As AI narratives heat up, how can DeFi benefit?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

As AI narratives heat up, how can DeFi benefit?
This article will explore specific use cases of AI in current DeFi protocols, the challenges faced, and the future development directions of AI in DeFi.
Author: DeSpread Research
Translation: TechFlow

Disclaimer: The content in this report represents the author's personal views and is for informational purposes only. This article does not intend to recommend buying or selling any tokens or using any protocols. Nothing in this report constitutes financial advice, nor should it be construed as such.
1. Introduction
With the advancement of the IT industry, enhanced computing power, and widespread use of big data, the performance of artificial intelligence (AI) models has significantly improved. In recent years, AI capabilities have reached or even surpassed human levels across many domains and are rapidly being applied in industries such as healthcare, finance, and education.
A prominent example of AI commercialization is ChatGPT, a generative AI model launched by OpenAI in November 2022 capable of understanding and responding to human natural language. ChatGPT attracted one million users within just five days of launch and reached 100 million monthly active users within two months, becoming the fastest-growing consumer application in history.
NVIDIA, the designer and manufacturer of GPUs essential for major AI platforms, has greatly benefited from this trend. In Q1 2024, NVIDIA’s net profit surged 628% year-on-year to $14.8 billion, its stock price nearly tripled compared to the previous year, and its market capitalization reached $3.2 trillion—remarkable performance.
The rise of the AI industry has had a significant impact on the crypto market. In June 2022, during the peak of NFT art projects, OpenAI released DALL-E 2—an AI model capable of generating high-quality images from text prompts—causing mentions of "AI" to increase eightfold in major Korean crypto Telegram channels. Additionally, starting in the second half of 2022, more direct attempts to integrate AI with blockchain led to another doubling of AI-related discussions.
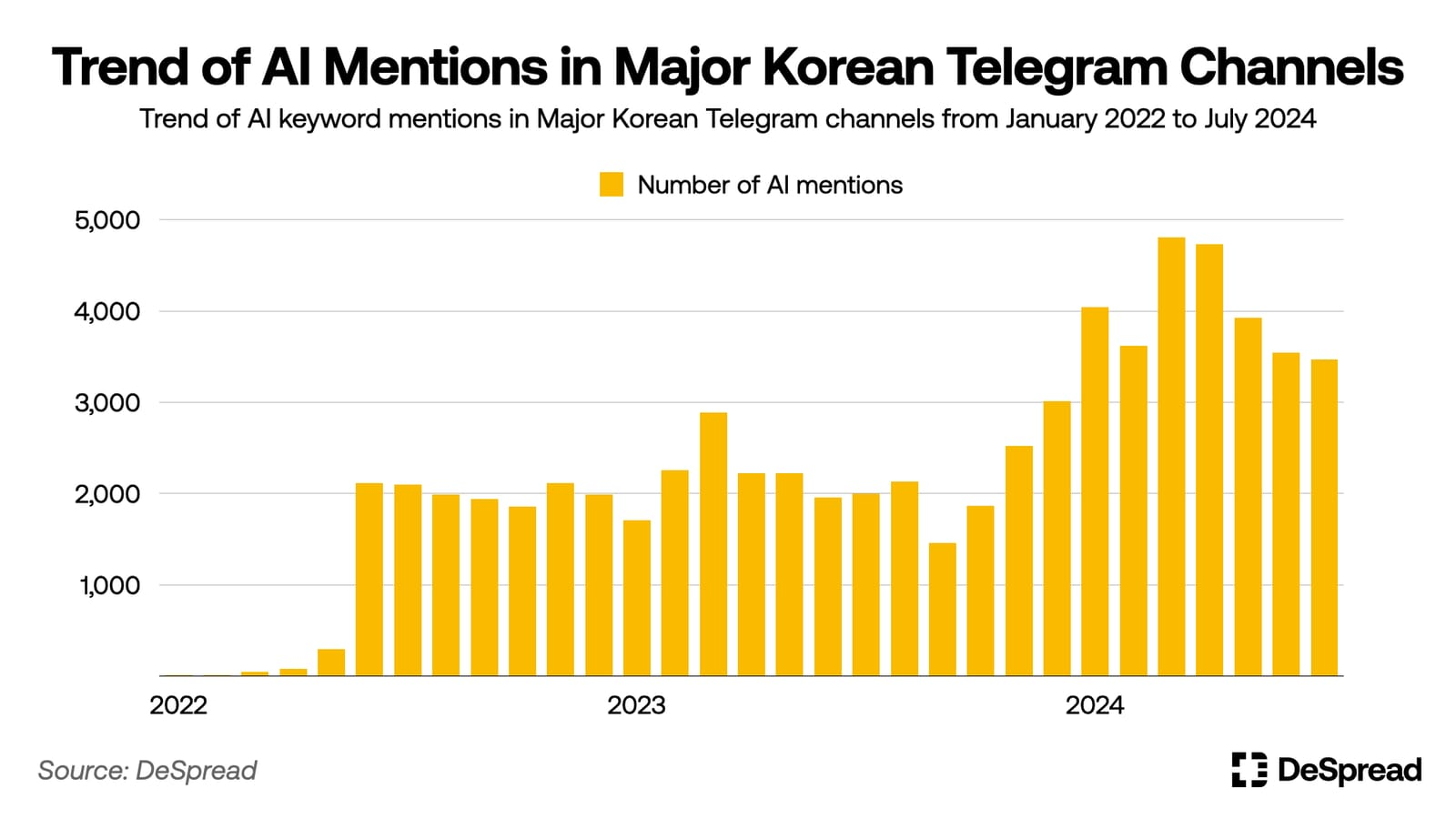
The crypto community’s strong interest in AI is also reflected in investment trends toward AI-related crypto projects. According to data from CoinGecko, a virtual asset statistics website, since mid-2022 when blockchain projects combining AI began emerging, the total market cap of 277 blockchain projects categorized under AI has rapidly grown to $2.1 billion by August 20, 2024—about 25% higher than the Layer2 category.
