A Comprehensive and In-Depth Analysis of the Past and Present of Memes and Inscriptions
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

A Comprehensive and In-Depth Analysis of the Past and Present of Memes and Inscriptions
How to identify and evaluate a promising inscription or meme project, and what mindset should one adopt toward such projects?
Authors: Bigdean, Chann
Introduction: Recently, social media has been flooded with news about certain KOLs earning hundreds or even thousands of times returns from inscriptions or meme coins—stories of explosive gains from projects like BOME/WIF continue to emerge, capturing massive attention. Meanwhile, many KOLs are speculating whether the third wave of inscription mania is about to begin. Traditional finance is increasingly investing in digital assets, and rumors are spreading that even some national teams are actively purchasing certain inscriptions.
These stories excite but also unsettle people. Seeing others reap enormous profits from memes and inscriptions leads many to wonder: why do these individuals repeatedly achieve such massive returns? Amid emotional imbalance and speculative desires, when most rush into the meme and inscription space driven by FOMO, after a while they often discover their wealth drastically eroded—most projects eventually go to zero.
How can one identify and evaluate a good inscription or meme project, and what mindset should be adopted toward them? As the saying goes, knowing yourself and your opponent ensures victory. This article by BIB Exchange will deeply analyze the past and present of memes and inscriptions, offering a comprehensive interpretation.
I. Overview
First, we need to clearly distinguish and define inscriptions and memes to avoid conflating the two. While from an investment return perspective, both are small-capitalization, intangible tokens based on speculation—and grouping them together isn't entirely unjustified—they differ fundamentally in nature.
-
"Inscription": The earliest concept of inscriptions comes from Harry Potter, Hong Kong films' "Ji Ji Ru Lü Ling," or Chinese novels where carving inscriptions enhances weapons. In general, an inscription refers to a mark etched onto a physical object—be it text, symbol, or graphic—and represents a unique identifier. In blockchain terms, inscriptions are created by attaching data to individual satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain. Their main features include native integration with Bitcoin and diverse potential uses and values.
-
"Meme": A meme coin (or "memecoin") is a token rooted in internet meme culture—essentially a faith-based currency symbolized by PEPE, DOGE, or SHIB. It originates from online community culture, built upon creatively humorous internet memes. Memes are typically created on blockchain platforms, focusing more on visual and textual content to convey social, cultural, or humorous meanings, and often circulate as NFTs (non-fungible tokens).
Investment analysts at BiB Exchange remind readers that despite similarities in investment appeal, inscriptions and memes differ significantly in technical implementation, value attributes, and application scenarios.
1.1 The Relationship Between Inscriptions and Memes
Inscriptions first emerged within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Their birth stemmed from Bitcoin community ideals—emphasizing fair issuance and first-come-first-served principles—which align closely with meme philosophy. Since their inception, inscriptions have evolved continuously, becoming a significant force within the meme sphere. Despite facing skepticism and prejudice, inscriptions have consistently demonstrated the potential and value of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The emergence of inscriptions signifies a new evolution in the Bitcoin ecosystem, reflecting the diversity of memes. At the same time, the cultural value of inscriptions has injected fresh vitality into the NFT space, enhancing liquidity by endowing holders with unique cultural attributes. Although different in form, NFTs and meme tokens share similar cultural transmission properties, collectively bringing distinctive cultural charm to the crypto world. Notably, inscriptions aren't limited to Bitcoin; they've also shone across numerous other public chains—an aspect we'll explore in detail later.
1.2 Why Inscriptions and Memes "Take Off"
According to BiB Exchange analysts, the sudden rise of memes and inscriptions can primarily be attributed to four factors:
-
Fair Distribution Model: This model is widely adopted during the early stages of meme and inscription projects. Through community activities, creation mining, and similar mechanisms, projects distribute tokens for free, attracting more users and building large, active communities. This fair distribution not only improves token liquidity and increases trading volume and price but also boosts project visibility and promotional effectiveness.
