Grayscale: Delving into Bittensor, the Decentralized AI Model Market
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Grayscale: Delving into Bittensor, the Decentralized AI Model Market
Bittensor is a platform that promotes the development of open and global AI systems by leveraging decentralized networks and economic incentives.
Author: Grayscale
Translation: Felix, PANews
Summary
Bittensor stands at the forefront of two of the most transformative and groundbreaking trends in software: blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI). While Bitcoin helped create the crypto industry as the first peer-to-peer monetary system and digital store of value, and Ethereum expanded the ecosystem through decentralized applications, Bittensor represents a completely new and unique use case—leveraging permissionless public blockchains and economically incentivized mechanisms to enable advanced AI software development via open, decentralized communities rather than centralized corporations.
Today, AI development is highly concentrated, with immense power held by just a few large technology companies. As AI evolves into increasingly powerful and critical tools, there is growing risk of control by a small number of entities—an outcome misaligned with human values and broader societal interests. In contrast, Bittensor is an economically incentivized platform that promotes open collaboration in AI development through its native token, TAO. By utilizing a public blockchain, Bittensor could help democratize ownership, enhance transparency in AI systems, and align decision-making in AI development with societal benefits. Bittensor aims to build an "Internet of AI," envisioning a future where numerous interconnected AI ecosystems—or subnets—form a global, decentralized AI platform. By connecting to the Bittensor network, the platform will enable anyone, anywhere, to easily build, deploy, and access AI applications.
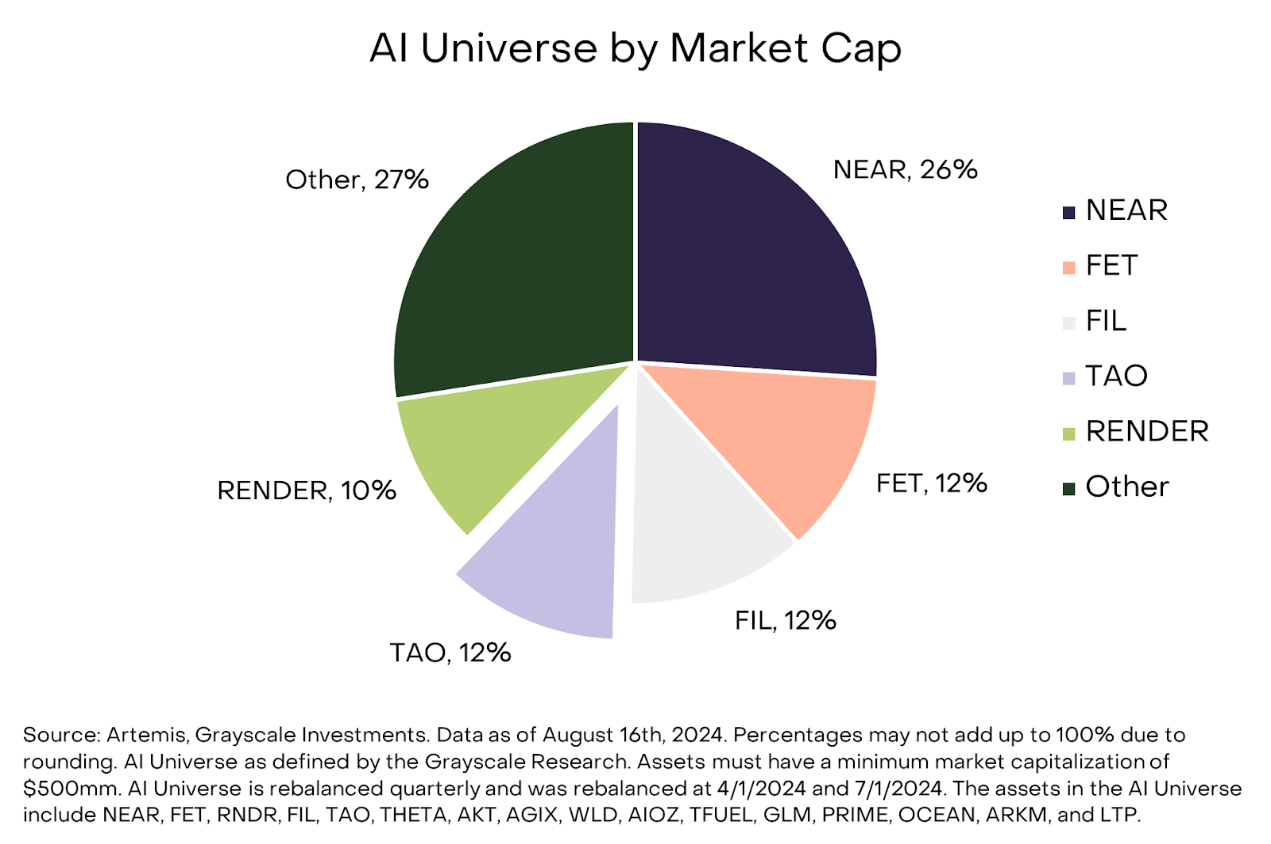
Figure 1: As of August 16, TAO accounted for 12% of Grayscale's AI Basket
Token
TAO is the native token of the Bittensor network. Holding TAO tokens represents partial ownership of the ecosystem (Figure 2). The token’s supply schedule mirrors Bitcoin exactly, with a maximum cap of 21 million and a halving approximately every four years. Bittensor’s first halving event is expected in August 2025.
