Will Gelato See a New Surge by Entering the RaaS Arena?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Will Gelato See a New Surge by Entering the RaaS Arena?
A Deep Dive into Gelato: Market Positioning, Competitive Advantages, and Token Economics
Authors: Charlotte, Kevin, Metrics Ventures
TL;DR
-
Founded in 2019, Gelato initially helped developers build automated, gasless smart contracts with off-chain computation capabilities, establishing itself as a leader in this space. In September 2023, Gelato completed its transformation into an RaaS (Rollup-as-a-Service) platform, opening up new market opportunities and growth potential through this narrative shift.
-
Layer2 solutions continue to grow rapidly. As more Dapps turn toward building appchains for scalability, customization, and reduced value leakage, demand for RaaS will rise. By lowering development costs and offering professional consulting services, RaaS platforms are poised to become middleware distributors in the Web3 world, enabling developers to quickly set up infrastructure.
-
While not first-movers in the RaaS space, Gelato has over four years of deep expertise in Web3 infrastructure development. Their accumulated technical achievements and resources translate directly into competitive advantages in RaaS: (1) native integration of Web3 middleware services, (2) mature account abstraction solutions, and (3) extensive third-party Web3 middleware distribution channels.
-
The RaaS sector is still relatively early-stage; it's difficult to identify clear leaders based on current technical features or ecosystem data alone. Ongoing monitoring of project competitiveness within the sector is essential.
-
From both narrative and timing perspectives, Gelato represents a compelling investment opportunity today: The upcoming Cancun upgrade is one of the most anticipated events in the market, while ALT’s listing has begun drawing mainstream attention to the RaaS sector. The value of RaaS is gradually being discovered.
1 Is RaaS a promising sector to invest in?
Before diving into Gelato specifically, we should first understand the importance and future prospects of the RaaS business model.
First, scaling remains a critical need—and key to achieving Web3 mass adoption. While existing Layer2s have partially addressed scalability, Dapps still compete for blockspace. For transaction-heavy use cases like gaming and socialfi, rising fees and long wait times continue to degrade user experience. During bull markets, surging transaction volumes further intensify demand for scaling. Indeed, steadily growing TVL reflects strong market demand, with L2s maintaining rapid growth since 2023.
