Bitlayer: A Bitcoin Layer2 Based on the BitVM Scheme
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Bitlayer: A Bitcoin Layer2 Based on the BitVM Scheme
Bitlayer's core objective is to resolve the trade-off between security and Turing completeness in Bitcoin Layer 2 technology.
Author: Bob Cong
Bitlayer is the first Bitcoin Layer 2 network security-equivalent project based on the BitVM scheme, aiming to provide security equivalent to Bitcoin while supporting Turing completeness—meaning it can execute any possible computation or program.

Bitlayer's core goal is to resolve the trade-off between security and Turing completeness in Bitcoin's Layer 2 technology. Its design draws inspiration from BitVM, DLC/LN (Discreet Log Contracts / Lightning Network) protocols, and multiple VMs (including EVM, the Ethereum Virtual Machine).
From these inspirations, the project’s technical team has abstracted three key tasks:
-
Trustless entry and exit for Layer 1 assets
-
State transitions using a Turing-complete Layer 2 virtual machine
-
Layer 1 validation of Layer 2 state transitions
Its core functions and operational principles are built around several key technical components to support more complex application scenarios such as smart contract execution, high-throughput transaction processing, and cross-chain asset transfers.
Core Features
-
Turing-complete smart contract support: By implementing a Turing-complete virtual machine compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)—called BitVM—Bitlayer enables developers to write and execute complex smart contracts on Bitcoin. This capability is not natively supported by Bitcoin and opens up broad possibilities for decentralized application (DApp) development within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
-
Efficient transaction processing: Leveraging optimistic rollup techniques and layered verification mechanisms, Bitlayer significantly improves transaction speed and system scalability. This allows large volumes of transactions to be processed on the second layer, with on-chain validation required only in case of disputes, reducing mainchain load and lowering transaction costs.
-
Secure cross-chain asset transfer: Through the OP_DLC bridge, Bitlayer enables secure and seamless transfer of Bitcoin and other assets between the Bitcoin mainchain and the second layer. This bridging technology supports liquidity across different blockchain platforms while ensuring asset security and user control.
Core Mechanisms
As a BitVM-based Bitcoin Layer 2 solution, Bitlayer adopts Layered Virtual Machine (LVM) technology, utilizing zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) and optimistic verification to support various complex computations. Additionally, Bitlayer establishes a dual-channel, two-way locked asset bridge via OP_DLC (Optimistic Discreet Log Contracts) and the BitVM bridge, achieving security equivalence with Bitcoin Layer 1.
BitVM
BitVM is the core component of the Bitlayer project—a Turing-complete virtual machine specifically designed for the Bitcoin ecosystem. Its primary purpose is to extend Bitcoin's functionality and programmability without compromising the inherent security and decentralization of the Bitcoin network. Below is a detailed introduction to BitVM:
Design Objectives
The design objective of BitVM is to overcome certain limitations of Bitcoin's native protocol, particularly in terms of smart contracts and complex computational capabilities. While Bitcoin is one of the most secure blockchains, it does not natively support complex smart contracts, limiting its use in applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi).
Turing Completeness
BitVM is Turing-complete, meaning it can perform arbitrarily complex computational tasks given sufficient resources. This feature enables developers to design and run various sophisticated decentralized applications on the Bitcoin network, such as automated trading strategies, financial derivatives, and smart contracts.
In summary, BitVM is the key technology behind the Bitlayer project. By providing a secure, scalable, and feature-rich virtual machine, it enables Bitcoin to better adapt to current and future blockchain application demands. It not only addresses Bitcoin's shortcomings in smart contracts and high-throughput applications but also preserves its status as a top cryptocurrency in terms of security and decentralization.