However, most currently popular AI-focused blockchain projects primarily leverage blockchain technology to address limitations exposed during AI development. Key application scenarios include:
-
Distributed GPU Networks: These projects utilize blockchain to create distributed GPU networks where anyone can contribute GPU computing power and receive token rewards, lowering entry barriers caused by expensive GPU costs for training AI models (e.g., IO.NET, Akash Network).
-
Decentralized AI Training and Model Development: These projects allow multiple participants to collaboratively train AI models and develop algorithms, receiving token incentives via blockchain, aiming to mitigate biases arising from centralized AI development environments (e.g., Bittensor).
-
On-chain AI Markets: These decentralized AI marketplaces use blockchain to transparently evaluate and trade AI models or agents based on performance and reliability, meeting diverse industry and functional demands (e.g., SingularityNET, Autonolas).
Beyond these examples, numerous new initiatives are emerging that leverage blockchain infrastructure—such as decentralized data markets and IP protocols—to tackle current challenges in the AI industry. By providing more robust foundational infrastructure for AI while expanding blockchain’s applicability, these efforts generate synergistic effects.
At the same time, integrating AI into the blockchain ecosystem holds immense developmental potential. Particularly in permissionless DeFi services, introducing AI could reduce reliance on trusted third parties, enabling functionalities difficult or impossible to achieve with existing smart contracts.
In this article, we will explore concrete applications of AI in current DeFi protocols, examine the challenges involved, and discuss future directions for AI in DeFi.
2. Intelligent DeFi
AI excels at real-time data analysis, drawing insights from vast datasets. This capability plays a crucial role in helping users execute capital operations and manage risk by concretizing yield and risk metrics provided by DeFi protocols. Currently, AI is mainly applied at the DApp user interface layer, allowing existing DeFi protocols to leverage AI without requiring major structural changes.
Yearn Finance serves as a typical example—a yield aggregator that is collaborating with the AI agent platform GIZAto build a real-time strategy risk assessment system for its v3 vaults, aiming to provide users with safer investment environments.
However, I am particularly interested in the potential for AI integration within the DeFi ecosystem to grant autonomy to DeFi protocols by leveraging AI's capacity for independent reasoning and action.
Current DeFi protocols typically respond passively to user transactions—smart contracts execute predefined logic upon user interaction. But by incorporating AI into DeFi protocols, systems can autonomously analyze market conditions, make optimal decisions, and proactively initiate transactions. This opens the door to entirely new types of financial services previously unattainable.
Let us now look closely at some intelligent DeFi protocols that apply AI within their core operational mechanisms.
2.1. Fyde Treasury: AI-Powered Token Fund
Fyde Treasury is a protocol offering a basket-style fund service called Liquid Vault, which manages a diversified portfolio of tokens through AI. Users receive liquid $TRSY tokens representing their stake in the assets deposited into the Liquid Vault.
2.1.1. Asset Selection and Fund Operations
The core objective of Liquid Vault is to increase allocations to low-volatility tokens during market downturns, minimizing losses for users and delivering superior long-term returns relative to other asset classes.
Fyde Treasury selects assets for inclusion in the Liquid Vault portfolio through three steps:
-
Evaluate whether trading liquidity is sufficient
-
Review the background of protocol founders and audit status of code to identify red flags
-
Use AI to analyze on-chain data assessing wash trading risks, token concentration, and organic growth trends
Tokens passing these criteria are included in the portfolio. Furthermore, Fyde Treasury employs AI throughout the asset management process, including:
-
Market Analysis and Forecasting: Analyze on-chain transaction data, market trends, and news to predict future market movements
-
Weight Calculation and Rebalancing: Compute optimal token weights and rebalance the portfolio based on predicted market trends and recent token performance and volatility
-
Risk Management and Response: Rapidly detect governance attacks, liquidity pool depletion, or abnormal wallet activity related to individual tokens and promptly adjust or isolate affected assets
-
Advanced Asset Management Strategies: Continuously assess portfolio performance, analyze strategy effectiveness, extract learnings to refine and develop new strategies, then conduct comparative testing before deploying improved strategies in production
As of August 23, the Liquid Vault portfolio contains 29 tokens, all Ethereum-based assets spanning various sectors.
Liquid Vault Dashboard, Source:Fyde
Additionally, Fyde Treasury enables users who deposit governance tokens of specific protocols into the Liquid Vault to retain voting rights via liquid tokens. Deposited governance tokens are represented as $gTRSY tokens sent to users’ wallets, which can be used to vote on corresponding protocol governance proposals through Fyde Treasury’s Governance tab.
However, voting power adjusts according to each token’s weight in the portfolio, so it may fluctuate whenever the portfolio is rebalanced.
2.1.2. Liquidity Mining Program
Fyde Treasury rewards liquidity providers who enhance market liquidity for $TRSY (the Liquid Vault liquidity token) with Fyde Points, promising future distribution of its governance token $FYDE based on accumulated points.
Unlike typical liquidity mining programs requiring users to directly deposit trading pairs on decentralized exchanges to earn tokens or points, Fyde Treasury allows users to deposit $FYDE into an internal liquidity mining contract, which then automatically provides liquidity directly on Uniswap v3—a DEX enabling range-based liquidity provision.
When providing liquidity on Uniswap v3, the system uses AI-driven simulations to calculate and execute the optimal path for converting part of the deposited $FYDE into $ETH. Moreover, AI dynamically manages and optimizes the liquidity position ranges on Uniswap v3 based on real-time market conditions, achieving approximately four times higher capital efficiency than standard DEX liquidity provision with equivalent capital.
