MEV Uncovered: Exploring the MEV Landscape in the BNB Chain Ecosystem
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

MEV Uncovered: Exploring the MEV Landscape in the BNB Chain Ecosystem
In this article, we will delve into the MEV landscape of the BNB Chain ecosystem.
Abstract
-
Introduction to MEV
-
BSC's PBS Implementation
-
BSC’s Transparent and Fair Block Marketplace
-
MEV Protection via BSC Block Builders
Introduction
MEV has become a core concept in the blockchain industry, especially within the context of decentralized finance (DeFi). MEV refers to the profits that miners, validators, and other participants can extract by reordering, censoring, or inserting transactions within blocks. MEV participants include users, wallets, searchers, builders, and miners, each with distinct roles and incentives. In this article, we will delve into the MEV landscape within the BNB Chain ecosystem.
Background and Progress
The industry has made significant progress in addressing MEV, developing various solutions to mitigate its negative impacts and improve efficiency. Since early 2023, the BNB Smart Chain community has undertaken substantial work on MEV and has ultimately moved toward offering MEV solutions to all validators.
The Ethereum ecosystem has been at the forefront of tackling MEV challenges, implementing multiple innovative solutions to reduce its adverse effects. Below are highlights of some current technical approaches in the Ethereum ecosystem:
-
Flashbots: Flashbots is a research and development organization that created a transparent market for MEV extraction. It allows searchers to send transaction bundles directly to miners, reducing harmful effects like gas price auctions and enabling more efficient value capture.
-
Archer Swap: A trading platform that helps users avoid frontrunning by routing transactions directly to miners instead of the public mempool. It offers better trade execution and protection against MEV-related risks.
-
MEV-Boost: Following Ethereum’s transition to proof-of-stake (the Merge), MEV-Boost is a middleware insertion architecture allowing validators to maximize censorship resistance by locally building low-MEV blocks while outsourcing high-MEV block construction.
-
SUAVE: Flashbots’ SUAVE project aims to decentralize the block-building process. It acts as a plug-and-play mempool and decentralized block builder for any blockchain, including Ethereum, enhancing network resilience.
-
COW Swap: A decentralized trading protocol providing MEV protection by using private liquidity sources and routing trades in ways that minimize exposure to frontrunning bots.
-
Gas Token Utilization: Some Ethereum searchers use gas tokens to pay transaction fees, optimizing gas savings and enabling higher bids during auctions.
-
Decentralized Builder Concept: Research into distributed builders and crLists (commit lists) aims to limit centralization of block builders, ensuring a more decentralized and resilient network.
-
MEV-Capturing AMMs: New automated market maker (AMM) designs are being explored to transfer transaction ordering rights to AMM designers and liquidity providers, allowing them to capture part of the MEV currently harvested by block builders and proposers.
-
Order Flow Auctions: This mechanism allows any searcher or builder to bid for user order flow, creating a more competitive and transparent market for MEV extraction.
-
Tornado Cash: A privacy solution that also mitigates certain MEV risks by breaking on-chain links between source and destination addresses.
These solutions represent the collective efforts of the EVM community to address the complex challenges posed by MEV. Ongoing research and development in this space reflect the industry’s maturation and active engagement with its most pressing issues.
Current On-Chain Analysis and Implementation
As of the latest data, approximately 22 validators have integrated with MEV providers, with 29 validators actively participating. This represents a significant portion of active validators and underscores the growing importance of MEV within the blockchain ecosystem. BloxRoute is emerging as a relay among BSC validator communities.
Growth Trends
The last quarter saw strong growth in integration, indicating increasing interest in MEV optimization among BSC validators. This trend is particularly notable given that only six validators were integrated with MEV providers by the end of 2022. The rapid increase in adoption reflects the perceived value and potential of MEV and suggests that this area will remain a focal point for innovation and investment in the coming months and years.
Many validators report improvements in both profitability and efficiency. Integration with MEV providers enables validators and delegators to tap into new revenue streams and optimize operations. This success has fueled growing interest in MEV across the BSC ecosystem.
On the other hand, some validators face difficulties related to integration, competitiveness, and transparency. The complexity of integrating MEV providers with existing systems may pose technical challenges. Additionally, concerns about the impact of MEV extraction on transparency and competitiveness raise questions about the long-term sustainability and public perception of these practices.