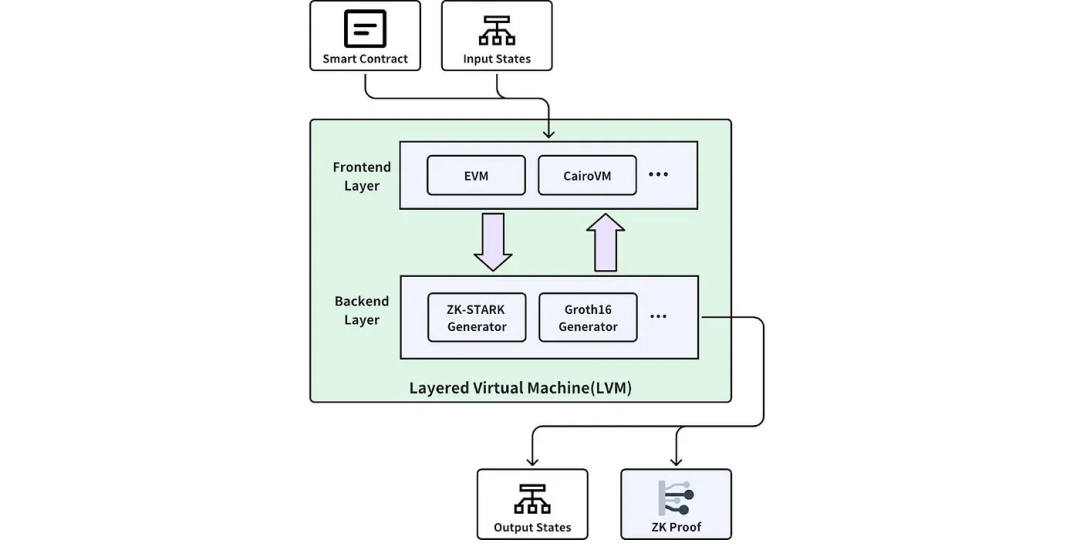
Layered Virtual Machine Technology (LVM)
Bitlayer’s Layered Virtual Machine (LVM) is an innovative architectural design aimed at enhancing the computational power and programmability of the Bitcoin network while preserving its core security and decentralization. This technology enables the execution of complex smart contracts and other applications on Bitcoin’s second layer without overburdening the main chain. Below is a detailed explanation of this technology’s key components and working principles.
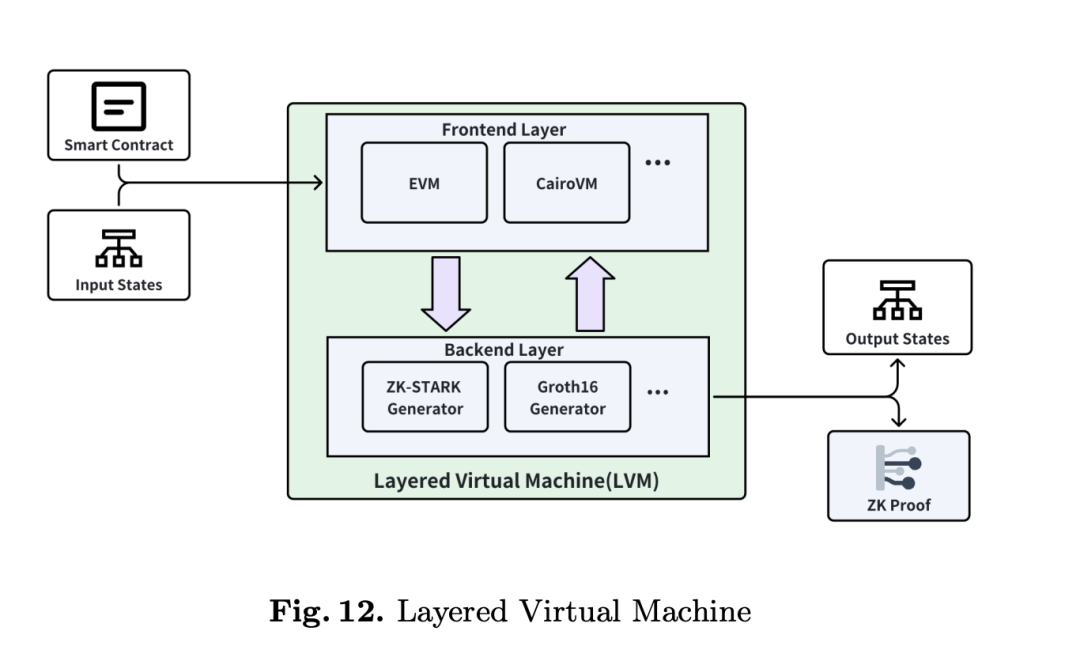
Key Components
-
Frontend Execution Environment: The frontend environment handles smart contract execution. It supports multiple smart contract languages and frameworks, allowing developers to choose the most suitable tools and languages for specific applications.