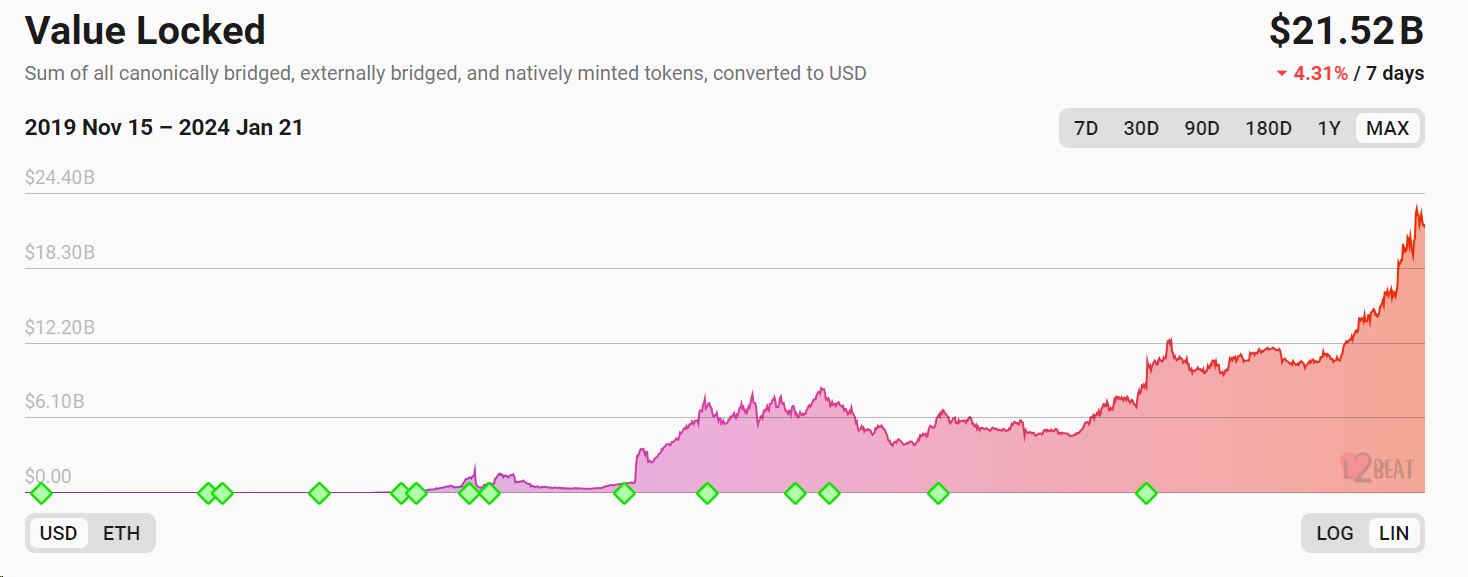
Second, demand for blockchain customization from Dapps continues to increase. As blockchain applications evolve, even successful Dapps on existing chains face limitations across multiple dimensions—including data availability flexibility, MEV revenue capture, block production time, scalability, user acquisition, token value accrual, economic design, and ecosystem expansion—driving them toward building their own customizable appchains, especially when composability requirements are low.
Third, transitioning from Dapp to appchain allows ecosystems to retain more revenue—reducing gas fee leakage that can instead be captured by the protocol or returned to users—while attracting more validators to stake tokens and increasing overall liquidity. This enhances utility for native tokens and significantly accelerates the economic flywheel.
Among various available chain architectures, Rollups stand out as one of the most important options. As Ethereum’s officially endorsed scaling solution, Rollups enjoy inherent legitimacy and benefit from Ethereum’s thriving ecosystem. General-purpose rollups have already been validated by the market, with mature technology and reusable development frameworks.
Going forward, much of the demand for new L2s may come from Dapps migrating to appchains. Appchains prioritize two things: customization to meet specific Dapp needs, and ecosystem development to attract and migrate users. Therefore, if a project's focus isn't on public chain innovation but rather on its core application, it shouldn’t spend significant time rebuilding from scratch. Instead, they should outsource development and maintenance, focusing resources on core product development. At the same time, these projects require expert technical teams to provide consultation across various Rollup frameworks, DA layers, and other architectural decisions.
The core business model of RaaS platforms is to become the AWS or Google Cloud of Web3—acting as distributors of blockchain middleware and capturing profits in the process. Thus, the scale and quality of the middleware ecosystem they can aggregate will be their primary competitive advantage. Additionally, as Rollup operators, RaaS platforms also capture transaction fees and MEV revenue.
According to Messari’s classification, the RaaS ecosystem currently consists of three main types of projects: SDKs, Shared Sequencer Sets, and No-code Deployment platforms. Gelato belongs to the No-code Deployment category, offering one-stop services by integrating SDKs and infrastructure providers. Other projects in this segment include Lumoz, Altlayer, Caldera, and Conduit.
