Introducing Smart Contracts to Federated Learning: How Flock Is Reshaping AI Production Relationships?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Introducing Smart Contracts to Federated Learning: How Flock Is Reshaping AI Production Relationships?
In the future, FLock also plans to introduce a more user-friendly task initiation mechanism to realize the vision of "everyone can participate in AI."
By: LINDABELL
During the last wave of decentralized AI enthusiasm, star projects such as Bittensor, io.net, and Olas rapidly emerged as industry leaders thanks to their innovative technologies and forward-looking strategies. However, as valuations for these established projects continue to rise, the barrier to entry for ordinary investors has also increased significantly. So, amid this current cycle of sector rotation, are there still new opportunities for participation?
Flock: A Decentralized AI Training and Validation Network
Flock is a decentralized platform for AI model training and application that combines federated learning with blockchain technology to provide users with a secure environment for model training and management, while protecting data privacy and enabling fair community participation. The term "Flock" first entered public view in 2022, when its founding team co-published an academic paper titled "FLock: Defending malicious behaviors in federated learning with blockchain," proposing the use of blockchain in federated learning to defend against malicious behavior. This paper explained how decentralized mechanisms could enhance data security and privacy protection during model training, and revealed the potential applications of this new architecture in distributed computing.
Following initial proof-of-concept work, Flock launched Flock Research—a decentralized multi-agent AI network—in 2023. In Flock Research, each agent is a large language model (LLM) fine-tuned for a specific domain, capable of collaborating to deliver insights across different fields. Then, in mid-May 2024, Flock officially opened the testnet for its decentralized AI training platform, allowing users to participate in model training and fine-tuning using test tokens (FML) and earn rewards. As of September 30, 2024, the Flock platform had surpassed 300 daily active AI engineers and accumulated over 15,000 model submissions.
As the project continues to evolve, Flock has drawn attention from capital markets. In March this year, Flock secured $6 million in funding led by Lightspeed Faction and Tagus Capital, with participation from DCG, OKX Ventures, Inception Capital, and Volt Capital. Notably, Flock was the only AI infrastructure project to receive a grant in the 2024 Ethereum Foundation Academic Grants round.

Rewriting the Foundations of AI Production: Introducing Smart Contracts to Federated Learning
Federated Learning (FL) is a machine learning approach that allows multiple entities—typically called clients—to collaboratively train models while keeping data stored locally. Unlike traditional machine learning, FL avoids uploading all data to a central server, instead preserving user privacy through local computation. Today, FL is already applied in various real-world scenarios. For example, Google has used FL in its Gboard keyboard since 2017 to improve typing suggestions and text prediction without uploading user input. Tesla similarly applies FL locally in its autonomous driving systems to enhance environmental perception capabilities while reducing the need to transmit massive video datasets.
However, these implementations still face challenges, particularly around privacy and security. First, users must trust centralized third parties. Second, during the transmission and aggregation of model parameters, there’s a risk of malicious nodes uploading fake data or corrupted parameters, which can skew overall model performance or produce incorrect predictions. According to research published by the FLock team in an IEEE journal, traditional FL models see accuracy drop to 96.3% when 10% of nodes are malicious. When malicious node ratios increase to 30% and 40%, accuracy falls further to 80.1% and 70.9%, respectively.
To address these issues, Flock integrates blockchain-based smart contracts into its federated learning architecture as a "trust engine." These smart contracts act as automated coordinators in a decentralized environment, handling parameter collection, validation, and unbiased release of model results, effectively preventing data tampering by malicious nodes. Compared to traditional FL approaches, FLock maintains model accuracy above 95.5% even when 40% of nodes are malicious.
Positioning at the AI Execution Layer: Understanding FLock's Three-Layer Architecture
A major pain point in today’s AI landscape is the extreme concentration of AI model training resources and data usage among a few large corporations. This leaves ordinary developers and users unable to effectively access or utilize these resources. As a result, most users are limited to pre-built, standardized models rather than being able to customize them according to their own needs. This mismatch between supply and demand means that despite abundant computing power and data reserves in the market, they cannot be efficiently transformed into usable models and applications.