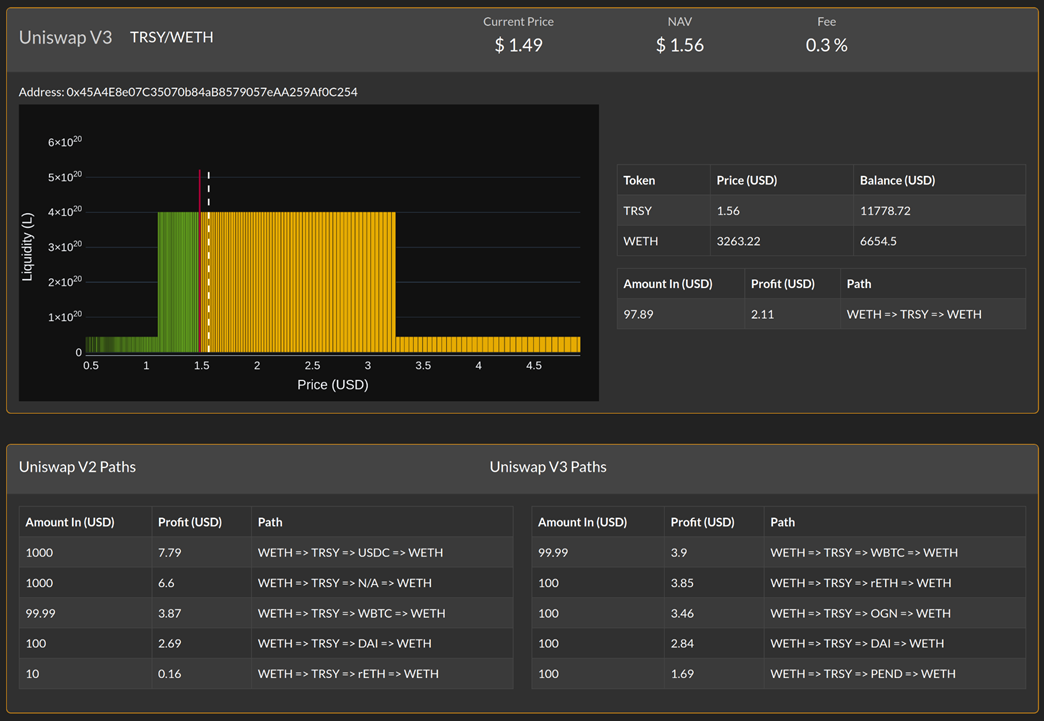
AI Simulation Dashboard, Source:Fyde Docs
In this way, Fyde Treasury is building a basket fund that leverages AI to actively manage user-deposited assets in real time, reducing human intervention and mitigating various market risks.
2.1.3. Protocol Performance
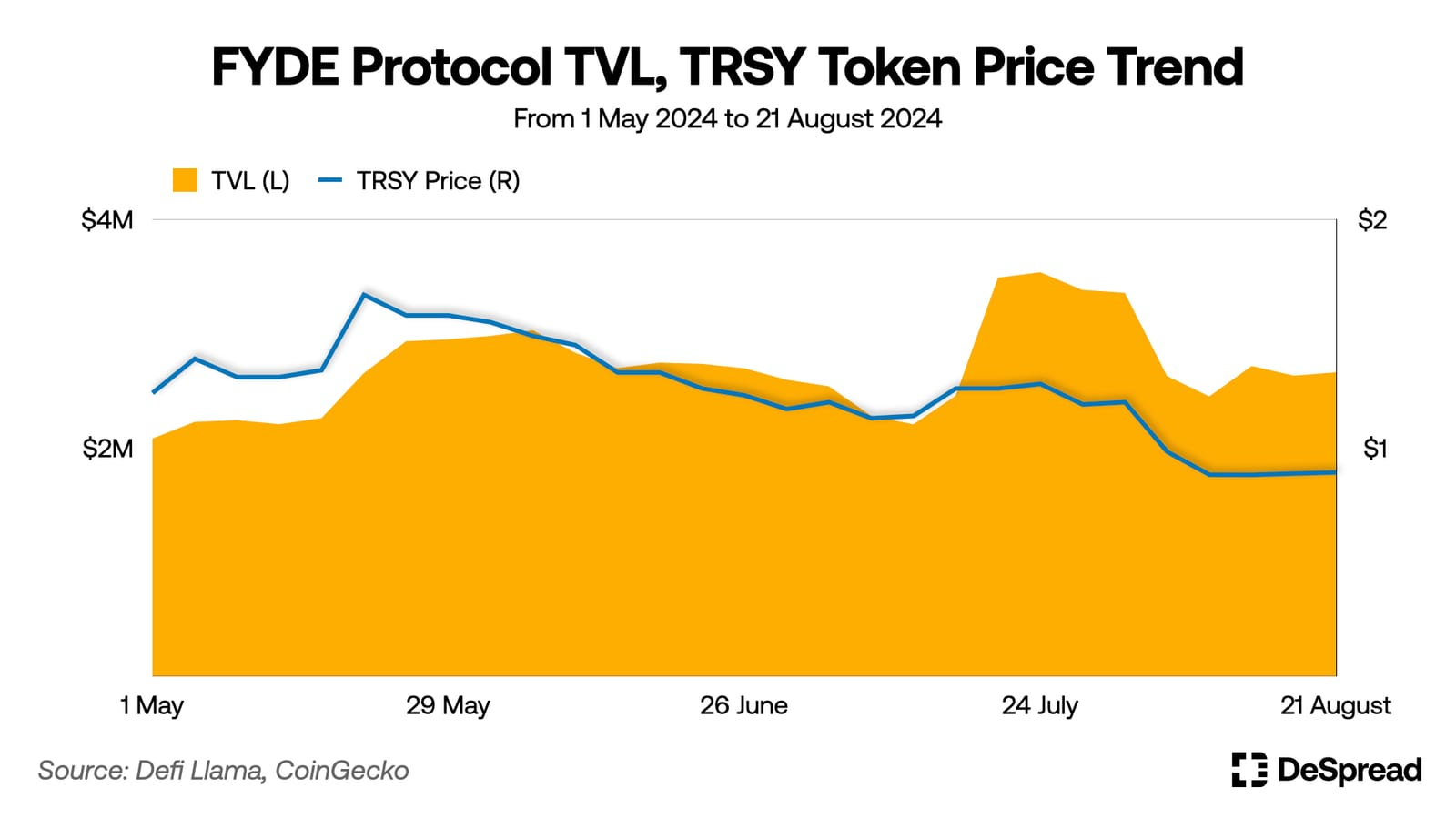
Since launching in January 2024, Fyde Treasury’s TVL has steadily increased, stabilizing around $2 million. However, due to persistent market weakness since late May, the $TRSY token has delivered a -35% return over the past three months.