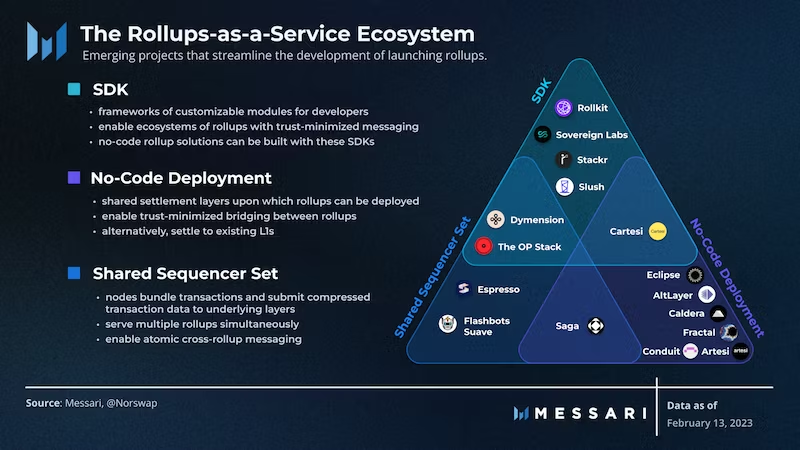
(Source: Messari)
2 From Smart Contracts to Layer2: Gelato’s Transition to a RaaS Platform
Founded in 2019, Gelato initially focused on helping developers create automated, gasless smart contracts capable of off-chain computation, becoming a leader in this domain. In September 2023, Gelato completed its transition to a RaaS platform, leveraging its years of technical expertise and infrastructure ecosystem advantages to establish strong competitiveness in this emerging field.
Gelato is still in the early stages of its RaaS business. Initially built on Polygon’s framework, Gelato announced support for OP Stack in December and plans to adopt additional frameworks in the future. On the data availability (DA) layer, it currently supports Ethereum, Celestia DA, Avail, and EigenLayer DA.
Two projects have already chosen Gelato as their RaaS provider: Astar and Lisk. Astar is the first L2 on Gelato using Polygon CDK. As of December 26, 2023, Astar zkEVM had deployed over 3,000 smart contracts, created more than 15,000 wallets, and processed over 300 million transactions. Lisk will be the first L2 on Gelato using the OP Stack framework, focusing on RWA and DePIN ecosystem development.

To lower development barriers, Gelato launched its Deployment Platform in December 2023, allowing developers to select Rollup frameworks, data availability layers, and integrated middleware, then deploy a Rollup with just a few clicks.

Gelato wasn’t the first entrant in the RaaS space—so where does its current competitive edge lie?
With four years of深耕 in smart contract development, Gelato now directly leverages this experience to expand into RaaS. Specifically, Gelato’s strengths manifest in three areas: (1) native integration of Web3 middleware services that greatly enhance L2 smart contract development experience; (2) mature account abstraction solutions; and (3) abundant third-party Web3 middleware distribution resources, providing developers with comprehensive dev toolkits.
1 Native Service Integration: Automation, Gasless Transactions, Off-Chain Computation & VRF
Originally serving as a decentralized backend for Web3, Gelato aims to improve the developer and user experience of smart contracts. Its core functionalities include four components: contract automation, gasless transactions via Relay, off-chain data sensing/computation, and VRF.
Contract Automation:
One often overlooked fact is that smart contract functions cannot trigger automatically—they must be executed via an on-chain transaction initiated by an EOA. Features like DEX limit orders, auto-compounding, and loan liquidations all require automation. Automate is Gelato’s flagship feature, eliminating the need for developers to manually operate or run bots themselves. Gelato acts as a marketplace connecting two parties: developers seeking automation, and infrastructure operators (bots/keepers) who scan for pending tasks and execute them in exchange for service fees.
Gelato’s network architecture includes three roles: Event Listener, Checker, and Executor. The Listener monitors on-chain events and submits user logic to the Checker once trigger conditions are met. The Checker evaluates whether the automation task can be executed at that moment. Once confirmed, it forwards the transaction to the Executor—a network of infrastructure operators (also known as bots or keepers)—who finalize the on-chain execution.
