Huobi Research latest report: Pectra Upgrade Survey – The Largest Ethereum Upgrade in History Following the Dencun Upgrade
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Huobi Research latest report: Pectra Upgrade Survey – The Largest Ethereum Upgrade in History Following the Dencun Upgrade
The Pectra upgrade introduces EIP-7594 (PeerDAS), which implements data availability sampling (DAS), benefiting ZK Prover networks and, in turn, the broader ZK ecosystem.
Key Insights
-
The major components of the Pectra upgrade (7702, 3074, 7623) will directly benefit projects in modular architecture, chain abstraction, and AA wallets;
-
EIP-7594 (PeerDAS) introduced in the Pectra upgrade brings data availability sampling (DAS), which benefits ZK Prover networks and, by extension, the broader ZK ecosystem;
-
Other minor EIPs offer moderate benefits such as reduced L2 data layer fees, faster transaction speeds, and lower data storage costs;
-
Considering the overall market, especially recent "high FDV, low liquidity" FUD, the approach of Q4 (Pectra release timeframe) may bring a strong rally to the Ethereum ecosystem;
-
From an investment perspective, amid the current market trend of “anti-VC,” VC-backed project valuations are no longer inflated. Q3 could present a favorable window for institutional entry into the primary market, particularly for DeFi and innovative DeFi projects;
-
The revenue-to-market-cap ratio for DeFi projects has reached a historical low.
Background
Recently, the most discussed topic within the Ethereum community is the Pectra upgrade. The Pectra upgrade combines two independent upgrades: the Prague upgrade and the Electra upgrade. Prague focuses on changes to the network's execution layer, while Electra impacts the consensus layer. Together, these are collectively referred to as the "Pectra" upgrade. This marks a significant event following the Dencun upgrade in March 2024 and could become the largest upgrade in Ethereum’s history.
According to ethereum.org (https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-7600), the Ethereum Pectra upgrade is expected to integrate several key Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) aimed at addressing scalability, security, and user experience challenges. These EIPs include:
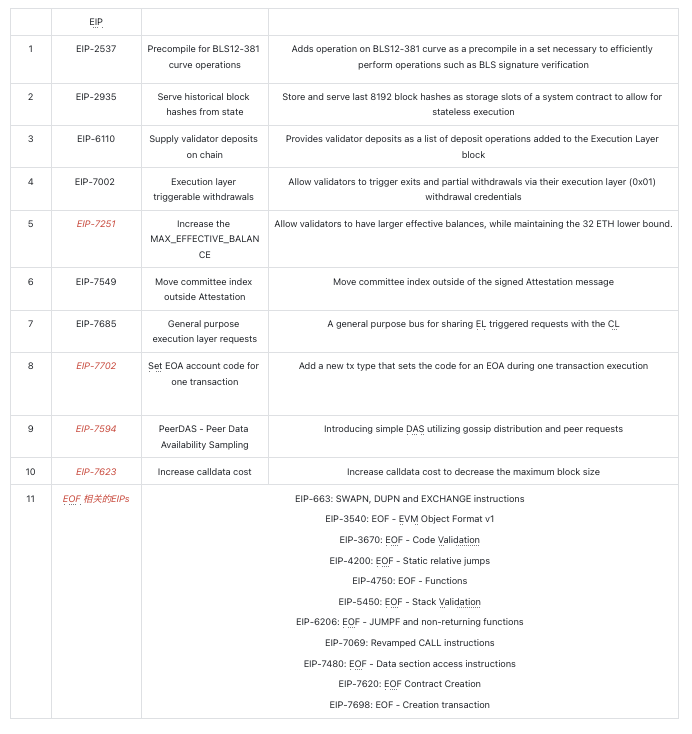
The Pectra upgrade is another milestone in Ethereum’s strategic development roadmap and is projected to launch officially in Q1 2025. Below, we analyze several key EIPs and forecast their potential impact.
