
In-depth Analysis of dappOS: A Unique Positioning Centered on "Intent," Empowering the Construction of a Seamlessly Connected Web3
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

In-depth Analysis of dappOS: A Unique Positioning Centered on "Intent," Empowering the Construction of a Seamlessly Connected Web3
Accessing different Web3 applications via dappOS is as convenient as launching mini-programs within WeChat—simply use a single-chain wallet account to seamlessly interact with apps across various chains.
Author: JUMPENG, Senior Researcher at Shilian Investment
Project Overview
dappOS is an intent-centric operating protocol designed to make dApps as user-friendly as mobile applications. As a unified Web3 operating protocol, dappOS virtualizes public blockchains by adding a new layer between users and blockchain infrastructure such as public chains and cross-chain bridges, thereby offering users a one-click, seamless interaction experience. For project teams, this platform functions like an App Store—projects need only deploy once to access traffic across all chains. For users, accessing different Web3 applications via dappOS is as convenient as launching mini-programs within WeChat; with just one wallet account on any chain, they can effortlessly use applications across various blockchains without noticing the underlying complexity.
1. Research Highlights
1.1. Core Investment Thesis
dappOS is a Web3 operating protocol aiming to provide users with one-click access to multi-chain Dapps across the entire ecosystem while offering Dapp builders solutions for multi-chain deployment and promotion. Leveraging innovations in account abstraction and cross-chain services, dappOS achieves blockchain virtualization, lowering barriers to entry and reducing costs for both users and projects. dappOS has the potential to become a one-stop gateway into Web3, capturing significant market opportunities and value. Its core investment value is primarily reflected in the following aspects:
dappOS has gained recognition and support from top-tier institutions: As a pioneer in intent-centric operating protocols, dappOS's vision and product have earned strong industry recognition. In November 2022, it was selected as one of the top 12 projects out of over 900 applicants in Batch 5 of Binance Labs Incubation Program. Binance Labs, a leading global blockchain incubator, maintains rigorous selection standards; dappOS’s inclusion highlights its disruptive product value. Additionally, dappOS secured seed funding from prominent investors including IDG Capital and Sequoia China. It has also established partnerships with more than 20 leading public chains and DApp projects such as GMX, Perpetual Protocol, and Avalanche. These achievements demonstrate widespread industry endorsement and strategic backing from elite institutions—one of dappOS’s key competitive advantages.
dappOS’s unique positioning centered on “intent” helps build a seamlessly connected Web3: Infrastructure is crucial in the blockchain space. dappOS has been driving three transformative phases—"account abstraction," "chain abstraction," and finally "intent-centric" design—to help users better understand the concept of "abstraction." Initially implementing account abstraction to eliminate complex recovery phrase mechanisms, then advancing to chain abstraction to hide Gas fee complexities, dappOS now places “intent” at its core—users no longer need to focus on intermediate technical steps but simply express their intentions to complete transactions. dappOS aims to aggregate major blockchains and DApps, simplifying actual user needs so that even non-technical users can interact easily, much like how internet users enjoy YouTube without understanding its backend technology. With dappOS, users will truly experience seamless Web3 interactions, removing foundational knowledge requirements—a currently unattainable goal in most Web3 scenarios. By empowering users through its intent-centric philosophy, dappOS also contributes to narrowing the gap between Web2 and Web3. It has the potential to become the first platform enabling mass adoption of Web3 applications, forming a core competitive edge.
Solving real pain points with a unique user experience for Dapps: dappOS addresses two major challenges commonly faced by current blockchain applications: complicated user experiences and fragmented public chain ecosystems. It offers users a friendly front-end interface that abstracts away blockchain’s technical complexities, making DApp access as simple as using Web2 apps. Simultaneously, by virtualizing different blockchain networks, it connects isolated blockchain silos, enabling interoperability of applications and assets. Consequently, dappOS provides significant convenience for ordinary users entering blockchain and reduces the difficulty for developers deploying across multiple chains. This dual value of enhancing user experience and connecting blockchain ecosystems makes it a vital innovation within blockchain infrastructure.