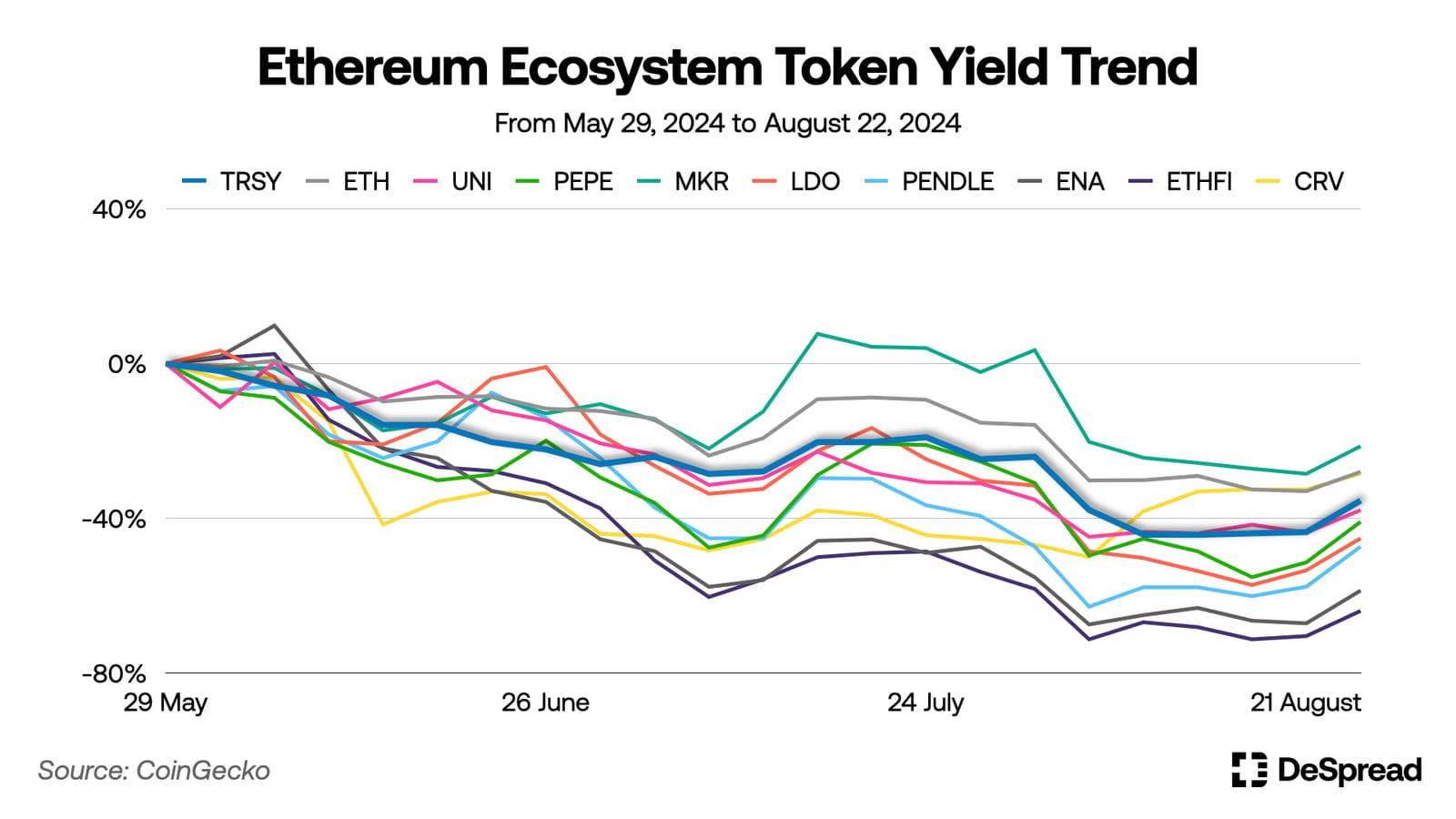
Nevertheless, compared to other major tokens in the Ethereum ecosystem, $TRSY has shown relatively stable price fluctuations and smaller drawdowns.
Although Fyde Treasury has been live for less than a year, its AI models have continuously learned and evolved using market data. As AI learning accumulates and improves, future performance may significantly improve—making Fyde Treasury’s trajectory worth watching.