This article was written by Huobi Research, a team currently under HTX Ventures. HTX Ventures is the global investment arm of HTX, integrating investment, incubation, and research to identify the world’s most talented and visionary teams. HTX Ventures currently supports over 300 projects across multiple blockchain sectors, with select high-quality projects already listed on HTX Exchange.
Analysis of Key EIPs
*EIP-7702: Revolutionary account abstraction wallet technology that supersedes EIP-4337; EIP-7702 enables existing EOAs to execute any smart contract code, potentially driving the emergence of rich-featured, user-friendly next-gen wallets and complex application use cases.
-
Although EIP-7702 is highly compatible with all prior work built on EIP-4337, many AA wallet teams have already invested substantial effort developing unique features based on the EIP-4337 standard. After EIP-7702, the distinctive market position previously held by AA wallets promoted by the Ethereum Foundation may vanish, as standard EOA wallets will gain capabilities once exclusive to AA wallets. This means AA wallets will now directly compete with high-adoption EOA wallets like MetaMask, forcing early-stage AA wallet startups to reposition their products.
-
Future EOA wallets will support new functionalities such as sponsored transactions (gas fee delegation), batch account management, and multi-transaction processing—all of which can be upgraded over time. These improvements are favorable for Web2 users and DeFi financial transactions, potentially catalyzing novel, complex applications that attract mainstream users, creating new opportunities.
Historical Context:
-
Poor adoption and compatibility of account abstraction (AA): The survival of the AA market hinges on ecosystem-wide adoption of EIP-4337, yet many dApps and L2s still lack support. The total number of smart contract wallets—estimated via Gnosis Safe and Argent combined—is only around 150,000.
-
Vague technical design in EIP-4337: While EIP-4337 defines contract interfaces for infrastructure components like Bundlers, Paymasters, and Signature Aggregators, the Ethereum Foundation has not provided clear solutions for many critical technical issues. This forces project teams to experiment repeatedly with different implementations.
*EIP-3074: Proposed in October 2020, included in Pectra upgrade on April 12, 2024
EIP-3074 allows external owned accounts (EOAs) to delegate control to smart contracts, enabling any EOA to act as a smart contract wallet without deploying one, thereby supporting more complex transaction schemes such as gas sponsorship and batched transactions.
-
How does EIP-3074 turn existing EOAs into smart contract-like entities? By introducing the AUTH and AUTHCALL opcodes, when used together, they allow a smart contract to send transactions on behalf of an EOA. This enables functionalities such as multisig, batch and sponsored transactions, key recovery, and easier CeFi exchange deposits.
-
In detail, users sign transactions off-chain, then either they or a gas sponsor submit the transaction to an Invoker contract (a special intermediary contract). The Invoker uses 'AUTH' and 'AUTHCALL' to verify and invoke target contracts, giving the smart contract greater authority to perform various user operations.
-
Each EOA address can set an Invoker logic contract to extend functionality. Invokers offer extensive customization in transaction logic and permission controls, making them highly flexible. They are deeply connected to the “intent-centric” sector. Optimizing user experience requires designing complex transaction logic within the Invoker contract—such as automated transaction execution, conditional triggers, asset auto-distribution, batched transaction aggregation, multi-signature approvals, time-limited transactions, integration with external systems, and transaction-based financial strategies—offering tailored services for specific user groups. Representative project ApertureFinance has processed $2.6 billion in volume and is popular among institutional traders. A major drawback is that if the Invoker contract turns malicious, it could cause severe asset loss for users.

*EIP-7702: Proposed by Vitalik Buterin, inherits core functionalities from EIP-3074
EIP-7702 allows externally owned accounts (EOAs) to temporarily act as smart contract wallets within a transaction, enabling EOAs to perform complex operations previously exclusive to smart contracts. This greatly enhances the functionality and flexibility of EOAs. The proposal operates at the protocol layer but applies smart contract code temporarily within transactions without permanently altering the EVM, ensuring high compatibility.
