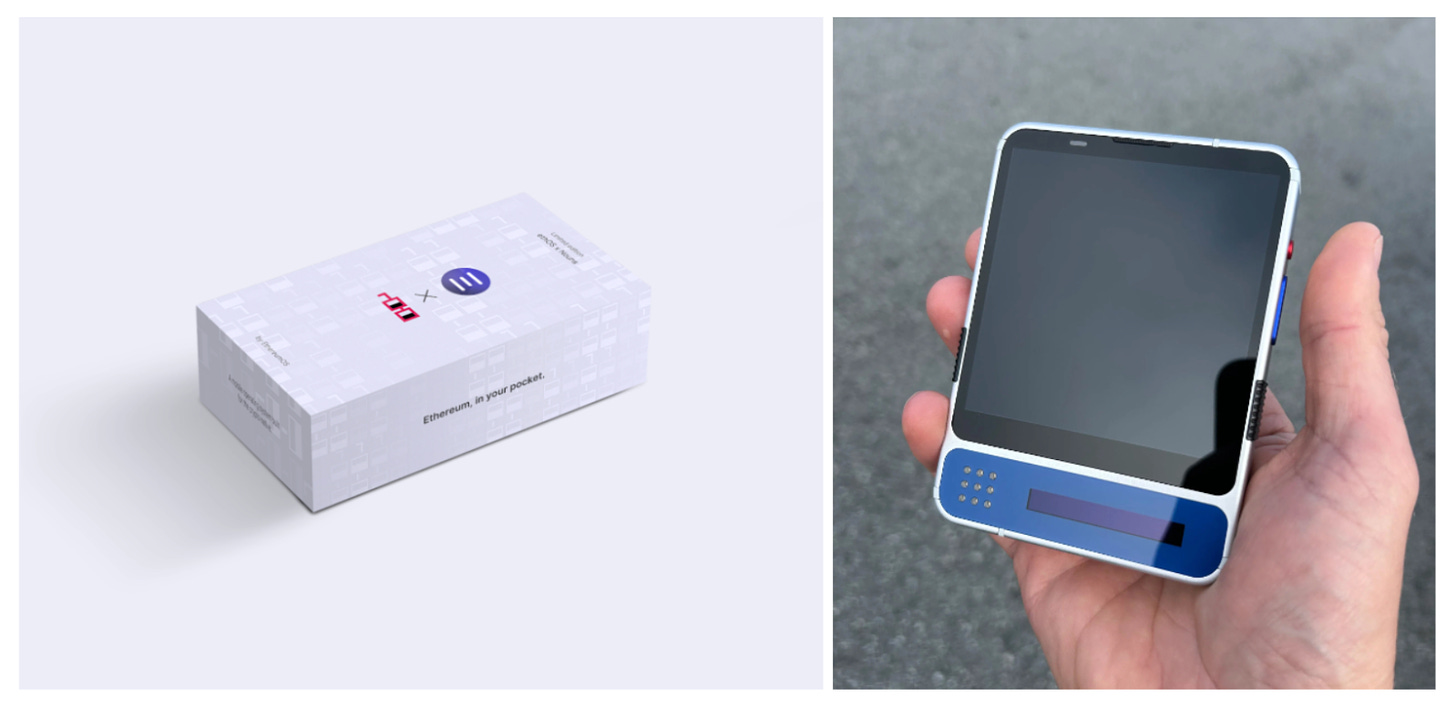

ethOS Nouns Edition (left), dGEN1 (right), Source: ethOS
A notable example is Freedom Factory’s ethOS. In 2023, supported by NounsDAO, ethOS launched its first prototype smartphone featuring an Ethereum-based Web3 operating system, achieving comprehensive system integration. Recently, the company released the dGEN1 smartphone, further enhancing its Web3-native capabilities. The built-in ethOS browser supports IPFS and ENS. Its light node functionality enables users to run on-chain dApps without relying on external RPC nodes. The OS-integrated Web3 wallet allows transaction signing without switching apps or using in-app browsers. Additional advanced features include SMS-based cryptocurrency transfers and the ability to mint gallery images as NFTs.

Source: Up Network
Likewise, Up Mobile, developed in collaboration with Movement Labs and Up Network, demonstrates high levels of Web3 integration. Its proprietary Web3 operating system, Up OS, offers system-level integration. The device's built-in Web3 wallet supports light node functionality and interface-less signing technology.
3. What Are the Advantages of Web3 Smartphones?
Interest in Web3 smartphone projects is steadily growing, with various experiments underway. This growth stems from expectations that Web3 smartphones will play a pivotal role in the mass adoption of Web3 technologies while addressing existing industry challenges. The advantages of Web3 smartphones can be analyzed across three dimensions.