2.2. Mozaic Finance: AI Yield Optimizer
Mozaic Finance is a yield optimization protocol using AI to optimize yield farming strategies across specific DeFi protocols. It offers users various asset management strategies packaged as vaults, utilizing two AI components for strategy optimization:
-
Conon: Real-time analysis of on-chain data to forecast market conditions and APY changes in yield farming strategies
-
Archimedes: Uses Conon’s predictions to compute optimal investment strategies and execute fund allocation
In Mozaic Finance, the AI agent Conon acts as an “analyst,” while Archimedes functions as the “strategist,” jointly managing user-deposited assets.
2.2.1. Vault Types
-
Hercules: A stablecoin-based yield farming vault where depositors receive MOZ-HER-LP tokens as liquidity tokens.
-
User assets are deployed to generate yield via the bridge protocol Stargate. AI continuously bridges and rebalances vault assets to liquidity pools with higher yields across different networks. Stargate’s design results in varying APYs for identical assets depending on network-specific liquidity imbalances.
-
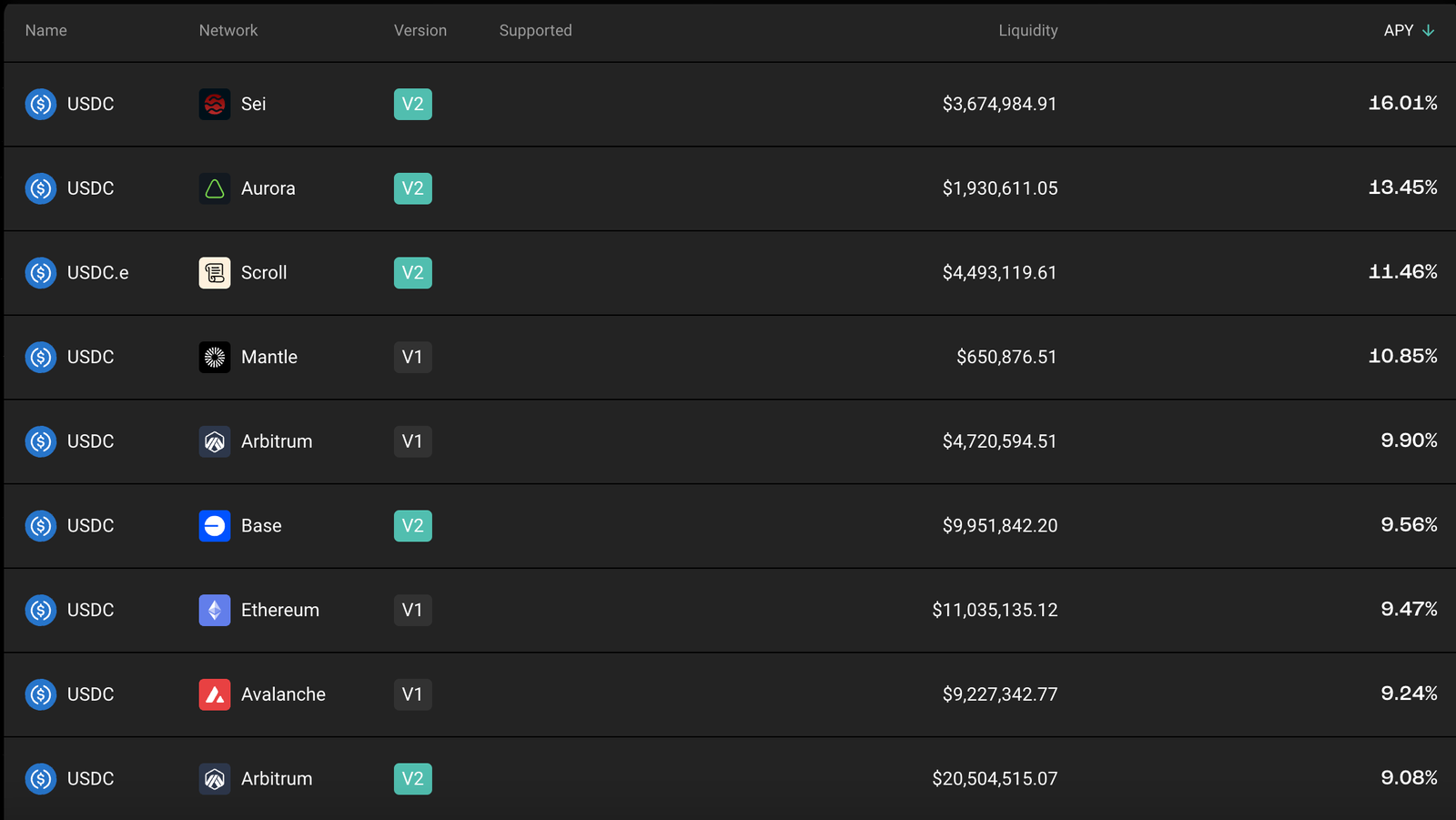
Stargate Farm Dashboard, Source:Stargate
Theseus: A yield-generating vault using volatile assets, where depositors receive MOZ-THE-LP tokens as liquidity tokens.
-
User funds are deposited into GMX’s GM Pools—decentralized perpetual futures exchange pools that provide liquidity to traders and earn incentives. Deployment considers volatility and interest rates of underlying assets in each GM Pool. Depending on market conditions, stablecoins may be allocated and deposited into Stargate to earn additional yield.
