Understanding Mango Network: Competing in the L1 New Arena as a Multi-VM Full-Chain Infrastructure Network
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Understanding Mango Network: Competing in the L1 New Arena as a Multi-VM Full-Chain Infrastructure Network
Mango Network, as an innovative full-chain infrastructure network, integrates the core advantages of OPStack technology and MoveVM to build an efficient blockchain network that supports cross-chain communication and multi-virtual machine interoperability.
The multi-VM architecture is the optimal solution to current blockchain scalability and performance bottlenecks, emerging as a new trend driving deeper integration within on-chain ecosystems. As an innovative full-stack infrastructure network, Mango Network combines the core advantages of OPStack technology and MoveVM to build a highly efficient blockchain network that supports cross-chain communication and multi-virtual machine interoperability. With superior compatibility, scalability, developer-friendliness, multi-chain interoperability, and vast future potential, Mango Network has gained broad market recognition.
Multi-VM Architecture: The Rising Star of the Blockchain Industry
Amid the excitement of Token2049 in Singapore, the blockchain industry is undergoing profound reflection and transformation. On the surface, the sector appears captivated by the flourishing landscape of "thousands of chains," but as decentralized application ecosystems grow increasingly diverse and complex, breaking down barriers between blockchain ecosystems and advancing cross-chain compatibility have become more urgent than ever. Today, "compatibility" has surpassed "high performance" as the central challenge in on-chain ecosystem development.
For years, many organizations in the blockchain space have viewed parallel execution (parallel EVM) as the key technical path to enhancing network performance. Parallel EVM networks such as Artela, MegaETH, and Sei aim to drive broader adoption of new applications by increasing throughput and transaction processing capacity. Indeed, parallel EVM excels in high-volume transaction environments, making it especially suitable for applications with stringent performance demands like DeFi and DEXs.
However, as blockchain ecosystems diversify, performance improvements alone are no longer sufficient to meet industry needs. The future development of on-chain ecosystems depends not only on enhanced transaction processing capabilities but also on stronger ecosystem compatibility—especially in the increasingly complex environment of cross-chain and multi-chain interactions.
As the importance of cross-chain interaction and interoperability becomes more evident, the multi-VM (Multi-Virtual Machine) architecture has gradually emerged as a pivotal technology. Thanks to its flexibility and adaptability across ecosystems, multi-VM is becoming essential in addressing these challenges. Against the backdrop of rapidly expanding on-chain application ecosystems, multi-VM architecture is now at the heart of competition among Layer 1 platforms, opening up new possibilities and innovation opportunities for the future of blockchain. This trend marks a shift in the industry—from a singular focus on "high performance" toward comprehensive "ecosystem integration," with multi-VM architecture serving as the core enabler of this vision.
In this context, multi-VM architecture is gaining increasing attention and adoption due to its multiple technical advantages. By supporting various virtual machines (such as EVM, MoveVM, WASM, etc.), multi-VM provides developers with greater tooling choices and flexibility, significantly lowering development barriers and attracting talent from diverse technical backgrounds. This enhances platform scalability and interoperability, bridging gaps between heterogeneous blockchains and improving capital liquidity across chains.
Projects like Mango Network exemplify the multi-VM approach, integrating the strengths of OPStack and MoveVM to create a full-chain infrastructure network supporting cross-chain communication and multi-VM interoperability. This innovation not only boosts platform scalability but also promotes interoperability among heterogeneous chains, solving the long-standing issue of fragmented on-chain capital liquidity.
In today’s blockchain market, the evolution of cross-chain applications demands higher levels of ecosystem integration. Multi-VM projects break down technical silos between different chain ecosystems by supporting multiple smart contract languages and virtual machines, providing broader space and flexibility for future decentralized applications. For large-scale dApps, compatibility will be the decisive factor for success. Such compatibility not only fuels sustainable ecosystem growth but also fosters the emergence of more innovative applications. As the market matures further, multi-VM architecture is poised to play a pivotal role in Layer 1 competition and become a core driver of next-generation blockchain innovation.