First, Web3 smartphones can significantly enhance accessibility to Web3 services by leveraging the strengths of mobile devices. With built-in Web3 wallets, private key management, and dApp services, users can easily access Web3 services anytime, anywhere. The synergistic effect between Web3 technology and financial services is particularly noteworthy. These devices enable users to utilize crypto-asset-based financial services without time or location constraints, making financial services more accessible even in developing countries with limited infrastructure.
Second, Web3 smartphones have the potential to address long-standing issues in the mobile market. Traditional app stores currently charge up to 30% in fees, reducing developer profits and constraining market growth. Web3 smartphone initiatives aim to solve this through decentralized alternatives. For example, Solana Mobile and Up Network are developing blockchain-based decentralized dApp stores, aiming to create a fee-free, decentralized application ecosystem.
Finally, the combination of these two advantages is expected to generate strong synergies within the Web3 industry. While demand for consumer-facing applications in Web3 continues to rise, there remains a lack of device environments supporting daily usage. Web3 smartphones could overcome this limitation and foster the development of new consumer applications. Just as the shift from PCs to mobile devices led to an explosion of innovative services, the rise of Web3 smartphones may trigger a similar wave of innovation. As mobile portability and sensor functionalities expanded IT service applications, Web3 smartphones could bring significant disruption to this space. In particular, a fee-free dApp store environment is expected to create a far more dynamic development ecosystem than today’s Web2 industry.
4. What Challenges Do Web3 Smartphones Face?
Despite their great potential, Web3 smartphones face several hurdles. First, their hardware specifications generally lag behind those of mainstream smartphones. Most Web3 smartphones underperform in areas such as camera quality and screen refresh rates, making them unsuitable for mass-market adoption. Moreover, models priced above $500 appear overpriced given their configurations, deterring average consumers. Staged pre-sale systems also lead to uncertain delivery timelines, reducing product accessibility. Thus, Web3 smartphones face challenges in hardware competitiveness, sales, and operational efficiency.