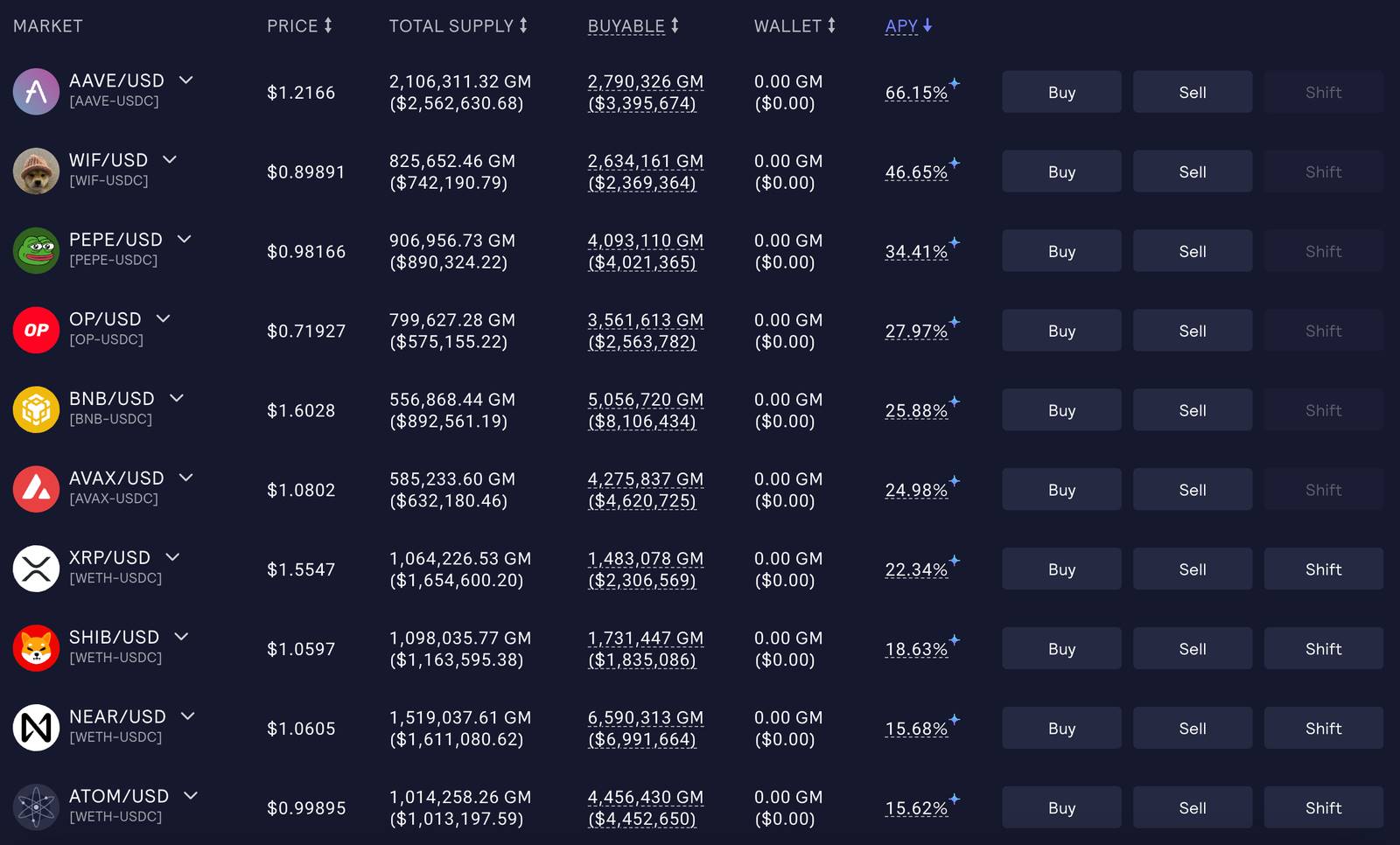 GMX GM Pool Dashboard, Source:GMX
GMX GM Pool Dashboard, Source:GMX
-
Perseus: A vault actively leveraging PoL (Proof-of-Liquidity) consensus mechanism by providing liquidity to ecosystem protocols ahead of the mainnet launch of Berachain. The Mozaic Finance team is developing and preparing to launch strategies using the Berachain testnet, with details to be announced later.
For more information about Berachain and the PoL consensus mechanism, refer to the article Berachain — The Bear Catching Two Rabbits: Liquidity and Security.
Unlike Fyde Treasury, which constructs a basketed token fund, Mozaic Finance focuses on optimizing liquidity provisioning strategies and processes through AI when depositing user assets into DeFi protocols, while managing associated risks.
As of January 2024, both Hercules and Theseus vaults were performing well, with projected APYs of approximately 11% and 50%, respectively. However, following a security breach resulting in stolen funds, both vaults have been suspended.

Expected annual returns for Hercules and Theseus Vaults as of January 2024, Source:@Mozaic_Fi
2.2.2. Fund Theft Incident and Mozaic 2.0
On March 15, 2024, Mozaic Finance suffered a fund theft incident. At the time, the team was transitioning to a new security solution developed by Hypernative to enhance on-chain risk and security. Before completing the upgrade, an internal developer discovered they could steal vault funds by accessing a core team member’s private key. They compromised the team member’s computer, obtained the private key, and used it to withdraw approximately $2 million in vault assets, later cashing out through centralized exchanges.
Following the incident, the Mozaic Finance team paused operations of the Hercules and Theseus vaults, and the value of governance and protocol fee collection token $MOZ dropped about 80%. Afterward, the team promptly disclosed incident details transparently, partnered with security firms to trace stolen assets, and requested exchanges holding the stolen funds to freeze and return them, striving to restore normal protocol operations.
Luckily, recovery of all stolen funds is currently underway. While awaiting fund returns from centralized exchanges, the team is preparing to launch Mozaic 2.0, featuring the following improvements:
-
Enhanced Security: Code audits and security enhancements conducted by specialized firms including Trust Security, Testmachine, and Hypernative.
-
AI Model Improvements: Complete overhaul of the existing Archimedes model, incorporating expert knowledge to anticipate and learn from potential black swan events. Implementation of anomaly detection flags for manual review and model refinement.
-
Improved User Experience: Upgraded DApp UI/UX and enhanced cross-chain accessibility via account abstraction and integrated bridging services.