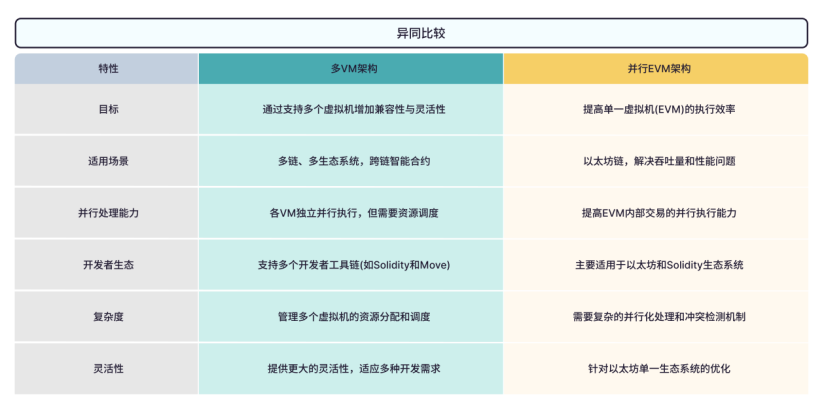
Mango: A Superior Architecture Powering a Multi-VM Full-Chain Infrastructure Network
Mango Network's Layer 1 solution is strongly supported by the Move language, offering developers and users a secure, modular, and high-performance Web3 infrastructure. With a transaction processing speed reaching up to 297,450 TPS, it demonstrates exceptional performance while maintaining high standards of standardization, scalability, and interoperability.
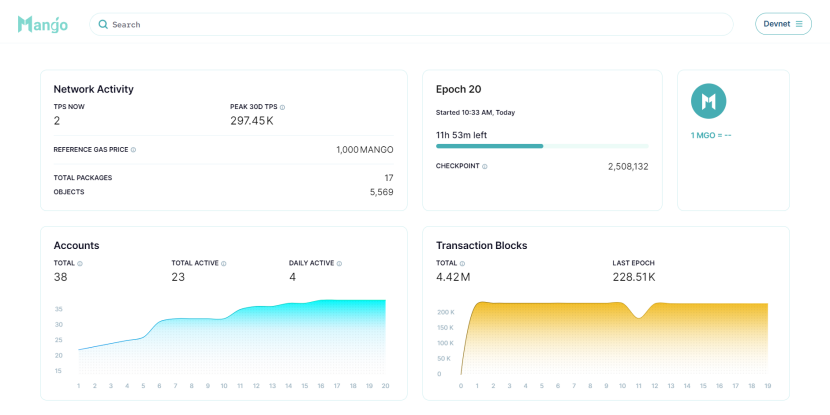
Mango Network Devnet Up to 297.45K TPS
Mango Network’s Layer 2 solution, OP-Mango—built on OPStack—offers robust cross-chain communication capabilities, setting it apart from traditional Layer 2 solutions. It connects Ethereum’s EVM layer with Mango Network’s MoveVM layer through cross-chain communication contracts, preserving compatibility with EVM smart contracts while enabling more flexible and secure asset management and contract operations via MoveVM. This design allows developers to leverage the strengths of both virtual machines, expand use cases, and deliver richer services to users. By integrating MoveVM and EVM, Mango Network achieves seamless cross-chain communication and multi-VM interoperability.
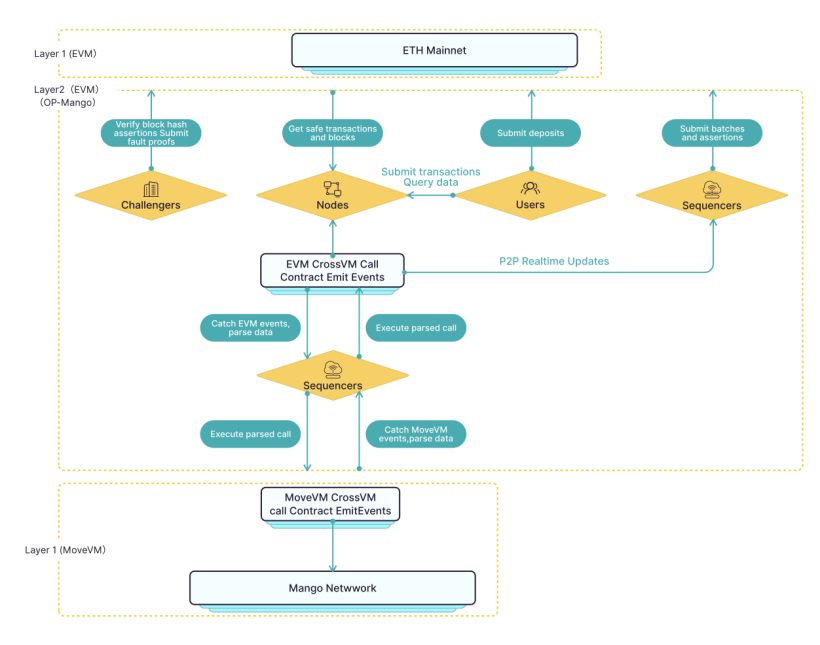
Mango Network: A Multi-VM Full-Chain Infrastructure Network
The multi-VM full-chain infrastructure of Mango Network relies on the following key technical principles:
1. Multi-Virtual Machine Parallel Execution Principle
Mango Network uses both MoveVM and EVM to process on-chain transactions and smart contract calls. Different virtual machines handle different types of contracts and operations, yet coordinate full-chain activities through cross-chain communication bridging.