-
Backend Verification Environment: The backend focuses on verifying the results of frontend execution. This part typically uses zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology to ensure the correctness of computational results without revealing execution details.
Working Principles
The core idea of the layered virtual machine is to separate computation and verification. This layered architecture allows extensive computation to occur on the second layer, with only essential verification data submitted to Bitcoin’s main chain, greatly reducing the burden on the main chain.
-
Smart Contract Execution:
-
Developers deploy smart contracts in the frontend execution environment. These contracts can include financial derivatives, games, or other applications requiring complex logic.
-
During execution, relevant computations take place on the second layer rather than directly on Bitcoin’s main chain.
-
Zero-Knowledge Proof Generation:
-
Once smart contract execution is complete, the backend verification environment generates zero-knowledge proofs that confirm the correctness of the frontend execution without exposing the actual content.
-
These proofs can then be submitted to the Bitcoin main chain for anyone who needs to verify the computations.
-
On-Chain Verification:
-
After zero-knowledge proofs are submitted to the Bitcoin main chain, anyone can verify that the smart contract was executed correctly without re-running the computation.
-
This ensures both transparency and verifiability of computations while protecting the privacy of execution details.
Advantages
-
Efficiency: By executing most computations on the second layer, the layered virtual machine significantly reduces pressure on the main chain, improving overall system throughput and efficiency.
-
Flexibility: Support for multiple smart contract languages and execution environments provides developers with broad choices, fostering innovation and development across various applications.
-
Security: Utilizes zero-knowledge proof technology to protect user privacy while ensuring the correctness and immutability of computational results.
Layered Virtual Machine technology is Bitlayer’s key approach to adding complex smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin network without sacrificing security and decentralization. This innovative technical framework opens new possibilities for extending Bitcoin’s functionality, enabling it to better serve modern blockchain application demands.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP)
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) is a cryptographic technique that allows one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true without revealing any information beyond the truth of that statement. This technology protects privacy while ensuring data integrity and security. In the Bitlayer project, ZKP is used to enhance security, improve efficiency, and protect user privacy.
Basic Principles
The core of zero-knowledge proofs is the ability to prove the correctness of information without disclosing the content itself. For example, a prover can demonstrate knowledge of a password without revealing the password. This is achieved through a series of mathematical challenges and responses that only someone with the correct information can successfully solve.
Applications in Bitlayer
In Bitlayer, zero-knowledge proofs are applied in several key areas:
-
Enhanced Privacy Protection: Using ZKP, users can prove they have sufficient funds for a transaction without revealing their exact account balance. This protects user privacy while ensuring network security.
-
Improved Transaction Efficiency: In traditional blockchain systems, every transaction detail must be publicly recorded on-chain, potentially leading to privacy leaks and network congestion. With ZKP, only transaction validity needs to be proven without showing all details, reducing data transmission and storage requirements.
-
Secure Execution of Smart Contracts: Using ZKP in smart contracts ensures the correctness of execution results without exposing internal states and logic. This is especially important for applications involving sensitive data and logic.
Technical Challenges
Despite the many advantages of zero-knowledge proofs, they also face some technical challenges:
-
Computational Complexity: Generating and verifying zero-knowledge proofs is typically computationally intensive, which may lead to performance issues, especially in resource-constrained environments.
-
Design Complexity: Designing effective and secure zero-knowledge proof systems requires advanced cryptographic knowledge and precise implementation; flawed designs may introduce security vulnerabilities.