1.2. Valuation
According to dappOS’s latest seed round financing announced on July 21, 2023, the project valuation stands at $50 million.
1.3. Project Risks
The main risks associated with dappOS include a relatively new project with ecosystem development still underway, competition from other players, uncertainties arising from technological and product maturity, and competitive threats, detailed further in Section 5.2 SWOT Analysis.
2. Project Overview
2.1. Project Introduction
dappOS is a Web3 operating protocol that creates an intermediary layer allowing users to express their goals rather than specifying every detail, thus eliminating technical complexity. The core technologies behind dappOS include dappOS Account and dappOS Network, which enable virtual wallets and cross-chain services respectively. Its product offerings include the dappOS SDK and Mini-Program Platform, providing B2B and B2C users with multi-chain deployment and access solutions. dappOS envisions becoming the one-click gateway to Web3, enabling broader participation in rich Web3 applications and value creation.
2.2. Team Background
2.2.1. Overall Profile
Core members of the dappOS team possess extensive experience from top tech companies and blockchain organizations, backed by strong technical and product expertise. Key management figures including the CEO, CTO, and COO come from prestigious institutions such as Stanford, Carnegie Mellon University, Tsinghua University, and Google, bringing visionary leadership and deep technical insight. The team includes not only experts in blockchain and cryptography but also seasoned product designers and operators from major corporations like Microsoft and Facebook. Notably, several team members have founded multiple tech startups, demonstrating rich entrepreneurial and managerial experience, along with profound understanding of blockchain infrastructure and applications. They are capable of forward-looking technical design. The team operates globally across the U.S. and Asia-Pacific regions, reflecting an international outlook. Core members maintain long-standing collaborations with low turnover rates.
2.2.2. Key Members
Ty Shen: Ty Shen is the founder and CEO of dappOS and former CTO and co-founder of Alchemy Pay, a blockchain payment company. His entrepreneurial journey includes founding VR startup Tsing Visual in 2016, later acquired, and co-founding cryptocurrency payments firm Alchemy Pay in 2017 where he served as CTO. At Alchemy Pay, he led R&D efforts to build a blockchain payment system. As dappOS’s founder and CEO, Ty oversees strategic planning and technical architecture, leading the core development team in building decentralized networks. He has received numerous accolades, including being named in Forbes’ 30 Under 30 list for top entrepreneurs, and his entrepreneurial story carries influence within the industry. Ty graduated from Tsinghua University with dual bachelor's degrees in Mathematics and Applied Software.
Isabella Yang: Isabella Yang is co-founder and COO of dappOS, bringing rich experience in tech entrepreneurship and investment. She holds a Bachelor of Computer Science from Carnegie Mellon University, where she received a graduate scholarship in artificial intelligence. Previously, she worked as a software engineer at Google HQ contributing to Chrome browser development, then joined venture capital firm HIG Capital investing in unicorn companies like Uber, Airbnb, and Dropbox. Isabella is also an early investor in cryptocurrencies and an angel investor in multiple Web3 startups. At dappOS, she leads business strategy and ecosystem development, leveraging her industry network to expand partnerships. Recognized as a Forbes 30 Under 30 honoree and LinkedIn Top Voice, Isabella leverages her technical and business background to make blockchain more accessible and usable. She is widely regarded as a leading female figure and investment expert in the blockchain industry.
2.3. Funding Status
In November 2022, dappOS was accepted into Binance Labs' fifth incubation program. On June 20, 2023, it received Pre-Seed funding from Binance Labs, though the amount was not disclosed.
On July 21, 2023, Web3 operating protocol dappOS announced the completion of its seed round at a $50 million valuation, led by IDG Capital and Sequoia China. Participating investors included OKX Ventures, HashKey Capital, KuCoin Ventures, TronDAO, Gate Labs, Taihill Ventures, Symbolic Capital, Foresight Ventures, BlueRun Ventures, Mirana Ventures, and Leland Ventures.

