Analyzing the Root Causes of NFT Market Stagnation: Market Dynamics, Malicious Arbitrage, and the Absence of Value Innovation
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Analyzing the Root Causes of NFT Market Stagnation: Market Dynamics, Malicious Arbitrage, and the Absence of Value Innovation
Many NFT projects lack long-term intrinsic value, making their prices extremely fragile during market panic.
In our previous article "Data Reveals Whether the 2023 NFT Market Growth Was Driven by New Capital or Just Internal Rotation," we noted that thanks to Blur's successful airdrop incentive campaign, the NFT market experienced a brief boom at the beginning of 2023—particularly between February and May, when capital inflows into the NFT market increased by 60% month-on-month. However, latest data shows that after reaching peak transaction volumes in February and March 2023, the market has begun a downward trend—NFTs have once again entered a bear market.
Some argue that NFT market growth typically lags behind cryptocurrency market growth by one to two quarters, suggesting that with recent gains in crypto, NFTs may soon rebound. However, we believe that beyond cyclical industry downturns, the current bear market stems from deeper structural issues that are directly causing the stagnation of the NFT market.
In this article, we will first present data illustrating the current bearish state of the NFT market, then analyze the key factors hindering its growth.
Data Across Dimensions Reveal a Shrinking NFT Market
1. Trading Volume, Sales Count, and Active Wallets Are All Declining
Notably, while weekly trading volume is roughly on par with levels seen during the 2022 bear market, both sales count and active wallet numbers have dropped significantly compared to 2022—indicating that both trading activity and participant numbers in the NFT market are now at their lowest levels in over a year.
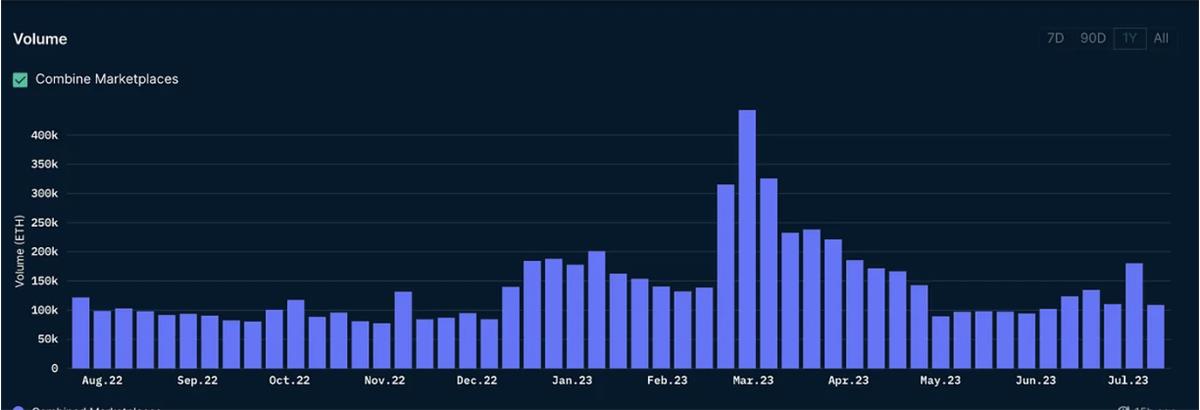
NFT Trading Volume
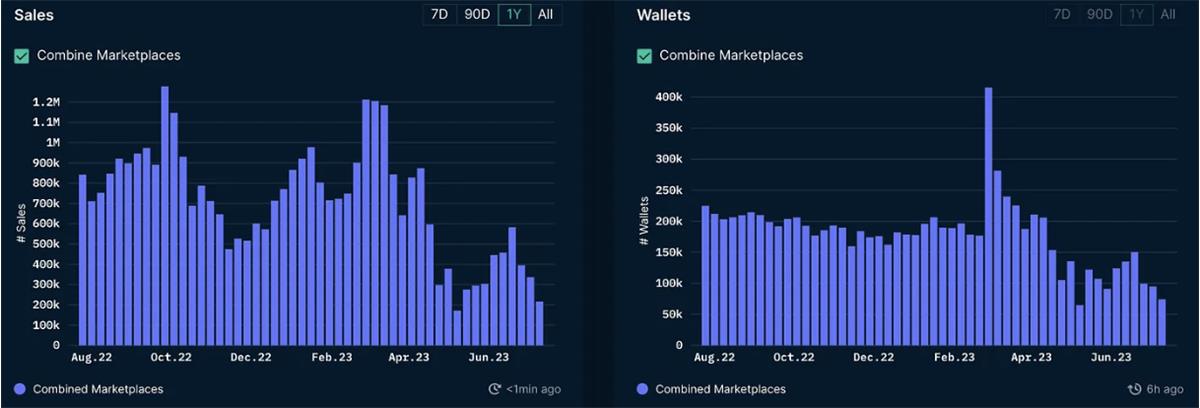
NFT Sales Count and Active Addresses
2. Blue-Chip NFT Collections Are Experiencing Continuous Value Decline
Nansen’s Blue-Chip-10 and NFT-500 indices measure the total market cap of top-tier NFT collections, reflecting overall market performance. Both indices have shown a sustained decline since April this year—the combined market value of blue-chip/top NFTs has plummeted by 70–80% from their February peaks.
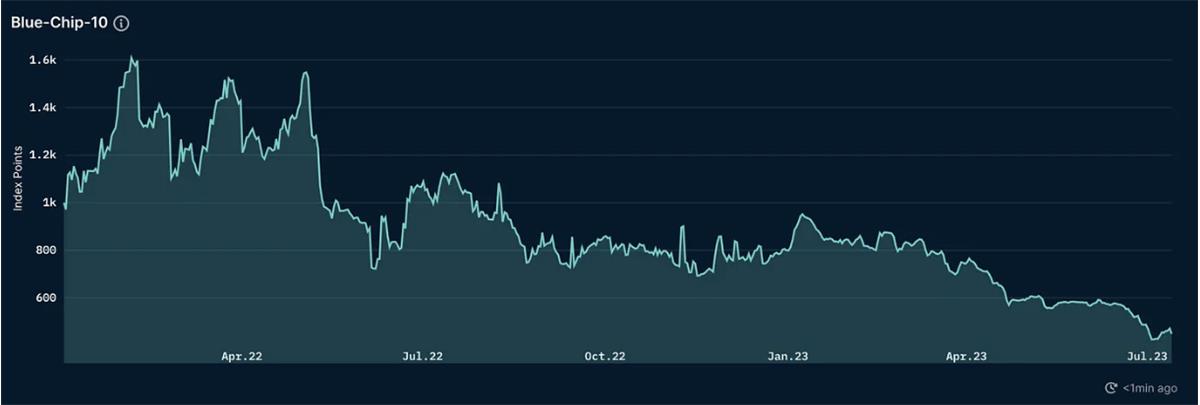
Blue-Chip-10 Index
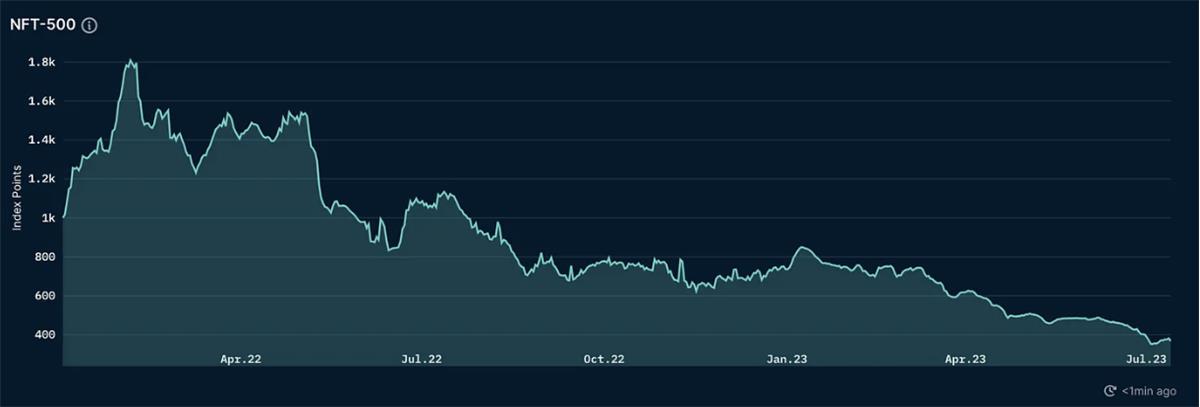
NFT-500 Index
3. Monthly Capital Inflows Into the NFT Market Are Decreasing by 20%–40%
Using the same method from our earlier article to calculate capital inflows into the NFT market, we analyzed monthly investments from February to June 2023. The data shows that monthly capital inflows into the NFT market have declined significantly each month (except for a minor increase from May to June). By June, investment levels had dropped to just 40% of February’s peak.