-
Low Investment Cost with High Return Expectations: Meme and inscription prices are typically low, allowing users to acquire large quantities with minimal capital. The extreme volatility of these tokens means even small investments could yield massive returns if successful—appealing especially to users with limited funds.
-
Strong Narratives: Successful meme and inscription narratives often involve derivative storytelling, associative themes, and counter-narratives. By keenly capturing pop culture and internet trends, creatively adapting content, and humorously or satirically interpreting events or topics, these projects craft uniquely appealing meme personas and stories that capture user attention and engagement.
Finally, community promotion and creative marketing play crucial roles in the success of memes and inscriptions. Through community events and innovative campaigns, projects attract more participants and design compelling product images, further driving development and outreach.
1.3 Industry Impact
As is well known, Bitcoin itself can arguably be considered the original meme. In January 2009, the Bitcoin system was born on a small server in Helsinki, Finland. Satoshi Nakamoto mined the first block—the so-called "genesis block"—and generated the initial 50 bitcoins. As the first successful cryptocurrency, Bitcoin carries profound philosophical meaning through its anonymous creator, Satoshi, and its spirit of resistance against traditional financial systems—giving it significance far beyond mere technology. Perhaps it's this very meme-like quality that has made Bitcoin a symbolic figurehead in the crypto world.
Inscriptions and memes play important roles in the cryptocurrency industry, prompting reflection and critique of concepts and technologies. The sustained popularity of inscriptions reflects the industry’s introspection regarding technological hype. Amid rapidly shifting narratives in the crypto space, the enduring presence of inscription culture prompts questions about blindly chasing new tech and concepts, pushing deeper thinking about the essence and practical applications of technology.
-
Emotional Transmission and Market Influence: As tools for conveying emotion, inscriptions spread quickly within crypto communities, triggering resonance and influencing investor sentiment and behavior. Successful inscriptions can generate widespread attention and discussion, driving short-term market price fluctuations.
-
Community Building and Identity Formation: Inscriptions are more than just forms of entertainment—they help build brand identity and community cohesion for crypto projects. By forming strong communities around specific inscriptions, projects can effectively promote themselves, attract new users, and strengthen their market position.
-
Public Chain Branding: Chains with stronger inscription ecosystems gain increasing advantages. Later in this article, we’ll discuss SOL and Base—two chains that have fully capitalized on the inscription boom during this bull market. Public chain projects now recognize the importance of inscriptions for branding and community building, actively leveraging inscription culture to enhance visibility, attract users, and boost influence.
II. Development and Comparison
NFTs (non-fungible tokens), meme tokens, and inscription tokens are three distinct types of digital assets in the cryptocurrency space, differing significantly in development history, use cases, and technical characteristics.
Development History:
-
NFT: Originally launched on the Ethereum blockchain, NFTs introduced the concept of digital asset uniqueness, enabling digital art, gaming items, virtual real estate, etc., to exist and trade as unique entities.
-
Meme Tokens: Meme tokens arise from the creation, sharing, and spread of internet culture, pop culture, and humor. They usually form part of crypto projects and spark community discussions and resonance in various ways.
-
Inscription Tokens: First appearing in the Bitcoin ecosystem, inscription tokens are created by attaching data to individual satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain. They are natively tied to Bitcoin and emphasize fair distribution and decentralization.
Use Cases:
-
NFT: Primarily used in digital art, virtual real estate, and gaming items, providing proof of ownership and uniqueness for digital assets in these fields.
-
Meme Tokens: Often serve as community incentives or components of token economies, aiming to attract participation and foster shared community spirit.
-
Inscription Tokens: Have relatively fewer use cases, mainly existing as part of the Bitcoin ecosystem, capable of carrying various attached data. However, similar concepts are beginning to appear on other blockchains.
Technical Characteristics:
-
NFT: Built on blockchain technology, using smart contracts to ensure digital asset uniqueness and indivisibility.
-
Meme Tokens: Typically based on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, technically similar to other tokens but placing greater emphasis on community consensus and participation.