Source: ROOTDATA
2.4. Development History and Roadmap
2.4.1. Historical Development

2.4.2. Development Plan and Roadmap
dappOS divides its roadmap into three phases based on development stages:
Phase 1: Super Stable. This phase focuses on testing and validating system security, stability, and universality. dappOS collaborates with select DApp partners, service nodes, and users to evaluate the functionality and effectiveness of dappOS V2. Whitelisted DApps and service nodes can freely integrate dappOS V2 independently, while end-user clients can access supported DApps without prior permission. This phase is expected to conclude by the end of 2023.
Phase 2: Permissionless Access. A critical step toward decentralization, this phase allows DApps and service nodes to independently integrate dappOS V2 without permission. The frontend SDK will be open-sourced, enabling any DApp to self-integrate, and introducing a platform for service nodes to independently connect with open-source solutions. This phase is expected to be completed in the first half of 2024.
Phase 3: Full Decentralization. This phase will achieve full decentralization of super nodes and governance. The dappOS token aims to decentralize transaction validation and implement a robust slashing mechanism. The team will work on decentralized bidding and order allocation systems and establish a DAO to oversee protocol revenue, system upgrades, and integration of new public chains. This phase is expected to be completed in the second half of 2024.

Source: dappOS Medium
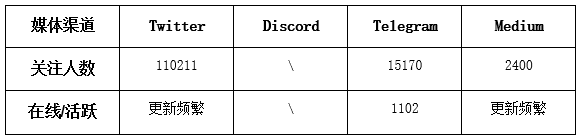
2.5. Social Media Data
As of October 27, 2023, dappOS shows high visibility across social media platforms. The project primarily operates on Twitter, Discord (invitation link expired), and Telegram. Its community engagement indicates solid performance in product operations, with a healthy community atmosphere proving essential during early-stage growth. Currently, dappOS’s Twitter account has attracted over 110,000 followers, regularly posting updates and engaging actively—the primary marketing channel and one of the most popular among users. Below are specific metrics per platform:
3. Project Analysis
3.1. Project Background
The development context of dappOS can be understood from both the evolution of Web2 and the operational landscape of Web3. Specifically:
1) Web2 Development Context
Web2.0 ushered in an era of internet prosperity, yet took 36 years to attract 100 million users. If Web3.0 is to achieve similar scale within a shorter timeframe, it faces even greater UX challenges. In the early internet era, lack of unified operating systems made usage difficult for users and created compatibility issues for developers, directly affecting ecosystem health. Later, the rise of mobile operating systems (e.g., Android) provided users with consistent, easy experiences and standardized environments for developers, fostering positive interactions among users, developers, and platforms. Web3.0 similarly faces ecosystem incompatibility issues. Today, users must create separate accounts per chain, and applications require customized versions for different environments, creating usability hurdles. Developers face higher development and maintenance costs. As the number of chains increases, these problems will intensify, hindering Web3.0’s ecosystem growth and user scalability. Hence, Web3.0 urgently requires a unified “operating system” to enable cross-chain compatibility, deliver seamless user experiences, and offer standardized developer support. Only through such unification can Web3.0 rapidly attract mainstream users and achieve large-scale adoption.
2) Web3 Adoption Context
Many skeptics point out that widespread adoption of Blockchain and Web3 faces significant obstacles due to complex and unfamiliar user experiences in Dapps. Interacting with Dapps and DeFi often involves navigating multiple applications, managing multiple wallet accounts, executing intricate transaction flows, and paying high Gas fees—all daunting for average users. Current decentralized applications present substantial barriers to mainstream adoption, mainly in two ways:
① Web3 account management is overly complex: Unlike Web2, Web3 accounts require users to manage private keys and recovery phrases—an abstract and challenging concept for many, posing a learning curve. Moreover, the inability to reset accounts introduces security risks, contrasting sharply with familiar Web2 account practices.
② Disjointed interaction workflows: Completing a full DApp operation typically requires multiple signature confirmations and Gas payments. This fragmented, repetitive process lacks the convenience of Web2 applications, especially in cross-chain scenarios.
These issues confine Web3 application users largely to tech enthusiasts, failing to attract mainstream audiences who should focus on app functionality—not technical details. dappOS seeks to resolve these issues by introducing an abstraction layer between users and infrastructure, enabling intent-based interactions with DApps without needing to understand underlying technical complexities. This approach could dramatically simplify user operations, deliver smoother experiences, overcome current DApp adoption bottlenecks, and truly enable large-scale Web3 deployment.
3.2. From Account Abstraction to Chain Abstraction
Before diving into dappOS’s mechanics, it’s important to clarify the concept of account abstraction for better understanding of subsequent content.
3.2.1. Account Abstraction
With rapid advancements in blockchain technology, wallets continue evolving to offer users more convenient and intelligent experiences. First-generation wallets (like MetaMask) offered basic connection and transaction approval features; second-generation wallets (like Phantom) made leaps in UI/UX design and added functionalities like NFT viewing. As markets mature, future mainstream wallet tools in the blockchain world are expected to evolve into operating systems capable of seamlessly connecting multiple public chains.
Meanwhile, user intent has recently gained prominence as a key direction for improving user experience. Unlike imperative execution models, intent-driven approaches advocate expressing user objectives declaratively rather than focusing on implementation details, leaving backend processes to solvers. Account Abstraction aligns perfectly with this trend. The vision of Account Abstraction is to unify Ethereum’s two account types—Externally Owned Accounts (EOA) and Contract Accounts (CA)—into a single CA-only model. This means users can manage funds via smart contracts without fully transferring control to them. This way, new wallets gain the programmability advantages of contract accounts while retaining the control capabilities of external accounts. Users don’t need to learn blockchain programming languages to authorize accounts or initiate transactions. Additionally, this enhances account security.
Account abstraction technology is poised to drive the evolution of blockchain wallets into operating systems, delivering smoother on-chain interaction experiences for everyday users. It serves as a foundational element for achieving multi-chain interoperability.

