Pantera's 2024 Key Focus Areas: AI Trends Continue Unabated, Web3 to Drive Progress in Inference, Data Privacy, and Incentives
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Pantera's 2024 Key Focus Areas: AI Trends Continue Unabated, Web3 to Drive Progress in Inference, Data Privacy, and Incentives
The speed of innovation within the blockchain technology ecosystem generates new markets and verticals in each cycle.
Author: Chia Jeng Yang & Caroline Cahilly, Pantera Capital
Translation: TechFlow
Pantera Capital recently released an in-depth long-form article detailing its outlook on the 2024 crypto market, investment strategies, key focus areas, and trend forecasts.
Due to the article's length, we have divided and translated it according to thematic sections.
This piece is the fourth installment of the full series, authored by Chia Jeng Yang, Managing Director at Pantera, and intern Caroline Cahilly.
It reflects their interest in the convergence of AI and Web3, offering a detailed breakdown of how AI and crypto can intersect. They believe Web3 can play a critical role in enhancing AI systems—particularly in reasoning, data privacy, and incentive design—and that this intersection presents significant investment opportunities.
TechFlow has translated this section. Below is the full text.
The pace of innovation within the blockchain ecosystem generates new markets and verticals with each cycle. Our research expands our thesis, helping us stay ahead while maximizing coverage when identifying and evaluating investment opportunities. In the following sections, we will share the areas we are actively monitoring.
AI x WEB3
AI: Merging Human and Machine Intelligence
The outputs generated by AI models, such as large language models (LLMs), should ideally represent the optimal interaction between human and machine intelligence, data, and incentive systems.
The ability to communicate in natural language is what makes LLMs so exciting—humans and AI can use the same language to describe complex processes. This is a crucial step toward future coordinated systems that integrate humans directly. To improve this collaboration, we still need to develop robust human-AI frameworks, mechanisms, and tools that encourage AI systems to think more effectively, produce more useful answers, and achieve optimal outcomes.
How Web3 Enhances This Interaction
Native digital incentive frameworks from Web3—through crowdsourcing, accountability, and token-based rewards—will shape how humans interact with AI. We aim to identify products that maximize or optimize interactions between computer/AI intelligence and human cognition (e.g., token holders, developers), with particular emphasis on mid- to long-term use cases.
Looking ahead, we will explore three key aspects of human-machine interaction in the age of AI:
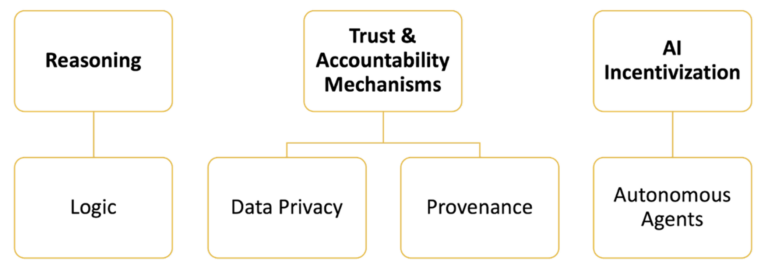
Below are some ways crypto can enhance AI—themes that will be explored throughout this paper:
-
Payments: Traditional financial payments involve rigid, well-defined boundaries. With cryptocurrency, integration requires only a few lines of code. Programmability enables simplified software integration—developers simply embed wallet addresses into their codebases. It also allows flexible, computation-based payments that would otherwise require extensive auditing under existing infrastructure. By bypassing outdated global financial systems, crypto lowers market entry barriers for products with international user bases. Additionally, crypto transactions typically incur lower fees than traditional payment methods. Simple and low-cost integration is especially beneficial for open-source projects, which often operate with limited resources—simplicity being key to collaboration and adoption.
-
Crowdsourcing: As human feedback becomes increasingly vital for improving LLMs, Web3 incentives enable faster and larger-scale data crowdsourcing. Structured reward (and penalty) systems can promote high-quality contributions and attract a broad pool of contributors from diverse backgrounds.
-
Data Control: Owning one’s own data—requiring provenance and privacy—is becoming increasingly important because:
-
a. Users may willingly control and share their data if they can be easily compensated or receive better experiences—a scenario now becoming feasible. With the rise of autonomous agents, users could be rewarded for their data without active intervention. Moreover, users who control their data should receive higher-quality personalized experiences than those currently provided by opaque algorithmic systems. Unlike previous attempts at data wallets, today’s LLMs can not only automate large-scale cross-platform data collection but also contextualize unstructured natural language data more effectively.