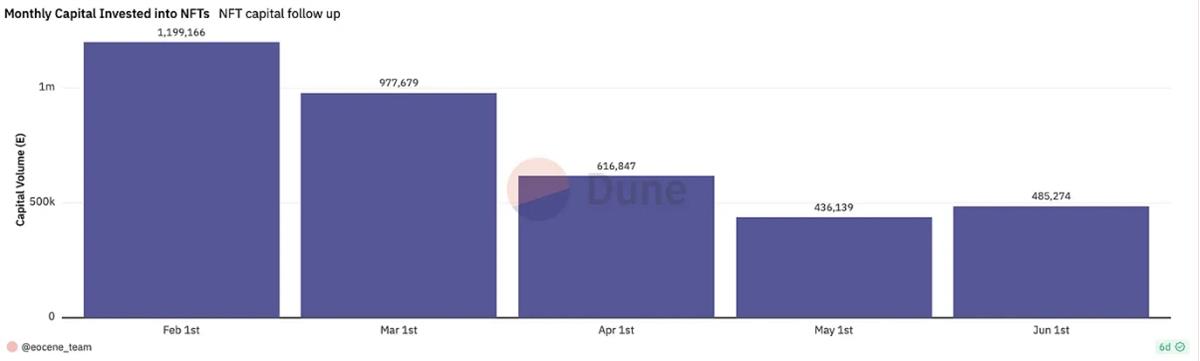
Monthly Inflows
These metrics collectively demonstrate that the NFT market is experiencing declining participation, reduced trading activity, shrinking investment, and falling prices. Across all dimensions, the evidence points to stagnation—or even contraction—of the NFT market.
Three Key Reasons Behind the NFT Market’s Stagnation
1. The "Bid for Airdrop" Mechanism Fundamentally Flaws Demand-Side Liquidity
Blur launched its airdrop incentive program at the end of 2022, primarily rewarding loyal users who list (sell) or place bids (buy orders) on its platform. Initially, many seasoned NFT players believed this would effectively boost liquidity, and early results seemed to confirm this—during Blur Season 1 through the start of Season 2, market liquidity and trading volume clearly improved.
However, shortly after Season 2 began, the situation reversed—the overall NFT market trading volume peaked in February 2023 and then entered a continuous decline.
Moreover, several blue-chip NFT collections saw sharp price drops in the following months—BAYC lost 60% of its market cap, Doodles fell by 70%, and Moonbirds plunged by as much as 80%! Many participants in these airdrops suffered heavy financial losses due to falling NFT values ("buy high, sell low"), and the token rewards they received were far from enough to offset these losses. As a result, despite ongoing airdrops, many players have chosen to exit.