-
Inscription Tokens: Created by attaching data to individual satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain, natively linked to Bitcoin, though similar functions can be implemented on other chains.
2.1 Starting with Memes
The Origin and Evolution of Meme Coins:
Memes originated in 2013, aiming to merge internet culture with crypto assets to attract broader participation. Their development can be divided into phases: Initial Stage (2009–2013), Growth Stage (2013–2017), Maturation Stage (2017–2020), Explosion Stage (2020–2023), and a New Boom Period (post-2023).
Memes reflect cultural expressiveness and derivativeness—comparable to genetic expression. Dogecoin, popularized by Elon Musk, exemplifies how memes can be applied in crypto, becoming a widely accepted digital currency and highlighting the market potential and influence of memes. Memes evolve through replication, selection, and mutation processes. For example, Pepe the Frog illustrates the diversity and generative nature of meme culture—showing how a simple image can evolve into a vast, diversified cultural ecosystem.
2.2 The Star: Bitcoin Inscriptions
Bitcoin inscriptions suddenly emerged as a mutation and offshoot of memes within the Bitcoin ecosystem, emphasizing community spirit, fair launch mechanics, market performance, and potential. A Bitcoin inscription is metadata etched onto a satoshi. The smallest unit of Bitcoin is the satoshi (sat), with 1 BTC divisible into 100 million sats. Each satoshi is ordered via ordinal theory and assigned a unique number. Bitcoin inscriptions use the Ordinals protocol to inscribe content—including text, images, videos, and audio—onto individual satoshis.
Bitcoin inscriptions possess five key characteristics:
-
"First Come, First Served": Higher fees get prioritized processing;
-
"Unique": Once inscribed, no duplicate inscription is allowed;
-
"Relatively Fair": Anyone can mint—success depends on speed and insight!
-
"Limited Supply": Minting quantity can be capped at creation and cannot be changed afterward;
-
"Immutable": Unlike uploading to IPFS, Bitcoin inscriptions are carved directly into satoshis and cannot be altered!
2.3 The Connection Between NFTs, Memes, and Inscriptions
Since many DEXs or online marketplaces list NFTs, inscriptions, and memes on the same page, let’s briefly compare NFTs with the latter two.
NFT vs. Inscription
Some claim inscriptions are part of NFTs, while others narrowly argue NFTs are a subset of inscriptions. Both views are somewhat forced.

Both NFTs and inscriptions are blockchain-created digital assets with unique identifiers, representing various digital content such as images, videos, and audio.
-
Technical Foundation: NFTs are typically built on blockchains like Ethereum, whereas inscriptions are created by attaching data to individual satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain.
-
Standards & Protocols: NFTs follow specific standards (e.g., ERC-721, ERC-1155), while inscriptions lack a universally accepted standard, relying instead on the flexibility and features of the Bitcoin protocol.
-
Fungibility: Inscriptions can be fungible, usable like any other Bitcoin—even for network fees—while NFTs are non-fungible, each having unique value and identity.
-
Community & Ecosystem: NFTs typically have independent communities and ecosystems centered around specific platforms and standards, while inscriptions are deeply integrated into the Bitcoin ecosystem, closely tied to the Bitcoin network.
NFT vs. Meme
Many articles point out that NFTs remain active partly due to support from memes. During the 2021 bull market, meme assets like DOGE surged in value, injecting new energy into the NFT market. For instance, in January 2022, Memeland launched CaptainZ, receiving over 9,999 deposits in just 11 minutes and generating over 9,800 ETH in revenue—an impressive case.
Although NFTs may have been among the earliest digital asset formats and have experienced ups and downs, their later development has been influenced by memes. Many NFT platforms have had to adapt strategies, incorporating meme elements as marketing hooks and showing favor to meme culture. On Solana, the convergence of image coins and memes is increasingly evident. As emerging digital assets, NFTs have also been impacted by memes in terms of cultural attributes and liquidity. BiB Exchange previously covered related topics in its article “Hidden ‘Master Plan’? Solana, NFTs, and ERC-404.”