Source: OKX Ventures
3.2.2. Chain Abstraction
Building upon account abstraction, chain abstraction takes on a higher-level task—abstracting (further simplifying) asset operations across different blockchains. The backdrop for chain abstraction lies in the limited cross-chain capabilities of current DeFi, where single-chain DApps struggle to attract users from other chains, while multi-chain support incurs high costs. In contrast, centralized exchanges (CEXs) excel at enabling asset swaps across networks, lowering user barriers. Chain abstraction can be seen as a typical practice under the intent paradigm. dappOS achieves chain abstraction by inserting a virtualization layer between users and chains, enabling cross-chain aggregation via auxiliary networks. This allows users to access DEXs as conveniently as CEXs—no need to worry about where assets are stored, as the system automatically handles migration and other technical tasks. This intent-centric interaction model and blockchain virtualization technology not only optimize user experience but also significantly lower the threshold for multi-chain deployment. By freeing DeFi products from technical intricacies and making them accessible to the masses, dappOS delivers a near-CEX one-click experience, addressing a key weakness preventing DEXs from competing with CEXs and laying the groundwork for sustained DeFi growth. dappOS leads in this domain and is expected to play a pivotal role in advancing DeFi adoption.
3.3. Intent-Centric Design
As noted above, account abstraction and chain abstraction are two implementations of the intent-centric approach, solving two major blockchain interaction pain points: account management and cross-chain operations. The intent-centric method allows users to express desired outcomes using natural language or simple commands, without worrying about execution details. This topic was covered in depth in our previous report on Anoma; interested readers may refer to it. Here we briefly recap.
Intent itself isn't a new concept—it existed in the Web2 era. With the rise of search engines, users could input intents to retrieve information; e-commerce platforms allowed expression of purchase intent (e.g., food delivery, online shopping), with platforms handling execution.
In blockchain, Paradium introduced the intent-centric concept, gradually gaining attention. Its core idea places user intent first, offering solutions based on user goals rather than merely interpreting behaviors. Currently, Web3 app usage is complex—users must participate in every step (e.g., interacting with a dApp on Optimism despite holding funds on Ethereum might involve nearly ten steps), unlike the highly encapsulated nature of Web2 apps.
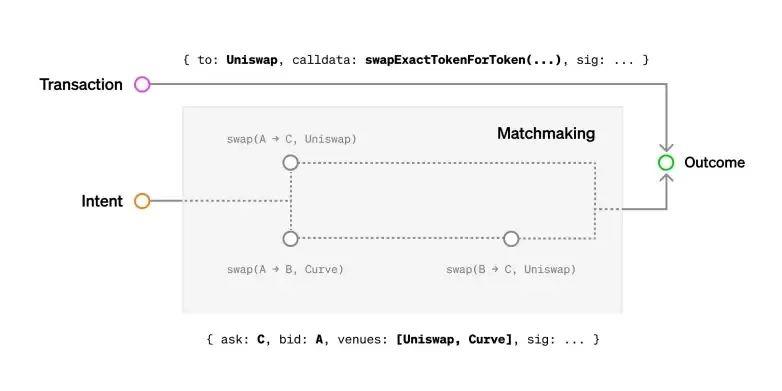
Source: paradium
dappOS is introducing an intent-centric model to deliver excellent user experiences where users can achieve their goals without understanding technical details. The emergence of this methodology will further propel blockchain technology toward mainstream adoption, representing a major leap in user experience and serving as a cornerstone for large-scale blockchain applications.
3.4. Project Mechanics
Based on the concepts discussed, we can summarize dappOS’s mission as bringing the convenience of intent-based transactions—commonly found in centralized platforms (e.g., internet shopping)—into the world of decentralized applications and Web3. To achieve the goal of “virtualizing public chains,” dappOS introduces two key innovations: technical and product-level. The technical innovations are dappOS Account and dappOS Network.
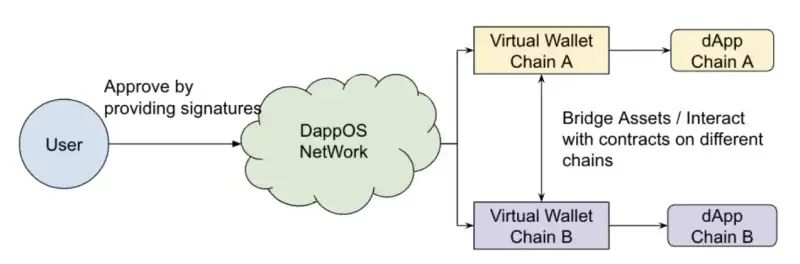
Source: dappOS Official Website
3.4.1. Technical Innovations
When users need to interact with a new chain, dappOS Network acts as an intermediary layer, automatically completing wallet creation and cross-chain asset transfers to finalize on-chain interactions. dappOS first creates a virtual wallet for the user. Supported by dappOS Network, these virtual wallets across different chains can interact, enabling cross-chain asset transfers. Thus, throughout the interaction flow, users only need to engage with dappOS, without concern for underlying chain specifics, to seamlessly use DApps across multiple public chains. This design greatly simplifies user complexity and delivers a smoother on-chain experience.
1) dappOS Account
As previously explained, dappOS’s virtual wallet creation leverages the popular account abstraction technology—already covered earlier. The significance of account abstraction lies in unifying blockchain account types into solely contract accounts. Within dappOS, users utilize these smart contract-based virtual wallets instead of traditional EOA accounts, offering several key advantages:
• Virtual wallets support flexible recovery mechanisms to reset control, enabling Web2 users to use and reset wallets without mnemonic phrases, eliminating cumbersome steps.
• Virtual wallets allow third-party nodes to assist users in chain interactions, enabling gas payments using any token accepted by the node.
• Virtual wallets support batch transaction processing without requiring contract redeployment. dappOS automatically creates these virtual wallets for users, greatly simplifying on-chain operations and enhancing usability.
Through this virtual wallet and node mechanism, dappOS drastically simplifies user on-chain interactions, enabling Web2 users to easily engage with on-chain resources and enjoy seamless experiences.
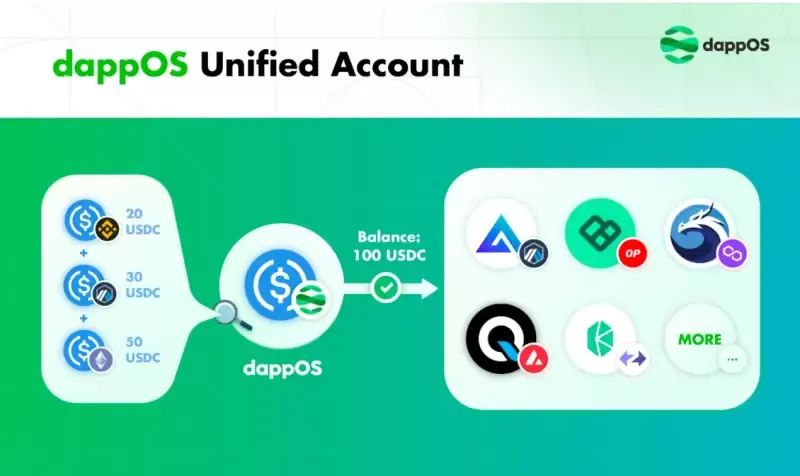
Source: dappOS Official Website
Within the dappOS wallet interface, users can view the total balance of multi-chain assets under a unified account—a key feature of dappOS V2.