-
MoveVM: MoveVM specializes in asset management, complex contract logic, and parallel execution. Its parallelism stems from dynamically scheduling transactions based on state dependencies among contracts and transactions, allowing non-conflicting transactions to execute simultaneously. This increases network throughput and improves overall execution efficiency.
-
EVM: As the core virtual machine of the Ethereum ecosystem, EVM supports a wide range of smart contracts. Integrated with OP-Mango, EVM can relay its transactions and contract events to MoveVM for processing, enabling cross-chain contract invocation.
2. Cross-VM Communication and Data Transfer Principle
A core challenge of multi-VM infrastructure lies in enabling data sharing and contract invocation between different virtual machines. Mango Network bridges EVM and MoveVM through OP-Mango, achieving cross-VM communication and collaboration. This relies on three critical components: event capture, data serialization, and cross-chain contract invocation:
-
Event Capture: When a smart contract within one VM triggers an event (e.g., asset transfer or contract execution), the cross-chain sequencer captures it. The sequencer is a system component responsible for monitoring state changes in virtual machines.
-
Data Serialization and Transmission: Captured events are serialized into a universal format recognizable and processable by the other VM. OP-Mango’s cross-chain sequencer ensures that event data from EVM is converted into a form usable by MoveVM, triggering corresponding contract executions in MoveVM.
-
Contract Inter-calling: The ultimate goal of cross-VM communication is to enable mutual contract invocation. Through cross-chain event transmission, smart contracts on EVM and MoveVM can call each other, ensuring complete execution of cross-chain logic. For example, after a contract on EVM completes an operation, MoveVM can receive the event and execute corresponding actions or contract logic accordingly.
3. Layer 2 Scaling and Batch Processing Principle
To enhance transaction processing efficiency, OP-Mango adopts a Layer 2 scaling solution that processes large volumes of transactions off-chain and periodically submits them to the mainnet for settlement. This architecture is built upon the following technical principles:
-
-
Batch Processing and Assertion: OP-Mango packages transactions from the Layer 2 network into batches, submitting them collectively to reduce congestion on the mainnet. Each batch includes state changes and assertions for multiple transactions. After submission to the Ethereum mainnet, MoveVM on Mango Network performs final validation and settlement.
-
Assertion and Dispute Resolution Mechanism: To ensure cross-chain transaction security, OP-Mango introduces an assertion mechanism. An assertion serves as proof of a series of transaction states; if no dispute arises after submission, the transaction is confirmed. In case of disputes, the network resolves conflicts by verifying evidence on the data chain. This mechanism guarantees the security and consistency of cross-chain transactions.
-
4. Cross-Chain Asset Management Principle
Cross-chain asset management in Mango Network primarily relies on the interoperability mechanism between EVM and MoveVM to enable secure cross-chain asset transfers and settlements. The core principles are as follows:
-
-
State Synchronization and Transfer: Cross-chain asset transfers are achieved through state synchronization via OP-Mango. Asset operations executed on EVM are serialized and transmitted to MoveVM, which updates the corresponding asset state, completing the transfer from EVM to MoveVM.
-
Two-Way Settlement: Cross-chain asset transfer and settlement are not limited to EVM-to-MoveVM direction; asset states in MoveVM can also be relayed back to EVM via the cross-chain sequencer, ensuring bidirectional settlement between virtual machines. This process guarantees end-to-end security of cross-chain operations and maintains transaction data consistency.
-
Core Functionality: The Internal Logic of Mango Network
OP-Mango, a Layer 2 network built on OPStack, leverages EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatibility to process user transaction requests. Users can submit transactions and query block data through nodes. OP-Mango nodes retrieve secure transaction data from the Ethereum mainnet and broadcast it via a P2P network, ensuring timely network synchronization.