-
Interoperability Issues: Standards and implementations of zero-knowledge proofs may not be compatible across different systems and platforms, potentially limiting cross-platform applicability.
In the Bitlayer project, zero-knowledge proof technology is a critical component, enabling the Bitcoin Layer 2 network to offer higher efficiency and better privacy protection while maintaining Bitcoin’s core security attributes. By applying ZKP where necessary, Bitlayer delivers a secure and efficient blockchain platform capable of supporting a wide range of complex and sensitive blockchain applications.
Optimistic Verification
Optimistic Verification is a technology used in blockchain Layer 2 solutions, particularly suited for expanding the capabilities of the main chain and reducing its load. This technique assumes honest behavior among participants and allows transactions and contract executions to proceed without immediate validation. Only when disputes arise is verification triggered, effectively reducing the number of on-chain operations, thereby improving overall network performance and scalability. In the Bitlayer project, Optimistic Verification is one of the key technologies enabling high throughput and low latency.
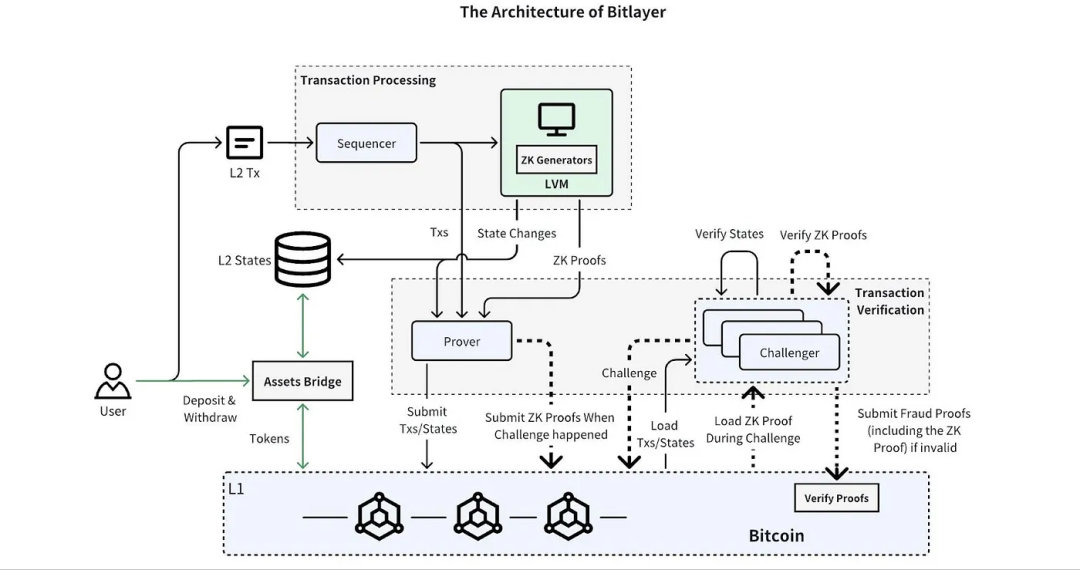
Working Principle
The basic principle of optimistic verification is that most transactions or contract executions are assumed correct, and verification is only triggered when necessary. This reduces the need for on-chain operations, lowering transaction fees and latency while increasing overall system scalability.
-
Submission Phase:
-
Transactions or state changes are first executed on the second-layer network (e.g., Bitlayer), assuming validity. No immediate on-chain verification is required during this phase, significantly reducing latency and fees.
-
Challenge Window:
-
Each submitted state or transaction has a "challenge window," during which network participants can dispute the submission. If no challenge occurs within this period, the transaction is considered valid.
-
Dispute Resolution:
-
If a challenge arises, on-chain verification is required to resolve the dispute. This involves submitting evidence to prove the validity or invalidity of the state. If the challenge succeeds, the incorrect state is rolled back; if it fails, the state is confirmed.
