ZKML: A technology integrating AI and blockchain to enable privacy-preserving model deployment
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

ZKML: A technology integrating AI and blockchain to enable privacy-preserving model deployment
What Exactly Is the Hype Around ZKML?
Author: Maggie, Foresight Research

ZKML (Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning) is a technology that applies zero-knowledge proofs to machine learning. ZKML serves as a bridge between AI and blockchain. ZKML addresses the challenges of privacy protection for AI models/inputs and verifiable inference processes, enabling small models or their zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to be deployed on-chain. The significance of putting models/inference proofs on-chain lies in:
-
Enabling blockchains to perceive the physical world. For example: a facial recognition model running on-chain allows the blockchain to detect faces and understand attributes such as gender or approximate age via on-chain AI models.
-
Allowing smart contracts to make decisions. For instance: an on-chain WETH price prediction model can assist smart contracts in making trading decisions.
-
Running AI models with privacy protection. For example: enterprises that have invested significant computational resources in training a model may want to offer inference services while preserving model confidentiality, or users may wish to keep their inputs private. ZKML enables protection of model/input privacy while proving that inference was correctly executed, achieving trustless inference.
Applications of ZKML
-
On-chain AI: Deploying AI models or their inference proofs on-chain so smart contracts can use AI for decision-making. For example: on-chain trading systems used for investment decisions.
-
Self-improving blockchains: Empowering blockchains with AI capabilities to continuously refine strategies based on historical data. For example: AI-driven reputation systems on-chain.
-
AIGC on-chain: Minting AIGC-generated content/artworks as NFTs on-chain, where ZK proofs verify the correctness of the generation process and confirm no copyrighted images were used in the dataset.
-
Wallet biometric authentication (KYC): On-chain verification of facial recognition proofs to complete wallet KYC procedures.
-
AI security: Using AI for fraud detection, Sybil attack prevention, etc.
-
On-chain ZKML games: On-chain AI chess players, NFT characters driven by neural networks, etc.
Technical Aspects of ZKML
-
Goal: Convert neural networks into ZK circuits. Challenges: 1. ZK circuits do not support floating-point numbers; 2. Large-scale neural networks are difficult to convert.
-
Current progress: The earliest ZKML library emerged two years ago—this field has a very short history. Currently, the latest ZKML libraries support ZK-ifying some simple neural networks and deploying them on blockchains. Basic linear regression models can reportedly be put on-chain, along with various smaller neural network models capable of generating on-chain proofs. However, demos remain rare—one known example is handwritten digit recognition. Some tools claim support for models with up to 100M parameters, while others claim they can convert GPT2 into ZK circuits and generate ZK proofs.
-
Development directions: Network Quantization—converting floating-point numbers in neural networks to fixed-point numbers and lightening the network (making it ZK-friendly). Exploring ways to convert large-parameter neural networks into ZK circuits and improving proof efficiency (expanding ZK capabilities).
Summary
ZKML is a bridge between AI and blockchain. Its significance lies in enabling blockchains to perceive the physical world, empowering smart contracts to make decisions, and securely running AI models with privacy protection—a highly promising technology.
Despite its short history, this technology is advancing rapidly. It is now possible to convert certain simple neural network models into ZK circuits, enabling either on-chain deployment of models or submission of inference proofs to the chain. Language models remain challenging—Ddkang/zkml claims to generate ZK versions of GPT2, BERT, and Diffusion natural language processing models, but practical performance remains unclear; these models might run locally but may not yet be deployable on-chain. We believe that with advancements in network quantization, ZK technologies, and blockchain scaling solutions, ZKML for language models will soon become viable.
1. Background
(If you are already familiar with ZK and ML, feel free to skip this section.)
Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZK): A zero-knowledge proof allows a prover to convince a verifier that a statement is true without revealing any information beyond the validity of the statement itself. ZK is primarily used to prove that a computation was correctly executed and to protect privacy.
Proving computational integrity: Take ZK-rollups as an example—their operation involves bundling multiple transactions, publishing them to L1, and simultaneously submitting a proof (using zero-knowledge proof technology) asserting the validity of those transactions. Once verified on L1, the state of the zk-rollup is updated.
Privacy protection: Using Aztec Protocol as an example, assets on Aztec's zk.money exist in note form, similar to Bitcoin’s UTXO model. Note amounts are encrypted. When users transfer funds, they destroy existing notes and create new ones for the recipient and themselves (as change). Zero-knowledge proofs are used to privately prove that the total amount of destroyed and newly created notes is equal and that the user controls the original notes.
