Interpreting the Talus Whitepaper: A Decentralized AI Agent Hub
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Interpreting the Talus Whitepaper: A Decentralized AI Agent Hub
How Talus chooses the right timing and catalysts to launch its network and incentivize users may become the key to the success or failure of its上市 strategy.
By TechFlow
Every AI project comes with a hard-to-understand whitepaper.
Although there is growing sentiment in the market that AI tokens are increasingly resembling Memes, quickly grasping the narrative of a trending AI project through its whitepaper remains crucial for assessing whether its token holds any real value.
In February this year, the new AI project Talus Network completed its first round of $3 million in funding, led by Polychain Capital, with participation from dao5, Hash3, TRGC, WAGMI Ventures, and Inception Capital.

Today, Talus has also released its litepaper, providing further clarification on its business scope and token economics.
Below is a summary of the key points from the litepaper to help you quickly understand Talus Network.
A Layer 1 for AI Agents
Talus is a platform designed to integrate AI with blockchain technology. By offering a high-throughput L1 blockchain powered by the Move programming language—and enhanced with native AI stacks—it enables intelligent agents to live, interact, and transact within the Web3 ecosystem.
You can think of Talus as a decentralized hub for intelligent AI agents, addressing critical issues such as data privacy, security, and accessibility, while fostering transparent and efficient interactions within the AI ecosystem.
AI narratives are undoubtedly hot right now—but does it make logical sense to build an L1 specifically tailored for AI agents?
Talus answers with:
On openness: The open and composable nature of blockchain applications makes it easier to view, track, and trust the behavior of AI agents; users can more easily find the most suitable AI agent based on verifiable performance history.
On autonomy: Blockchain infrastructure allows smart agents to interact autonomously, enabling them to execute outcome-driven decisions.
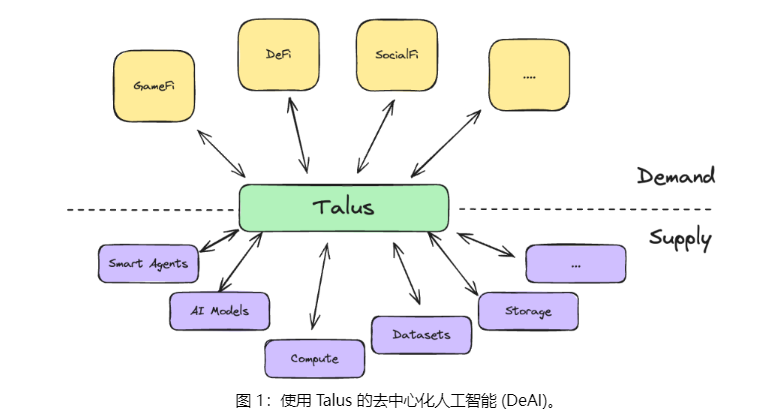
Specifically, Talus enables the native design and deployment of decentralized on-chain intelligent agents that seamlessly, trustlessly, and interoperably leverage both on-chain and off-chain resources and services.
It establishes a protocol for representing, utilizing, and trading these agents, resources, and services in a permissionless and verifiable manner.
Combination of Existing Components and New Features
So, how will Talus achieve this?
The answer lies in combining existing technologies with new functionalities. These components work together to deliver a decentralized, efficient, and secure platform for intelligent agents. The key components—from bottom to top—can be summarized as follows:
1. Protochain Node:
-
At the core of Talus is a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain node built on Cosmos SDK and CometBFT, called the Protochain Node. This architecture offers flexibility, robustness, and high performance.
-
This technical foundation ensures the security and scalability of the Talus blockchain, providing a solid base for running intelligent agents.
2. Sui Move and MoveVM:
-
Talus adopts Sui Move as its smart contract language. The Move language is known for its high performance, security, and strong programming semantics.
-
By using Move, Talus enhances the security of on-chain logic and simplifies the creation, transfer, and management of digital assets, enabling more efficient execution of smart contracts.
3. IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol):
-
By integrating IBC, Talus achieves seamless interoperability between different blockchains, allowing intelligent agents to interact across multiple chains and utilize data or assets from various ecosystems.
-
IBC provides atomicity and scalability for cross-chain transactions, ensuring reliability and consistency of operations.
4. Mirror Objects:
-
Talus introduces the concept of Mirror Objects to represent and verify off-chain resources—such as models, data, and compute objects—on-chain.
-
Mirror Objects bridge the gap between the high computational demands of AI processes and the blockchain environment, ensuring uniqueness and tradability of resources.
5. AI Stack:
-
Talus provides an SDK and integration components to support the development of intelligent agents and their interaction with off-chain resources.
-
The AI stack also includes integration with Oracles, ensuring that intelligent agents can access real-world data for decision-making and responsiveness.