Application in Bitlayer
In the Bitlayer project, optimistic verification enables significantly faster transaction processing and greater system scalability while preserving Bitcoin’s core security attributes. Key applications include:
-
Smart Contract Execution:
-
Bitlayer can execute complex smart contracts on the second layer, requiring on-chain verification only in case of disputes. This allows Bitlayer to support more complex and feature-rich applications than Bitcoin’s native protocol while maintaining core security and decentralization.
-
Batch Transaction Processing:
-
Through optimistic verification, Bitlayer can process large batches of transactions on the second layer before committing their final state as a single batch to the Bitcoin main chain. This reduces main chain load and increases overall transaction throughput.
-
Cost Efficiency:
-
By reducing the need for immediate on-chain verification, optimistic verification greatly lowers transaction fees, making small-value transactions economically viable on the blockchain.
Challenges and Considerations
Although optimistic verification offers significant performance benefits, it introduces challenges related to security and data integrity. Since correctness relies on a challenge mechanism, the system must be carefully designed to prevent fraud and ensure participants can respond promptly and effectively to potential disputes. Additionally, the duration of the challenge window and the design of dispute resolution mechanisms require careful consideration to ensure fairness and efficiency.
Overall, optimistic verification provides an effective scaling path for Layer 2 solutions like Bitlayer, significantly improving blockchain scalability and economic viability by minimizing on-chain operations while maintaining security.
OP_DLC Bridge (Optimistic Discreet Log Contracts Bridge)
The OP_DLC Bridge (Optimistic Discreet Log Contracts Bridge) is a key technology in the Bitlayer project for enabling cross-chain asset transfers. Based on Discreet Log Contracts (DLC) and optimistic protocols, it aims to provide a secure, reliable, and decentralized method for assets to flow between the Bitcoin main chain and Bitlayer’s second layer.
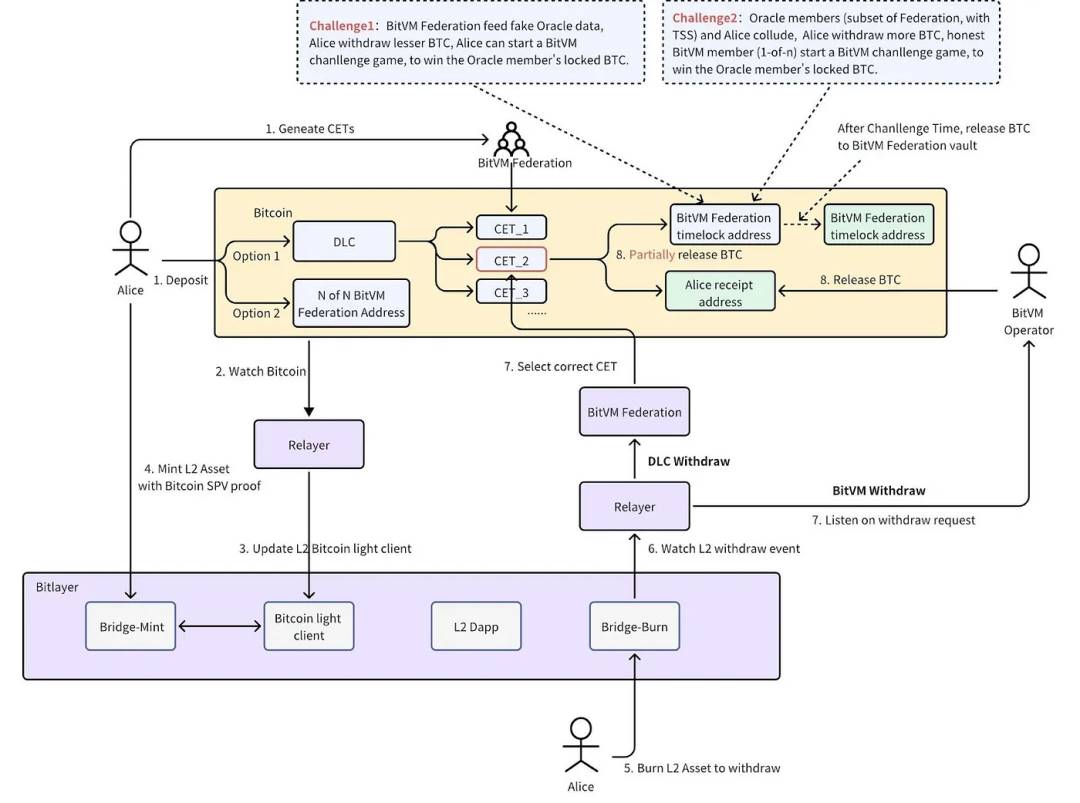
Discreet Log Contracts (DLC)
Discreet Log Contracts are a form of Bitcoin-based smart contracts that allow execution based on predefined conditions without relying on external oracles. DLC implementations primarily rely on Bitcoin scripts and multi-signature technology, ensuring contract execution is fully on-chain, transparent, and tamper-proof.
