Opportunities in Ethereum's Roadmap, DevCon, and the Pectra Upgrade
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Opportunities in Ethereum's Roadmap, DevCon, and the Pectra Upgrade
Interoperability and liquidity sharing among Layer2 (rollups) are the top concerns for developers.
By: Zeqing Guo, Jeffrey Hu

Looking back at history, it's clear that many cutting-edge technical discussions within the Ethereum developer community have eventually evolved into today’s mainstream applications—ranging from DEXs and lending protocols to rollups and data availability (DA) solutions. These developments naturally present strategic investment opportunities.
So, at the beginning of 2025, what valuable insights can we extract from Ethereum’s roadmap, recent DevCon discussions, and the upcoming Pectra upgrade? This article aims to summarize and explore these topics.
Ethereum Roadmap
The Ethereum roadmap remains a key reference for understanding future directions, encompassing phases such as The Merge, The Surge, The Scourge, The Verge, The Purge, and The Splurge. Vitalik published a series of detailed posts in October outlining each phase:
-
The Merge: Primarily completed the transition from PoW to PoS by merging execution and consensus layers. It also includes improvements to the consensus protocol, such as single-slot finality and lowering validator entry barriers.
-
The Surge: Focuses on scalability enhancements to better support rollups at the base layer. EIP-4844 has already launched; future priorities include PeerDAS (to reduce node load) and cross-rollup interoperability.
-
The Scourge: Aims to mitigate MEV-related issues, including excessive centralization of block builders and concentration of MEV value among large liquid staking providers.
-
The Verge: Involves transitioning from Merkle trees to Verkle trees and SNARK-enabling the EVM.
-
The Purge: Reduces node storage and state maintenance overhead by deleting or archiving historical data, while also addressing technical debt.
-
The Splurge: Encompasses more experimental upgrades, including low-level EVM improvements, account abstraction, and advanced cryptographic applications (e.g., VDFs).
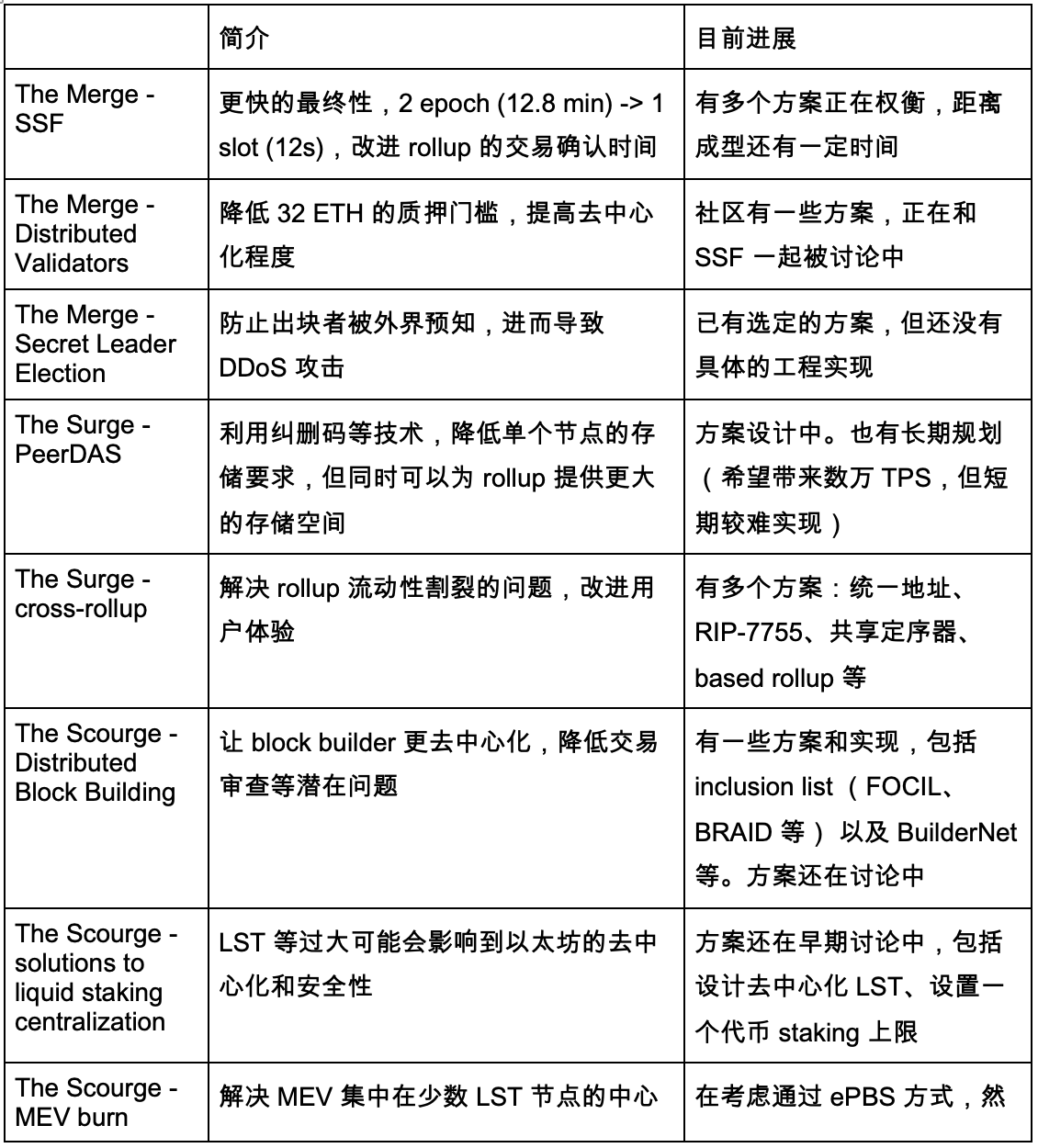
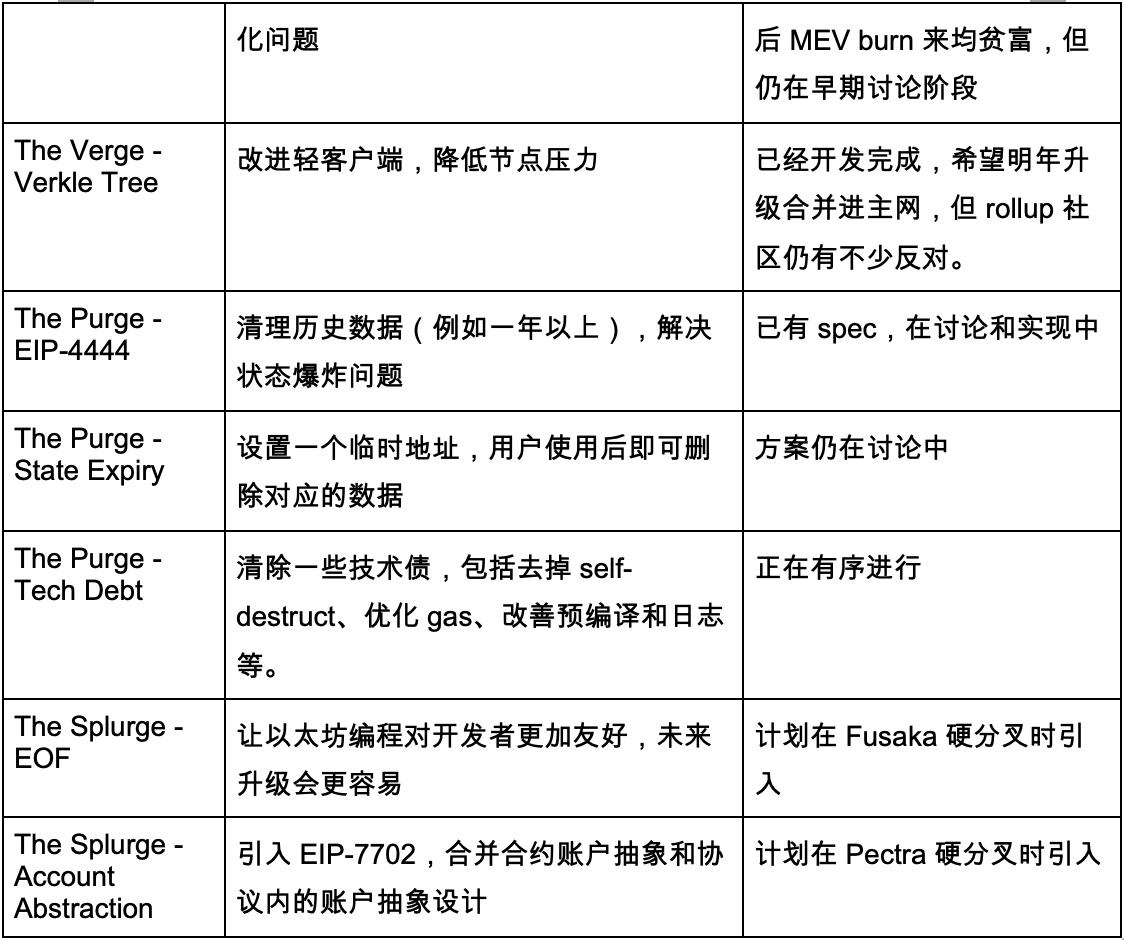
Below is a summary table highlighting key improvements across these phases, their intended effects, and current progress.
DevCon Insights
Beyond the official roadmap, another rich source of insight comes from the recent Ethereum DevCon, where developers discussed pressing challenges and potential solutions.
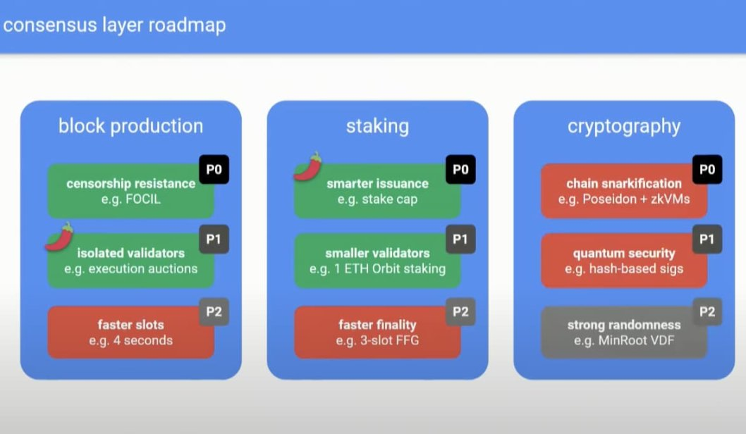
One of the most talked-about topics was Beam Chain. Though jokingly dubbed “Ethereum 3.0” — an inaccurate but telling label — it reflects the community’s appetite for bold new directions. Beam Chain proposes deep architectural changes, including full SNARKification of the stack and redesigns to block production and staking. However, its implementation timeline spans approximately five years, so immediate attention may not be warranted.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gjuenkv1zrw
Rollup-related discussions remained central at DevCon. A major focus was the fragmentation of liquidity and poor interoperability between rollups, which degrades user experience. Multiple talks and panels addressed this challenge and proposed solutions. Additionally, there was discussion around the current maturity level of L2s: only Optimism and Arbitrum have reached Stage 1 (permissioned fraud proofs), while most other L2 projects remain at Stage 0 (centralized upgrades, no fraud proofs), requiring alignment with L1 upgrades.
Other concentrated themes included chain abstraction, pre-confirmations, cryptographic applications, and future network upgrades. We’ll now examine one of the most imminent upgrades: Pectra.
Pectra Upgrade
A near-term development to watch is the expected Q1 2025 Ethereum Pectra upgrade, which includes multiple changes spanning infrastructure to end-user functionality.