Machine Learning (ML): Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence. ML theory focuses on designing and analyzing algorithms that allow computers to automatically "learn." One class of ML algorithms automatically discovers patterns from data and uses these patterns to predict unknown data. ML has been widely applied in computer vision, natural language processing, biometric identification, search engines, medical diagnosis, credit card fraud detection, securities market analysis, DNA sequencing, speech and handwriting recognition, gaming, and robotics.
2. What Problems Does ZKML Solve?
ZKML is a research and development area that has caused a stir in the cryptography community in recent years. Applying zero-knowledge proofs to machine learning, this technology aims to solve privacy and verifiability issues in machine learning using ZK proofs. This enables small models or inference ZKPs to go on-chain, serving as a bridge between AI and blockchain:
-
Model-on-chain: Converting ML models into ZK circuits and storing lightweight ZKML models within blockchain smart contracts. Users can invoke model functions via smart contract calls. For example, Modulus Labs' RockyBot deploys an on-chain AI model to predict WETH prices for trading decisions.
-
Inference proofs on-chain: Convert ML models into ZK circuits, perform inference off-chain, and generate ZK proofs. These proofs demonstrate that the inference process was correctly executed. The inference result and ZK proof are submitted on-chain for callers to reference and for smart contracts to verify.
Why is putting models/inference proofs on-chain meaningful?
-
Enables blockchains to perceive the physical world. For example: a facial recognition model running on-chain allows the blockchain to detect faces and understand attributes such as gender or approximate age via on-chain AI models.
-
Allows smart contracts to make decisions. For instance: an on-chain WETH price prediction model helps smart contracts make trading decisions.
-
Runs AI models with privacy protection. For example: companies investing heavily in training a model may want to offer inference services while protecting model privacy, or users may want to ensure input privacy. ZKML ensures both model/input privacy and proves that inference was correctly performed, achieving trustless inference.
The role of zero-knowledge proofs in ZKML:
1. Privacy Protection: Safeguarding the privacy of ML models or input data during prediction.
-
Data Privacy (Public Model + Private Data): I have sensitive data such as medical records or facial images. I can use ZKML to protect input data privacy, run public neural network models on this data, and obtain results—for example, a facial recognition model.
-
Model Privacy (Private Model + Public Data): Suppose I’ve spent considerable cost training a proprietary model and don’t want to expose it. I can use ZKML to run a private, privacy-preserving neural network model that performs inference on public inputs to produce outputs.
2. Verifiability: Using ZKPs to prove correct execution of ML inference, making the machine learning process verifiable.
-
Suppose the model runs not on my server, but I still need assurance that inference was correctly executed. With ZKML, I can perform inference on specific inputs and models, producing an output. The ZKP proves the process was correctly executed. Even if the computation didn’t occur on my device, I can verify the ZKP to confirm the inference was accurate and thus trust the result.
3. Use Cases of ZKML
-
Computational Integrity
-
On-chain AI: Deploying AI models on blockchains so smart contracts can leverage AI for decision-making.
-
Modulus Labs: RockyBot On-chain verifiable ML trading bot
-
-
Self-improving blockchains: Enabling blockchains to utilize AI capabilities to continuously improve and adjust strategies based on historical data.
-
Enhancing Lyra Finance’s AMM with AI.
-
Creating AI-based reputation systems for Astraly.
-
Developing AI-powered compliance features at the smart contract level for Aztec Protocol.
-
Modulus Labs: Blockchains that self-improve (link):
-
-
AIGC on-chain: Minting AIGC-generated content/artworks as NFTs on-chain, where ZK proofs verify the integrity of the process and confirm no copyrighted images were used in the dataset.
-
ML as a Service (MLaaS) transparency (link)
-
AI Security: Using AI for fraud detection, Sybil attack prevention, etc. Train AI anomaly detection models on smart contract data; pause contracts when anomalies occur, and submit anomaly detection proofs on-chain using ZK.
-
On-chain ZKML games: On-chain AI chess players, NFT characters powered by neural networks, etc.
-
Verifiable AI model benchmarking: Using ZK to provide proofs for model benchmarks, offering verifiability for performance and efficacy test results.
-
Proof of correct model training: Since model training is resource-intensive, using ZK to prove training correctness is currently impractical. However, many believe the technology is feasible and aim to use ZK to prove whether a model used certain data or not, addressing copyright concerns in AIGC.