How the OP_DLC Bridge Works
-
Asset Locking:
-
Users first lock their assets on the Bitcoin main chain via a DLC contract. This means the assets are held in a specific smart contract address and can only be released or transferred upon meeting contract conditions.
-
Cross-Chain Transfer:
-
Once assets are locked on the main chain, corresponding tokens representing those assets are created on Bitlayer’s second layer. These tokens are fully controlled by the DLC contract, ensuring a one-to-one correspondence with main chain assets.
-
Users can freely trade these tokens on Bitlayer, enjoying low-cost and high-speed transactions.
-
Asset Redemption:
-
When users wish to redeem their second-layer tokens back into main chain assets, they initiate a redemption request on Bitlayer.
-
This triggers execution of the DLC contract: tokens are burned, and the corresponding assets are released from the smart contract and sent to the user’s Bitcoin address.
-
Optimistic Verification:
-
Throughout the process, the optimistic protocol ensures that on-chain verification is only needed in case of disputes, greatly improving system efficiency and scalability.
Advantages of the OP_DLC Bridge
-
Security: Using Bitcoin-based DLC contracts ensures secure and transparent asset locking and transfer.
-
Efficiency: The optimistic protocol reduces the need for on-chain verification, improving transaction speed and lowering costs.
-
Decentralization: Does not rely on centralized oracles or third-party services—all operations are automatically completed on-chain, ensuring decentralization.
-
Flexibility: Supports various types of cross-chain asset transfers, expanding Bitcoin’s ecosystem use cases.
In summary, the OP_DLC Bridge is the core technology enabling secure and efficient circulation of assets between the Bitcoin main chain and Bitlayer’s second layer. By combining the security of DLC with the efficiency of optimistic protocols, it provides users with a powerful cross-chain asset management tool.
Bitlayer NFT
Bitlayer announced that following the launch of its Mainnet V1, it will release its first official NFT—the Bitlayer Lucky Helmet. This NFT is not just an image but a symbol representing the identity and contributions of Bitlayer community builders. A total of 5,000 Lucky Helmets will be distributed via whitelist to active participants in the Bitcoin and Bitlayer communities.

Holders of the Lucky Helmet will enjoy a range of practical rights and benefits, including priority governance rights, potential token airdrops, official event points, and multiplier advantages in ecosystem projects. Additionally, the Lucky Helmet adopts the Ordinals issuance paradigm, optimizing circulation efficiency and minimizing transaction costs.
Ways to obtain the Lucky Helmet include Priority Passes and Public Allowlists, targeting the earliest and most active participants in the Bitlayer ecosystem, as well as limited whitelists available through the Bitlayer x OKX Wallet campaign. These NFTs will be minted within a specified timeframe and require completion of the minting process on the official website within the designated time.
Team / Partners / Funding
Bitlayer was co-founded by Charlie Yechuan Hu and Kevin He.

Charlie Yechuan Hu is a co-founder of Bitlayer and previously served as Managing Partner at LucidBlue Ventures. He has also been involved with projects such as Polygon, Tezos, and Polkadot. He graduated from Nyenrode Business University and Beijing Foreign Studies University. Charlie Hu played a crucial role in expanding the influence of Tezos and Polygon, notably serving as Head of Business Development for Tezos China and later overseeing Polygon’s operations in China and Southeast Asia.