Bittensor aims to apply Bitcoin-style incentives to AI development, using TAO tokens to reward participants who perform intended functions within the network. These participants include network validators, subnet owners, subnet validators, and subnet miners. Beyond incentive rewards, TAO currently serves primarily as a staking deposit required for subnet owners to register their subnets. As the nascent Bittensor network matures, potential additional uses for TAO may include: (i) gas fees for network transactions, (ii) voting rights in allocating TAO emissions to subnets, and (iii) general network governance decisions. In the long term, Bittensor might monetize the network by charging end-users of applications built on its subnets, potentially generating value for the TAO token.
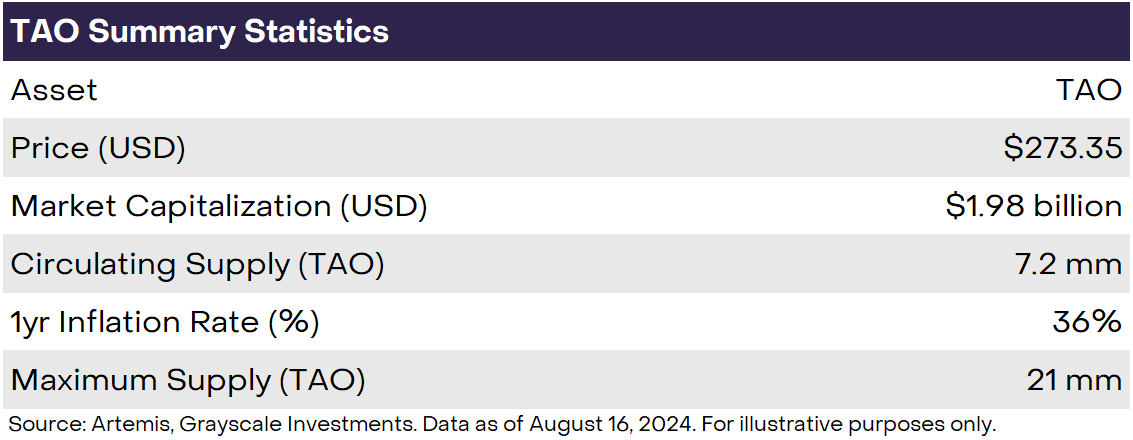
Figure 2: TAO Token Basics
Network and Technology
On Bittensor, developers compete to build the best AI models in exchange for TAO rewards. The system supports a range of AI-related services, including chatbots, video generation, deepfake detection, storage, and computation. To democratize AI development, Bittensor enables AI researchers and independent open-source developers to monetize their innovations and contribute to a more equitable distribution of AI benefits.
Bittensor employs various specialized subnets designed for distinct machine learning tasks. For example, one subnet focuses on AI image generation, another on AI music generation, and another on detecting AI-generated deepfakes. Each subnet involves three primary types of participants: subnet owners, subnet miners, and subnet validators. On any given subnet, miners compete to produce the “best” output, while validators assess which miners performed “best” (see below). While specific details vary by subnet, the overall process works as follows:
How It Works
-
End users prompt the network through consumer-facing applications—similar to asking a question of ChatGPT.
-
Subnet miners run AI models on the relevant subnet and compete to generate the best response to a given prompt. For instance, on a chatbot subnet, miners compete to provide the best answer to a user query.