In a healthy, liquid market, prices tend to remain stable and not fluctuate violently due to individual trades. Blur aimed to improve NFT market liquidity by encouraging bidding—an intention well-placed. But instead of stabilizing prices, most collections spiraled downward, as previously mentioned.
Because placing bids on Blur could earn potential BLUR token airdrops, most bidders weren’t genuinely interested in buying NFTs—they simply wanted the reward. When they “unfortunately” ended up acquiring an NFT, they rushed to offload it, often at a lower price than purchase. This drove down floor prices, which in turn lowered bid levels, prompting further sell-offs at even lower prices—a vicious cycle leading to a death spiral in prices, completely opposite to the goal of "high liquidity stabilizing prices."
The root cause is that bids on Blur do not represent real market demand, indicating that airmen generally lack confidence in most NFTs, largely because most lack long-term intrinsic value.
While Blur’s incentive mechanism failed to generate genuine liquidity, it does offer valuable lessons for achieving true NFT liquidity. Although Blur’s Airdrop Season 2 continues, the NFT market has grown fatigued—many participants incurred heavy losses early in Season 2 and chose to withdraw, while others learned from earlier mistakes and became more cautious. Regardless of the reason, the airdrop incentive model cannot sustainably provide healthy liquidity to the NFT market.
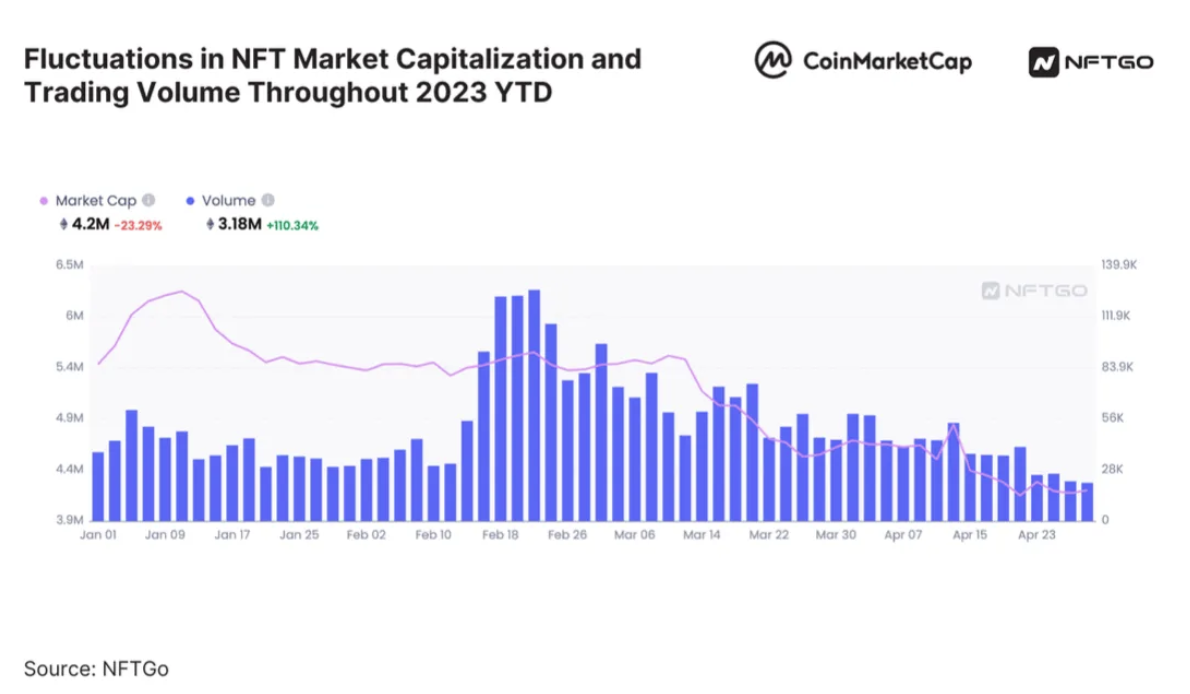
Total NFT market cap sharply declined during Blur Season 2
2. Most Project Teams Lack Experience in Market Cap Management
Blur’s incentives attracted not only those seeking BLUR tokens but also malicious arbitrageurs.