Despite facing a major fund theft crisis, Mozaic Finance is actively preparing for the launch of Mozaic 2.0, committed to delivering safer and more efficient asset management services to users.
3. Challenges: Decentralization and Scalability Dilemma of AI
Through case studies of Fyde Treasury and Mozaic Finance, we’ve seen how intelligent DeFi protocols incorporate AI as a core component. Advantages offered by AI in DeFi include:
-
Enabling novel DeFi protocol models through autonomous operation
-
Improving capital efficiency by analyzing and optimizing capital deployment
-
Real-time detection and response to anomalous transactions and risks
Currently, most integrations between blockchain and AI focus on building blockchain infrastructure to overcome AI limitations. However, given the aforementioned advantages, more efforts are expected to embed AI directly into DeFi protocols. Naturally, several challenges must be addressed in merging these two fields.
AI requires environments capable of rapidly processing massive volumes of data, but current blockchain infrastructure cannot match such throughput. For instance, the ChatGPT-3 model reportedly needs to process trillions of data points per second to answer queries—roughly ten million times faster than Solana’s maximum TPS of 65,000.
Even if blockchain infrastructure advances enough to support AI computation, public blockchains’ transparency could expose AI model training data and decision weights to the public. This would render AI-generated trades predictable and vulnerable to various external attacks.
Therefore, DeFi protocols like Fyde Treasury and Mozaic Finance that wish to leverage AI currently run AI models on centralized servers and interact with blockchains based on their outputs.
However, this approach forces users to trust the honesty of the team managing the AI when depositing assets into the protocol—undermining DeFi’s core principle of eliminating reliance on trusted third parties through smart contracts to enable trustless transactions.
In applying AI to blockchains, the issues of decentralization and scalability represent critical challenges that must be resolved for effective AI-powered DeFi. In this context, zkML (zero-knowledge machine learning) has emerged as a promising solution.
3.1. zkML (Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning)
zkML combines zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) with machine learning (ML). Zero-knowledge proofs are cryptographic techniques that verify data authenticity without revealing the data itself, enabling privacy preservation and integrity verification. zkML applies these properties to machine learning, allowing verification of model outputs without disclosing inputs, parameters, or internal mechanisms of the AI model.
Furthermore, by designing DeFi protocol smart contracts to validate zero-knowledge proofs, on-chain transactions are only executed when the AI model operates honestly and free from interference—enabling secure integration of AI into DeFi protocols.
For example, Mozaic Finance, mentioned earlier, plans to introduce zero-knowledge proof technology into its protocol. Their documentation states that this technology will enhance real-time validation of Archimedes’ honest decision-making and vault management.
However, zero-knowledge proof technology remains nascent, requiring extensive research and development before practical implementation. Especially for complex AI models, generating ZKPs—while more efficient than running AI directly on-chain—still demands computational and storage resources beyond current blockchain capabilities. Thus, further technological advancements and optimizations in both ZKP and blockchain infrastructure are necessary for zkML to become practically viable.
4. Agent-Based Economy and Identity Verification
I anticipate that as blockchain and AI technologies continue advancing, they will gradually overcome the technical hurdles required for deeper integration. Based on this progression, I believe that in the near future, most DeFi protocols will incorporate AI into their operational frameworks.
Moreover, with the emergence and maturation of AI agent deployment and trading platforms like SingularityNET and Autonolas, AI integration won’t be limited to protocol-level applications but will empower individual users to easily build and use personalized AI agents. In other words, every participant in the blockchain ecosystem could construct and operate customized intelligent DeFi protocols tailored to their needs.
For instance, Autonolas’ AI agents on Gnosis’ prediction market platform Omen have steadily increased in number and activity by analyzing on- and off-chain data to place bets. Within one year starting July 2023, these agents generated over one million transactions.
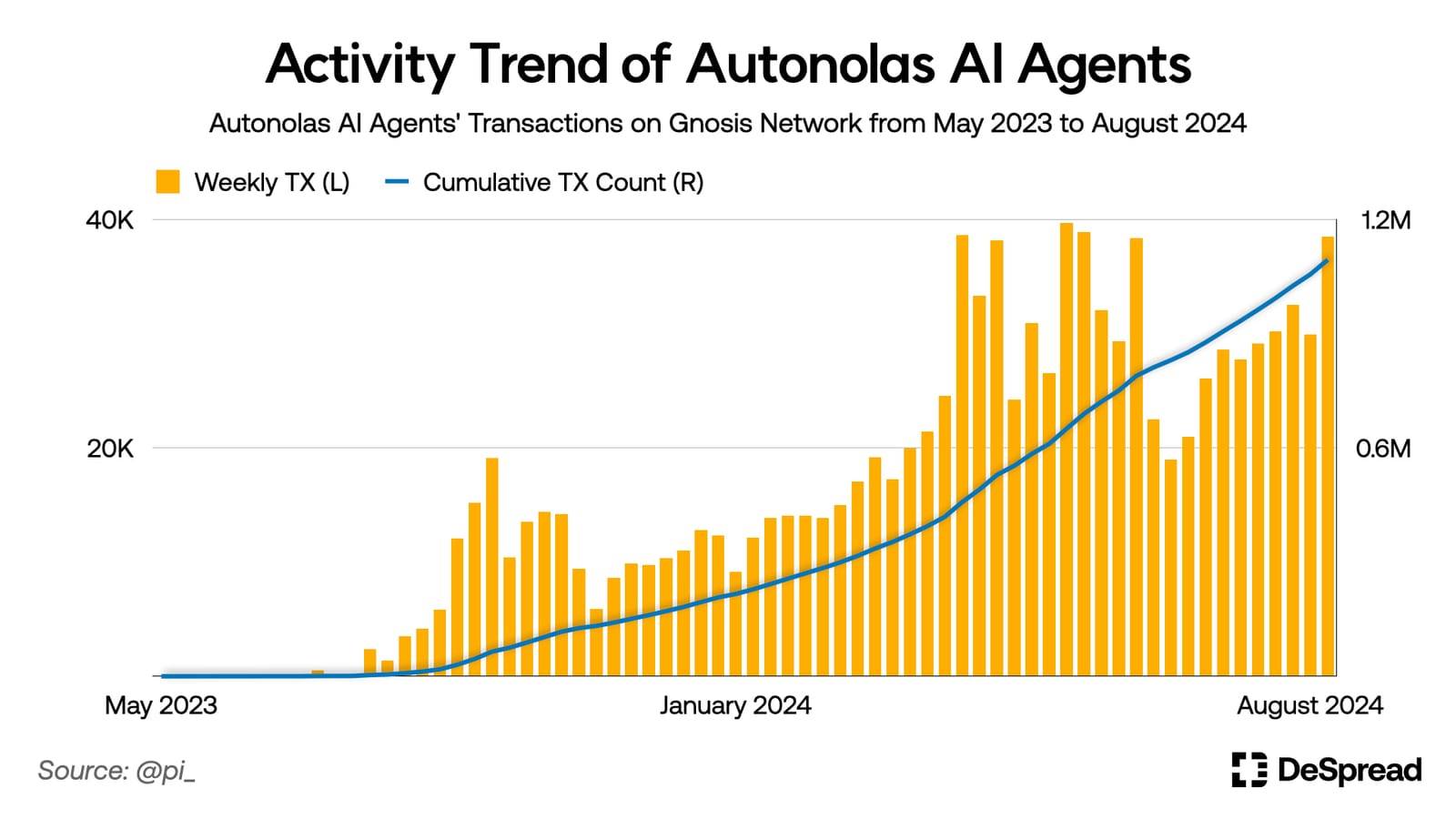