Source: Jambo Phone (left), Goosefx (right)
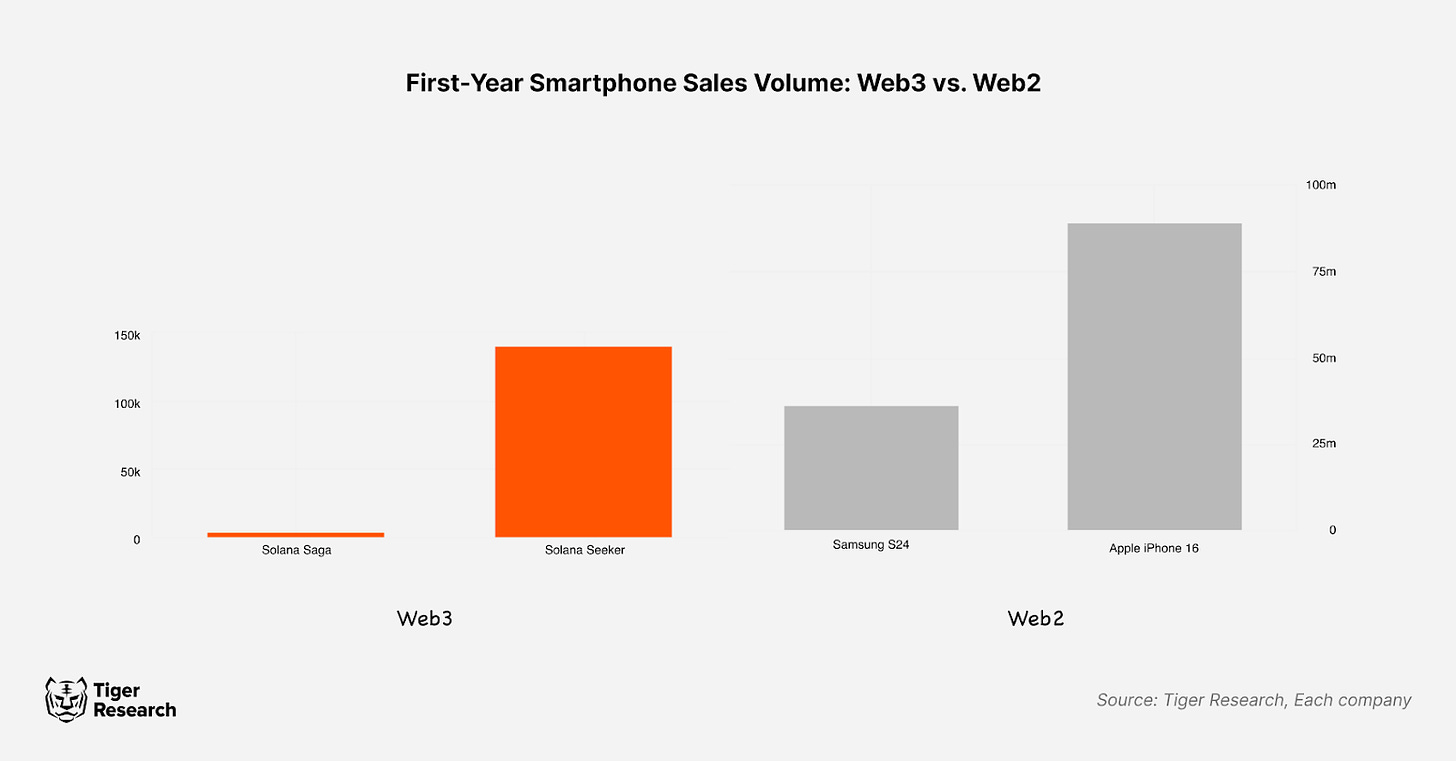
The second issue is that Web3 smartphones often emphasize rewards like airdrops over technological innovation. Solana’s first Web3 smartphone, the Saga, exemplifies this. Initially facing low sales, Saga was forced to reduce its price. Demand surged when the meme coin $BONK received by users sharply increased in value, causing resold units to reach prices as high as $5,000. Pre-orders for its successor, Seeker, have now exceeded 140,000 units. Similarly, Jambo Phone garnered significant attention by distributing the Aptos-based meme coin Gui Inu ($GUI) for free. These cases highlight how the Web3 smartphone market is influenced by speculative factors such as free tokens and resale value. This raises concerns that Web3 smartphones may represent a short-lived trend rather than a sustainable ecosystem.
Finally, Web3 smartphones face operational challenges. One concern is that their decentralized operations may be too radical to fully replace the practical value offered by traditional centralized platforms. While Google Play and Apple App Store charge up to 30% fees, they provide critical services—including abuse prevention, infrastructure maintenance for payments and apps, and customer support. The unique dApp experience on Web3 smartphones may also introduce new user experience issues. Much like preinstalled apps from manufacturers or carriers that previously annoyed users, preloaded blockchain infrastructure and dApp configurations on Web3 smartphones might be imposed based on manufacturer and partner interests. Therefore, Web3 smartphones must go beyond technical integration and develop comprehensive operational strategies to address these challenges.
5. How Are Traditional Smartphone Manufacturers Responding?
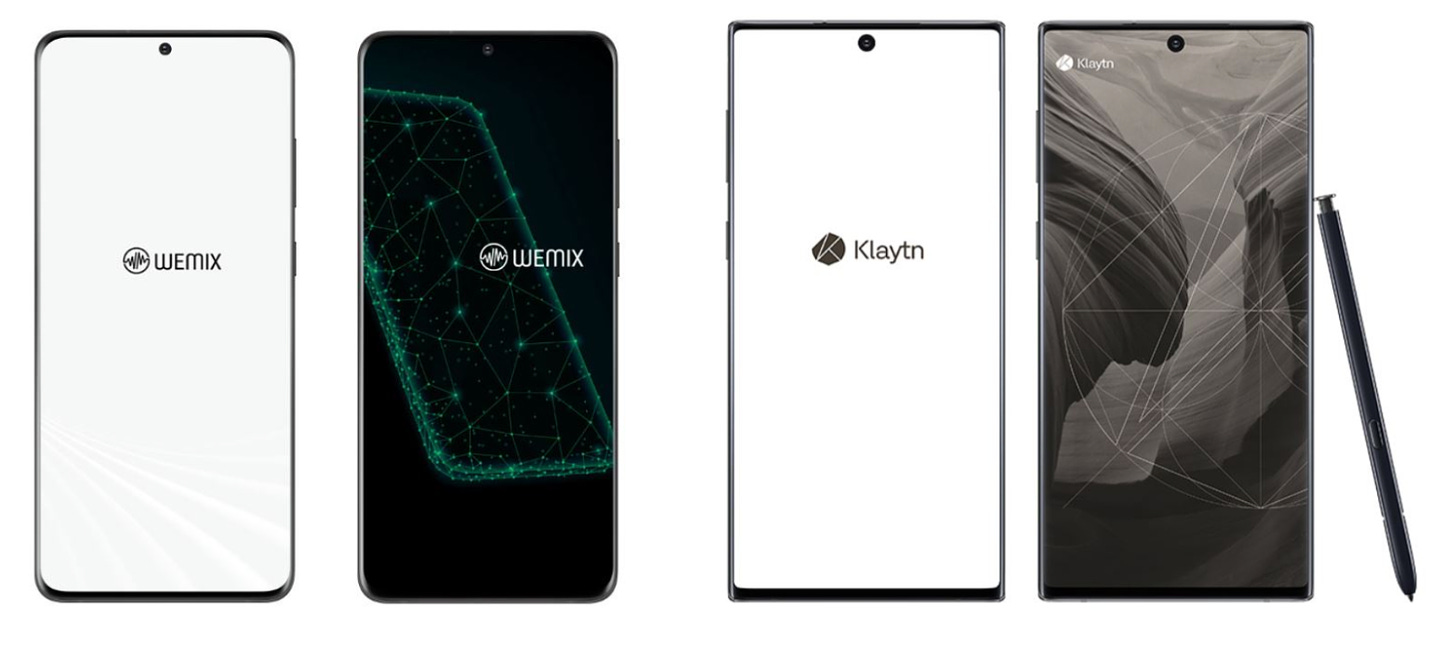

Galaxy S20 Wemix Edition (left), Galaxy Note10 Klaytn Edition, Source: Samsung
Traditional smartphone manufacturers are beginning to show interest in integrating Web3 technologies into their devices. Initially, most efforts were limited to one-time promotional campaigns with little substantive differentiation. For example, Samsung partnered with WeMade Tree (now merged with WeMade) and GroundX (formerly Klaytn developer) to release a series of Web3 smartphones preloaded with dApps from respective mainnets. Beyond basic wallet apps and token incentives, however, these devices lacked standout features.