EIP-7702 introduces a new transaction type that accepts both contract_code and signature fields. At the start of a transaction, the signer’s account code is set to the provided contract_code. At the end of the transaction, it resets to empty.
Smart contract code is stored in the "contract code" field. Since EOAs are not contracts, this field is typically empty. During transaction execution, some smart contract code is temporarily injected into this field.
-
EOAs can dynamically introduce smart contract code within a transaction, enabling multiple operations—like batching and complex instructions—in a single transaction. This streamlines processes, reduces transaction costs, and lowers operational complexity. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for highly interactive financial applications such as DeFi platforms.
-
Secondly, EIP-7702 introduces a new permission management mechanism known as privilege degradation. This allows account holders to assign specific permissions to sub-keys, enhancing account security. Through fine-grained permission control, users can restrict the scope of sub-key operations, preventing unauthorized transactions and misuse.
-
EIP-7702 also supports transaction sponsorship, allowing one account to pay gas fees for another. For example, service providers might cover transaction fees for their customers, improving user experience and encouraging platform adoption.
-
EIP-7702 was recently added to the Pectra upgrade, and some details remain unclear. However, given its connection to the most critical web3 entry point—wallets—its impact could mirror how MetaMask fueled DeFi Summer. A new Web2-friendly wallet paradigm may catalyze a wave of new applications, warranting close monitoring. Core DeFi applications like Uniswap have already shown positive responses to EIP-7702.
EIP-7623: Proposed by Vitalik, increases calldata cost, reduces block size, and improves overall Layer 2 performance
Content and Background
-
Since EIP-1559, the block gas limit has not increased, yet average block size continues to grow due to rollups publishing increasing amounts of data to Ethereum calldata.
-
Calldata refers to the data passed as function call parameters in Ethereum smart contracts, including function selectors and arguments. Although calldata is only used temporarily during transaction execution and discarded afterward to reduce storage pressure, it still consumes block space and gas fees.
-
After EIP-4844, rollups began storing data in blobs, making blob storage the preferred solution for data availability (DA).
-
This shift necessitates a reassessment of calldata pricing, especially regarding inefficiencies between average and maximum block sizes. The current fee model and block size limits do not effectively optimize calldata usage, leading to suboptimal resource utilization and high costs.
-
The theoretical maximum Ethereum block size is 1,875,000 bytes (~1831KB), but the actual average is only about 100KB. The real block size remains far below the theoretical maximum due to high gas fees associated with calldata, reducing transaction volume and underutilizing block space, negatively impacting network efficiency and scalability.
-
By introducing a calldata-based base fee for transactions primarily using Ethereum for DA, this proposal aims to reduce maximum block size, freeing up space for additional blobs.
Additionally, there is a related proposal:
-
Vitalik Buterin proposed EIP-7706, which creates a separate fee market for calldata with its own base fee and gas limit, further optimizing transaction costs and network performance.
Overall Impact
-
Improves Ethereum's cost-effectiveness: Further optimizes transaction processing speed and resource efficiency, avoids unnecessary fee spikes, and makes calldata cheaper. This helps reduce per-transaction costs and improves overall network performance.
-
Benefits Layer 2: Complements the blob data design introduced in EIP-4844. By unifying base fee adjustment mechanisms, Layer 2 solutions can utilize Layer 1 resources more efficiently, improving overall Layer 2 and application performance.
-
Benefits sequencers: Optimizing the fee structure for calldata and blob data significantly reduces data publishing costs for sequencers. Decentralized sequencer projects such as Morph, Metis, Espresso, EigenLayer, Astria, SUAVE, and Radius will benefit from these improvements.
EOF-Related Upgrades
What is EOF?
Ethereum Object Format (EOF) is a new standard introduced as part of the Pectra hard fork. EOF aims to improve how smart contracts are created and executed on the Ethereum network. By providing a more structured and efficient way to handle smart contracts, EOF simplifies the development process and enhances security.
