Swift to Launch Digital Asset Experiment (2025): A Multidimensional Analysis and Discussion of Market Impact
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Swift to Launch Digital Asset Experiment (2025): A Multidimensional Analysis and Discussion of Market Impact
On October 3, Swift announced that it is conducting experiments on digital asset and digital currency transactions, with plans to launch enhanced testing next year.
Author: Cage / Mat / Darl / WolfDAO
Proofreading: Punko
Editor-in-Chief: Vessel
Preface
As the central hub of the global cross-border payment system, Swift (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) has long ensured the smooth operation of international financial transactions through standardized payment protocols and centralized oversight. Today, by deeply integrating blockchain and Web3 technologies, Swift is expanding into digital asset trading and exploring the transformation of future global payment systems. This initiative not only aims to optimize the efficiency of existing payment infrastructures but also signals a profound convergence between traditional finance and blockchain technology—its implications extending far beyond mere payment innovation. This article provides an in-depth analysis of Swift’s digital asset transaction experiments from multiple perspectives including technology, market dynamics, compliance, risk management, and competitive landscape, examining the driving forces behind this shift, its future prospects, and its broader impact on the global financial ecosystem.

I. Technological Innovation: From Traditional Cross-Border Payments to Blockchain Interoperability
1. Pain Points of Traditional Payments and the Disruptive Potential of Blockchain
Traditional cross-border payments suffer from slow processing times, high costs, and limited transparency. Although Swift connects over 11,500 financial institutions globally, transaction settlement can still take several days. In particular, small-value, high-frequency transactions remain costly and inefficient. In contrast, blockchain technology leverages decentralized ledgers and smart contracts to drastically reduce transaction times and enhance transparency. For example, Ripple enables cross-border payments within seconds, while traditional Swift transfers typically require one to three days.
-
Traditional Payments + Blockchain Technology
Swift is experimenting with blockchain integration by leveraging distributed ledger technology to optimize payment pathways. Through collaboration with Chainlink, Swift employs the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) to seamlessly connect different blockchains, breaking down data silos and enhancing payment efficiency to build a more flexible global payment network.
-
Previous Test Results
On August 31, 2023, Swift conducted blockchain-based payment transfer trials in a test environment, successfully demonstrating that its infrastructure can facilitate tokenized value transfers across multiple public and private blockchains. This experiment addressed interoperability challenges associated with managing tokenized assets across disparate blockchain networks.
Swift released findings from a series of new experiments showing its infrastructure can seamlessly enable tokenized value transfers across multiple public and private blockchains. These results could eliminate major friction points hindering the growth of the tokenized asset market, enabling it to scale globally as it matures.
Source: Swift unlocks potential of tokenisation with successful blockchain experiments
To address these challenges, Swift has partnered with over a dozen leading financial institutions and Chainlink, coordinating real-world institutional resources and using Chainlink to establish secure, operable channels for on-chain interoperability.
Swift's partners include:
-
TradiFi: Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited (ANZ), BNP Paribas, The Bank of New York Mellon, Citibank, Clearstream, Euroclear, Lloyds Banking Group, SIX Digital Exchange (SDX), and The Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation.
-
Web3: Chainlink serves as an enterprise abstraction layer, securely connecting the Swift network to the Ethereum Sepolia network, while Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) enables full interoperability between source and destination blockchains.
The results indicate that Swift has successfully demonstrated its ability to provide single-point access to multiple public blockchains by leveraging existing Web3 security infrastructure, reducing operational complexities and minimizing the support required from investment institutions developing RWA (Real World Assets) applications.
2. Cross-Chain Interoperability: Breaking Down Blockchain Silos
Cross-chain interoperability remains one of the key bottlenecks limiting widespread blockchain adoption. Each public blockchain operates with its own architecture and consensus mechanism, making asset transfers between chains extremely challenging. By partnering with Chainlink and adopting its Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), Swift is exploring ways to manage liquidity across multiple blockchains.