-
Validators rank the miners’ responses based on quality and return the top-ranked response to the end user who issued the prompt.
Validators determine miner performance through a novel process called Yuma Consensus. This consensus mechanism aggregates rankings from each validator and weights them by the amount of TAO they have staked, producing a collective ranking of miner performance.
The broader Bittensor blockchain operates under a “proof-of-authority” consensus mechanism, where certain nodes are granted permission to order on-chain transactions and help maintain network integrity. Bittensor blocks store updated state changes and token balances, reflecting newly released tokens to network validators as well as subnet owners, miners, and validators.
Use Cases
Bittensor has a wide range of potential use cases, with each subnet representing a different application. Examples include:
-
Image Generation Subnet: Tailored for AI models specialized in creating high-quality generative images.
-
Chatbot Subnet: Optimized for AI models focused on natural language processing, enabling consumers to access responsive virtual assistants.
-
Deepfake Detection Subnet: Leverages advanced generative and discriminative AI models across the Bittensor network to detect AI-generated images.
Within the crypto space’s decentralized AI solutions, several direct competitors to Bittensor are tackling AI development comprehensively. For example, the Allora Network focuses on AI development for financial services, offering a platform for automated trading strategies on decentralized exchanges and prediction markets. Other early-stage projects aiming to solve decentralized AI at the infrastructure level include Sentient and Sahara AI.
Beyond these direct competitors, certain protocols compete with specific Bittensor subnets. For instance, Akash competes somewhat with the compute subnet, Filecoin with the data storage subnet, and Gensyn with pre-training and fine-tuning subnets. However, several notable AI companies (such as Wombo and MyShell) and crypto teams (including Masa, Kaito, and Foundry) have already launched their own subnets on Bittensor.
Opportunities to Consider
Large market opportunity with growth potential: The centralized AI market is estimated at $215 billion in 2024, with a projected compound annual growth rate of 35.7%. Grayscale views Bittensor as representing a new and unique use case within cryptocurrency. Decentralized AI is currently valued at just $19 billion, reflecting its early-stage status. At a time when a handful of tech firms appear to dominate AI, Bittensor represents an early investment in this convergence.
Permissionless access to develop and use powerful technology: As AI continues evolving into a more powerful and essential tool, regulations or restrictions on who can build or access such applications may increase. Bittensor offers an alternative—permissionless access to resources for developing and using AI.
Economic incentives promoting fair AI development: Compared to centralized alternatives, Bittensor could provide independent AI developers with greater access to AI resources such as computing power, storage, and data. It may also allow AI researchers and open-source developers to monetize their contributions and fund their operations. If successful, Bittensor’s open and distributed ecosystem could help balance closed-source models developed by tech giants and ensure broader sharing of AI’s economic benefits.
Growing adoption and recognition: Bittensor has gained early attention, hosting over 40 subnets dedicated to specific AI tasks and earning recognition from prominent tech and AI leaders. Companies are raising venture capital to build subnets and applications on Bittensor, signaling increasing interest from investors and developers. This momentum suggests Bittensor has the potential to expand its network effects.
Investment Risks
Adoption and network growth: Bittensor’s long-term success depends on attracting a large number of developers and AI projects to build on the platform. If it fails to achieve widespread adoption, the network may struggle to reach its full potential. Moreover, given the network’s early stage, most activity remains focused at the infrastructure and subnet levels. Over time, Bittensor must grow both the number and quality of application end users to enhance token value accrual and relevance to everyday consumers.
Decentralization and network resilience: Bittensor’s operations rely on the smooth functioning of a broad network of participants. Any disruptions—such as technical failures, bugs, or cyberattacks—could impact performance and reputation. Bittensor also needs to improve overall network decentralization and distribute voting power from TAO emissions more widely across the network.
Incentive design implementation: To fully realize its potential, Grayscale believes Bittensor must ensure subnet owners design appropriate incentive mechanisms for their subnets and that the network correctly allocates emissions to suitable subnets over time.
Competing networks: Bittensor faces competition from AI-focused crypto assets attempting to address AI development through token incentives, such as Allora, Sentient, and Sahara AI, as well as other assets covering various AI-related use cases like Filecoin and Gensyn. As this sector matures, the list of competitors is likely to grow over time.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














