FreeWavm: Goplus's latest research findings on vulnerability discovery in WebAssembly virtual machines have been officially accepted as a full paper at ISSTA 2025.
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

FreeWavm: Goplus's latest research findings on vulnerability discovery in WebAssembly virtual machines have been officially accepted as a full paper at ISSTA 2025.
A WebAssembly runtime is the infrastructure that executes WebAssembly code and is widely used as an execution engine in web browsers and blockchain systems.
Recently, Goplus's latest research on vulnerability discovery in WebAssembly virtual machines has been officially accepted as a full paper at ISSTA 2025!
ISSTA, one of the four top-tier conferences in software engineering and classified as a Category A international academic conference by the China Computer Federation (CCF), focuses on publishing cutting-edge advancements from global research institutions and technology companies in software engineering and software testing.

1. Problem Definition
WebAssembly runtimes form the foundational infrastructure for executing WebAssembly code and are widely used as execution engines in web browsers and blockchain systems. For instance, Ethereum 2.0 and Polkadot have adopted WebAssembly runtimes as execution environments for smart contracts to enhance efficiency and security. Despite their growing popularity, WebAssembly runtimes also introduce new attack surfaces. Defects and flaws within these runtimes may lead to unexpected behaviors, incorrect results, or even severe security consequences—particularly for blockchain platforms that rely on smart contracts compiled into WebAssembly bytecode.
2. Fuzzing Framework for Blockchain Smart Contract Virtual Machines
To address vulnerability discovery in WebAssembly virtual machines, this paper presents FreeWavm, a fuzzing framework based on parse tree mutation and snapshot-guided testing.
FreeWavm consists of four key components:
(1) To capture structural features of WebAssembly code, we designed a WebAssembly module parser that converts WebAssembly bytecode into a parse tree structure.
(2) Next, we developed a structure-aware mutation module to generate meaningful test inputs for WebAssembly runtimes. This involves applying a customized node-prioritization strategy to identify interesting nodes from the parse tree, followed by performing targeted mutations on these nodes.
(3) To ensure the integrity of mutated test inputs, we introduced an automated repair mechanism to correct modified parse trees. This guarantees that the module parser can successfully parse newly generated test cases, thereby enabling effective continuous mutation.
(4) We built a snapshot pool to maintain incomplete parse tree structures—those that either triggered crashes or covered new execution paths in the target runtime—allowing prior knowledge to guide future mutations and increasing the likelihood of uncovering deep vulnerabilities in WebAssembly runtimes.
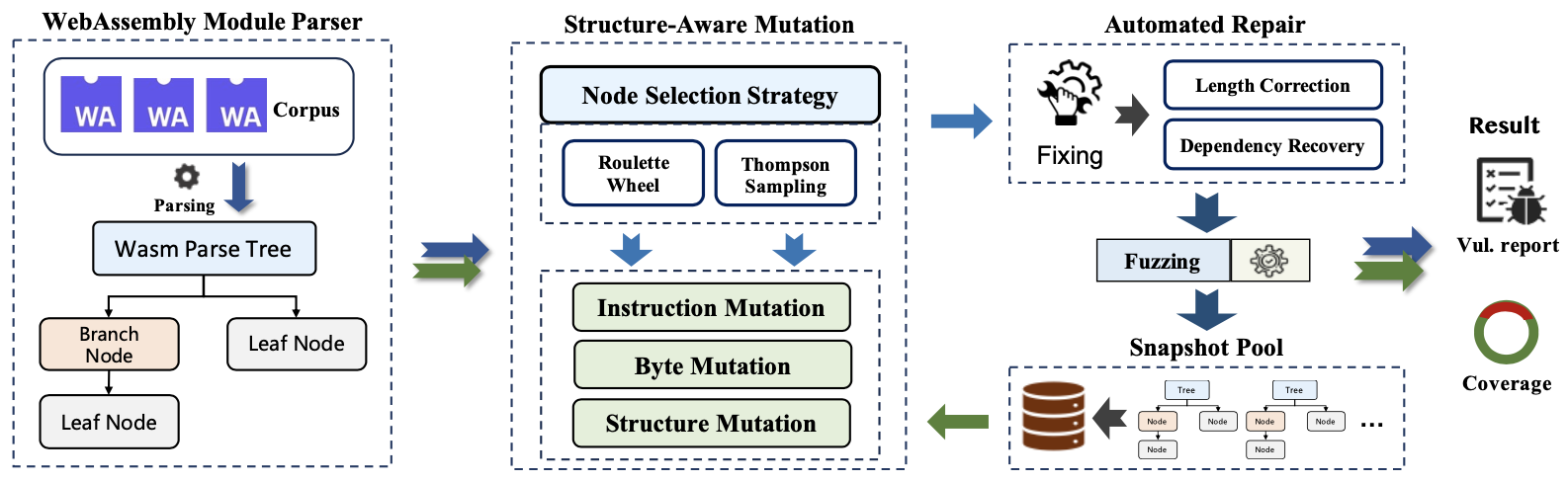
Overall architecture of FreeWavm
We conducted extensive experiments on multiple WebAssembly virtual machines. FreeWavm successfully discovered 69 previously unknown vulnerabilities, 24 of which have been assigned CVE identifiers. In comparison with existing tools, FreeWavm outperforms them in both code coverage and the number of vulnerabilities triggered within a 24-hour testing period.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