EOF introduces a new format for Ethereum smart contracts, making them easier to read and manage. This new format clearly defines contract behavior, helping reduce errors and improve security. For developers, this means fewer bugs and vulnerabilities, resulting in more reliable applications on Ethereum.
EOF also improves the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), the core component responsible for executing smart contracts. These enhancements make the EVM more efficient, enabling it to process more transactions simultaneously without slowing down. As the number of users and applications grows, this is crucial for maintaining a responsive network.
Impact on Pectra Update
Including EOF in the Pectra hard fork amplifies the overall effectiveness of the upgrade. By making smart contracts safer and easier to develop, EOF helps ensure that new features introduced in Pectra—such as social recovery and transaction batching—can be implemented securely and efficiently.
EOF also supports the scalability improvements brought by Pectra. As the Ethereum network grows, it must handle more transactions and run more smart contracts without compromising speed or security. EOF’s enhancements to the EVM and smart contract structure play a key role in achieving this goal.
Benefits for Developers and Users
For developers, EOF simplifies the process of creating and maintaining smart contracts. Clearer rules and better tools mean fewer errors and stronger applications. In turn, users benefit from more reliable and secure decentralized applications on Ethereum.
For users, the improvements from EOF translate into a better overall experience. Faster transaction processing and more secure applications make Ethereum more appealing for daily use. Whether for financial transactions, gaming, or other applications, users enjoy a smoother and more secure experience on the Ethereum network.
Overall, EOF is a vital component of the Pectra hard fork. It strengthens smart contract security and efficiency, supporting the broader goals of the Pectra update. By improving developer experience and ensuring better performance and security, EOF contributes to Ethereum’s continued growth and innovation in the blockchain space.
EIP-7594 - PeerDAS: Data Availability Sampling in the Pectra Upgrade
Protocol Overview
PeerDAS, also known as EIP-7594, implements data availability sampling (DAS) on Ethereum and is expected to significantly enhance the network’s ability to support rollups and their data availability demands. In practice, PeerDAS is projected to increase the number of blob transactions validators can attach to a block from 3 per block to 64 or more.
The Pectra upgrade is expected to be released by the end of Q1 2025, with PeerDAS being one of its most notable improvements. PeerDAS, or data availability sampling, aims to solve Ethereum’s scalability challenges by leveraging existing peer-to-peer (P2P) components to ensure data distribution and availability.
Main Features and Advantages of PeerDAS
-
Scalability and Efficiency: PeerDAS enhances Ethereum’s scalability by distributing the responsibility for data availability across the network. Instead of relying on a few nodes to store and verify all data, the workload is shared among many nodes, improving overall network efficiency and resilience.
-
Improved Data Availability: Through data availability sampling, PeerDAS ensures that data required to validate transactions is available without overburdening any single node. The mechanism checks small, randomly selected subsets of data to confirm the availability of the entire dataset, reducing strain on individual nodes.
-
Enhanced Network Resilience: By leveraging Ethereum’s existing P2P infrastructure, PeerDAS improves the network’s resistance to attacks and disruptions. Enhanced data availability makes single points of failure less likely to compromise overall network operation.
-
Integration with Other Upgrades: PeerDAS is part of a suite of improvements in the Pectra upgrade, including the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) Object Format (EOF) and new Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) such as EIP-7702. Together, these aim to optimize transaction processing, enhance smart contract capabilities, and improve user experience and security.
Overall, PeerDAS represents a critical step toward ensuring Ethereum can scale effectively while maintaining resilience. By improving data availability and leveraging Ethereum’s decentralized network, PeerDAS lays the foundation for a stronger, more efficient blockchain ecosystem.
Two Major Advantages
Driving DeFi (Decentralized Finance) Development
-
Faster Transaction Speed and Efficiency: PeerDAS improves Ethereum’s transaction speed and efficiency, enabling DeFi applications to process large volumes of transactions more quickly, reducing wait times and enhancing user experience.
-
Lower Transaction Costs: By improving network efficiency, PeerDAS helps reduce transaction costs, lowering operational expenses for DeFi projects and attracting more users.