III. Inscriptions
The inscription market mainly consists of three sectors: cross-chain NFTs, BTC protocol inscriptions, and multi-chain inscriptions. Readers may also refer to BiB Exchange’s earlier article “The Rise and Development of the Inscription Market: A New Era in Web3,” which comprehensively explores the evolution of the inscription market, including BTC protocol inscriptions, multi-chain inscriptions, the rise of runes, key market players, and technological innovations.
-
Cross-chain NFTs: Includes various NFT projects on different chains, such as Blue Boxes and chain-specific NFTs.
-
BTC Protocol Inscriptions: Mainly dominated by BRC20, followed by Ordi, ARC20, SRC20, Runes, etc.
Specific websites:
https://openstamp.io/home
https://runealpha.xyz/runes
https://unisat.io/brc20
https://atomicalmarket.com/market/token?ticker=atom
-
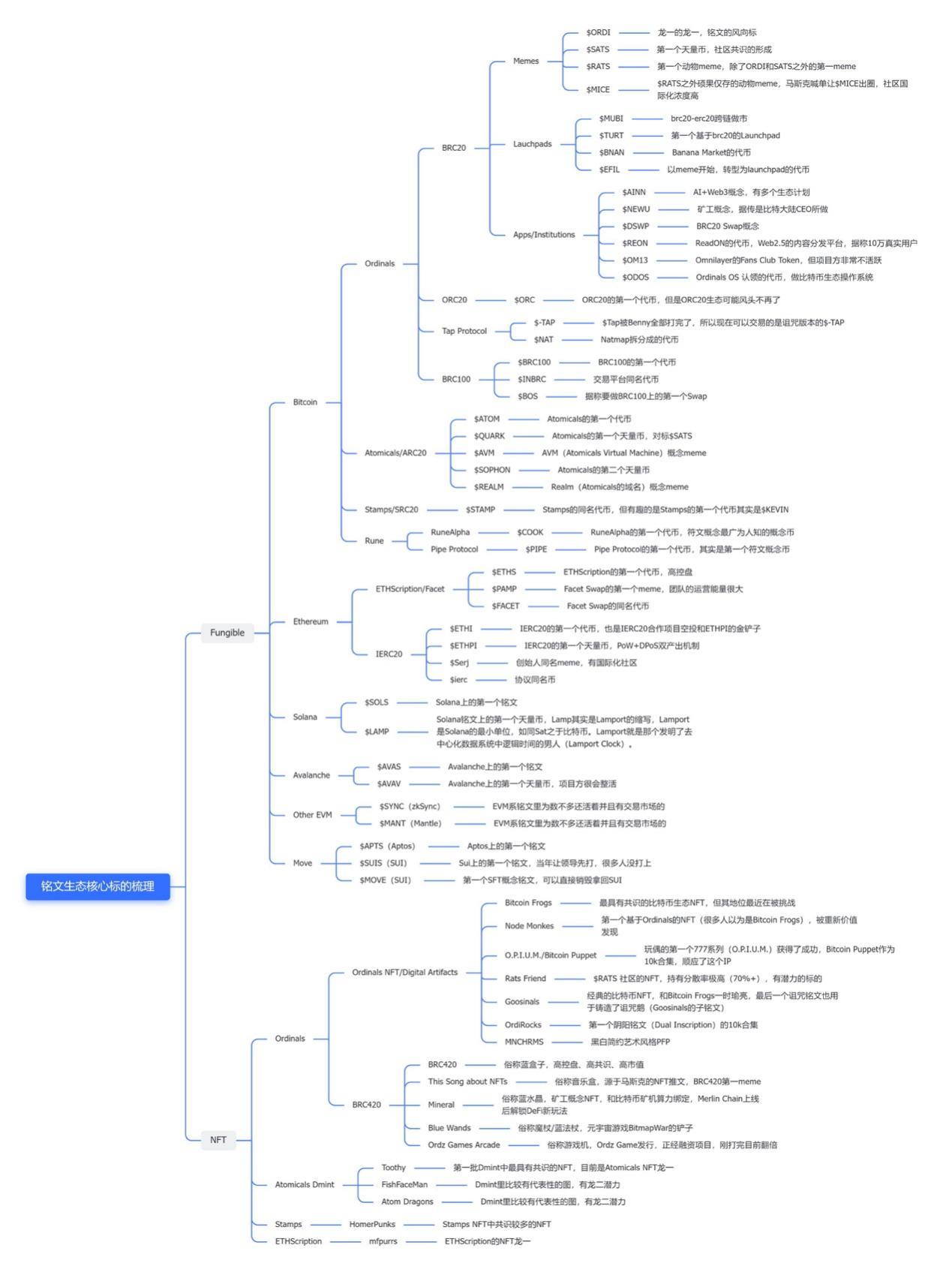
Multi-chain Inscriptions: Represented by ETHS, Sols, AVAV—nearly every public chain now has its own inscription ecosystem.