6. Onchain Smart Agents:
-
At the heart of Talus is an economy of intelligent agents capable of autonomous operation—making decisions, executing transactions, and interacting with both on-chain and off-chain resources.
-
These smart agents possess autonomy, social capability, reactivity, and proactiveness. Autonomy allows them to operate without human intervention; social capability enables interaction with other agents and humans; reactivity allows them to perceive environmental changes and respond promptly; and proactiveness empowers them to take actions based on goals, predictions, or anticipated future states.
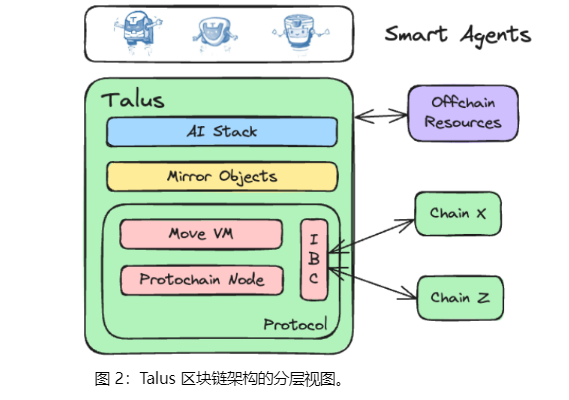
The diagram below illustrates the architectural blueprint of Talus' intelligent agents, showing how each component works together.
SDK: Acts as a bridge between intelligent agents and other components (such as resources, oracles, UIs, and smart contracts). It provides essential libraries and tools to assist developers in building and integrating intelligent agents. The SDK streamlines development by offering a unified interface, enabling agents to efficiently leverage platform resources and services.
Resources: Include AI models, GPUs, and other computing resources. These interact with intelligent agents via the SDK, providing the necessary computational power and data support. Pre-trained models can be used by agents for inference and decision-making.
Oracles: Supply external data to intelligent agents, enabling them to make decisions based on up-to-date real-world information.
UI Components: Allow users to interact with intelligent agents. Through user-friendly interfaces, users can configure, manage, and monitor the operational status of agents.
Through this architecture, Talus achieves agent autonomy and decentralization, ensures efficient resource utilization, and maintains system transparency—accelerating the convergence of AI and blockchain technologies.
Tokenomics and Applications
At the center of the Talus ecosystem is the TAI token, which serves multiple functions on the platform. Below are the key roles of the TAI token:
-
Medium of Exchange: All usage of intelligent agents, resource purchases, and transactions are conducted in TAI tokens. This ensures all economic activity within the ecosystem revolves around TAI, increasing token circulation and demand.
-
Resource Purchases: Resource providers earn TAI tokens by offering computing power, data, or models. Conversely, developers and users spend TAI tokens to access these resources, driving ecosystem growth.
-
Network Security: TAI token holders can participate in the network’s Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism by staking tokens to secure the network and maintain consensus, earning rewards in return.
-
Governance: TAI holders can participate in platform governance, proposing and voting on improvements and future directions, ensuring democratic and transparent community oversight.
However, the litepaper does not yet disclose the full tokenomic model for TAI. It appears the details are still under development and will be supplemented in future updates.
Regarding application scenarios for AI intelligent agents in Web3, Talus outlines the following use cases:
-
User Experience Enhancement: Smart wallets and intelligent analytics tools that monitor and analyze transaction and asset status in real time, delivering personalized blockchain browsing and project management experiences.
-
DeFi: Optimizing liquidity management, automating on-chain portfolio tracking and management, and enhancing DeFi efficiency through smart swap aggregation and path optimization.
-
DAOs: Supporting automated treasury and asset management, along with AI-powered governance and decision-making assistance.
-
IoT: Managing IoT device ecosystems, scheduling intelligent maintenance, ensuring device identity and security, and optimizing logistics and supply chain operations.
-
Gaming / SocialFi: Personalized on-chain storytelling, virtual economy management, intelligent NPCs, and agent-to-agent social networks, bringing new levels of experience and interactivity to gaming and social applications.
-
AI and Data Ecosystems: Facilitating collaboration between model developers and data providers, promoting the development and monetization of specialized AI models, enabling efficient use and monetization of data and computing resources, and supporting crowdfunding models for research and development.
Based on the current content of the litepaper, Talus has only clearly defined its business scope and use cases. More technical details, economic models, and practical results remain largely absent—consistent with the release of a "Litepaper" version.
Nonetheless, competition in the AI space is intensifying, and high-performing AI agent projects continue to emerge. For Talus, choosing the right timing and catalysts to launch its network and incentivize user adoption may prove pivotal to the success of its go-to-market strategy.
After all, in today’s market—where VC-backed investments often feature high FDV and low circulating supply—the ability to attract more users and win over the community with solid products and strong technology will be the key to capturing real value for ambitious AI projects.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