Source: dappOS Official Website
In dappOS wallet’s specific asset balance display, the shown quantity represents the sum of that asset across multiple chains in the user’s accounts. For example, if approximately 7.95 USDC is displayed, this indicates the total USDC balance held by the user across public chains like Avalanche, BNB Chain, and Polygon. Users can expand to view exact values per chain. When conducting on-chain transactions via dappOS wallet, users only need to consider the total multi-chain balance and can perform one-click payments from this unified account without complex multi-chain operations. This design dramatically reduces cognitive load and operational complexity. What users perceive is a single virtual unified wallet, sharply contrasting traditional models. This highly encapsulated interaction lowers learning curves and improves user experience.
2) dappOS Network
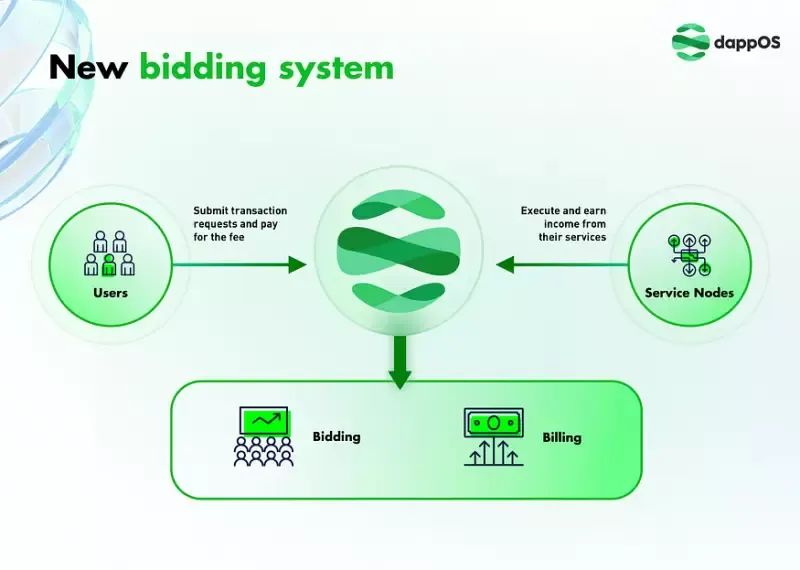
The dappOS Network, acting as the intermediary layer responsible for final chain interaction, incorporates deeper native innovations. dappOS Network is a network layer composed of super nodes and service nodes responsible for receiving and executing user-initiated orders, sharing revenue from transaction fees. User orders may involve two fundamental services:
• Cross-chain asset transfer: Users can move assets from one public chain to another without manually operating bridges or protocols. dappOS Network automatically completes asset transfers and switches, deducting a portion of the user’s transaction fee as compensation. In most cases, the Gas fee paid is slightly higher than traditional cross-chain methods, but time and steps are significantly reduced.
• Executing on-chain transactions from virtual wallets: Users can pay gas fees using any asset—whether tokens from different chains, CEX-held assets, or even fiat currency. dappOS Network fulfills asset exchange and payment according to user intent and objectives, deducting a portion of the transaction fee as compensation. Users can leverage virtual wallets to use DApps across different chains without switching between wallets.
In practice, the workflow proceeds as follows: super nodes receive and confirm orders, then delegate them to corresponding service nodes, which execute customer orders and share in the transaction fees.

Source: dappOS Official Website
A. Super Nodes
Super nodes are responsible for accepting orders, delegating them to service nodes, monitoring order fulfillment, and penalizing misconduct—using staked deposits from service nodes to compensate customers if errors occur. Super nodes operate under a DPoS consensus mechanism, with 20 nodes planned at mainnet launch, each required to stake platform tokens. Super nodes rank service nodes comprehensively based on cost, speed, and stake size, selecting optimal nodes for order execution.
B. Service Nodes
Service nodes execute customer orders and earn compensation from transaction fees. They must stake collateral and can deposit or withdraw funds at any time. When penalties apply, super nodes first deduct funds in exit status. Collateral deductions require confirmation from over half of the super nodes.
The bidding and billing system in dappOS V2 enables nodes to participate in the network and earn income from their services.
Source: dappOS Official Website
From the above process, it is evident that with dappOS Network support, users complete multiple on-chain operations with a single interaction—contrasting traditional DApp models requiring individual confirmations per step. This is a capability enabled by dappOS V2—supporting task dependencies. dappOS V2 allows users to confirm complex, interdependent transactions across chains with a single signature, regardless of whether they occur sequentially or in parallel.