These successes and challenges paint a nuanced picture of the current state of on-chain MEV analysis and implementation. They highlight the need for ongoing research, development, and dialogue to ensure that MEV continues to evolve in a way that balances profitability, accountability, and transparency. The current situation emphasizes the necessity of improving competitiveness and introducing more relays to ensure innovation, greater efficiency, and a more balanced and robust MEV ecosystem on BSC.
Challenges and Opportunities
MEV presents both challenges and opportunities for the blockchain industry. While it raises complex issues related to fairness, centralization, and ethics, it also holds potential for improving efficiency, profitability, and innovation. Attracting more relays requires a multifaceted approach emphasizing transparency, incentives, ease of integration, community engagement, and regulatory compliance.
Challenges in Implementing MEV
-
Fairness in Transaction Prioritization: Ensuring fair transaction processing without manipulation by miners or validators is a major challenge. The ability to reorder or exclude transactions can lead to frontrunning and other exploitative behaviors.
-
Implementation Complexity: Creating a system that efficiently captures MEV while maintaining network integrity and performance is highly complex. It requires careful consideration of various factors, including transaction fees, gas prices, and network congestion.
-
Centralization Risks: MEV can incentivize centralization, where a few powerful entities control most of the computational power. This could undermine the decentralized nature of blockchains and create vulnerabilities.
-
Ethical Considerations: The extraction of MEV raises ethical questions about fairness and transparency in blockchains. It may create an uneven playing field where certain participants gain advantages over others.
Opportunities for New Implementations
-
Improved Efficiency: When properly implemented, MEV can lead to more efficient block production and transaction processing. By optimizing transactions, miners can maximize profits while enhancing network performance.
-
Profitability for Diverse Participants: MEV offers miners, searchers, block builders, and proposers opportunities to earn additional income. By strategically including transactions, they can capture value that would otherwise be lost.
-
Innovation in Transaction Processing: MEV opens doors to innovative solutions in transaction handling, including batch auctions, fair sequencing, and threshold encryption. These can alleviate some MEV-related challenges and enhance the overall user experience.
-
Collaboration with Layer 2 Solutions: Integrating MEV with Layer 2 solutions such as rollups can create synergies, enhancing scalability and performance. It also allows experimentation with different MEV models and approaches.
Community Development and Multiple Technical Proposal Approaches to Address Challenges and Moving Forward
Multiple approaches, including various architectural solutions, represent a collaborative strategy to tackle MEV challenges and help move forward within the broader ecosystem. By leveraging diverse expertise and innovative solutions within the community, we highlight the following implementations reflecting joint efforts to improve network efficiency, security, and profitability, thereby fostering a more resilient and adaptive blockchain infrastructure.
Bid Relays within MEV infrastructure serve as critical bridges connecting various transaction stakeholders, streamlining the identification and utilization of MEV opportunities. Their bidding process not only ensures transparency and fairness but also optimizes profits for validators and searchers. By acting as intermediaries, Bid Relays enhance network efficiency, reduce congestion, and strengthen security, aligning with blockchain decentralization. Their integration is essential for a robust, scalable, and fair MEV infrastructure, ensuring optimal transaction processing and profit maximization.
Let us first introduce the bid relay.
A Bid Relay is a sophisticated approach to managing MEV in blockchain networks. Its focus is on creating a more transparent, efficient, and fair environment for transaction inclusion. Below are its components and the significance of each design element:
Components and Workflow
Searchers: Identify MEV opportunities and submit bids to the MEV Relay.
MEV Relay: Centralizes the bidding process, collecting and aggregating bids.
Miners/Validators: Decide on transaction inclusion based on proposals from the MEV Relay.
Importance of Each Design Element
Role of Searchers: Creates a competitive environment where different entities can identify and bid on MEV opportunities, promoting innovation and efficiency.
Role of MEV Relay: Acts as a transparent intermediary, reducing network congestion and ensuring a fair bidding process.
Role of Miners/Validators: Makes informed decisions on transaction inclusion based on aggregated bids, enhancing network integrity.
Overall Importance
Efficiency: Centralized bidding reduces complexity and accelerates transaction processing.
Transparency: Ensures equal access and understanding of the process for all participants.