To tackle this issue, Flock aims to become an efficient coordination system that connects demand, resources, computing power, and data. Drawing inspiration from Web3 tech stacks, Flock positions itself as the “execution layer,” responsible for assigning users’ customized AI tasks to decentralized nodes for training and orchestrating these tasks globally via smart contracts.
Additionally, to ensure fairness and efficiency across the ecosystem, FLock handles both “settlement” and “consensus.” Settlement refers to incentivizing and managing participant contributions through rewards and penalties based on task completion. Consensus ensures the quality of training outcomes is evaluated and optimized so that the final model represents a globally optimal solution.
The overall FLock product architecture consists of three core modules: AI Arena, FL Alliance, and AI Marketplace. AI Arena handles decentralized foundational model training, FL Alliance manages model fine-tuning under smart contract governance, and AI Marketplace serves as the final marketplace for model applications.
AI Arena: Localized Model Training with Verification and Incentives
AI Arena is Flock’s decentralized AI training platform where users can participate by staking the Flock testnet token FML and earn corresponding staking rewards. After defining their desired model and submitting a task, training nodes within AI Arena perform local training using a given base model architecture—without uploading raw data to any centralized server. Once each node completes training, validators assess the quality of the trained models and assign scores. Users who do not wish to participate directly in validation can delegate their tokens to validators and still earn rewards.
In AI Arena, reward distribution for all roles depends on two key factors: stake size and task quality. Stake size reflects a participant’s commitment, while task quality measures their actual contribution. For instance, training node rewards depend on both stake amount and the ranking of submitted model quality. Validator rewards are determined by how closely their votes align with consensus, their staked token quantity, and their number of successful validations. Delegators’ returns depend on the validator they choose and the amount staked.
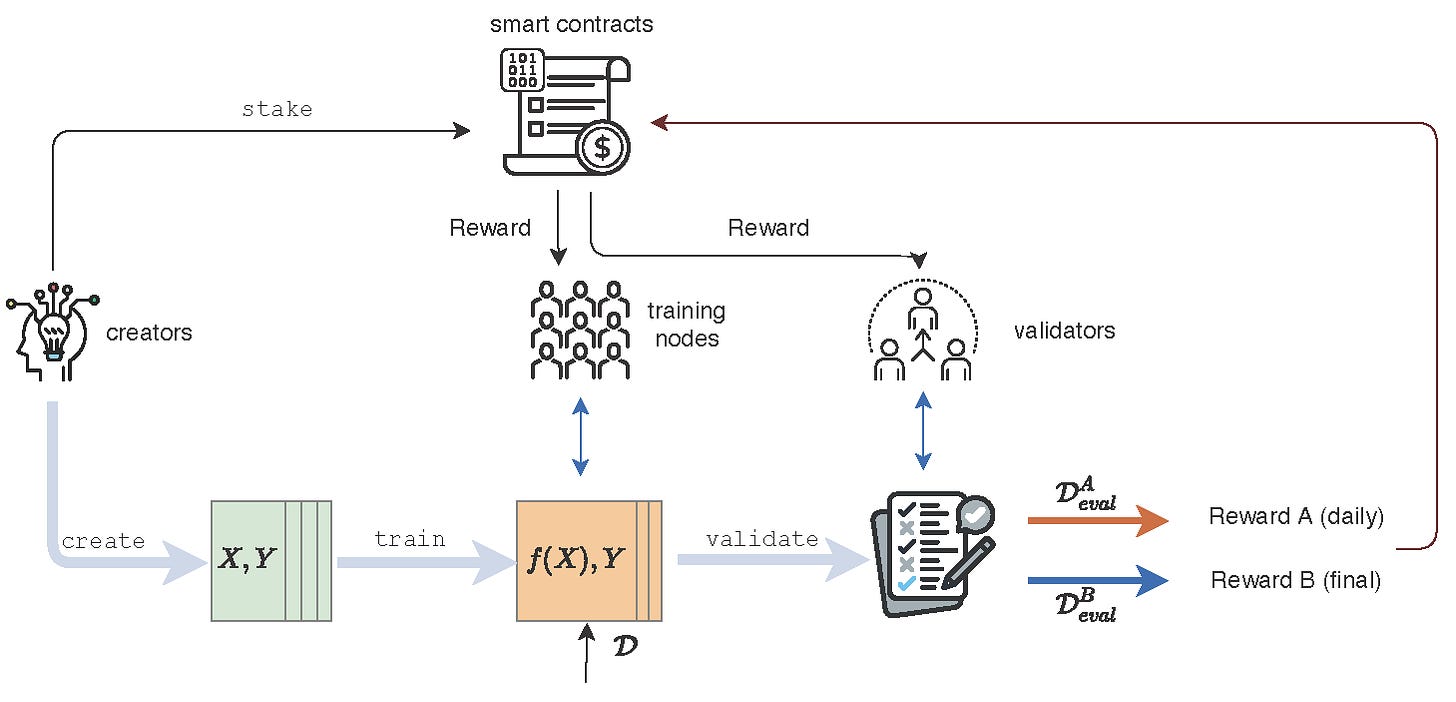
AI Arena supports traditional machine learning training modes, and users can opt to train using either local private data or public datasets to maximize final model performance. Currently, the AI Arena testnet hosts 496 active training nodes, 871 validators, and 72 delegators. The platform’s current staking ratio is 97.74%, with average monthly returns of 40.57% for training nodes and 24.70% for validator nodes.
