Rebranding? Transformation? Overhaul? What Exactly Happened from Fantom to Sonic
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Rebranding? Transformation? Overhaul? What Exactly Happened from Fantom to Sonic
The Fantom official team has officially announced its rebranding to Sonic Labs, planning to gain support by launching a large-scale incentive program.
The veteran public blockchain Fantom has recently regained attention.
Last October, the Fantom Foundation announced the Sonic upgrade plan, claiming that this initiative introduced several technological innovations capable of significantly enhancing the performance and scalability of the Fantom network.
On August 2nd this year, the official team formally announced that Fantom would be rebranded as Sonic Labs, planning to gain support through a large-scale incentive program. Sonic will use the $S token. This new token will enter the ecosystem via massive airdrops, simplified staking, and incentive programs. Although the transition from Fantom to Sonic Labs has been completed, the full launch of Sonic is scheduled for Q4.

Additionally, on August 14th, the Sonic Labs team announced on X that Andre Cronje, a director at Sonic Labs, has officially become its new Chief Technology Officer (CTO). Andre will continue leading the design and development of the Sonic network, with a focus on building the new native bridging technology called “Sonic Gateway,” which will greatly enhance the security and convenience of transferring assets from other chains (such as Ethereum) to Sonic.
So, what exactly has changed on this chain since the shift from Fantom to Sonic Labs?
To understand these changes, we need to first look back at Fantom’s history.
Fantom's History
Fantom is an L1 blockchain founded by computer scientist Ahn Byung, originally aiming to overcome the traditional blockchain trilemma of scalability, security, and decentralization through innovative technology.

Fantom’s technical foundation lies in Lachesis, an advanced asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (aBFT) consensus mechanism based on Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG), allowing different blockchains to exist asynchronously without slowing down the main network. This innovation gave Fantom significant advantages in processing speed and cost efficiency.
In 2019, Fantom launched its Opera mainnet, compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). By supporting Solidity and EVM, Fantom could seamlessly support Ethereum-based dApps, enabling developers to easily migrate their applications. This feature attracted widespread market attention, and Fantom was even briefly dubbed an “Ethereum killer.”
Between 2020 and 2021, as the DeFi sector rapidly expanded, Fantom became one of the most popular projects in the space due to its high transaction efficiency and low fees. Andre Cronje, a leading figure in DeFi, joined the Fantom Foundation during this period and drove the growth of Fantom’s DeFi ecosystem. He launched star projects like Yearn Finance and brought in numerous developers and users, pushing Fantom’s Total Value Locked (TVL) to a peak of $8 billion during the 2021 bull market.
In 2022, after Andre Cronje announced his temporary exit from the DeFi industry, market confidence in Fantom plummeted, causing the FTM token price to drop from a high of $30 to just $0.19.
Beyond DeFi challenges, as next-generation Layer-1 blockchains (such as Solana and Avalanche) raised the bar for performance and scalability, Fantom also struggled to keep pace in terms of transaction throughput, storage efficiency, and smart contract execution speed.
Therefore, to continue attracting developers and users, Fantom needed a more efficient and scalable technical foundation—one that not only improved existing technologies but also provided sufficient flexibility for future expansion. It was against this backdrop that the Sonic upgrade plan was proposed.
Simply put, the Sonic Chain in this upgrade will consist of an L1 Sonic Network and a fully Ethereum-connected native L2. From Ethereum’s perspective, Fantom will function like an L2, yet deliver L1-level speed and security. Sonic will be a hybrid L1/L2 EVM network, fully integrated into Ethereum. The upgrade primarily involves two core components: the Fantom Virtual Machine, and the Carmen data storage solution and optimizations.
Core Components of the Sonic Upgrade
Fantom Virtual Machine (FVM)
The Fantom Virtual Machine (FVM) is one of the key components of the Sonic upgrade—a major improvement over the existing Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). FVM aims to resolve performance bottlenecks in EVM and provide developers and users with a more efficient environment for executing smart contracts.
FVM is fully compatible with EVM, meaning all existing EVM-based smart contracts can be seamlessly migrated to the Fantom network without any code modifications. For developers, this compatibility reduces migration costs and development effort while maintaining broad support from the EVM ecosystem.
Moreover, the engine architecture of FVM has been comprehensively optimized, supporting a far more efficient execution environment than EVM. Performance improvements are evident in the following areas:
-
Faster smart contract execution: FVM significantly exceeds EVM in both throughput and speed when processing smart contracts, greatly reducing execution time for complex contracts.
-
Lower transaction latency: FVM processes transactions and generates blocks faster, reducing user wait times and improving overall user experience.
-
Higher resource utilization: By optimizing computation and storage resources, FVM reduces the resource consumption required for smart contract execution, making network operations more efficient and economical.
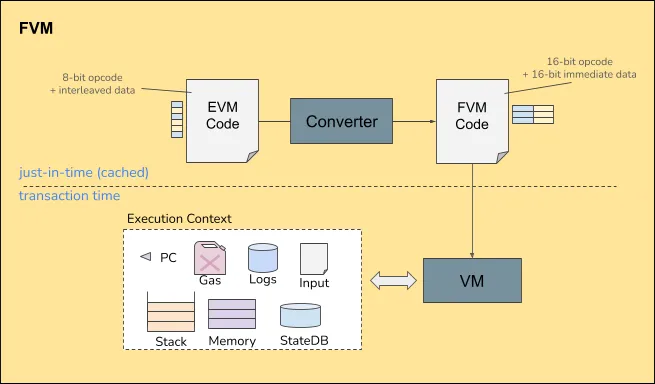
For developers, FVM not only claims superior performance compared to EVM but also offers enhanced debugging tools, making the development and testing of smart contracts smoother and more efficient. While still supporting mainstream smart contract languages like Solidity, FVM also expands support for additional programming languages, giving developers greater flexibility to work with their preferred tools and frameworks. Built-in optimization strategies allow developers finer control over contract execution, further improving performance and security.
FVM also includes an automated security check mechanism that detects potential vulnerabilities or risks before smart contract execution, helping developers identify and fix issues early. Its built-in sandbox environment ensures that smart contract execution does not affect other parts of the network, enhancing overall stability and security.
Carmen Data Storage Solution
The Carmen data storage solution is another critical component of the Fantom Sonic upgrade, designed to address challenges related to data storage in blockchain networks.
As blockchain networks expand, the rapid increase in storage demands places a heavy burden on node operations. Carmen introduces an innovative data storage structure that reduces storage requirements and improves network efficiency and scalability.