Swift’s experiments go beyond solving cross-chain liquidity issues—they enhance the flexibility of its network, allowing financial institutions to explore multi-chain digital asset management without compromising security or regulatory compliance. This lays the technical foundation for more complex financial use cases in the future, such as cross-border tokenized asset trading and real-time settlement.
Once matured, this cross-chain interoperability will allow global financial institutions to freely move assets across different blockchain networks, accelerating large-scale adoption of digital currencies and tokenized assets in global markets. In the long term, this will significantly lower operating costs for financial institutions and increase global asset liquidity.
II. Market Expansion: The Future of Tokenized Assets and Digital Currencies
1. The Rise of Tokenized Assets and Global Market Impact
Tokenized assets refer to real-world assets—such as real estate, bonds, stocks, and artworks—that are digitized and managed or traded on blockchains. Market analyses project that the global tokenized asset market could reach $30 trillion by 2030. The increased liquidity, transparency, and efficiency brought by tokenization are poised to have a transformative impact on global financial markets.
One of Swift’s experimental goals is to leverage its existing global network to support cross-border flows of tokenized assets. By combining on-chain and off-chain mechanisms, Swift can streamline the tokenization process and offer a standardized financial infrastructure that ensures diverse asset types can circulate freely worldwide. This framework isn't just designed for today’s digital assets—it prepares the ground for increasingly complex and diversified financial products in the future.
If successfully scaled, Swift’s experiments could fundamentally transform how financial institutions manage and trade assets. More high-value assets will be tokenized, investor portfolios will become more flexible and diversified, and barriers to cross-border investment will fall—greatly deepening and expanding global capital markets.
2. Integration of Digital Currencies and CBDCs
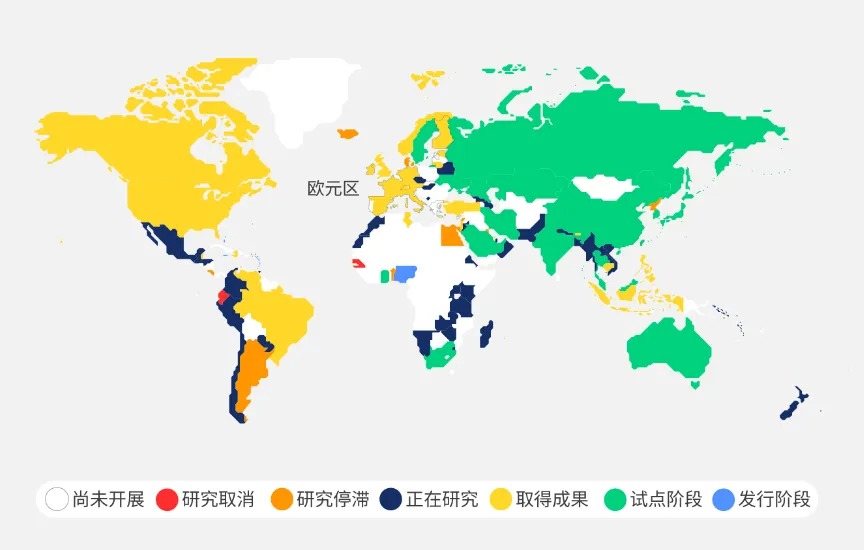
Nations around the world are actively researching and developing central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). For instance, China’s digital yuan has entered pilot stages, while Singapore, the European Union, and others are exploring their own CBDC initiatives. CBDCs aim to redefine the global payment and monetary system by reducing intermediaries, lowering transaction costs, and improving transparency.
Global Status of Central Bank Digital Currency Development – Source: World Economic Forum @10xWolfDAO compilation
Swift’s experiments demonstrate its technical capability to integrate digital currencies, including CBDCs. By combining its global payment network with blockchain interoperability technology, Swift offers a standardized global platform for digital currency trading, enabling seamless interoperability among central banks. This provides technical support for interconnected monetary policies and simplifies cross-border payment and settlement processes.
Swift’s support for CBDCs could become a pivotal component of the global digital currency ecosystem. In the future, central banks may leverage Swift’s global network to enable cross-border CBDC flows, accelerating the modernization and digitization of the global monetary system. For financial institutions, this would greatly simplify cross-border payments and settlements while offering compliant and secure channels for digital currency transactions.