-
-
Privacy Protection
-
Wallet Biometric Authentication / Digital Identity
-
WorldCoin uses its biometric orb device to scan irises, providing users with unique, verifiable digital identities. WorldCoin is researching zkml to upgrade World ID. After the upgrade, users will store signed biometric data autonomously in encrypted storage on their mobile devices, download ML models for iris code generation, and locally create zero-knowledge proofs confirming that their iris codes were indeed generated from signed images using the correct model.
-
-
Blockchain-based Machine Learning Bounty Platforms
-
Companies post bounties and provide both public and private datasets—public data for model training, private data for predictions. AI service providers train models, convert them into ZK circuits, encrypt the models, and submit them to contracts for validation. They then perform predictions on private data, generate results and ZK proofs, which are submitted to the contract for verification. Upon completing these steps, the AI provider receives the bounty. zkML: Demo for circomlib-ml on Goerli testnet
-
-
Privacy-preserving inference: For example, using private patient data for medical diagnosis and sending sensitive inference results (e.g., cancer detection outcomes) securely to patients. (vCNN paper, page 2/16)
-
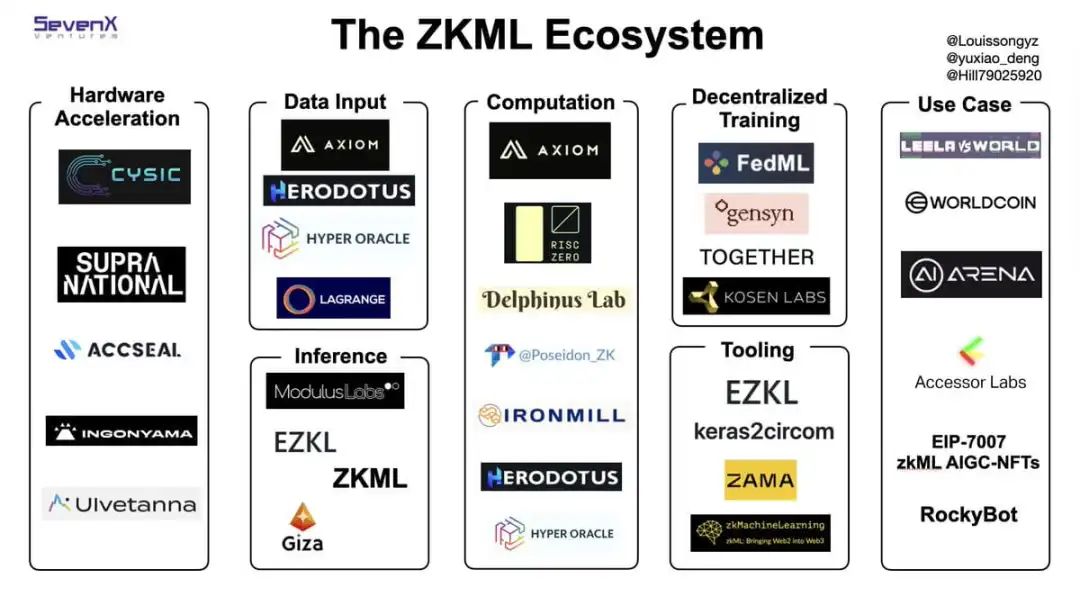
4. ZKML Landscape
According to the ZKML landscape compiled by SevenX Ventures:
-
Hardware Acceleration: Multiple organizations are actively developing hardware acceleration for ZKPs, benefiting ZKML development. Acceleration is typically achieved via FPGA, GPU, or ASIC chips. For example: Accseal is developing ASIC chips for ZKP hardware acceleration; Ingonyama is building ICICLE, a ZK acceleration library designed for CUDA-enabled GPUs; Supranational focuses on GPU acceleration; Cysic and Ulvetanna specialize in FPGA acceleration.
-
Inputs: To enable on-chain data usage, Axiom, Herodotus, Hyper Oracle, and Lagrange improve user access to blockchain data and provide richer on-chain data views. ML input data can then be extracted from imported historical data.
-
Inference: ModulusLabs is developing a new zkSNARK system specifically for ZKML. This overlaps with the ZKML toolset category, focusing on ZK-ifying models and providing necessary tools. Giza is a machine learning platform built on StarkNet focused on fully on-chain model deployment and scalability.
-
Computation: Focused on building decentralized computing networks to train AI models accessible to all, allowing people to train AI models at lower costs using edge computing resources.