Source: dappOS Official Website
Take Perpetual Protocol as an example: users can directly use USDT on BSC to pay transaction fees for Perpetual Protocol on OP chain, completing the entire process with just one click. In contrast, the traditional process involves multiple tedious steps—cross-chain transfer → cross-chain fee payment → asset conversion—typically taking 30 minutes. With dappOS Network, the entire process takes only minutes, greatly simplifying user operations.

Source: AvatarDAO
Overall, this innovative workflow relies on dappOS Network’s comprehensive service mechanism: order acceptance, delegation, node compensation, etc.—enabling single actions to fulfill multiple needs and delivering a novel user experience. dappOS Network redefines interaction details, significantly optimizing user experience fluidity, marking a new beginning in process restructuring and efficiency enhancement.
3.4.2. Product Innovations
Beyond the aforementioned technical innovations, the platform offers well-designed functional modules for both B2B and B2C users.
1) B2B Product: dappOS SDK
dappOS SDK is a B2B product enabling DApp developers to achieve multi-chain deployment without rewriting or redeploying contracts, thus capturing traffic across multiple chains. dappOS SDK is a front-end SDK allowing users from different chains to seamlessly use DApps on other chains as if they were native. Users can directly experience DApp features and benefits without going through introductory processes like asset bridging, purchasing gas tokens, or setting up wallets.
For DApp project teams, dappOS SDK is a highly attractive proposition, enabling effortless expansion of user base and market share without excessive time or resource investment. For instance, DApps deployed on other chains can easily attract Ethereum users without requiring them to switch chains. Similarly, multi-chain-deployed DApps can break down barriers between chains, achieving cross-chain interoperability and collaboration. dappOS’s B2B offering, dappOS SDK, is an innovative and disruptive technology with the potential to become Web3’s connector and catalyst.
2) C2C Product: Mini-Program Platform
The Mini-Program Platform is a C2C product allowing users to seamlessly access DApps across multiple public chains on mobile devices without downloading traditional wallet apps. Built on dappOS’s account abstraction and chain abstraction technologies, the platform delivers Web2-like user experiences. Key advantages include:
• Accounts: Users don’t need to create and manage multiple chain-specific wallet accounts or remember complex mnemonics or private keys. Instead, they can log in and use the platform with a simple password or fingerprint. The platform creates a unified virtual account supporting easier management methods like multi-signature and social recovery. Users don’t need to know chain details—only total asset amounts. They can also easily perform combined payments using tokens from different chains.
• DApp Interaction: When interacting with DApps, users don’t need to handle auxiliary steps like Gas payment, asset bridging, or authorization—they only confirm the total fee with one click, and all interactions complete automatically. Aside from blockchain confirmation times, the user experience matches that of Web2 apps. Users can browse and use various DApps on the mini-program platform as conveniently as launching mini-programs in WeChat.
The Mini-Program Platform is dappOS’s C2C product, bringing Web3 and DApps to mobile devices and delivering Web2-like convenience and friendliness. It enables users to interact solely with dappOS to achieve multi-chain DApp usage.

Source: dappOS Official Website
3.4.3. dappOS Fees
In the dappOS network, a certain network operating fee is charged for each order processing. These fees support the operation and maintenance of the dappOS network and are shared between super nodes and service nodes.
1) Order Fee Calculation
When submitting an order, users must provide the following information, as shown in the official GitBook:

Source: dappOS Official GitBook
As seen in the image, during transaction processing, users must pay: Priority Fee + Bridge Fee + Gas Fee × Gas Price + Input Asset Quantity. Among these: 1) Priority Fee and Bridge Fee are set by nodes; 2) Gas Fee is calculated based on actual Gas consumption; 3) Gas Price follows the current network estimate but does not exceed the user-defined Gas Price limit. After transaction completion, users receive: Output Asset Quantity + Gas Refund, where the Gas Refund refers to unused portions of the paid Gas Fee.
2) Service Nodes Submit Quotations to Super Nodes
When service nodes quote prices to super nodes, they provide the following information, as shown in the official GitBook:

Source: dappOS Official GitBook
After transaction completion, nodes receive: Priority Fee + Bridge Fee + Gas Revenue. Meanwhile, super nodes select the optimal node for user orders considering comprehensive factors like node quotes, processing speed, and staked amounts. Overall, this fee structure significantly reduces financial burden during DApp interactions and eliminates multiple signature requests and steps, particularly beneficial in cross-chain bridging scenarios.
3.5. dappOS Security
As a protocol where wallets play a crucial role, project security is paramount. dappOS has developed robust security methodologies, adopting stringent measures across all operational mechanisms and undergoing multiple audits by Certik, Bits of Trail, and Secure3. Specific aspects include:

Source: dappOS Official Website
1) dappOS Account Security
dappOS accounts adopt a decentralized, non-custodial model, with security depending solely on user-managed private keys and the underlying public chain network. Notably, the chosen wallet recovery method affects security levels—for example, using email as recovery introduces potential risks via email servers. Each dappOS account can only be accessed via correct signatures, with owner addresses recorded at creation. Every transaction requires signature verification, effectively preventing unauthorized access.
Source: dappOS Official Website
2) dappOS Network Security
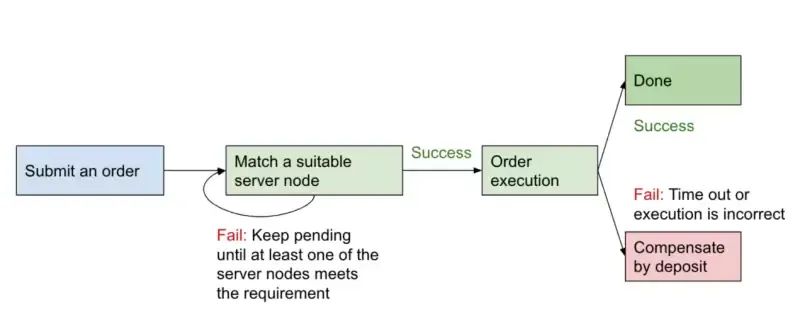
For users, asset loss only occurs if sent to a node unable to provide service—but this risk is mitigated through over-collateralization. dappOS ensures that nodes receiving user inputs lock more assets than the input amount, guaranteeing correct order execution or refunds.
3) Network Node Security
For dappOS network nodes, security is ensured by DPoS consensus. Super nodes cannot access service node assets. In worst-case scenarios, only the server node’s deposit is lost. Compared to regular bridges, exposure is smaller because dappOS only locks assets involved in ongoing transactions, not entire pools. Locking $2–5 million in assets is generally sufficient to support $1 billion in daily trading volume.
3.6. Project Ecosystem
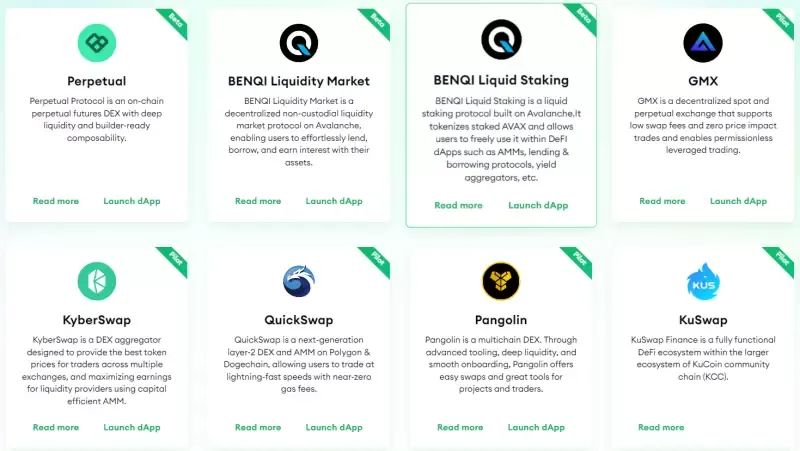
dappOS continuously removes user experience limitations, striving to build a comprehensive ecosystem. To date, dappOS has partnered with numerous leading DApps—here are some highlights:
Source: dappOS Official Website
1) Perpetual
A decentralized perpetual contract DEX offering deep liquidity and builder-friendly composability. Perpetual Protocol runs on Optimism and uses a virtual automated market maker (vAMM) model for perpetual swaps. Users can go long or short positions with up to 10x leverage. By integrating dappOS, Perpetual Protocol enables users to pay gas fees with any asset and use other DApps cross-chain.
2) Benqi
Benqi is a decentralized finance protocol built on Avalanche, comprising Benqi Markets and Benqi Liquid Staking. Benqi Markets enables users to easily lend, borrow, and earn interest. Benqi Liquid Staking is an Avalanche liquid staking solution that tokenizes staked AVAX. Through dappOS integration, Benqi allows users to use assets from other chains without manual cross-chain transfers, enjoying higher capital efficiency.
3) GMX
A decentralized leveraged trading platform supporting any ERC20 token pair. GMX allows borrowing assets at interest rates as low as 0.01%, with up to 30x leverage. GMX also offers a governance token, GMX, enabling users to participate in platform decisions and share profits. By integrating dappOS, GMX lets users pay gas fees with any asset and use other DApps cross-chain.
Source: GMX Official Website
4) KyberSwap
A multi-chain DEX aggregator and liquidity source featuring capital-efficient liquidity pools that generate fees for liquidity providers. KyberSwap aggregates liquidity from multiple DEX protocols (including Kyber Pools) to offer optimal trade pricing. By integrating dappOS, KyberSwap enables users to bypass auxiliary steps like Gas payment, asset bridging, and authorization—simply confirming the total fee with one click to automatically complete all interactions.
The above examples represent only part of dappOS’s ecosystem. More outstanding DApps will join, collectively advancing Web3 innovation and development. Overall, dappOS is partnering with major leading DApps. As more DApps integrate with dappOS, user convenience will significantly improve, further increasing DApp attractiveness. Clearly, if cold-start success is achieved, the platform will generate a rising flywheel effect. In the future, dappOS will undoubtedly connect more top-tier projects, co-building a full-scenario Web3 ecosystem.