FL Alliance: A Fine-Tuning Platform Managed by Smart Contracts
The highest-scoring models from AI Arena are selected as “consensus models” and moved to FL Alliance for further fine-tuning. This process occurs over multiple rounds. At the start of each round, the system automatically creates a FL-specific smart contract tied to the task, which governs execution and reward distribution. Participants must again stake a certain amount of FML tokens. They are randomly assigned roles as either proposers or voters. Proposers train the model using their local dataset and upload updated parameters or weights to other participants. Voters then aggregate and evaluate these updates through voting. All results are submitted to the smart contract, which compares each round’s score with the previous one to determine whether model performance has improved or declined. If performance improves, the system advances to the next training phase; if it declines, the previously validated model is used to initiate another round of training, aggregation, and evaluation.
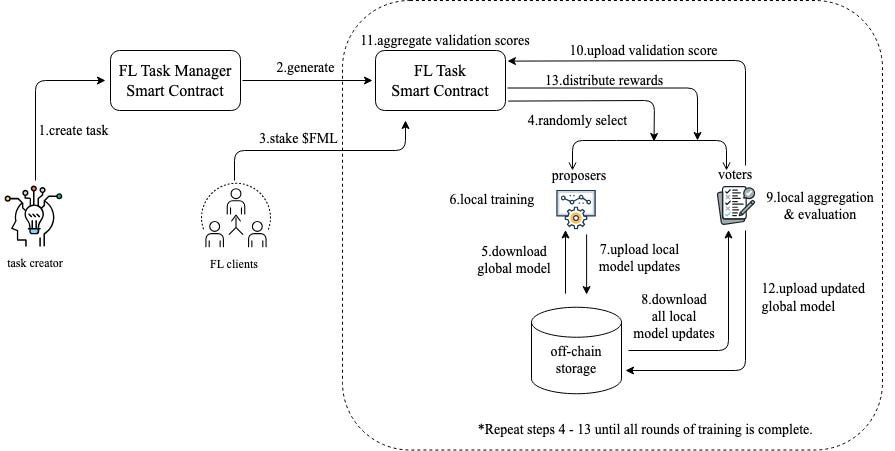
By integrating federated learning with smart contract automation, FL Alliance enables multiple participants to jointly train a global model while preserving data sovereignty. By combining diverse datasets and aggregating weights, it builds higher-performing, more capable global models. Furthermore, participants signal commitment through token staking and receive rewards based on model quality and consensus outcomes, creating a fair and transparent ecosystem.
AI Marketplace: Delivering Personalized AI Services
Models trained in AI Arena and fine-tuned in FL Alliance are ultimately deployed to the AI Marketplace, where they can be accessed and utilized by external applications. Unlike traditional model markets, AI Marketplace does not merely offer off-the-shelf models—it also allows users to modify models and integrate new data sources to suit different application scenarios. Additionally, the marketplace incorporates RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technology to improve model accuracy in specialized domains. RAG enhances large language models by retrieving relevant information from external knowledge bases during response generation, ensuring outputs are more accurate and personalized.