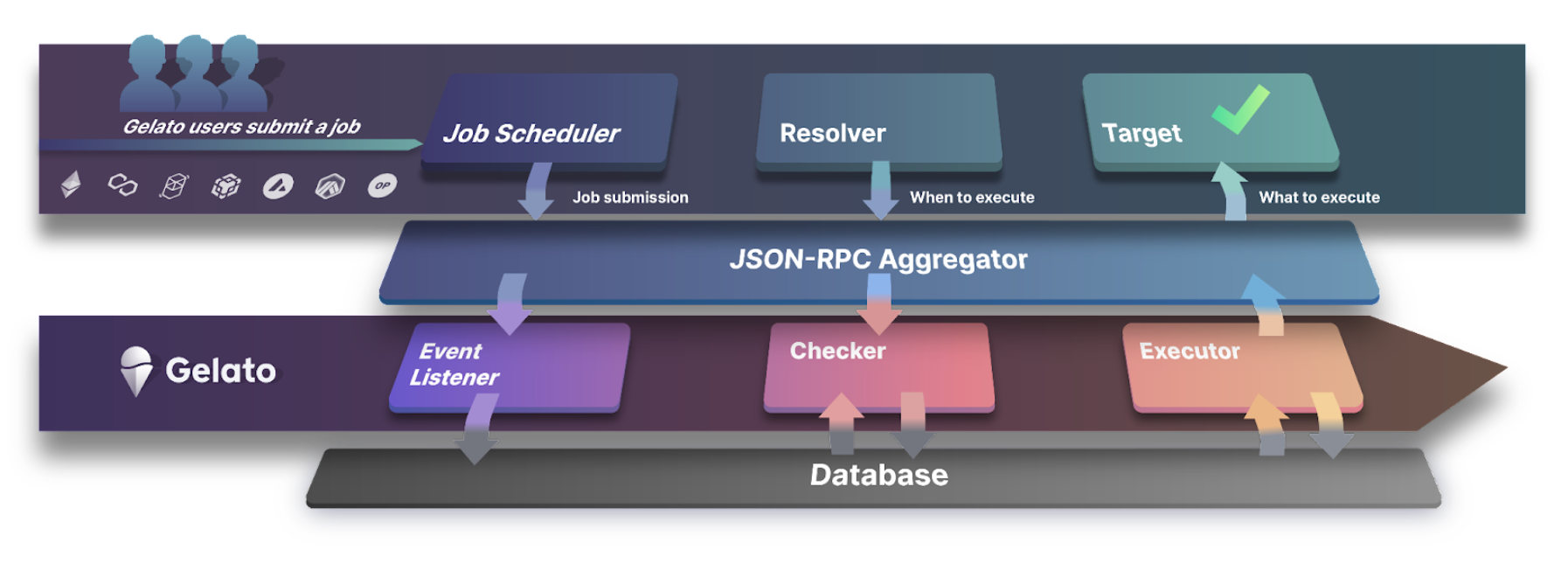
Relayer & Gasless Transactions:
In standard on-chain transactions, users must first deposit native tokens into their EOA wallet to pay gas fees before interacting with dApps—an obstacle to smooth UX. Gelato Relayer solves this: users sign messages off-chain to interact with Web3 apps; these messages are sent via API call to Gelato Relay, which verifies the signature on-chain and uses its controlled EOA to submit the transaction and cover gas fees. This enables flexible payment models such as using a single balance to pay for transactions across all EVM chains or having developers sponsor user gas costs.
Off-Chain Data Sensing & Computation:
Gelato upgraded Automate into Web3 Functions, overcoming the limitation of smart contracts being unable to access off-chain data. Developers can now write TypeScript functions stored on IPFS and executed by Gelato, enabling seamless integration with external data sources, enhanced computational capacity (avoiding high gas costs from complex on-chain computations), and customizable execution logic.
VRF (Verifiable Random Function):
VRF is widely used in gaming, NFT minting, and random validator selection. The key requirement is that the operator generates a random number along with cryptographic proof verifying its randomness and integrity—ensuring the output is unbiased and unpredictable, while others can verify no manipulation occurred.
Gelato’s VRF relies on Drand, a decentralized network of nodes. Before generating randomness, all nodes agree on a threshold parameter. Each node creates a partial signature and broadcasts it. Once enough signatures are collected (meeting the threshold), the final node generates a BLS signature verifiable by the entire network. The random number is derived as the hash of this signature.