Profit Maximization: Facilitates profit maximization for miners and searchers through a structured bidding process.
Adaptability: Its design allows implementation across various blockchain networks.
In summary, the Bid Relay MEV architecture provides a balanced and innovative approach to handling MEV. By focusing on the roles of searchers, MEV Relays, and miners/validators, it promotes fairness, efficiency, and transparency. Its unique design elements make it a promising solution for addressing ongoing MEV-related challenges in blockchain ecosystems.
BloxRoute's Flashbots-like solution for BSC, currently adopted by 9 validators:
Introduction
Flashbots is an open-source, permissionless, and transparent solution for extracting MEV (Miner Extractable Value) on Ethereum. Since BSC is EVM-based, replicating it on BSC is natural with minor modifications. The introduction of mev-boost in Ethereum created a win-win situation for searchers, block builders, and proposers. To this end, the BloxRoute team proposed an initiative aiming to uphold the same spirit of profit maximization and profit sharing on BNB Smart Chain.
Overview
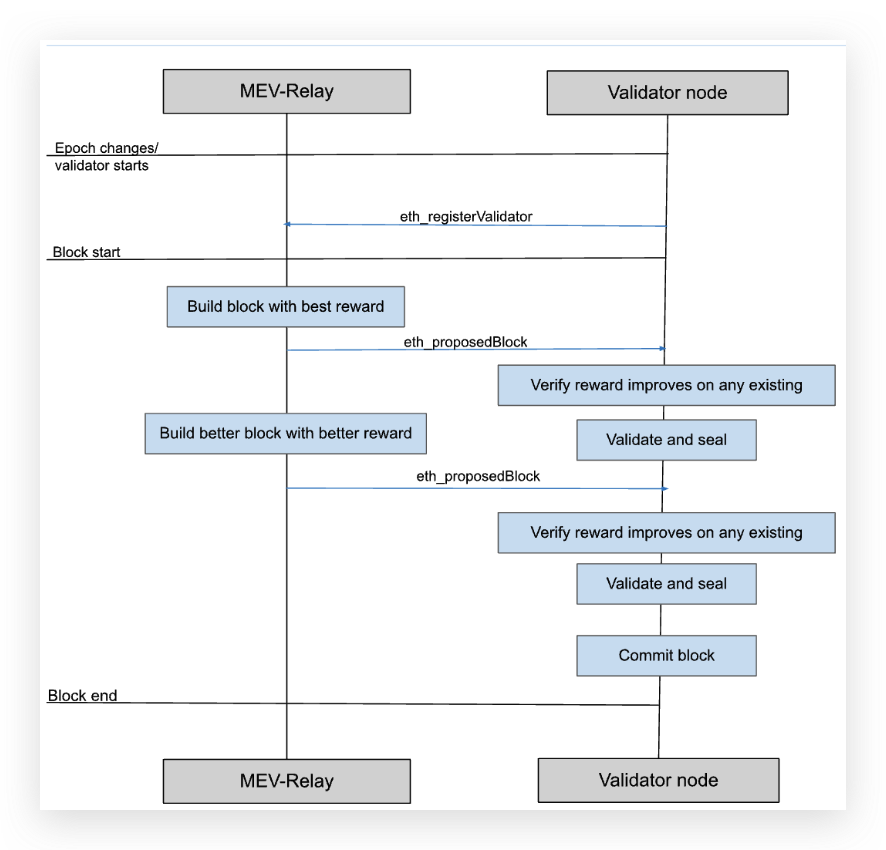
The MEV-Relay will propose potential blocks to connected validators. Unlike validators, the MEV-Relay can receive transaction "bundles" built by MEV searchers, thus maximizing profits for all stakeholders.
Architecture:
This architecture integrates the roles of searchers, builders, and relayers to generate the most profitable blocks using MEV builders. However, additional modifications to the validator program are required.
Execution
MEV-Relay Proposes Blocks: Within a given block interval, MEV-Relay can propose multiple blocks if a new block offers better rewards. Validators verify and seal each proposed value-enhancing block.
-
Validator Node Changes:
-
Open HTTP Endpoints: Whitelist relays and implement endpoints such as eth_proposeBlock and eth_registerValidator.
-
Parallel Production: Validators also generate blocks from mempool transactions and select the highest-reward block to submit to the network.