EIP-7702: Account Abstraction (AA)
The most user-facing change is EIP-7702. Building on EIP-3074 and advancing EIP-4337, it grants every externally owned account (EOA) the ability to temporarily act as a smart contract account. This enables improved UX features like batched transactions via single signature and gasless interactions. However, it may increase risks such as signature phishing attacks. Since EIP-7702 applies universally to all EOAs, wallet providers must adapt accordingly. Overall, though, the activation of EIP-7702 presents renewed opportunities for AA-focused projects. For deeper analysis, refer to our earlier report.
EIP-7691: Increase Blob Count
Pectra plans to raise the target number of blobs per block from 3 to 6, and the maximum from 6 to 9. Blobs provide cheaper data storage for rollups; increasing their count will further lower rollup costs and strengthen Ethereum’s competitiveness in data availability—albeit at the expense of higher node operational costs. This change benefits rollup projects broadly. Additionally, adjusting both target and cap values allows gas prices to drop faster when blob demand is low and rise more gradually when capacity is saturated.
EIP-7251: Raise Staking Limit
Pectra proposes raising the staking limit per validator from 32 ETH to 2048 ETH. This allows staking providers and large holders to consolidate their stakes into fewer validator slots, reducing the total number of active validators and simplifying operations.
Future Opportunities
All these technical evolutions and research directions could unlock new opportunities. Below are some of the most promising areas.
Inter-Rollup Interoperability
From both the roadmap and DevCon discussions, seamless liquidity transfer and interaction between Layer 2 rollups stand out as top priorities for developers.
The community has proposed various approaches to solve cross-rollup liquidity and composability challenges:
-
Based Rollups: Most current L2s rely on relatively centralized sequencers to order transactions before publishing them to L1, limiting fast and trust-minimized interoperation. One solution is to use L1 itself for transaction ordering, ensuring atomicity across L2s that adopt this shared sequencing mechanism.
-
Shared Sequencers: An alternative approach involves multiple L2s sharing a common set of sequencers to coordinate transaction ordering.
-
Cross-chain Intents: Beyond sequencing, intent-based architectures offer another path to fulfill cross-rollup user demands efficiently.
Several implementations are already progressing: Spire Labs’ Based Stack for based rollups is expected to launch in Q1 2025; shared sequencer projects like Astria, Espresso, and Polygon AggLayer are rolling out and iterating; ERC-7683 is being adopted by Unichain and Arbitrum to address cross-chain liquidity; and Optimism’s ERC-7802 introduces SuperchainERC20, enabling standardized asset representation and seamless transfers across the Superchain ecosystem. These competing models may converge toward a dominant design by 2025.
Account Abstraction
Given that EIP-7702 affects all existing EOA addresses, its activation offers a significant opportunity for account abstraction (AA) projects. When combined with chain abstraction and intent-centric designs, EIP-7702 could enable sophisticated multi-chain or cross-chain workflows. However, given the lukewarm market reception to ERC-4337 so far, the Pectra upgrade might represent the last chance for the AA ecosystem to achieve product-market fit (PMF).
Teams that proactively prepare for EIP-7702—such as Zerodev—could see substantial growth following the Q1 2025 upgrade. Early-mover advantage will likely be decisive.
Cryptographic Applications
Cryptography remains a central theme in both the Ethereum roadmap and DevCon discussions. On the technical front, zkEVM and zkVM frameworks are maturing rapidly. Combining ZKPs with MPC and FHE opens up new hybrid application possibilities. Moreover, emerging cryptographic concepts—such as indistinguishability obfuscation (iO), often called the "crown jewel" of cryptography—attracted notable interest during DevCon.
On the application side, consumer-facing crypto applications present growing opportunities. Zero-knowledge authentication tools—such as ZK Email (especially implementations based on Aztec Noir) and zkTLS—are likely to see broader adoption. Furthermore, recent legal developments—such as the U.S. court ruling that OFAC’s sanctions against Tornado Cash exceeded its authority—may alleviate compliance concerns around privacy-preserving applications.
Special thanks to Zhixiong Pan and Yan for their review and suggestions!
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News