Supporting Emerging Applications and Innovation
-
Expanded Smart Contract Capabilities: Combined with other upgrades like EIP-7702, PeerDAS enables more flexible smart contract operations, supporting innovative use cases such as decentralized identity verification and complex financial derivatives.
-
Cross-Chain Interoperability: Improved data availability and network performance make it easier for Ethereum to interoperate with other blockchains, accelerating the development of cross-chain applications and innovation.
Benefiting ZK Prover Networks
Despite their power, ZK technologies currently face challenges such as long ZKP generation times and centralized provers. Hardware acceleration for ZKP generation and decentralized Prover networks have emerged as the latest hot sector in the ZK space after ZK Rollups in the primary market.

Succinct @SuccinctLabs and Cysic @cysic_xyz, two leaders in this space, recently raised $55M and $12M respectively.
Taking Cysic @cysic_xyz as an example, the team possesses expertise in ZK hardware accelerator chip design and has launched the ZK proving layer, Cysic Network.
Currently, the ZKP generation service market is still in its early stages. Revenue generated cannot yet cover hardware depreciation, electricity, and operational costs for Provers. Therefore, ZK Prover networks rely on token issuance to raise funds and distribute rewards to Prover nodes via PoW-like mechanisms to incentivize network adoption.
Just as the Cancun upgrade catalyzed a wave of L2s with $1B–$100B FDV, the Pectra upgrade is expected to catalyze a new wave of ZK Prover networks with similar valuation potential.
EIP-7251: Increase Maximum Effective Balance — Validator staking cap raised from 32 ETH to 2048 ETH
Protocol Overview
EIP-7251, also known as "maxeb", is an enhancement proposed for the upcoming Ethereum Pectra hard fork. This change aims to reduce the risk of beacon chain instability when staked ETH approaches or exceeds 50% of the network.
Maxeb allows merging multiple validators into fewer “super validators”, aiming to simplify operations without affecting monetary policy or rewards. It also benefits individual stakers by enabling them to accumulate rewards beyond 32 ETH.
Despite potential advantages, the Ethereum community remains divided on including maxeb in Pectra. Concerns center on its impact on network decentralization and validator diversity, with fears of increased centralization and reduced participation from smaller validators.
Motivation and Expected Impact
-
Reduce Validator Count
-
By increasing the maximum effective balance, the total number of validators can be reduced, easing network load and improving efficiency.
-
-
Enhance Economic Security
-
Raising the maximum effective balance strengthens economic security by mitigating instability caused by a highly fragmented validator pool.
-
-
Lower Operational Costs
-
For large node operators, reducing the need to run multiple validators lowers DevOps costs and maximizes returns.
-
Ethereum developers have discussed capping staking ratios at 1/4. This change would allow individual validators to stake more than 32 ETH—up to 2,048 ETH instead of the current 32 ETH cap. Increasing the maximum effective validator balance would enable operators to manage fewer but higher-stake validators, potentially reducing complexity.
Latest Developments
-
On June 27, 2024, Ethereum developers discussed and coordinated changes to the Ethereum consensus layer (CL), also known as the beacon chain. Topics included new research on client diversity data collection and multi-client block validation.
-
Pectra Devnet 1 is nearing readiness. The Ethereum Foundation’s DevOps team is awaiting readiness from execution layer (EL) clients. PeerDAS Devnet 1 has already launched with three different consensus layer client implementations.