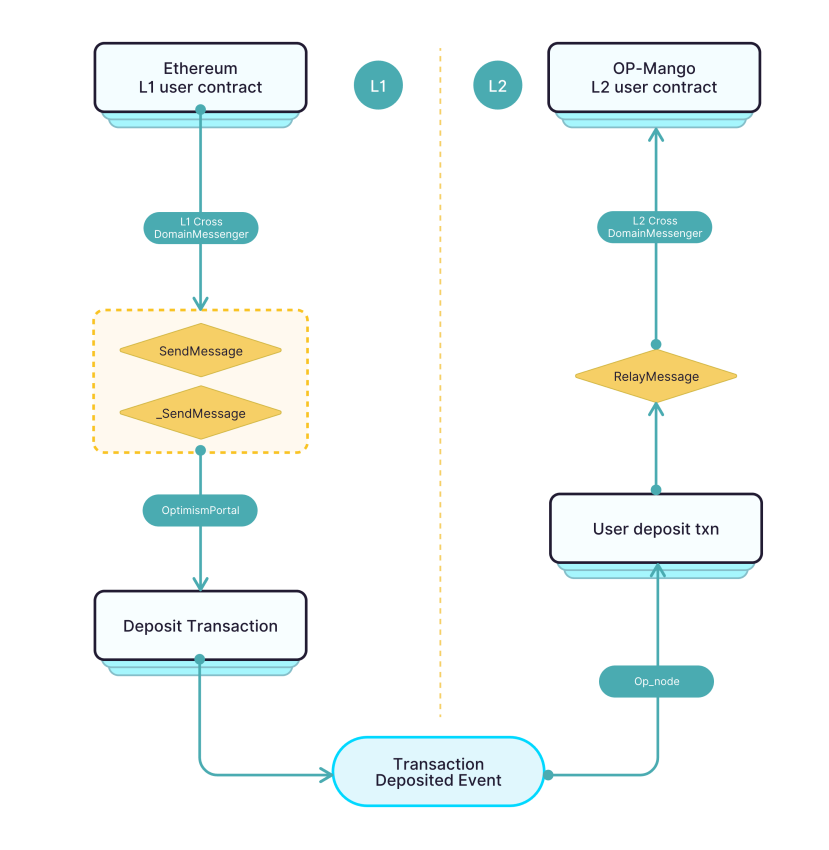
Ethereum and OP-Mango Cross-Chain Communication
In this process, the Sequencer is responsible for ordering, packaging, and submitting batch data for the Layer 2 network. Specifically, the Sequencer receives transactions from users and nodes, orders them, and packages them into batches submitted to the Ethereum mainnet. The native token MGO serves as gas for batching. Meanwhile, the Sequencer performs assertion operations, submitting state updates and transaction records from the Layer 2 network in bulk to validators on the mainnet, ensuring consistency between OP-Mango and Ethereum.
The defining feature of OP-Mango is its tight interaction and settlement with MoveVM on the Mango Network via cross-chain communication contracts. This design enables the Layer 2 network to not only support EVM but also interact directly with MoveVM smart contracts, achieving true cross-chain interoperability. In the architecture diagram, the Sequencer captures events from either EVM or MoveVM, parses them into cross-chain calls, and triggers contract execution in the other virtual machine. Through this cross-VM sequencer, OP-Mango enables contract interoperability across different VM environments, completing secure settlements and data synchronization between EVM and MoveVM. While MoveVM focuses on security and programmability, offering a more flexible contract execution environment, it complements the EVM layer. This design empowers developers to harness the strengths of both virtual machines simultaneously.
Technology-Driven: Architectural Advantages and Market Positioning
In Mango Network, the security features of MoveVM are fully leveraged. Its design philosophy emphasizes minimizing security vulnerabilities and runtime errors through static type checking and modular programming patterns. Furthermore, the multi-VM architecture brings greater flexibility and scalability to the network, allowing developers to freely deploy and execute smart contracts across different virtual machines, thereby advancing cross-chain communication and asset interoperability.
As the first multi-VM execution network to adopt MoveVM, Mango Network successfully integrates MoveVM’s outstanding asset security characteristics with the scalability offered by a multi-VM environment. This combination not only ensures asset security but also effectively addresses liquidity limitations within the Move ecosystem and bridges the gap with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) ecosystem by providing a diversified VM execution environment. Through this innovative integration, Mango Network achieves a powerful synergy between asset security and EVM-based liquidity, laying a solid technical foundation for building a comprehensive on-chain foundational trading infrastructure.
-
Mango Network official
-
Web: https://mangonet.io
-
X: https://twitter.com/MangoOS_Network
-
Mail: BD@mangonet.io
-
Telegram: https://t.me/MangoNetwork
-
Discord: https://discord.com/invite/mangonetwork
-
Mango Network Dev
-
Blockchain Browser: https://mgoscan.com
-
Github: https://github.com/MangoNet-Labs
-
Developer Documentation: https://docs.mangonet.io
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News