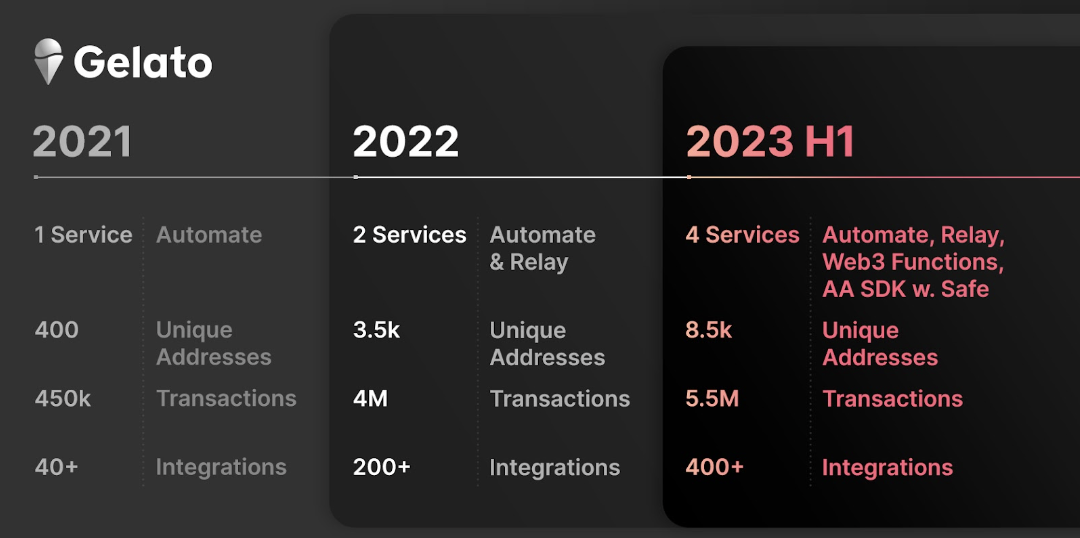
Gelato holds strong competitiveness in its native services. It supports up to 15 blockchain networks. According to H1 2023 reports, over 400 applications have integrated Gelato, executing more than 5.5 million transactions—including major projects like MakerDAO, Gnosis Pay, and PancakeSwap. Currently, Chainlink is the only direct competitor in this space.
2 Mature Account Abstraction Solution Integration
Building on its Relay service, Gelato developed the Relay Kit in collaboration with Safe to create an account abstraction SDK. Safe’s account abstraction comprises multiple kits—some developed in-house, others sourced from third parties. Gelato’s Relay Kit enables Payment Abstraction, allowing users to pay Ethereum transaction fees directly using native tokens or ERC-20 tokens—not limited to ETH.
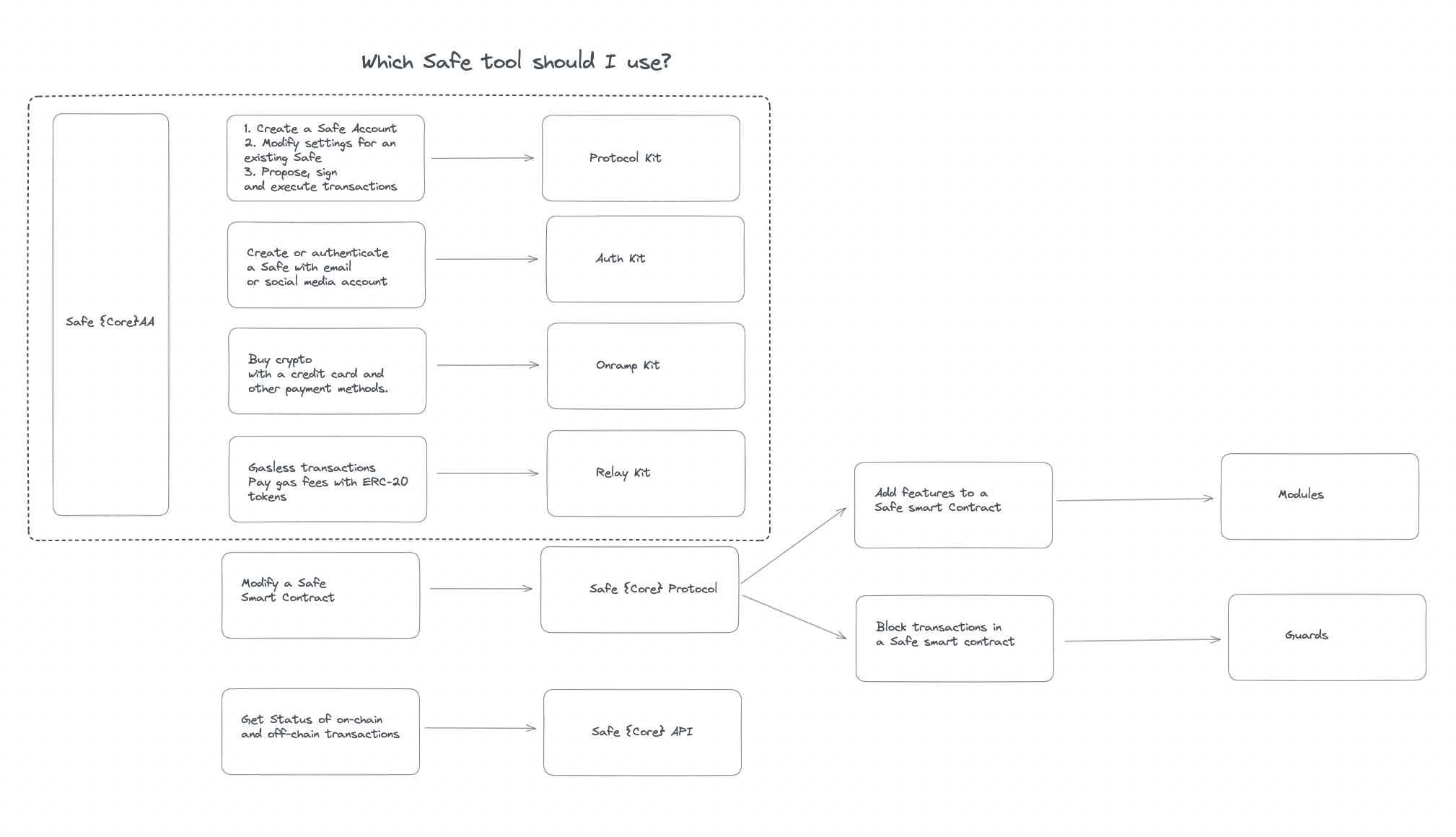
Account abstraction involves two key steps: Signature Abstraction and Payment Abstraction. The former allows contract accounts to use various signing schemes (e.g., single private key, multisig aggregation), while the latter enables flexible fee payment options including gas sponsorship. While ZK-Rollups like zkSync and StarkNet have implemented native account abstraction, how does Gelato’s solution compare?
In short, most ZK-Rollups have effectively implemented Signature Abstraction, but Payment Abstraction remains underdeveloped. Gelato, leveraging its Relay and 1Balance services, has proven capabilities in flexible payments and gasless transactions, offering a mature solution for Payment Abstraction—the most direct way to improve user experience. Moreover, the jointly integrated AA SDK with Safe can be readily adopted, enabling social login and seedless wallet experiences.
3 Rich Web3 Middleware Distribution Resources
As previously noted, middleware distribution capability is one of the most crucial competitive edges for RaaS platforms. Although general-purpose L2s offer SDKs, launching a chain requires additional components like block explorers, indexers, oracles, and bridges. Over its four-year development history, Gelato has built extensive partnerships with infrastructure and middleware providers, enabling plug-and-play toolkits for instant chain deployment. Currently, Gelato RaaS Marketplace offers 27 integrated middleware services. Notably, Gelato’s Web3 Functions business already integrates over 400 applications—these clients represent a vast reservoir of potential distribution partners, significantly accelerating the growth of Gelato’s RaaS ecosystem.