-
b. Companies may lead the way in controlling data to protect sensitive information, setting standards that will eventually apply to individuals as well.
Three particularly promising ideas we’re excited about:
-
Human Feedback for Reasoning: Using crowdsourced (zk) knowledge graphs to perform logical reasoning
-
Machine Learning (ML) Tracking for AI-Generated Content (AIGC) Royalties: Using ML tracking to calculate royalties for original data sources behind AIGC
-
Advertising Digital Twins: As LLMs replace search engines as the primary mode of information retrieval, user preferences will be gathered through interactions with LLMs rather than website visits. Advertising in the AI era will require infrastructure enabling ad tech platforms to automatically extract personal preferences from digital twins.
Reasoning
Despite market hype, LLMs struggle with planning, reasoning, understanding the physical world, and similar tasks—areas where humans excel. These shortcomings arise because most LLMs imitate reasoning based on data patterns without truly understanding underlying logic or physics, making them inadequate by human standards.
Principled reasoning is valuable precisely because it enables handling novel, unseen problems—especially given strong evidence that transformers cannot go beyond their training data. We are seeking solutions that address reasoning limitations, benefiting both foundational models and current LLM-integrated systems, with a focus on human feedback mechanisms to improve reasoning quality.
Logic
Knowledge graphs—structured databases capturing relationships among entities, events, and concepts—offer a compelling method to incorporate logical reasoning into LLMs.
Here are two ways they can be integrated:
-
Dynamic Knowledge Retrieval: Relevant information is dynamically retrieved from the graph during inference using attention mechanisms.
-
Feedback Loop: If model outputs significantly deviate from the knowledge graph’s understanding, this discrepancy can be used for further fine-tuning.
Crowdsourced Knowledge Graphs: Crowdsourcing will redefine how information is collected and verified, helping build a “repository encompassing all human knowledge and culture.”
In a crowdsourced knowledge graph, users are incentivized to contribute data and its logical connections, receiving automatic payments whenever models access their contributions. To ensure accuracy, incorrect submissions are penalized by a group of validators enforcing agreed-upon standards. Defining these standards (per graph) will be one of the most critical success factors.
Web3 offers a scalable mechanism to incentivize the creation of knowledge graphs. Moreover, as gaps in LLM reasoning remain a moving target, Web3 enables targeted incentives to fill emerging data voids in real time.
Additionally, structured reward (and penalty) systems will promote high-quality information and attract a large number of contributors from diverse backgrounds. Importantly, users create value by sharing data in a productive, non-zero-sum manner—unlike zero-sum prediction markets or decentralized oracles.
Finally, under current AI limitations, crowdsourcing these graphs helps maintain relevance and accuracy—avoiding mere replication of existing LLM reasoning flaws.
Trust and Accountability Mechanisms
1. Data Privacy
User-controlled AI over personal data is rapidly approaching the level of integration seen in Apple’s hardware ecosystem. Data privacy must be addressed because:
-
As AI seamlessly integrates into every aspect of life—from smart home devices to healthcare applications—the volume of AI-collected data is growing exponentially.
-
We are approaching a tipping point in both AI’s ability to generate personalized content (e.g., via LLMs) and user belief in that capability. As users increasingly seek AI-driven personalized experiences at scale, the rate of data sharing with AI will surge.
Therefore, data privacy is essential for building user trust in AI systems and for protecting developers against misuse—such as unauthorized access, identity theft, and manipulation.
Web3 technologies like zero-knowledge proofs (zk-SNARKs) and fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) enable encrypted interactions, ensuring sensitive information remains under user control while allowing AI to derive insights.
Recent U.S. executive orders on AI emphasize the importance of “strengthening privacy-preserving research and technologies, such as cryptographic tools,” and introduce reporting requirements for large models. This signals increasing regulatory openness toward Web3 privacy and provenance approaches, which may even become compliance standards.
Crowdsourced ZK Knowledge Graphs: Through zero-knowledge knowledge graphs, AI can benefit from private data. Specifically, these graphs contain “public” nodes (with public data) and “private” nodes (with encrypted data). Models can use logical connections between nodes to derive answers without revealing the private data itself—only publicly verifiable nodes appear in the final answer, while private nodes used in reasoning remain hidden.
These graphs also make user data deletion easier, as real-time access (e.g., via dynamic retrieval) avoids implicit storage within trained models.
2. Provenance
Without provenance tracking, AI risks creating environments rife with deepfakes and uncontrolled use of personal, private, or proprietary data. Web3 enables verifiable provenance for NFTs, media assets, and training data, offering numerous promising solutions.