A typical case of "malicious arbitrage" during Blur’s airdrop: An arbitrageur first buys a large number of tokens from an NFT collection at a low floor price, then lists them at a higher price to artificially inflate the floor. Simultaneously, they place fake buy orders (bids) close to their listing price on Blur. Other players aiming to earn points (aka miners) then place bids in the second or third tiers to reduce the chance of actually acquiring the NFT. Since these miners don’t realize the top bidders are the same people listing the NFTs—and since sellers can choose which bidders to accept—once the second and third tier bid pools are sufficiently deep, the arbitrageur dumps their NFTs onto these unsuspecting miners.
Such arbitrageurs often repeat this process multiple times on the same collection, though each time they raise the price less than before, avoiding buying back their own dumped tokens at inflated prices. Through this method, they achieve "buy low, sell high" profits.
Arbitrageurs usually hold substantial capital (tens to hundreds of ETH), enabling them to profit from this "game." However, many NFT projects—especially those launched before Blur introduced its reward system—did not anticipate such malicious behavior and thus failed to reserve sufficient NFTs and funds to counter large-scale manipulation. As a result, they were powerless to defend their project’s market cap when attacked.
3. Many NFT Projects Lack Long-Term Intrinsic Value, Making Prices Extremely Fragile During Market Panic
This may be the most fundamental reason behind the NFT market’s growth困境.
During the initial NFT hype waves of 2020 and 2021, project teams laid out ambitious roadmaps, promising real value for NFT holders.
Yet two years later, many of these roadmaps have become empty promises, with little delivered and no tangible value provided to holders. Some teams did execute activities—like producing T-shirts, figurines, or hosting IRL meetups—but the value offered was mismatched with the high prices of the NFTs and lacked innovation.
These shortcomings mean most NFT projects lack genuine intrinsic value, leading fewer users to invest based on value or hold long-term. Consequently, the NFT market has increasingly become a “speculators’ market.”
How to Revive the NFT Market
Based on our deep analysis of the causes behind the NFT market’s contraction, we offer the following perspectives on revitalizing it.
First, we must strive to build an NFT ecosystem with real value. This means project teams should continuously deliver tangible value to holders, ensuring sustainable development. Moreover, the sharp price declines across many NFT collections during this bear market aren’t necessarily negative—they act as a “survival of the fittest” mechanism, weeding out low-quality, inactive projects while incentivizing others to innovate and deliver real utility. Those series that genuinely work hard and consistently create value for NFT holders and the broader ecosystem may suffer short-term price impacts from mechanisms like Blur’s mining, but we believe they will endure. For example, despite Moonbirds suffering heavy malicious shorting, I still have great hope for the PROOF team because they continue creating high-quality content and value.
Second, project teams must recognize the importance of market cap management. After the events surrounding Blur’s airdrop, the significance of proactive market cap defense has become clear. To avoid repeating past mistakes, teams should proactively reserve sufficient tokens and maintain adequate funds and expertise, so they can intervene promptly when prices are manipulated and stabilize their project’s valuation.
Finally, regarding liquidity: We don’t lack products aimed at improving liquidity. Blur’s pro-trader platform, along with other solutions like NFT fractionalization protocols and NFT lending protocols, are all solid innovations. However, the core issue remains—most projects lack real value, resulting in weak underlying demand. Therefore, we believe the key to creating genuine liquidity lies in shifting focus away from short-term gains toward long-term value creation. Only by doing so can projects stimulate real demand and attract value-driven investors.
Although the recent stagnation of the NFT market is disappointing, identifying the root problems allows us to focus on solving them. We still have a long way to go before fully realizing the true potential and value of NFTs.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News