Based on prior public data, illustrated below:
3.1 Why Does Bitcoin Need L2, and Why Are Inscriptions the Answer?
Bitcoin L2 emerged alongside growing demand for inscription assets and the overall boom in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin L2 aims to resolve the “impossible trinity” of security, decentralization, and scalability on the Bitcoin mainnet by finding balance. Traditional Bitcoin Layer2 solutions may remain conceptual—opting for traditional consensus might mean accepting limitations in scalability.
Second, Bitcoin lacks the data availability (DA) capabilities of Ethereum, relying mainly on off-chain indexers for accounting and validation. Due to Bitcoin’s limited interoperability, it cannot effectively coordinate with Layer2, unlike Ethereum, whose mainnet can coordinate Layer2 via smart contracts.
Third, Bitcoin’s UTXO security model suits only simple “payment” scenarios, similar to Ethereum’s Plasma Layer2. Implementing complex smart contracts on Bitcoin requires adding extra consensus mechanisms off-chain.
2) Solutions – Approaches to L2
Solution One: Use Bitcoin as a payment solution, including Lightning Network, Taproot Assets, RGB client validation—but these face reduced security levels in complex smart contract scenarios.
Solution Two: Use Bitcoin as a settlement layer, building independent consensus for Layer2—but this risks issues similar to Ethereum’s settlement chains.
Different approaches include sidechains, Lightning Network, Taproot Assets, RGB, BitVM, etc., all attempting to scale Bitcoin Layer2. For example, Merlin Chain focuses on serving Bitcoin’s native users and assets, offering a fully Bitcoin-native scaling solution. It collaborates on wallet integration, enabling seamless switching between Layer1 and Layer2 across wallets, builds cross-chain bridges, and adopts ZK Rollup technology to enhance functionality and security of Bitcoin Layer2.
Ligo, previously invested in by BiB Exchange, is another Bitcoin L2 solution. BiB Exchange will continue to focus on the Bitcoin ecosystem—stay tuned for more updates!
3) Implementation – Via Inscriptions
At this point, launching Bitcoin Layer2 via inscriptions can be seen as an innovative approach—leveraging the potential of the Bitcoin ecosystem to enable higher-level functionalities and applications.
Merlin launched a People’s Launchpad, adopting a distribution method similar to Bitcoin Layer1. Other projects, such as BEVM (using Taproot multisig for threshold signatures, earning points through Odyssey events); B2 (focusing on mining and team invites, rewarding staked assets with halving rewards monthly); Ligo (staking model with parallel inscription launches)—over 100 projects claiming to be Bitcoin L2—all utilize inscription issuance to varying degrees.
Many of these projects conduct private fundraising through inscription minting, then transition toward expanding Bitcoin ecosystem usage and replacing Bitcoin gas consumption as a path to L2 realization. Through inscriptions, Layer2 can achieve greater decentralization, as inscriptions themselves are issued and managed via Bitcoin’s decentralized network.