Machine Learning Tracking for AIGC Royalties: Beyond deepfakes, the rise of AIGC in creative fields poses unique challenges for intellectual property and royalty distribution. For example, if an AIGC system creates a mashup of songs by two famous artists, how should credit and compensation be allocated? Given the complexity and variability of AIGC, traditional attribution models are increasingly inadequate.
Machine learning tracking offers a way to identify the original components of AIGC works. Controlling provenance at the moment of AIGC generation is crucial for enabling such tracking.
In the absence of a robust global payment infrastructure for AIGC, platforms like YouTube—with existing royalty systems—gain a competitive edge and risk further centralizing their power.
To democratize AIGC creation and ensure fair artist compensation, a new payment system is needed. Blockchain payment networks, natively integrated with AIGC models, can enable instant global payments from day one. When combined with machine learning tracking, blockchain can be embedded across platforms, reducing the advantages currently held by incumbents like YouTube.
Investing in this technology supports fair royalty distribution and fosters innovation in AIGC by opening opportunities for more creators.
AI Incentives
As AI models grow increasingly autonomous, we need systems that incentivize them to act in alignment with human intentions.
Autonomous Agents
Autonomous agents are models capable of intelligently interacting with their environment—using tools, making API calls to access real-time data, engaging in algorithmic reasoning and decision-making, and acting independently of direct human control. They exhibit goal-directed behavior and learn from experience, though reliability remains limited to narrow domains (e.g., self-driving cars). As AI shifts from information retrieval to performing actions on behalf of users, autonomous agents—authorized and verifiable by human users—may see increased adoption, especially when paired with digital-native currencies for commerce.
Digital Twin Targeting: Traditional search-based advertising is declining, as conversational AI models like ChatGPT emerge as primary information sources. This poses a challenge for AdTech, as traditional methods relying on search engines and cookies face diminishing returns.
When the market recognizes that personal AI models—not cookies—are the fundamental unit for understanding user preferences, new systems enabling advertisers to extract preferences from these models may dominate. Such systems allow unprecedented personalization while preserving user privacy through cryptographic techniques.
A platform facilitating this interaction could bypass established software and hardware giants like Google and Apple.
Specifically, when a user chooses to create a digital twin, they grant it access to their search history, accounts (e.g., Google, ChatGPT, Amazon), hard drives, etc. The twin builds an initial summary of their data—including companies they engage with, interests, and behaviors—and keeps it continuously updated.
Users then set permissions for how and with whom their digital twin can share data. For instance, imagine a button labeled “Let my ad agent talk to GPT-4, Meta AI, etc.” The digital twin autonomously interacts with advertisers’ AI models. Advertisers’ models assess whether targeting is worthwhile—even without knowing the user’s identity. When targeted, users receive ads in various formats (e.g., text, LLM conversations) and are rewarded in return.
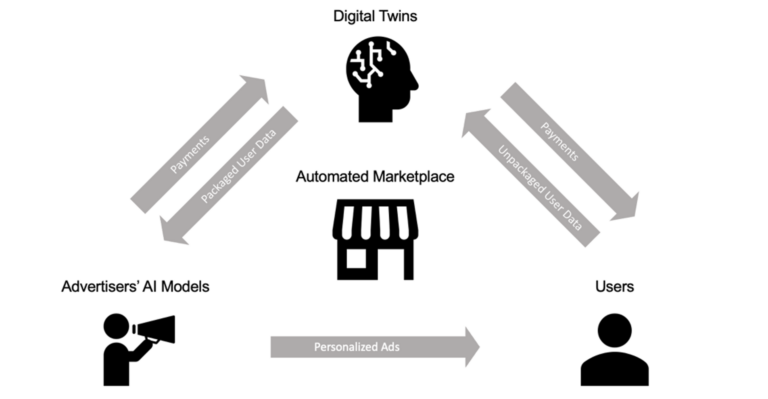
In this digital twin marketplace, crypto payment networks offer the simplest way for models to compensate each other—transactions requiring only a few lines of code. Furthermore, incentive design should ensure that targeted digital twins deliver maximum value to advertisers. Thus, advertisers should prioritize twins with clean, accurate data that genuinely reflect user preferences.
Conclusion
The convergence of AI and Web3 technologies holds transformative potential in AI reasoning, data privacy, and incentive design. Blockchain-based solutions can enable secure, efficient transactions and data processing, while incentivizing contributions from diverse sources to enhance AI development and deployment. This symbiosis between AI and crypto could give rise to stronger, more efficient, and user-centric AI systems—effectively addressing some of the most pressing challenges in the field.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News