3 Competitive Landscape: The RaaS Sector Is Still Early
Other No-code Deployment players in the RaaS space include Conduit, Altlayer, Caldera, and Lumoz. Basic information about each project is summarized below.
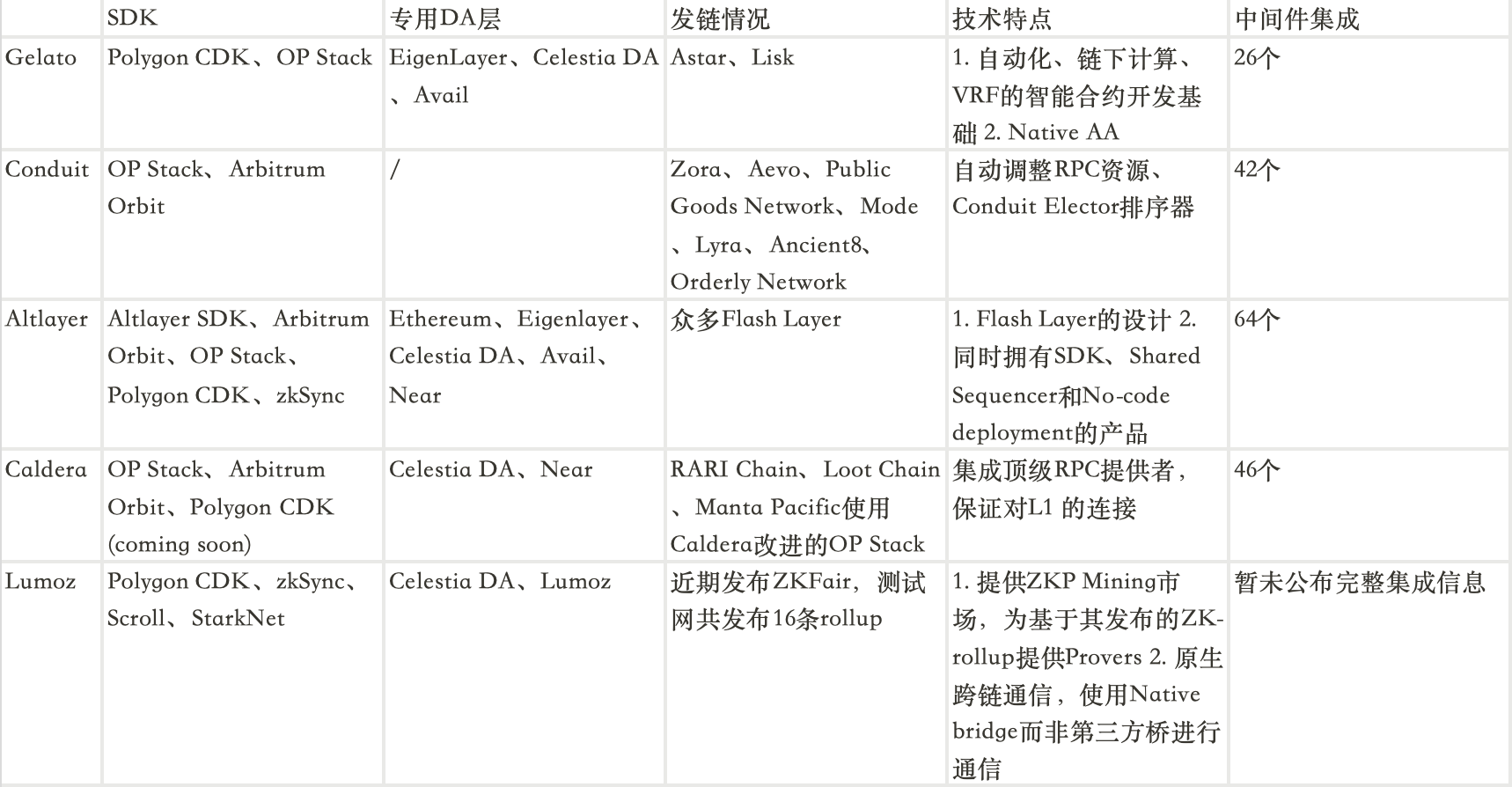
In terms of ecosystem expansion, the number of chains launched via RaaS remains small. Many early RaaS entrants lack impressive metrics, making it difficult to assess competitiveness purely based on chain deployment numbers.