III. Risk Management: Security and Stability in Digital Assets
1. Risk Control for Tokenized Assets
The rapid expansion of tokenized assets brings heightened market volatility and operational risks, particularly during cross-chain transfers and asset management. Swift’s experiments focus not only on payment efficiency but also on enhancing the security and transparency of digital assets through technological solutions.
Through its partnership with Chainlink, Swift leverages decentralized oracle price feeds and blockchain immutability to ensure high levels of transparency and security during cross-chain transfers of tokenized assets. Additionally, Swift’s off-chain global network provides critical security support, enabling financial institutions to conduct digital asset transactions under controlled risk conditions.
If Swift’s experiments effectively mitigate risks associated with tokenized assets, they could significantly boost institutional confidence. This would not only promote broader market adoption but also provide valuable insights for global regulators, helping lay the groundwork for more refined digital asset management regulations.
2. Market Volatility and Financial Stability
High volatility and lack of regulation in blockchain markets remain top concerns for traditional financial institutions. Beyond improving transaction efficiency, Swift is testing how the robustness of its global payment network can buffer the impact of market volatility on financial stability.
By establishing an interoperable framework between on-chain technologies and off-chain financial infrastructure, Swift creates a shock-absorbing mechanism that maintains transaction safety and stability even during turbulent periods. If proven effective, this approach could encourage more financial institutions to enter the digital asset market, significantly increasing market liquidity and accelerating the digital transformation of global capital markets.
IV. Regulation and Compliance: Challenges in Cross-Border Digital Asset Transactions
1. Divergence and Harmonization of Global Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory approaches to digital assets vary significantly across jurisdictions. The United States enforces strict oversight on cryptocurrencies, while regions like Singapore and Europe adopt relatively open attitudes toward blockchain and digital assets. As a core pillar of the global payment system, Swift must navigate this fragmented regulatory landscape and find a balanced path forward.
Swift’s experiments showcase its efforts to ensure compliance across diverse regulatory environments. By collaborating with numerous global financial institutions, Swift tests the regulatory compatibility of its technical solutions in various jurisdictions. This provides practical reference points for future cross-border digital asset transactions and supports gradual harmonization of global regulatory standards.
Successful outcomes from Swift’s experiments will offer valuable lessons to global regulators, promoting standardized development in digital asset markets. With clearer regulatory frameworks, cross-border digital asset transactions can proceed with reduced compliance risks, fostering wider adoption.
2. Compliance Needs of Central Banks and Financial Institutions
As more central banks and major financial institutions engage in digital asset and CBDC development and trading, compliance becomes a critical factor determining large-scale adoption. Swift’s current experiments demonstrate its capacity to address compliance challenges, offering a model for compliant operations in the digital asset space.
As a long-trusted provider of global financial infrastructure, Swift has accumulated extensive experience in regulatory compliance. By integrating blockchain technology with its global network, Swift delivers actionable compliance frameworks for digital asset transactions and CBDC management. In the future, this will empower global financial institutions to participate confidently in digital asset markets while meeting stringent regulatory requirements across jurisdictions.
Swift’s compliance-focused experiments lay a solid foundation for the broad adoption of digital assets. Central banks and financial institutions will be able to leverage Swift’s global network to engage in digital asset trading and cross-border payments—secure in the knowledge that compliance is assured.
V. Competition and Strategy: Reshaping the Payment Landscape
1. Competition from Fintech and Blockchain Payment Networks
Blockchain-based payment networks like Ripple and Stellar, along with fintech companies such as PayPal and Square, are rapidly gaining ground and challenging the dominance of traditional payment systems. With innovative solutions and low fees, they are gradually eroding Swift’s share of the cross-border payment market.
Swift’s digital asset experiments represent a proactive response to this competitive pressure. By incorporating blockchain technology, Swift not only defends its central role in the global payment ecosystem but also explores new models for the future of payments. This initiative marks not just a technical upgrade, but the beginning of a strategic transformation.