In the future, the number of personalized AI agents capable of efficiently managing capital around the clock is expected to grow, actively participating in the blockchain ecosystem. This will promote better utilization of idle liquidity and more efficient capital flows, significantly boosting overall ecosystem liquidity. Eventually, transactions among AI agents may dominate ecosystem activity, forming a new economic system built on autonomous agents.
Additionally, as personalized AI agent models become increasingly sophisticated, their activities may expand into areas traditionally designed for “humans,” such as personalized on-chain asset management, identifying and participating in airdrops, and engaging in governance voting.
As AI agents become increasingly adept at simulating human behavior, distinguishing between “real” human users and AI agents will become progressively harder. Consequently, identity verification—mechanisms proving user identity and uniqueness—are expected to gain growing importance, especially in protocols that value human agency and fairness.
4.1. Identity Verification
Identity verification links unique human characteristics to digital accounts to confirm identity and uniqueness online. Current approaches under discussion and development fall into two main categories:
-
Physical Authentication-Based Methods: Use hardware devices to capture unique biometric data such as facial recognition, fingerprints, or iris scans.
-
Behavioral Analysis-Based Methods: Analyze social graph structures, reputation scores, and patterns of online activity to determine account authenticity and uniqueness. These rely on a user’s network footprint and interactions with other accounts.
Behavioral analysis-based identity verification offers better privacy protection and does not require special hardware. However, ensuring accuracy and reliability demands extensive network data. As AI agents grow more sophisticated, detection efficacy may decline, suggesting physical authentication methods will likely see broader adoption in the future.
A representative protocol using physical authentication for identity verification is Worldcoin. Co-founded by OpenAI founder Sam Altman—the creator of ChatGPT—Worldcoin aims to assign a unique digital ID to every person globally through identity verification and distribute $WLD tokens to those with verified IDs. This initiative explores the feasibility of universal basic income in anticipation of job displacement driven by AI advancements.
4.1.1. Worldcoin
Worldcoin is a physical authentication-based identity project that uses a specialized hardware device called Orb to scan human irises. After successful iris scanning, the Worldcoin network issues a World ID and generates a private key on the user’s personal device to access that ID.

Worldcoin Orb, Source:Worldcoin Whitepaper
Currently, the Worldcoin network stores only hash values of scanned iris data, preventing reconstruction or identification of actual irises. When verifying a World ID, the user’s device generates a zero-knowledge proof sent to the network, preserving privacy of on-chain activities. However, because iris verification occurs only at World ID issuance, challenges remain—such as transferring World IDs via private key device sales or AI agents gaining access to private keys. To address these, Worldcoin is exploring implementing biometric verification during World ID usage and developing AI-based behavioral detection algorithms.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we explored emerging service protocols enabled by AI integration into the blockchain ecosystem, examined existing challenges, and discussed the future of agent-driven blockchain ecosystems.
Going forward, AI and blockchain technologies will continue evolving and converging, compensating for each other’s weaknesses. This convergence is expected to provide individuals with easier access to and utilization of both AI and blockchain technologies.
Especially in a future on-chain economic ecosystem centered around AI agents, people will be able to effortlessly use and offer financial services without deep financial expertise. This will dramatically boost on-chain liquidity and expand financial inclusivity.
Moreover, AI and blockchain not only influence each other but also hold the potential to become foundational infrastructures across industries. Thus, the development of these technologies will profoundly impact human society as a whole, extending far beyond individual sectors.
However, regulatory developments—including data privacy, AI accountability, and classification of tokens as securities—will significantly shape the future direction and structure of these industries. Therefore, we must closely monitor upcoming regulations governing AI and blockchain.
We ultimately hope that the advancement of these technologies creates better environments for humanity and helps solve pressing societal challenges.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