Source: Envato
More recently, practical applications of Web3 technology show promising potential. For instance, Circle announced a Tap to Pay feature that will allow iPhone users to make payments using the USDC stablecoin via Apple’s NFC technology. Although not directly developed by Apple, this indicates that Web3 payments can be implemented on devices like the iPhone.
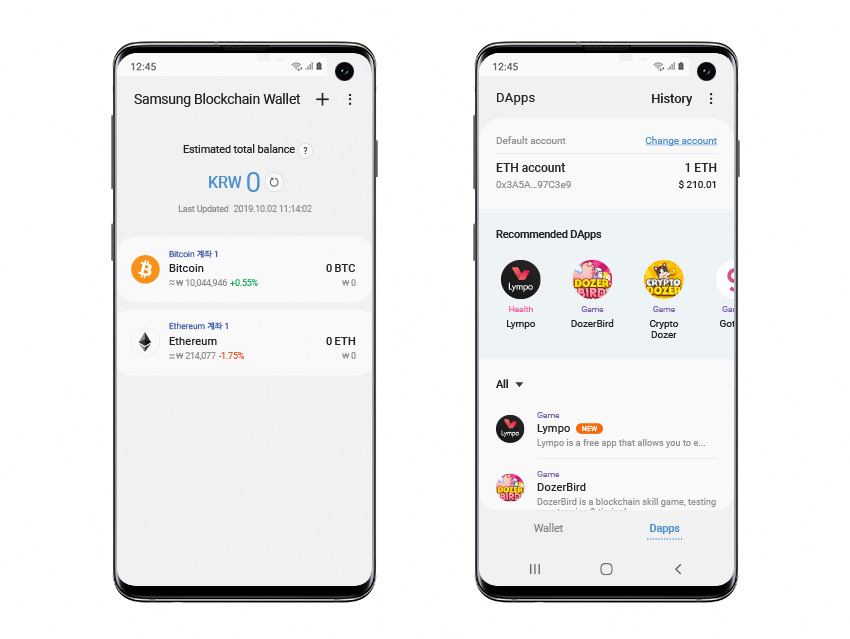
Samsung Blockchain Wallet, Source: Samsung
Samsung has supported integration with external Web3 wallets like MetaMask and Coinbase Wallet since 2019 through its Blockchain Keystore. It continues to support blockchain wallet apps on its latest models. Recently, Samsung partnered with South Korea’s Ministry of the Interior and Safety to launch a blockchain-based mobile ID that can be used within Samsung Pay. The potential adoption of Web3 technologies by leading smartphone manufacturers may signal a new breakthrough for Web3 in the mainstream market.
6. Conclusion
Web3 smartphones represent a disruptive concept, but the market remains in its infancy. Some projects attract attention through token incentives, yet their scale is minuscule compared to traditional smartphone shipments. Global smartphone users number 6.4 billion—76% of the world population—while Web3 users total only 10 million, just 0.156%. Given that the Web3 industry itself has not yet achieved widespread adoption, the Web3 smartphone market appears even more constrained.
Furthermore, Web3 smartphones face clear technical limitations. They lag significantly behind traditional manufacturers in hardware performance and production capacity. As a result, Web3 smartphone projects may seek long-term partnerships with established phone makers. By leveraging traditional manufacturers’ strengths in operating systems and software interfaces, Web3 initiatives can complement their own hardware expertise—a model similar to the Android-Samsung partnership. While building a user-friendly dApp ecosystem remains challenging, combining the hardware strength of traditional manufacturers with the software expertise of Web3 projects could accelerate the development of Web3 smartphones.
Dive deeper into Asia’s Web3 landscape with Tiger Research. Join over 4,000 pioneers and gain exclusive market insights.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News