Specifically, Carmen dynamically manages data storage and deletion based on actual network needs, reducing validator node storage requirements from 2000 GB to just 300 GB. This optimization lowers node operating costs, enabling more nodes to participate in network validation, thereby strengthening decentralization and security. For example, historical data no longer frequently accessed can be compressed or moved, reducing real-time storage pressure.
Furthermore, Carmen reduces archive node storage needs from over 11 TB to under 1 TB. This dramatic reduction significantly lowers the cost of storing historical data, improving the operability and economic viability of archive nodes.
In terms of data access and processing, Carmen introduces intelligent storage strategies that automatically adjust storage methods based on data importance and access frequency. This approach enhances storage efficiency while ensuring the security and accessibility of critical data. Optimized for fast retrieval, Carmen’s data structure improves overall efficiency—especially important for applications requiring frequent access to specific data, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
Notably, Carmen also supports parallel processing of data requests, allowing the network to maintain high response speeds even under heavy load—an essential feature for highly scalable blockchain networks.
$S Token
The Sonic token ($S) is a new token introduced by Fantom as part of its Sonic upgrade, set to replace the current FTM token and drive the development of the Sonic network ecosystem.

The initial supply of the Sonic token is 3.175 billion, matching the total supply of the FTM token.
At the launch of the Sonic network, Fantom provides a 1:1 conversion mechanism from FTM to Sonic tokens. Existing FTM holders can choose to convert their tokens to Sonic tokens, enabling a seamless transition to the new network. Additionally, six months after the Sonic mainnet launch, an extra 6% of Sonic tokens will be issued as rewards for users and developers on both Opera and Sonic networks.
Six months after mainnet launch, an annual issuance of 15% additional Sonic tokens (approximately 47.625 million) will fund network growth, team expansion, and marketing efforts. Unused tokens will be burned to prevent inflation.
According to official statements, the target Annual Percentage Rate (APR) for Sonic is set at 3.5%. To maintain this yield over the first four years without triggering inflation, the team will reallocate remaining FTM block rewards from Opera to Sonic, directing them toward validator and staker rewards—these are already included within the initial 3.175 billion $S token supply.
In short, the Sonic token is not only the core asset of the Sonic network but also plays a crucial role in incentivizing ecosystem participants, supporting dApp development, and maintaining network security.
Its specific functions include:
-
Payment of network transaction fees
Sonic tokens can be used to pay transaction fees on the Sonic network. Whenever users conduct transactions or execute smart contracts, they must pay a certain amount of Sonic tokens as gas fees. These fees help maintain network operations and security while incentivizing node participation in validation.
-
Network security and consensus mechanism
Sonic tokens play a vital role in the network’s consensus mechanism. Users holding Sonic tokens can stake them to support network validation and participate in consensus. Validators who stake tokens gain the right to verify transactions and earn corresponding rewards, helping maintain decentralization and security.
-
Liquidity mining
Users can earn Sonic token rewards by providing liquidity, which helps increase network liquidity and attract more users and projects.
-
Running validator nodes
To run a validator node on the Sonic network, a minimum of 50,000 Sonic tokens must be staked. These nodes are responsible for verifying transactions and ensuring network security.
-
Developer rewards
Developers can earn Sonic token rewards by building dApps on the Sonic network and attracting user engagement. This mechanism encourages more developers to join the Sonic ecosystem.
-
Community participation rewards
Community members who participate in network governance, promotion, and usage of the Sonic network can also receive Sonic token rewards, fostering higher community engagement and activity.
Beyond various mechanisms and token upgrades, the Fantom Foundation also established an incubator named Sonic Labs in December last year, committing substantial resources and technical support to help developers build new projects within its ecosystem.

According to publicly announced winners of Sonic Labs’ startup accelerator program, the incubator has already achieved some success. To date, there are 351 applications in its ecosystem, spanning innovations across multiple domains including perpetual DEXs (decentralized exchanges), social protocols, P2P lending platforms, green tech startups, and RPG blockchain games.
Reliable sources indicate the team holds over 450 million FTM; more than $100 million in stablecoins; over $100 million in crypto assets; and $50 million in non-crypto assets. At a current burn rate of $7 million per year in salaries, the project is financially sustainable for 30 years.
In summary, although the mainnet has yet to launch, as market interest grows around Layer 2 solutions for blockchain scalability, Sonic’s technological upgrades in scalability and security—achieving 2000 TPS transaction processing speed and sub-second performance—suggest promising future potential. Let us wait and see as Sonic continues to break new ground and grow within the blockchain landscape.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