The AI Marketplace already features numerous custom GPT models tailored to specific use cases, including BTC GPT, Farcaster GPT, Scroll GPT, and Ethereum GPT. To illustrate the difference between custom and general-purpose models, consider the following example:
In December 2023, when asked “What is ARC20?” simultaneously:
-
BTC GPT responded: “The ARC20 protocol is built on the Bitcoin network and allows users to create, transfer, and upgrade digital assets such as NFTs and fungible tokens. Using the ARC20 protocol, both non-fungible NFTs and fungible tokens can be issued on the Bitcoin network. The primary token of the ARC20 protocol is ATOM, used for various purposes within the protocol.”
-
ChatGPT replied: “As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, there is no widely recognized standard or technology named ARC20 in tech, finance, or other common fields. It’s possible a new technology or standard named ARC20 has emerged since then, but I have no information about it.”
This comparison clearly demonstrates the importance and advantages of customized GPT models. Unlike general-purpose language models, customized GPTs are trained on domain-specific data, enabling them to deliver more precise and contextually relevant responses.

Both Backed by DCG: How Does Flock Compare to Bittensor?
With the AI sector rebounding, Bittensor—one of the flagship decentralized AI projects—has seen its token surge over 93.7% in the past 30 days, briefly approaching its all-time high and pushing its market cap back above $4 billion. Notably, DCG, an investor in Flock, is also one of the largest validators and miners in the Bittensor ecosystem. According to insiders, DCG holds approximately $100 million worth of TAO. In a 2021 article by Business Insider, DCG investor Matthew Beck listed Bittensor as one of the 53 most promising crypto startups.
Despite shared backing from DCG, Flock and Bittensor differ significantly in focus and design. Bittensor aims to build a decentralized AI internet, using “subnets” as its fundamental unit. Each subnet functions as a decentralized market where participants join as “miners” or “validators.” Currently, the Bittensor ecosystem includes 49 subnets spanning areas like text-to-speech, content generation, and LLM fine-tuning.
Since last year, Bittensor has remained a market focal point—not only due to its rapid price appreciation, climbing from $80 in October 2023 to a peak of $730 this year, but also due to growing skepticism. Critics question whether its reliance on token incentives to attract developers is sustainable. Moreover, concerns have been raised about centralization risks: the top three validators (Opentensor Foundation, Taostats & Corcel, Foundry) collectively hold nearly 40% of staked TAO.
In contrast, FLock focuses on introducing blockchain into federated learning to deliver personalized AI services. Flock sees itself as the “Uber of AI,” acting as a decentralized dispatch system that matches AI demand with developer capacity. Using on-chain smart contracts, it automates task assignment, result verification, and reward settlement, ensuring every participant receives fair compensation based on contribution. Like Bittensor, Flock also offers delegation options for users who don’t want to run nodes directly.
Specifically:
-
Training Nodes: Participate in AI training tasks by staking tokens—ideal for users with computational resources and AI development experience.
-
Validators: Also required to stake tokens, validators assess the quality of models submitted by training nodes and influence reward distribution through their scoring.
-
Delegators: Can stake tokens through validators or miners to increase their weight in task allocation and share in the rewards. This allows non-technical users to participate and earn passive income.
FLock.io has now officially opened its delegation feature, allowing any user to stake FML tokens and earn returns. Users can select nodes with the highest expected annualized yield to maximize staking returns. Flock also notes that staking and related activities on the testnet will influence eligibility for potential airdrops upon mainnet launch.

Looking ahead, FLock plans to introduce more user-friendly task initiation tools, enabling individuals without AI expertise to easily participate in model creation and training—fulfilling its vision of “AI for everyone.” Meanwhile, Flock is actively pursuing collaborations, such as developing an on-chain credit scoring model with Request Finance, building trading bot models with Morpheus and Ritual, providing one-click deployable training node templates for developers to run models on Akash, and training a Move language programming assistant for Aptos developers.
Overall, although Bittensor and Flock differ in market positioning, both are leveraging distinct decentralized architectures to redefine production relationships within the AI ecosystem. Their shared goal—breaking the monopoly of centralized giants over AI resources and building a more open and equitable AI landscape—is precisely what the market urgently needs today.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