-
Decentralized Training / Compute Power: Building decentralized computing networks to train universally accessible AI models, enabling low-cost use of edge computing resources for AI training.
-
ZKML Toolsets: See Chapter 5 for technical evolution. ZAMA in the diagram primarily uses Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) for ML privacy protection. Compared to ZKML, FHEML only provides privacy without trustless verification.
-
Use Cases: Worldcoin uses ZKML for digital identity authentication—users securely store signed biometrics on their devices, ZK-ify iris recognition ML models, run models during identity verification, and use ZKPs to prove correct execution. Modulus Labs builds on-chain AI trading bots. Cathie’s EIP7007 proposes a zkML AIGC-NFT standard. On-chain AI chess players, NFT characters driven by neural networks, etc.
5. Technical Evolution of ZKML
The main challenges in converting neural networks into ZK circuits are:
-
Circuits require fixed-point arithmetic, but neural networks heavily rely on floating-point numbers.
-
Model size: large models are difficult to convert due to high complexity and circuit size.
The evolution of ZKML libraries:
- 2021: zk-ml/linear-regression-demo, Peiyuan Liao
Implemented a linear regression circuit. Linear regression is a fundamental predictive algorithm assuming a linear relationship between output and input variables, suitable for predicting numerical values and studying variable relationships—e.g., predicting house prices based on area and other features, or forecasting future sales from historical data.
- 2022: 0xZKML/zk-mnist, 0xZKML
Built a ZK circuit based on the MNIST dataset to recognize handwritten digits. For example: writing the digit '2', the handwriting is recognized as '2', and a proof of the inference process is generated. This proof can be submitted on-chain and verified using ethers + snarkjs.
In practice, the zk-mnist library only converts the final layer into a circuit, not the entire neural network.
- 2022: socathie/zkML, Cathie
Compared to zk-mnist, ZKML converts the full neural network into a circuit. Cathie’s zkMachineLearning provides multiple ZKML toolkits like cirocmlib-ml and keras2circom to help ML engineers convert models into circuits.
-
November 2022: zk-ml/uchikoma, Peiyuan Liao
Converts floating-point operations in neural networks into fixed-point operations. Created and open-sourced a general-purpose framework capable of transforming nearly all machine learning algorithms into zero-knowledge proof circuits easily integrable with blockchains.
-
Vision models → AIGC
-
Language models → chatbots, writing assistants
-
Linear models and decision trees → fraud detection, Sybil attack prevention
-
Multimodal models → recommendation systems
Trained a blockchain-friendly AIGC model and converted it into a ZK circuit. It can generate artworks, produce compact ZK proofs, and mint the artwork as an NFT.
-
July 2022, updated March 2023: zkonduit/ezkl
ezkl is a library and command-line tool for performing inference on deep learning models and other computational graphs within zk-SNARKs (ZKML), using Halo2 as the proof system.
Users can define computational graphs such as neural networks, then use ezkl to generate ZK-SNARK circuits. The ZKPs generated for inference can be verified by smart contracts.
Claims to support models with up to 100M parameters, though potentially resource-intensive.
-
May 2023: Ddkang/zkml (Link)
zkml claims to ZK-ify GPT2, BERT, and Diffusion models. However, it may require substantial memory, and it’s unclear whether the resulting proofs can be stored in smart contracts.
zkml can verify model execution achieving 92.4% accuracy on ImageNet, and can prove an MNIST model within four seconds at 99% accuracy.
-
May 2023: zkp-gravity/0g
Lightweight neural networks supporting private data + public models.
In summary, current exploration directions in ZKML include:
-
Network Quantization: Converting floating-point numbers in neural networks to fixed-point numbers and lightening the network (ZK-friendly).
-
Attempting to convert large-parameter neural networks into ZK circuits and improving proof efficiency (expanding ZK capabilities).
6. Conclusion
ZKML is a bridge between AI and blockchain. Its value lies in enabling blockchains to perceive the physical world, empowering smart contracts to make decisions, and securely running AI models with privacy protection—a highly promising technology.
ZKML has a short history but rapid development. Today, simple neural network models can already be converted into ZK circuits, enabling on-chain model deployment or inference proof submission. Language models remain challenging—Ddkang/zkml claims to generate ZK versions of GPT2, BERT, and Diffusion models. We believe that with advances in network quantization, ZK technologies, and blockchain scalability, ZKML for language models will soon become practical.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