If successful, Swift’s experiments will redefine the competitive dynamics of the global payment industry. The future landscape will be more diverse, with accelerated modernization driven by both competition and collaboration among traditional financial institutions, blockchain firms, and fintech innovators.
2. Strategic Vision for Future Payment Architecture
Through its experiments, Swift is showcasing its technological innovation capabilities and laying out a strategic blueprint for the future of payment systems. As blockchain technology and the tokenized asset market expand, Swift may evolve from a global payment network provider into a foundational infrastructure player for the global digital asset market.
Swift is building the architecture for future payments—an infrastructure increasingly reliant on blockchain and decentralized networks. By deeply integrating with traditional financial institutions, Swift retains its existing client base while delivering more flexible and innovative solutions for digital asset trading and management.
However, alongside its positive momentum, Swift’s limitations cannot be ignored. As a cornerstone of global financial infrastructure, Swift must strictly adhere to international financial regulations—making full decentralization practically unattainable.
VI. Swift’s Geopolitical Role and Centralized Control
1. Could It Become an Enhanced Tool for Political Monopoly?
Swift’s digital asset transaction experiments are closely tied to geopolitical dynamics, especially its role in international sanctions. As the backbone of the global payment system, Swift has been used by the U.S. and Western nations as a key instrument for imposing economic sanctions. Countries like Russia and Iran, affected by geopolitical conflicts and excluded from the Swift system, have begun seeking alternatives. Russia’s TON chain (The Open Network), which has developed rapidly and now includes payment and financial services, exemplifies such an effort.
In this context, Swift’s digital asset experiments can be seen as the traditional financial system’s response to the rise of decentralization. The experiments illustrate how Swift aims to integrate digital currencies with fiat systems, preparing for a future multipolar financial ecosystem.
From a geopolitical standpoint, the rapid development of decentralized finance (DeFi) could undermine the effectiveness of Western-led sanctions enforced via Swift. Therefore, Swift’s collaboration with Web3 technologies may not solely be about improving efficiency and innovation—it may also reflect a strategic move to adapt to shifting balances of global financial power.
2. Does This Signal a Political Shift Toward Easing Restrictions on Crypto Assets?
Swift’s experiments do not necessarily indicate a relaxation of regulatory constraints on crypto assets within mainstream finance. Rather, they reflect traditional institutions exploring how to harness blockchain’s efficiency and security benefits within a compliant framework. By incorporating digital asset transactions into its global payment network, Swift is paving the way for the legitimization and regulation of crypto assets—not enabling their unrestricted growth. Thus, this initiative resembles an attempt to formalize and regulate crypto assets, rather than a political signal of broad deregulation.
In the current geopolitical climate, Swift is likely prioritizing the security and traceability of financial transactions worldwide. Therefore, its experiments reflect a cautious embrace and integration of crypto assets—not a loosening of cryptocurrency regulations or a move toward deeper alignment with decentralized ecosystems. This suggests that Swift’s digital asset initiatives are primarily exploratory, focusing on how to leverage decentralized technologies within regulated frameworks.
3. The Future of Global Payments: Convergence of Mainstream Finance and Blockchain
Swift’s experiments do not eliminate its role as an intermediary. Unlike fully decentralized consensus mechanisms such as those used by Bitcoin or Ethereum, Swift enhances the flexibility and operability of its centralized network using blockchain technology. While Swift may enable digital asset trading on its network, it retains centralized control over participants and transaction processes.
These experiments reflect traditional financial institutions’ growing recognition of blockchain and crypto assets’ potential in the future global financial system—but without relinquishing control. Instead, Swift is integrating regulatory frameworks and technological innovations to ensure crypto assets are incorporated into the existing system in a compliant manner.
Swift’s approach represents a hybrid model—one that adopts blockchain’s technological advantages while preserving the core control and regulatory structure of traditional finance. The goal is to maintain efficiency and transparency in the financial system without weakening regulatory oversight or centralized authority.
This gradual fusion may foreshadow a future global payment landscape defined by hybridity: a coexistence of traditional fiat systems, digital assets, and decentralized finance—where the latter remains subject to strict regulation and control.