Regarding middleware resources, Gelato RaaS Marketplace doesn’t lead in integration count. However, its ecosystem of over 400 applications serves as a deep bench, and we should closely monitor future growth in integrations to evaluate its evolving RaaS competitiveness.
Overall, the RaaS sector remains in its infancy, with many projects still on testnet. It’s too early to determine clear leaders based on current data. Altlayer recently launched on Binance Launchpad. Currently, only Altlayer and Gelato have issued tokens, making them the only two tradable assets in the RaaS space. In terms of valuation, Altlayer has a market cap of $451,466,031 and FDV of $4,104,236,647, whereas Gelato’s market cap is $167,412,873 and FDV is $287,476,805. Whether measured by market cap or FDV, Gelato offers better value.
4 The Gelato Flywheel: Tokenomics
GEL is Gelato’s native token. Current tokenomics are still centered around the Automate business and haven’t yet been extended to RaaS operations.
Bot operators running Automate must stake GEL to participate in the network. Revenue comes from two sources: (1) transaction fees per execution, and (2) identifying arbitrage opportunities and performing back-running. Malicious behavior results in slashing penalties.
In July 2023, Gelato updated its staking and task allocation mechanism to accelerate the flywheel effect. Under the new system, bots still need to stake GEL (minimum 150k GEL) with a three-month unstaking period. However, task allocation frequency is now proportional to the amount of GEL staked, incentivizing operators to stake more. Additionally, gas costs incurred by bots are reimbursed in real-time from fees paid by dApps or retail users, further reinforcing the staking flywheel.
Future tokenomics should incorporate RaaS business incentives—this remains to be seen in upcoming developments.

5 Conclusion: Gelato Is in the Early Stages of Value Discovery
Gelato’s expansion into RaaS opens up a stronger narrative—shifting from an invisible backend development service to a visible, market-facing RaaS platform, unlocking new growth potential. Technically, Gelato’s native services—automation and account abstraction—directly enhance L2 development, improving experiences for both developers and end-users. Meanwhile, automation and advanced account features introduce more complex on-chain interactions and higher gas costs; executing these on L2s dramatically reduces expenses, creating fertile ground for Gelato’s core offerings. Years of accumulated middleware client relationships can now be rapidly repurposed to empower L2 builders, enabling powerful cross-pollination between its legacy and new businesses.
In terms of token performance, Gelato’s announcement of its RaaS pivot in September last year did not immediately drive price appreciation. Only in the past month has the market begun recognizing this transformation, pushing prices up over 100% from $0.3. This rally has been fueled by speculation around the Cancun upgrade and ALT’s Binance listing, bringing renewed attention to the RaaS sector. Historically lacking tradable assets, the RaaS space has received limited market interest. Now, with Cancun being one of the most watched events and ALT drawing retail attention, the sector’s value is slowly being recognized. With few secondary market options available, speculative capital is likely to concentrate on ALT and GEL. Gelato boasts a long development history, solid fundamentals, and a robust ecosystem. Its current market cap remains relatively undervalued—making now a critical window for positioning. That said, Gelato hasn’t yet secured a dominant position in the RaaS race, so ongoing monitoring of its competitive evolution is crucial.
Key watchpoints going forward include adoption of RaaS services, exchange listings, and potential shifts in tokenomics. Having already established leadership in automation services, securing a leading position in RaaS would strongly validate its future upside potential.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News