Kevin He is a co-founder of Bitlayer and formerly served as Vice President of Technology at NewHuobi, Senior Technical Director at Huobi, and Chief Scientist at YOUChain. He holds a Master’s degree in Software Engineering from Peking University.

To date, Bitlayer has successfully completed a $5 million seed funding round led by Framework Ventures and ABCDE Capital, with participation from prominent investors including StarkWare, OKX Ventures, Alliance DAO, UTXO Management, and Asymmetric Capital. Additionally, the project has attracted notable angel investors such as Ryan Selkis (CEO of Messari), Dan McArdle (co-founder of Messari), and Dan Held (founder of Asymmetric Capital).
Furthermore, Bitlayer announced that its $50 million developer airdrop initiative has attracted over 500 project teams, covering infrastructure, DeFi, inscriptions, SocialFi, and cross-chain bridges. Within 48 hours of launch, over 300,000 users had voted for their preferred projects. The application window remains open until April 29, with the official competition expected to begin in mid-May, allowing teams to compete for $50 million in token airdrops and grants based on leaderboard rankings and accelerator programs.
Project Evaluation
Sector Analysis
The Bitlayer project falls within the Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions sector, focusing on expanding Bitcoin’s functionality, increasing transaction speed and programmability, while preserving its security and decentralization. The key challenge in this sector is addressing Bitcoin’s scalability and flexibility issues to enable support for more complex financial and commercial applications.
Similar Projects
-
Lightning Network: One of the most well-known Bitcoin Layer 2 scaling solutions, primarily addressing Bitcoin’s transaction speed and scalability. By establishing payment channels, it enables near-instant transactions, significantly reducing costs and increasing network throughput.
-
Liquid Network: Developed by Blockstream, Liquid Network is a sidechain technology based on Bitcoin, primarily targeting exchanges, brokers, market makers, and other financial institutions. It supports faster Bitcoin transactions and asset issuance with enhanced privacy features.
-
RSK (Rootstock): Another sidechain project introducing smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin network. RSK aims to deliver Ethereum-like capabilities, including support for Turing-complete smart contracts, while maintaining Bitcoin’s security properties.
Target Customers
-
Blockchain Developers: Offers a rich, EVM-compatible development environment to attract developers from Ethereum and other blockchain platforms to build and deploy applications on Bitlayer.
-
Enterprise Users: Provides efficient, low-cost blockchain solutions for businesses handling large transaction volumes, especially those seeking to optimize business processes or explore new business models using blockchain technology.
-
Financial Institutions: Offers secure cross-chain asset transfer and management services, helping financial institutions conduct asset management, trading, and settlement on blockchain.
-
Cryptocurrency Investors and Traders: Provides a secure and fast trading platform, particularly attractive to high-frequency traders needing instant execution and low fees.
-
Privacy- and Security-Conscious Users: Leverages zero-knowledge proof technology to provide enhanced security for privacy-focused users, protecting their transactions and data from exposure.
Project Advantages
Bitlayer’s strengths lie primarily in its unique technological innovations and strong ecosystem partnerships:
-
Layered Virtual Machine technology provides flexible frontend smart contract execution and backend zero-knowledge proof generation. This layered approach optimizes computation and verification, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
-
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) enhance privacy and security. Bitlayer can verify transaction correctness without revealing transaction details, offering users higher privacy protection.
-
Optimistic Verification returns to on-chain validation only when disputes arise, effectively reducing network congestion and transaction fees.
-
The OP_DLC Bridge achieves high-security interoperability with the Bitcoin main chain. This technology enables secure locking and transfer of assets between chains while maintaining full user control.
-
Bitlayer has established ecosystem collaboration intentions with over 80 projects, spanning infrastructure, stablecoins, wallet services, and other key domains. This broad partnership network offers users a rich array of services and applications, enhancing platform attractiveness and competitiveness.