The ultimate outcome of this hybrid model will depend on the level of cooperation among global financial institutions, regulators, and technology providers. Swift’s experiments offer a significant directional signal—but they lean more toward controlling the evolution of crypto assets than liberalizing them.

VII. Impact on the Existing Crypto Market
Swift’s digital asset transaction experiments aim to deeply integrate blockchain technology with the global financial network. This move is expected to significantly affect multiple sectors and specific projects within the crypto market:
1. Cross-Border Payments ⬇️
Cross-border payments are a major segment in the crypto market. Many crypto projects offer fast, low-cost cross-border payment services via blockchain. As the backbone of the global payment network, Swift’s entry into this space will bring substantial disruption.
1.1 Ripple (XRP)
Ripple provides real-time cross-border payment solutions through its XRP Ledger and has already attracted numerous banks and financial institutions. Its core competitive advantage lies in high-speed payments and extensive network coverage. However, Swift’s digital asset experiments, which also enable cross-chain and real-time payments via blockchain, could directly undermine Ripple’s market position.
Customer attrition risk: As Swift integrates blockchain technology into its network, existing Ripple banking clients may be drawn to Swift’s globally recognized and highly compliant payment infrastructure—especially given the SEC’s ongoing legal scrutiny of Ripple, compared to Swift’s strong regulatory standing.
1.2 Stellar (XLM)
Stellar, similar to Ripple, focuses on cross-border payments, particularly in small-to-medium transactions and financial inclusion. It offers fast, low-cost payment channels, attracting financial institutions and enterprises in developing countries.
-
Market share at risk: Swift’s entry could diminish Stellar’s appeal in the cross-border payments market, as financial institutions may prefer Swift’s blockchain solution for its broader global reach and stronger compliance support.
2. Stablecoins and Fiat Payment Solutions ⬇️
Swift’s global payment network is progressively integrating blockchain technology, particularly in the area of tokenized assets and fiat payment integration. This poses direct challenges to stablecoins and fiat-linked payment platforms.
2.1 USDC and USDT
USDC and USDT are the two most widely used stablecoins, serving cross-border payments, DeFi, and exchange trading. Their success stems largely from bridging fiat and crypto assets.
-
Compliance competition: Swift enjoys a significant advantage with its global compliance infrastructure. If Swift’s digital asset network offers functionality comparable to stablecoins but with superior adherence to global regulatory standards, USDC and USDT may lose institutional appeal—especially in large-scale cross-border transactions. (While USDT is working toward compliance and USDC boasts strong institutional backing, both would still be at a disadvantage relative to Swift.)
-
Declining demand for stablecoins: If Swift’s tokenized fiat payment network enables seamless cross-border transactions, financial institutions and large corporations may reduce reliance on USDC and USDT—particularly when strict regulatory compliance is required.
2.2 Facebook (Meta)'s Diem
Although Facebook’s Diem (formerly Libra) project has been shelved, its original vision was to create a global payment network using stablecoins. Swift’s digital asset experiments may attract institutions and corporate clients who once considered Diem, steering them toward Swift as a safer, more compliant alternative.
-
Loss of market opportunity: Swift’s global influence and regulatory network would severely weaken the competitiveness of Diem-like stablecoin projects. Financial institutions are more likely to choose Swift for fiat-digital asset conversion and payments.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ⬇️
The DeFi sector has grown rapidly, with decentralized lending, liquidity mining, and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) attracting massive user bases and capital. However, Swift’s compliant blockchain-based payment and asset management network could disrupt this space.
3.1 Aave and Compound (Lending Platforms)
Aave and Compound are leading decentralized lending platforms where users borrow funds by collateralizing crypto assets. The appeal of DeFi lending lies in its non-custodial and decentralized nature.
-
Risk of institutional customer loss: Swift’s compliance and connections to global financial institutions may attract institutional investors who have been hesitant to enter DeFi. These institutions may prefer conducting lending activities within Swift’s blockchain network to ensure global regulatory compliance.
