Interpreting the Technical Principles of Layer Zero: Ultra-Light Nodes, Standing Out from the Crowd
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Interpreting the Technical Principles of Layer Zero: Ultra-Light Nodes, Standing Out from the Crowd
This article will introduce Layer Zero's technology and features, as well as how it enables communication and cross-chain transactions between blockchains.
Author: Salazar
Compiled by: TechFlow
Recently, Layer Zero completed its second round of financing, raising $120 million with a valuation reaching $3 billion.
With the rise of DeFi projects, cross-chain interoperability has become a hot topic in the blockchain space. Among numerous cross-chain platforms, Layer Zero stands out due to its unique technology and design. This article will introduce Layer Zero's technical architecture and key features, explaining how it enables communication and cross-chain transactions between blockchains.

Let’s consider a scenario:
For example, in the image below, a "Degen Trader" discovers a mining opportunity on AVAX that requires ETH.
However, he cannot directly transfer his ETH to AVAX and must use a cross-chain bridge to complete the process.
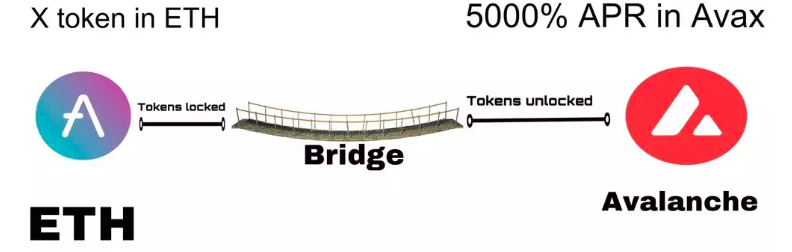
After sending ETH to the bridge, the bridge confirms that the funds have been locked. It then unlocks an equivalent amount on AVAX and sends the tokens over. However, the trader receives an AVAX-wrapped version of ETH instead of native ETH, requiring additional gas-consuming transactions to manage.
The key point here is that the trader relies on the cross-chain bridge to access ETH on AVAX. Past incidents have shown that hacks on bridges can be devastating, so caution is crucial.
Below are some notable cases where cross-chain bridges were hacked:

How Layer Zero Steps In / The Basics
What I explain here is at a fundamental level, making it understandable even for beginners.
From the image below, we can see that each chain hosts a LayerZero endpoint managed by the LayerZero team. When a user sends a transaction to AAVE on Ethereum, this transaction is first sent to the LayerZero endpoint on Ethereum.
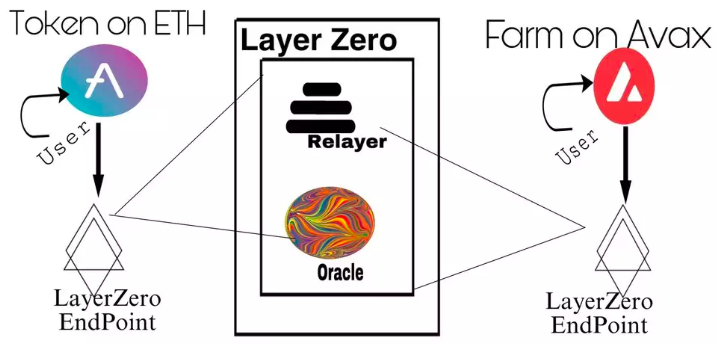
Then, the endpoint verifies via LayerZero (oracle and relayer) that the user indeed holds the tokens on the Ethereum chain and intends to send them to AVAX.
LayerZero communicates with the endpoint on AVAX and processes the transaction—resulting in native ETH on AVAX, not a wrapped version from another chain.
This enables interoperability between chains, allowing developers to build DEXs or other DeFi applications on specific chains. With LayerZero, users can remain on their original chain while using yield aggregators or DEXs to participate in liquidity mining across target chains.
In this process, the oracle (Chainlink) provides updated and accurate price data, while the relayer ensures historical information is correct before updating each endpoint.
LayerZero Technology
You might come across phrases online like: "LayerZero is a trustless omnichain interoperability platform enabling users to..." But it doesn’t need to be so complex. Simply put—LayerZero is a universal messaging platform, essentially a universal message hub.
The foundation of LayerZero technology lies in two independent entities—the oracle and the relayer, which work together to enable efficient cross-chain transaction delivery.
A key feature of LayerZero is its ultra-lightweight node design. This lightweight approach allows it to operate on expensive L1s like Ethereum without incurring excessive costs. This is achieved through the use of light clients, enabling LayerZero to efficiently process transactions and verify cross-chain interactions.
Another important characteristic of LayerZero is its support for native transactions across chains.
Thanks to its innovative endpoint design, LayerZero can easily scale to support any new chain. Endpoints are modules within LayerZero that run on each participating blockchain and facilitate inter-chain communication via information exchange with relayers. Think of them as interfaces between LayerZero and the specific blockchain it operates on.
Conclusion
So, what sets LayerZero apart from networks like Polkadot or Cosmos?
Exactly—its ultra-light nodes. Combined with its relayers, oracle (Chainlink), and endpoints, LayerZero makes universal messaging across different chains in Web3 a reality.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News