Source: dappOS Official Website
Beyond the DApp partnerships listed above, dappOS continues exploring infrastructure collaborations to comprehensively strengthen its ecosystem. In addition to DApp cooperation, dappOS has established partnerships with the following foundational platforms:
A. Partner Chains: Such as Avalanche and Polygon, supporting rapid multi-chain deployment for DApps.
B. Payment Gateways: Collaboration with Alchemy Pay to provide premium fiat on/off-ramp experiences.
C. Node Service Providers: Actively selecting node providers to build a professional network supporting transaction processing.
D. Security Audit Firms: Partnering with industry-leading auditors to enhance system protection.
3.7. Project Metrics
According to official data, dappOS currently partners with over 20 DApps spanning DeFi, NFT, and other verticals. User numbers steadily grow, reaching 50,000 total users with over 210,000 transactions processed. Supported public chains continue expanding—now covering 10 major networks—effectively boosting DApp cross-chain development. This demonstrates dappOS’s ability to quickly attract top-tier projects and sustain user growth, thanks to its pursuit of excellence in technology and product design, alongside multidimensional collaboration with underlying infrastructure. Looking ahead, as more use cases emerge, the ecosystem will become increasingly diverse. It is foreseeable that as the ecosystem deepens, dappOS’s commercial impact and influence will rapidly expand, potentially becoming a vital bridge transcending traditional public chain limitations in the Web3 space. Overall, dappOS’s contributions will greatly advance Web3 openness and development, yielding abundant benefits for users and the industry.

Source: dappOS Official Website
4. Market Opportunity and Potential
4.1. Market Overview
4.1.1. Market Positioning
dappOS occupies a unique market position, classifiable either as a Web3 infrastructure project or an intent-focused project. Initially positioned as providing interfaces for DApps—offering wallet-like and cross-chain functionalities—dappOS repositioned itself as the first intent-centric operating protocol following Paradium’s introduction of the “intent-centric” concept and dappOS’s timely release of its V2 version.
4.1.2. Market Size
Based on the positioning analysis above, dappOS fits within the Web3 interaction layer segment, whose market size closely correlates with the overall Web3 ecosystem. Statistics show that last year alone, active DApp count surpassed 6,000 globally, with active user (addresses) exceeding 20 million—DeFi and NFT being the largest verticals. This reflects growing demand for Web3 applications in finance, gaming, and social sectors. Projections suggest the DApp market could exceed $360 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual rate of 56.1%. Concurrently, demand for improved interaction experiences and efficiency continues rising. As a standard for Web3 interaction layers, dappOS precisely meets these needs, offering enhanced UX, simplified operations, and multi-chain integration. Therefore, as the Web3 ecosystem expands and functional demands increase, the interaction-layer market dappOS operates in will grow accordingly. Moreover, dappOS could become a primary entry platform, potentially triggering massive market expansion. Overall, the Web3 market is vast and rapidly growing—meeting user needs while advancing the ecosystem, dappOS’s market potential is boundless.
4.1.3. Competitive Landscape
As mentioned earlier, analyzing dappOS’s competitive landscape requires examining its positioning across different development stages.
1) General-Purpose Intent-Centric Solutions
For this segment, please refer to our previous Anoma report at https://www.panewslab.com/zh/articledetails/i87kqyp86674.html for detailed coverage—we’ll only briefly touch on it here. From this angle, the market remains in early stages, lacking clear leaders or defined structures. It can be loosely categorized into four areas:
① Infrastructure: Projects providing underlying intent-centric protocols and architectures enabling users to express and fulfill needs across chains. Examples include Flashbots (SUAVE), a dedicated intent layer introducing a new architecture with plug-and-play mempools and decentralized block builders; and Anoma Network, a privacy-focused intent-centric architecture introducing new paradigms for infrastructure layers and OS for decentralized apps.
② Supporting Infrastructure: Projects offering intent-related, account-abstraction wallet-compatible infrastructure, helping users create, broadcast, and execute intents more easily. Examples include ERC-4337, a user operation standard converting user intents into executable messages; and Juvix, an intent-based programming language enabling developers to write high-level programs.
③ Enterprise Applications: Projects integrating DApp intent infrastructure, providing APIs, modular intent layers, and domain-specific parsers, allowing users to customize and optimize trades flexibly. Examples include PropellerHeads, a trade routing API finding optimal paths based on user preferences and market conditions; and Essential, a composable intent toolkit enabling complex intent creation executed via smart contracts.
④ Consumer Applications: Projects offering intelligent user interfaces—wallets, DEXs, Web3 AI agents, smart search engines—that simplify, accelerate, and privatize Web3 interactions. Examples include CowSwap, an intent-based DEX chaining complex operations like trading, bridging, and staking; and Unibot, a Web3 AI agent understanding natural language to provide optimal DeFi advice.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