3.2 Uniswap and SushiSwap (Decentralized Exchanges)
DEXs like Uniswap and SushiSwap rely on liquidity providers to offer peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. Their core strengths are openness and decentralized trading mechanisms.
-
Liquidity competition: Swift’s network could divert liquidity from decentralized exchanges by integrating financial institutions and mainstream investors. Institutional traders may favor a regulated, compliant platform over a DEX.
-
Increased compliance and technical pressure: As Swift attracts more compliant transaction volume, DEXs may face greater pressure to meet regulatory standards. They will need to balance compliance with innovation to retain users.
4. Tokenized Asset Platforms ⬇️
Swift’s digital asset experiments focus heavily on cross-border movement and management of tokenized assets—especially the tokenization of traditional assets like real estate and bonds—and their circulation within the global financial system. Existing tokenized asset platforms will face direct competition from Swift’s market entry.
4.1 Polymath and Securitize
Platforms like Polymath and Securitize specialize in tokenizing securities and other assets, offering blockchain-based solutions for financial institutions to digitize and manage traditional assets.
-
Compliance competition: Swift’s global payment network offers a more mature and compliant framework. Financial institutions may opt for Swift over decentralized platforms to ensure adherence to international regulations.
-
Market share competition: Given Swift’s global reach, its tokenized asset solutions could attract more large institutional clients, directly threatening the market positions of existing decentralized platforms.
4.2 RealT and Propy (Real Estate Tokenization Platforms)
RealT and Propy focus on real estate tokenization, using blockchain to streamline property transactions—particularly in cross-border investments.
-
Risk of losing cross-border investment clients: Swift’s compliant cross-border investment channels, powered by its global network and blockchain tech, may attract high-net-worth individuals and institutions, reducing demand for decentralized platforms. This could lead to market erosion for RealT and Propy, especially in premium real estate investment.
-
Liquidity competition for tokenized assets: Swift’s entry could boost market liquidity for high-value tokenized assets, placing immense competitive pressure on existing decentralized real estate platforms.
5. Cross-Chain Interoperability Platforms ⬆️
Swift’s collaboration with Chainlink enables interoperability across multiple blockchains. Unlike its disruptive impact on other sectors, this development could benefit existing cross-chain platforms.
5.1 Chainlink
While Chainlink is a key partner in Swift’s cross-chain interoperability efforts, its position as a leader in decentralized oracles and cross-chain solutions may face new challenges as Swift’s experiments mature.
-
Shift in technical direction: As Swift integrates cross-chain functionality, Chainlink may need to further advance its technology or expand into more decentralized use cases to maintain market leadership.
-
Market synergy: At the same time, Swift’s experiments could drive broader adoption of Chainlink’s technology in global financial markets, enhancing its overall market value.
6. Digital Currency Sector ⬆️
Swift’s digital asset experiments will inevitably influence the digital currency space, particularly in the competition between central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and stablecoins.
6.1 CBDC Projects
Central banks worldwide are actively developing and piloting CBDCs, including China’s digital yuan and the European digital euro. If Swift’s blockchain payment network can seamlessly integrate CBDCs, it could bring greater liquidity and innovation to the global payment system.
-
Accelerated globalization of CBDCs: Swift’s integration of CBDCs could speed up their global adoption, enabling faster integration into mainstream payment systems and weakening the position of decentralized stablecoins in the crypto market.
Conclusion
Swift’s digital asset transaction experiments represent more than just a technological exploration—they are a cornerstone of its future payment strategy. By integrating blockchain technology, Swift is innovating and strategically positioning itself across payment efficiency, tokenized asset management, risk control, compliance, and global competition. The success of these experiments could dramatically improve the efficiency of global payment systems and drive widespread adoption of digital currencies and tokenized assets.
Going forward, Swift will continue to play a pivotal role in financial and technological innovation. The outcomes of its experiments will profoundly shape the global payment network and financial markets, accelerating the transition toward a more efficient, secure, and digital financial ecosystem. However, its inherent centralization means it won’t be welcomed with open arms by the crypto community. On the contrary, due to its dominant market position and payment-centric nature, Swift’s move could significantly disrupt and reshape the existing crypto landscape.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News