-
Rate Limiter: Implement rate limiting on eth_proposedBlock by IP.
-
Launch Parameters: Accept parameters like miner.mevrelays and miner.mevproposedblockuri.
-
Endpoints:
-
eth_proposedBlock: Indicates a proposed block from the relay.
-
eth_registerValidator: Validators compute the hash of the URI bytes presented to accept and sign eth_proposedBlock.
-
Validator Launch Parameters
-
miner.mevrelays: Destination for registering validators every epoch.
-
miner.mevproposedblockuri: Validator URI to which the MEV relay should send proposed blocks.
-
miner.mevproposeblocknamespace: Specifies whether the validator should accept proposed blocks under eth or mev namespace.
-
Timing: Initially, the MEV-Relay will start proposing blocks 2.5 seconds after the current block’s start time, due to BSC’s fast block times. Validators must verify and propose a block within 3 seconds (see this blog for more on the importance of these 3 seconds).
-
Customization: Customizing validator code is necessary, but long-term upgrade and maintenance costs are high.
Open Source Code:
https://github.com/bloXroute-Labs/bsc-mev-validator/pull/1
Advantages:
-
Profit Maximization: By allowing MEV-Relay to propose potential blocks, this solution enables profit maximization for all stakeholders, including searchers, block builders, and proposers.
-
Transparency and Collaboration: As an open-source project, it encourages community collaboration and ensures transparency in the development process.
-
Parallel Production: Validators can produce blocks in parallel from mempool transactions, optimizing the block selection process.
-
Rate Limiting: Implementing rate limiters on eth_proposedBlock by IP helps manage traffic and prevent abuse.
-
Enhanced Functionality: Through specific endpoints, methods, and configurations, this solution enhances the overall functionality of BNB Smart Chain.
Disadvantages
-
Customization Complexity: Customizing validator code is necessary, but long-term upgrade and maintenance costs are high. This could be a barrier for some validators needing updates per upcoming BSC upgrades.
-
Potential Security Issues: Opening HTTP endpoints and implementing new methods, if not handled carefully, could introduce potential security vulnerabilities.
-
Dependency on Validators: The solution’s success depends on validators’ willingness to implement required changes, which may not always be guaranteed.
-
Time Constraints: Fast block times within the BSC network impose timing restrictions on block proposals. Validators must verify and propose a block within 3 seconds, which can be challenging.
-
Potential Centralization Risk: If implemented without considering decentralization, this solution could lead to centralization risks where a few entities control most MEV extraction.
BloxRoute’s Flashbots-like solution for BSC represents a significant advancement in profit and efficiency maximization within BNB Smart Chain. While it offers numerous benefits such as profit maximization, transparency, and enhanced functionality, it also presents challenges related to customization complexity, potential security issues, and time constraints. Careful consideration and robust implementation are crucial to harnessing the advantages of this innovative solution while minimizing its drawbacks.
BSC MEV – Leveraging Sentinel Nodes
Implementing MEV solutions within the BSC context can be complex and poses potential risks to network stability as block sizes grow and the number of validators increases. Utilizing sentinel nodes as part of an MEV solution offers a method to mitigate these risks and enhance network stability.
Architecture Overview
This architecture focuses on the use of sentinel nodes, which act as protective barriers for validator nodes, ensuring the network can withstand denial-of-service attacks. Key features of this architecture include:
-
No Changes Required to Validator Nodes: By concentrating MEV implementation on sentinel nodes, validator nodes remain unchanged, enhancing network stability and security.
-
Sentinel Node Modifications: Only sentinel nodes require modification, enabling a more controlled and secure implementation of MEV solutions.
-
Private Connection Between Validator and Sentinel Nodes: Validator nodes establish private connections with their corresponding sentinel nodes, which communicate with other nodes in the public P2P network.
-
Security Through Isolation: Validator nodes are effectively surrounded by sentinel nodes, isolating them from direct exposure to the public network and potential attacks.
-
Configured Direct Send and Pull Mechanism: Set sentinel nodes to use Push method to send transactions to validator nodes, while using Pull method for other nodes in the public P2P network.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance: Implement monitoring tools to track the performance and security of sentinel nodes. Regular maintenance and updates are crucial for optimal operation.