-
By combining technological innovation with an extensive partnership network, Bitlayer delivers not only efficient and secure technical solutions but also strong market-level ecosystem support. This positions Bitlayer favorably in the competitive blockchain landscape and lays a solid foundation for future growth.
Potential Project Drawbacks
Although Bitlayer excels in technological innovation and ecosystem development, like many tech projects, it faces potential challenges and drawbacks that could affect widespread adoption and ultimate success. Key potential disadvantages include:
Technical Complexity
-
User Adoption Barrier: Bitlayer’s advanced features, such as the layered virtual machine and zero-knowledge proofs, while powerful, may be too complex for average users and developers to understand and use, potentially hindering broad adoption.
-
Maintenance and Upgrade Challenges: Highly complex systems may face greater technical hurdles during maintenance and upgrades. Minor errors or vulnerabilities could lead to security risks or performance issues.
Security Issues
-
Security Risks of New Technologies: Despite using advanced cryptography and security measures, introducing new technologies always carries unknown risks. For example, flaws in zero-knowledge proofs or optimistic verification mechanisms could be exploited.
-
Dependence on External Systems: Some of Bitlayer’s functionalities may rely on external systems or services, such as cross-chain bridges. The security and stability of these systems could impact Bitlayer’s overall security.
Market Competition
-
Competition with Other Layer 2 Solutions: Numerous other Layer 2 solutions exist, such as the Lightning Network and Liquid Network, which already have mature technologies and user bases. Bitlayer must demonstrate superior and unique value to stand out.
-
Market Adoption Speed: Despite technical sophistication, Bitlayer’s market acceptance and adoption rate will depend on real-world use cases, user experience, and broader market conditions.
Economic and Regulatory Factors
-
Funding Requirements: Advanced blockchain projects require substantial funding for development and operation. Insufficient future financing could hinder sustained progress.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: Blockchain technologies, especially those involving financial applications, face strict and evolving regulatory environments. Regulatory uncertainty could impact Bitlayer’s operations and expansion.
Future Plans
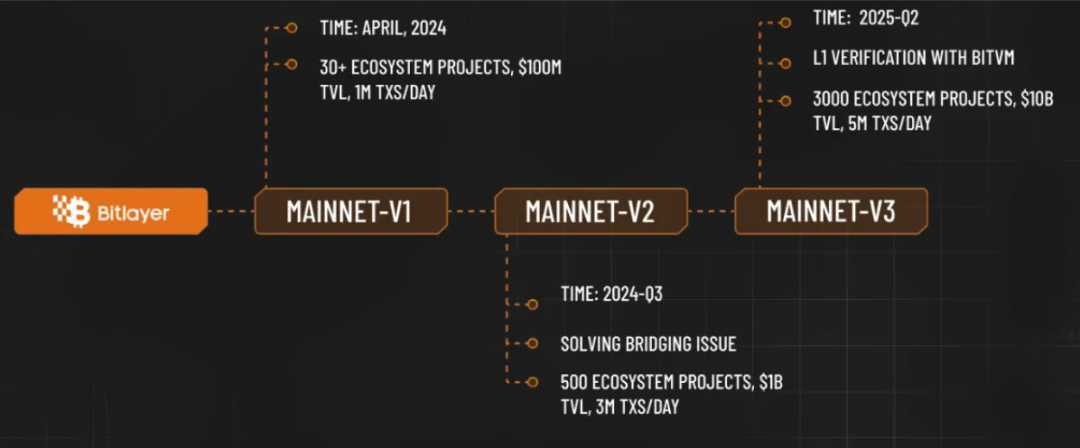
Bitlayer’s development roadmap outlines major milestones across upcoming versions:
-
Mainnet-V1 (expected April 2024):
-
Over 30 ecosystem projects planned.
-
Total Value Locked (TVL) target: $100 million.
-
Daily transaction volume (TXs) target: 1 million.
-
Mainnet-V2 (expected Q3 2024):
-
Focus on solving cross-chain bridging issues.
-
Expand ecosystem to 500 projects.
-
Increase TVL to
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