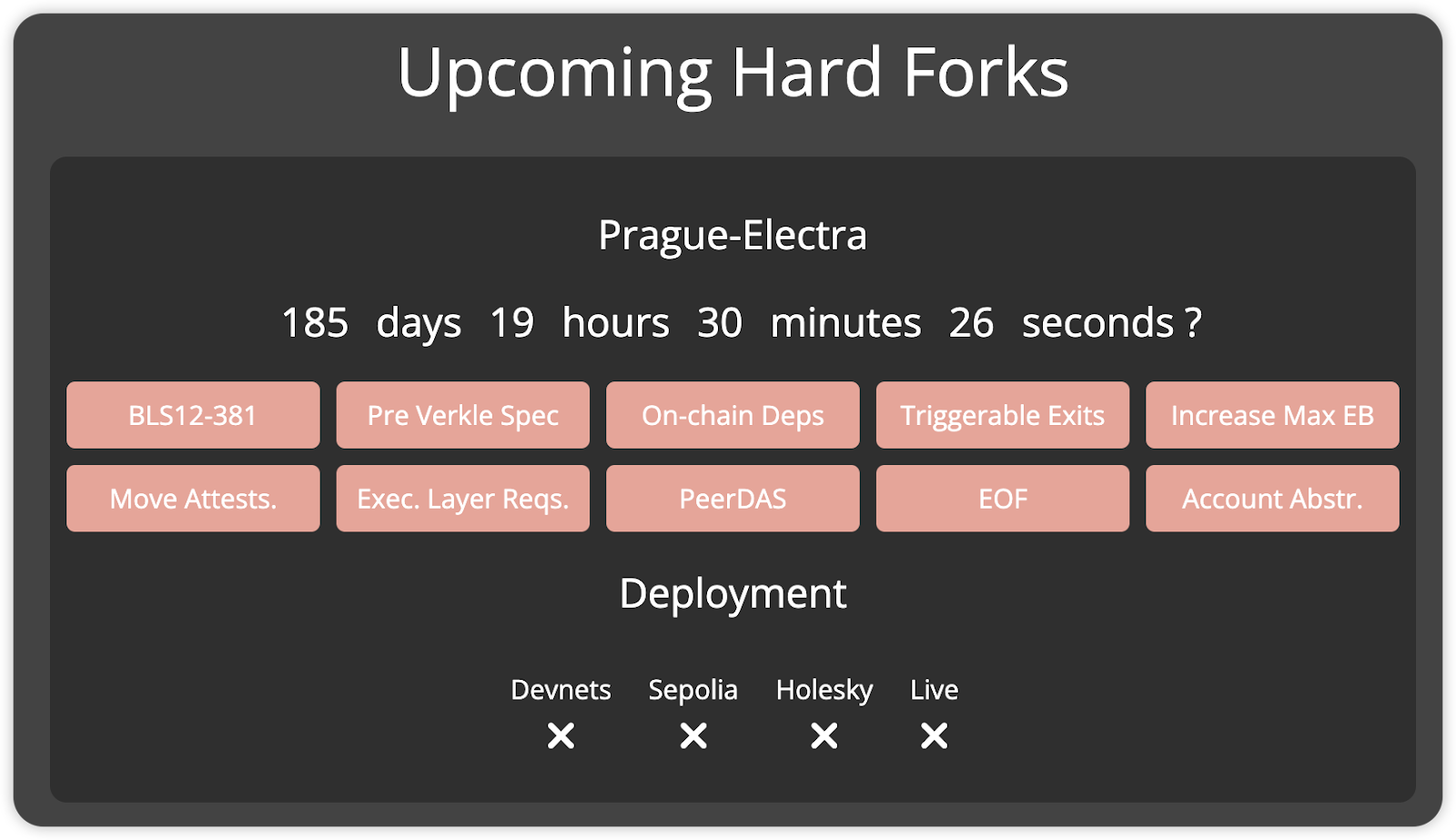
References:
https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-7600
https://cryptomaniaks.com/ethereum-pectra-hard-fork-eof-cfi-prague-electra
https://github.com/ethereum/ercs/blob/master/ERCS/erc-4337.md?ref=blog.quicknode.com#backwards-compatibility
https://www.galaxy.com/insights/research/ethereum-all-core-developers-execution-call-187/
https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/eip-7623-increase-calldata-cost/18647
https://ethroadmap.com/?ref=bankless.ghost.io#pectra%20sticky (Ethereum Upgrade Roadmap)
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