In the P2P network, transactions can propagate in two ways:
-
Push: The sending node directly sends the complete transaction to the receiving validator node. This method is faster due to the critical 3-second window for block validation and is preferred in the BSC network.
-
Pull: The sending node only transmits the transaction hash; the receiving node pulls the full transaction from the sentinel node if not locally available. This method is slower due to additional round-trip communication.
MEV Builder Integration
MEV builders can be integrated into the sentinel node architecture to prioritize MEV extraction. By ensuring that sentinel nodes only send transaction hashes to validator nodes while MEV builders send complete transactions, MEV builders gain a timing advantage. This priority enables more efficient and effective MEV extraction.
Some benefits of implementation via sentinel nodes:
-
Enhanced Security: Sentinel nodes act as protective barriers around validator nodes, shielding them from direct exposure to potential attacks. This isolation offers significant advantages compared to Flashbots-like solutions, where validator nodes may be more exposed.
-
Stability: By centralizing MEV implementation on sentinel nodes and keeping validator nodes unchanged, the core functionality of the network remains stable. Flashbots-like solutions might require more extensive future modifications to validator nodes, potentially introducing instability.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: Sentry nodes can quickly launch or change their IP addresses. This flexibility allows easier scaling and adaptation to changing network conditions, which might be more challenging for Flashbots-like solutions.
-
Efficient MEV Extraction: The architecture optimizes MEV extraction by prioritizing MEV builders in transaction arrival timing. Such efficiency may be harder to achieve in Flashbots-like solutions where transaction propagation may be uncontrolled.
-
Lower Maintenance Costs: Implementing MEV via sentinel nodes may require fewer changes to existing network infrastructure compared to Flashbots-like solutions. This can reduce long-term upgrade and maintenance costs.
-
Customization: Sentinel nodes provide a more controlled environment for specific optimizations and customizations tailored to MEV extraction. Flashbots-like solutions may not offer the same level of control and customization.
-
Alignment with Existing Network Topology: Many networks already use sentinel nodes for security purposes. Implementing MEV via sentinel nodes aligns with existing topologies, enabling a more seamless integration.
Using sentinel nodes as Web3 to implement MEV in the BSC network can provide a robust and efficient solution. By centralizing implementation on Sentinel Nodes and integrating MEV builders, the architecture ensures security, stability, and efficiency. It represents a promising alternative direction for the continued evolution and enhancement of the BSC network, aligning with broader goals of transparency, profitability, and resilience within the blockchain ecosystem.
Overall
The BSC network faces a complex landscape when implementing MEV solutions, with different approaches offering unique advantages and challenges. Two solutions emerge: the Flashbots-like solution introduced by BloxRoute and the Sentry Node architecture. Both approaches have merits but also present unique challenges that must be carefully managed.
The Flashbots-like solution offers a transparent, open-source approach capable of maximizing profits for all stakeholders. However, it requires extensive customization and may introduce security vulnerabilities and centralization risks. On the other hand, the sentinel node architecture emphasizes security and stability by isolating validator nodes and centralizing MEV implementation on sentinel nodes. This approach offers enhanced security, scalability, and efficiency, though it may have its own complexities and limitations.
Future Directions and Conclusion
MEV represents a complex interplay among various stakeholders, each seeking to maximize their gains while preserving network stability and integrity. Several architectural solutions have emerged to address MEV challenges, including Flashbots-like solutions and sentinel node utilization. These approaches leverage diverse expertise and innovative solutions within the community, aiming to create win-win scenarios for all participants.
Transparency is key to building trust and fostering collaboration within blockchain communities. Integrating MEV transparently, while ensuring blockchain explorers have clear visibility into transaction flows, enables all stakeholders to understand and engage with the ecosystem more effectively.
For a more detailed research report on MEV, please refer here.
The future of MEV in the BSC ecosystem holds exciting possibilities. From enhancing security and efficiency to improving transparency and collaboration, MEV is poised to play a central role in the ongoing development of the blockchain space. With careful and innovative responses to its challenges, validators, searchers, and the broader community can benefit from these advancements. The integration of MEV with explorers, in particular, represents an important step toward a more transparent and resilient network. By adopting a community-driven collaborative approach, the BSC ecosystem can fully harness the potential of MEV.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News