3.2 Inscriptions, Runes, and the Big Picture
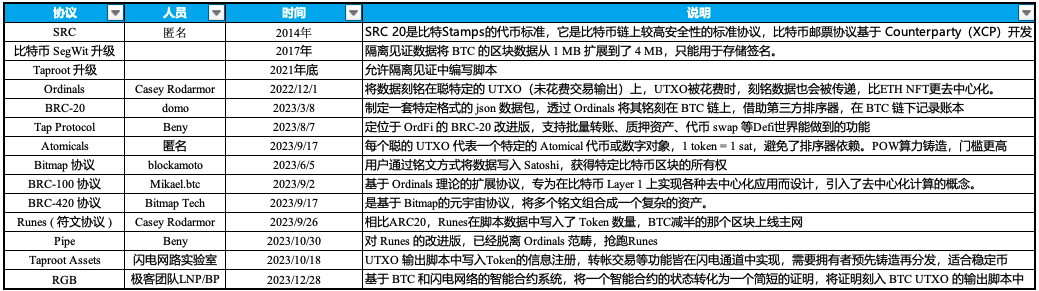
It must be emphasized that inscriptions and runes are different concepts and should not be confused. BRC20 is a standardized protocol for issuing assets on the Bitcoin chain, built atop the Ordinals protocol. However, BRC-20 based on SegWit causes Bitcoin chain congestion, leading to Rune—a UTXO-based improved protocol—for fungible tokens.
-
Runes: A simple, UTXO-based fungible token protocol offering better user experience for Bitcoin users. Rune token balances are directly embedded within UTXOs, which can contain any amount of Rune tokens.
-
Inscriptions: Metadata inscribed onto satoshis via the Ordinals protocol—also known as “Bitcoin NFTs.”
-
A key difference between Bitcoin inscriptions and runes lies in storage: inscriptions are stored in SegWit data, while runes are stored in OP_RETURN.
-
BRC-20 (Inscriptions): Ordi, Sats, Rats, TRAC
-
ARC-20 (Inscriptions): ATOM, Quark
-
SRC-20 (Stamps): Stamp, Luffy, Utxo
-
Tap Protocol: Cursed inscription CSRD-TAP
-
Rune: Pipe, COOK, PSBTS
Therefore, BiB Exchange has compiled the following table summarizing Bitcoin protocol-related inscription/rune standards:
3.3 The Futures Trio Based on RUNES: RUNESTONE / COOK / RSIC
As discussed above, Casey (co-founder of Ordi) has long been dissatisfied with BRC-20, a fungible token protocol parasitic on the Ordinals protocol. In September 2023, Casey proposed a new FT protocol called Runes. In December 2023, at Taipei Blockchain Week, Casey announced Runes would launch on mainnet at Bitcoin block height 840,000—around late April—coinciding with Bitcoin’s fourth halving.
On March 31, 2024, he posted on social media stating: Runes will fully open the first 10 Genesis Runes (0–9), distributed over four years via Open Mint.
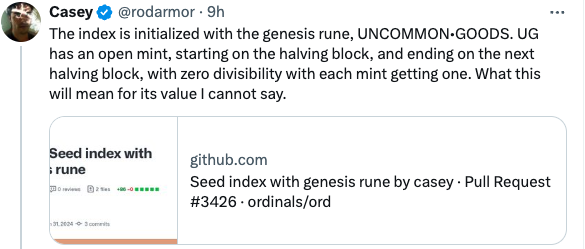
Casey himself once tweeted that the first 10 “Rune” tokens might be “hardcoded”—not open for deployment but written directly into code. These first 10 Rune tokens will undergo fair, open mints without pre-mining or pre-allocation.
RUNE Stone
RUNE Stone is still an image inscription issued under the Ordinals protocol. The project team stated that after the Rune protocol launches, they will issue
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News












